Abstract
During the strand-exchange events of bacteriophage lambda integration, pairs of phosphodiester bonds are broken and then rejoined to form novel DNA linkages. The reaction proceeds in vitro in the absence of an external energy source; the bond energy needed to rejoin broken strands of DNA must therefore be conserved during cleavage. Although some of this conservation involves a covalent intermediate between DNA and the recombinase Int, it is possible that such an intermediate is formed with only one of the two phosphodiesters. In such an asymmetric mechanism, the second phosphodiester would be attacked by a nucleophile that is exposed by cleavage of the first DNA strand. In contrast, a symmetric mechanism hypothesizes nucleophilic attack by Int on both phosphodiesters. We have distinguished these two mechanisms by removing potential nucleophiles from the integrative recombination reaction. Our data are inconsistent with an asymmetric mechanism. We conclude that during strand exchange both phosphodiesters proceed through a covalent protein-DNA intermediate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin A., Roca H., Luetke K., Sadowski P. D. Synapsis, strand scission, and strand exchange induced by the FLP recombinase: analysis with half-FRT sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4497–4508. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
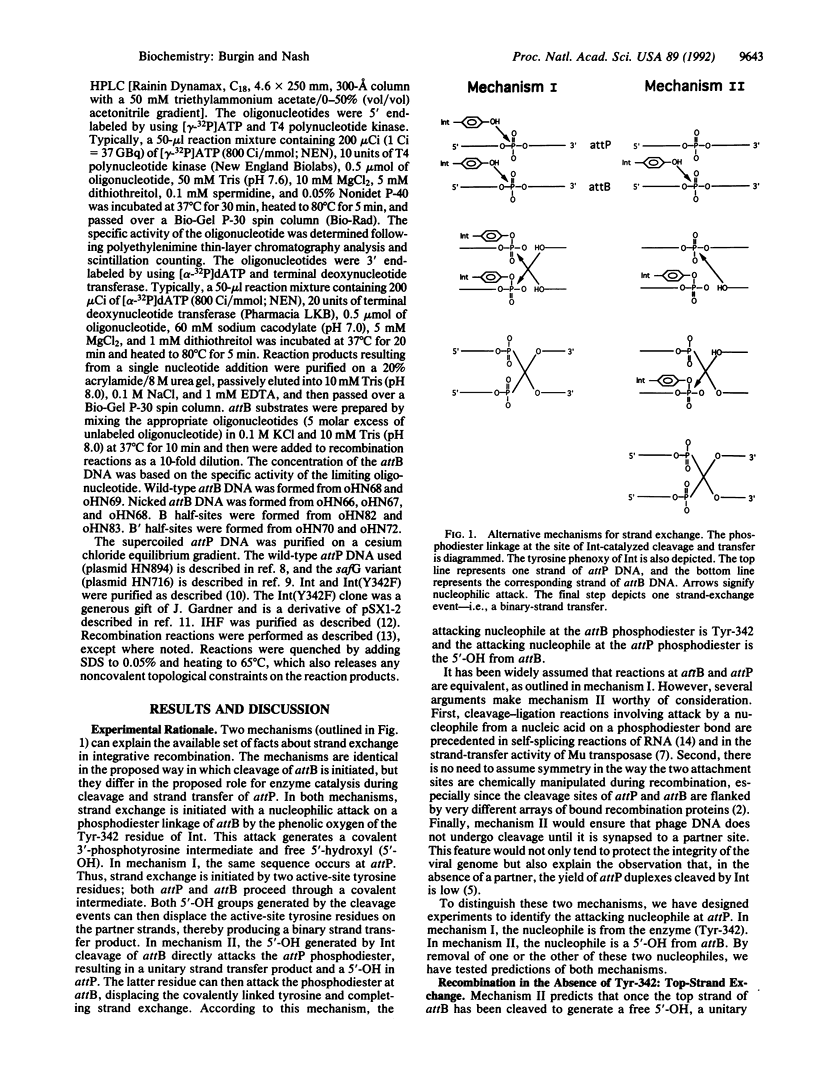
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. The mechanism of phage lambda site-specific recombination: site-specific breakage of DNA by Int topoisomerase. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L. The mechanism of conservative site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:77–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
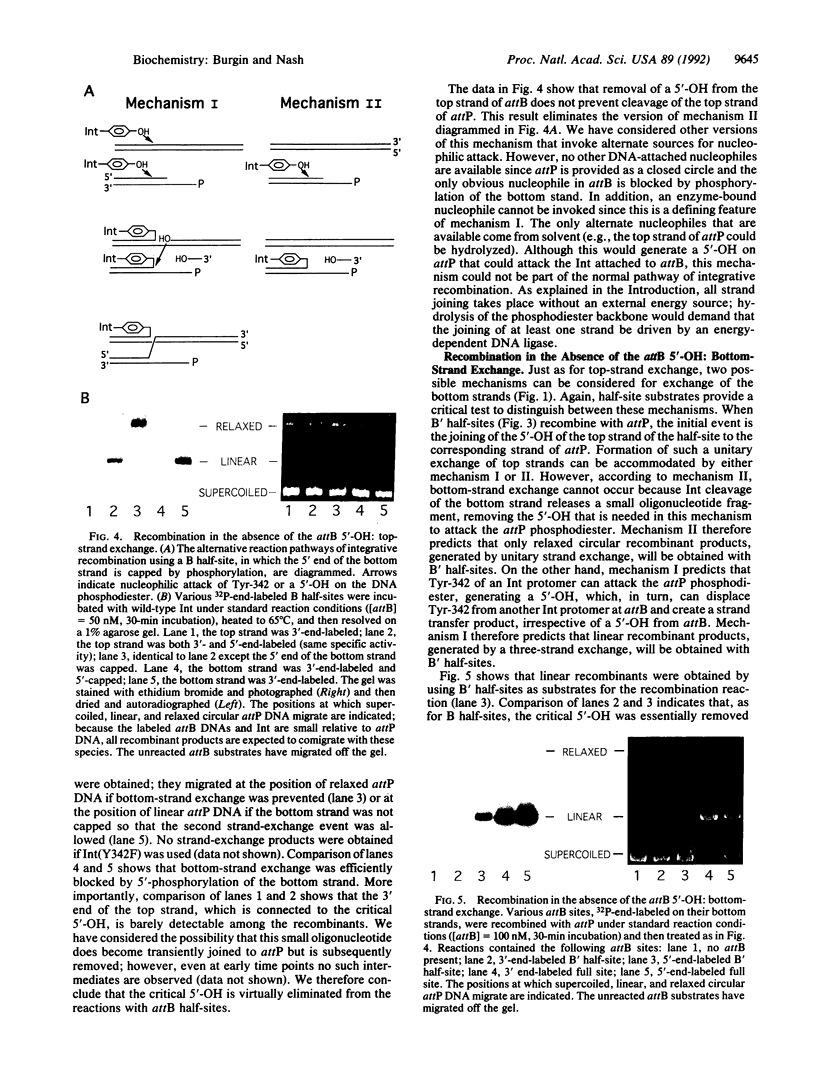
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Homology-dependent interactions in phage lambda site-specific recombination. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):346–348. doi: 10.1038/329346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A. Dynamic, structural, and regulatory aspects of lambda site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:913–949. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSwiggen J. A., Cech T. R. Stereochemistry of RNA cleavage by the Tetrahymena ribozyme and evidence that the chemical step is not rate-limiting. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):679–683. doi: 10.1126/science.2470150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Adzuma K. Inversion of the phosphate chirality at the target site of Mu DNA strand transfer: evidence for a one-step transesterification mechanism. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90145-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Bauer C. E., Gardner J. F. Role of homology in site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda: evidence against joining of cohesive ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4049–4053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A., Flamm E., Weisberg R. A., Miller H. I. Overproduction of Escherichia coli integration host factor, a protein with nonidentical subunits. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4124–4127. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4124-4127.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A. Heteroduplex substrates for bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination: cleavage and strand transfer products. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3523–3533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli protein factor required for lambda integrative recombination. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9246–9253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numrych T. E., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. A genetic analysis of Xis and FIS interactions with their binding sites in bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):5954–5963. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.5954-5963.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Half-att site substrates reveal the homology independence and minimal protein requirements for productive synapsis in lambda excisive recombination. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90881-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Site-specific recombination intermediates trapped with suicide substrates. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pargellis C. A., Nunes-Düby S. E., de Vargas L. M., Landy A. Suicide recombination substrates yield covalent lambda integrase-DNA complexes and lead to identification of the active site tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7678–7685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X. H., Inman R. B., Cox M. M. Reactions between half- and full-FLP recombination target sites. A model system for analyzing early steps in FLP protein-mediated site-specific recombination. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7794–7805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serre M. C., Evans B. R., Araki H., Oshima Y., Jayaram M. Half-site recombinations mediated by yeast site-specific recombinases Flp and R. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):621–642. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg R. A., Enquist L. W., Foeller C., Landy A. Role for DNA homology in site-specific recombination. The isolation and characterization of a site affinity mutant of coliphage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):319–342. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]