Abstract
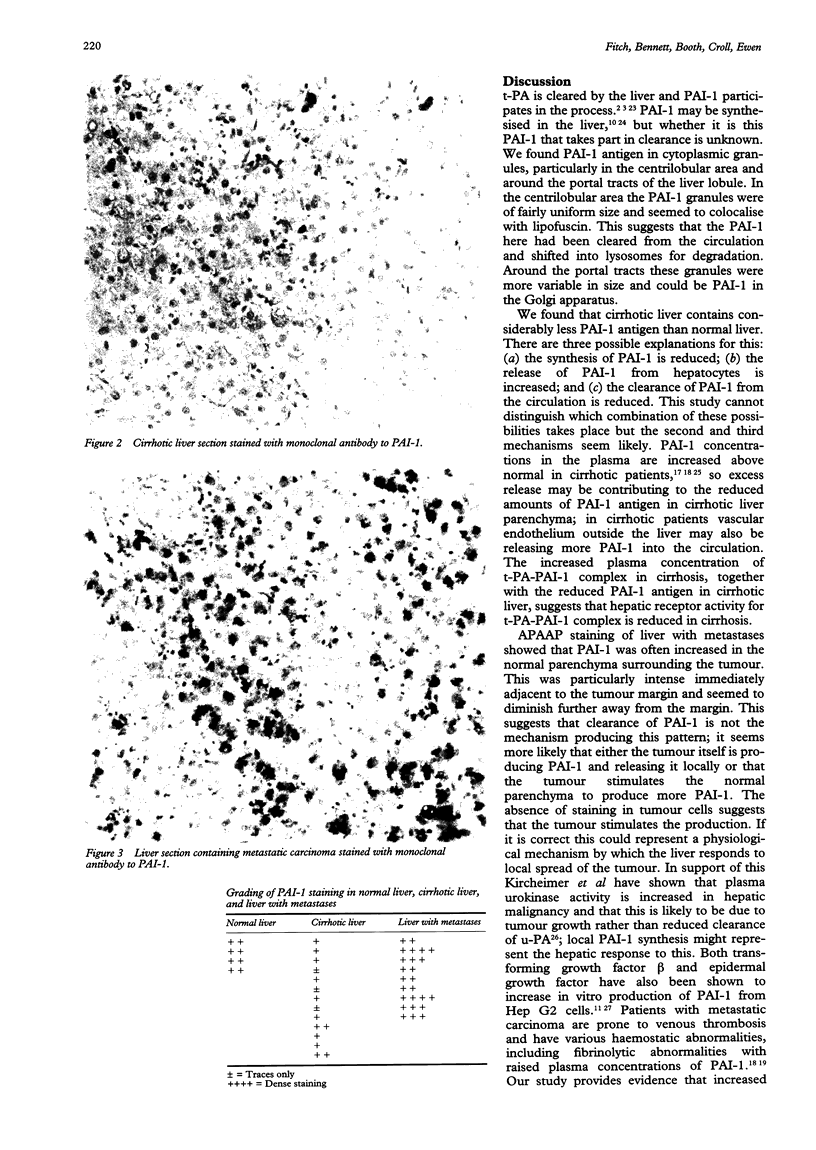
AIMS--To examine the distribution of PAI-1 antigen in normal and cirrhotic liver and liver with metastases. METHODS--Sections of normal and cirrhotic liver and liver with metastases were stained using the alkaline phosphatase antialkaline phosphatase (APAAP) technique and monoclonal antibody specific for plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1). RESULTS--PAI-1 antigen was identified as discrete granules in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes in normal liver, particularly around portal tracts and central veins of the liver lobule. In cirrhotic liver a striking reduction of PAI-1 antigen was noted. In liver with metastases increased amounts of PAI-1 antigen were concentrated in hepatocytes around the margins of malignant deposits. CONCLUSIONS--Cirrhotic liver contains considerably less PAI-1 antigen than does normal liver, despite raised plasma concentrations of PAI-1. This may reflect release of hepatic PAI-1 into the circulation or decreased clearance of PAI-1 from the plasma. Secondary malignant deposits in the liver seem to stimulate production of PAI-1 in adjacent hepatocytes. This may influence the invasive process and may contribute to the thrombotic tendency associated with malignancy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett B., Croll A., Ferguson K., Booth N. A. Complexing of tissue plasminogen activator with PAI-1, alpha 2-macroglobulin, and C1-inhibitor: studies in patients with defibrination and a fibrinolytic state after electroshock or complicated labor. Blood. 1990 Feb 1;75(3):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth N. A., Anderson J. A., Bennett B. Plasminogen activators in alcoholic cirrhosis: demonstration of increased tissue type and urokinase type activator. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;37(7):772–777. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.7.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE NICOLA P., SOARDI F. Fibrinolysis in liver diseases; study of 109 cases by means of the fibrin plate method. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 Sep 1;2(3-4):290–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson M., Hggroth L., Mattsson C. Elimination of native and carbohydrate-modified tissue plasminogen activator in rabbits. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Dec 29;62(4):1088–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., BIEDERMAN O., MOORE D., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. ABNORMAL PLASMINOGEN-PLASMIN SYSTEM ACTIVITY (FIBRINOLYSIS) IN PATIENTS WITH HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS: ITS CAUSE AND CONSEQUENCES. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:681–695. doi: 10.1172/JCI104953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Lucore C. L., Hopkins W. E., Billadello J. J., Sobel B. E. Induction of synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 by tissue-type plasminogen activator in human hepatic and endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Nov 30;64(3):412–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Lucore C. L., Hopkins W. E., Billadello J. J., Sobel B. E. Potential attenuation of fibrinolysis by growth factors released from platelets and their pharmacologic implications. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Jun 15;63(20):1505–1511. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KWAAN H. C., LO R., MCFADZEAN A. J. Antifibrinolytic activity in primary carcinoma of the liver. Clin Sci. 1959 May;18:251–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Huber K., Polterauer P., Binder B. R. Urokinase antigen in plasma of patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatoma. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):617–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiper K., Croll A., Booth N. A., Moore N. R., Sinclair T., Bennett B. Tissue plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitors, and activator-inhibitor complex in liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Mar;47(3):214–217. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucore C. L., Fujii S., Wun T. C., Sobel B. E., Billadello J. J. Regulation of the expression of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in Hep G2 cells by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15845–15848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nand S., Messmore H. Hemostasis in malignancy. Am J Hematol. 1990 Sep;35(1):45–55. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830350111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson A. J., Booth N. A., Moore N. R., Bennett B. Distribution of plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) in tissues. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Feb;44(2):139–143. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Einarsson M. Clearance of tissue plasminogen activator by mannose and galactose receptors in the liver. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Feb 19;63(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Einarsson M., Pertoft H. Tissue plasminogen activator is endocytosed by mannose and galactose receptors of rat liver cells. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Jun 16;59(3):480–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengers E. D., Princen H. M., Kooistra T., van Hinsbergh V. W. Inhibition of plasminogen activators by conditioned medium of human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line Hep G2. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jun;105(6):751–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran-Thang C., Fasel-Felley J., Pralong G., Hofstetter J. R., Bachmann F., Kruithof E. K. Plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors in liver deficiencies caused by chronic alcoholism or infectious hepatitis. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):651–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. R., Bennett B., Booth N. A. The receptor for tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) in complex with its inhibitor, PAI-1, on human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 14;278(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80092-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. R., Hawksworth G. M., Bennett B., Booth N. A. Clearance of t-PA, PAI-1, and t-PA-PAI-1 complex in an isolated perfused rat liver system. J Lab Clin Med. 1991 Feb;117(2):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]