Abstract
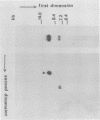
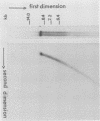
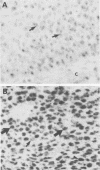
AIMS--To investigate the integration of human papillomavirus (HPV)16 in 13 HPV16 positive cervical squamous carcinomas. METHODS--Samples were investigated by Southern blot analysis of the Pst I digestion pattern, two-dimensional gel-electrophoresis, and in situ hybridisation. RESULTS--Integration of HPV16 was found in all cases. In 12 biopsy specimens episomal HPV16 DNA and integrated HPV16 DNA were seen. The episomal DNA occurred as dimers and multimers. In situ hybridisation showed that both integrated and episomal HPV16 DNA were present in the same cell in most tumour cell nuclei. CONCLUSIONS--An intact episomal E2 gene is present in most cases of these cervical cancers, and could therefore replace the regulatory function of an integrated defective E2 gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Choo K. B., Lee H. H., Pan C. C., Wu S. M., Liew L. N., Cheung W. F., Han S. H. Sequence duplication and internal deletion in the integrated human papillomavirus type 16 genome cloned from a cervical carcinoma. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1659–1666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1659-1666.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. B., Pan C. C., Han S. H. Integration of human papillomavirus type 16 into cellular DNA of cervical carcinoma: preferential deletion of the E2 gene and invariable retention of the long control region and the E6/E7 open reading frames. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):259–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K., Herrington C. S., Stickland J. E., Evans M. F., McGee J. O. Episomal and integrated human papillomavirus in cervical neoplasia shown by non-isotopic in situ hybridisation. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Dec;44(12):990–996. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.12.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe T. P., Haugen T. H., Turk J. P., Tabatabai F., Schmid P. G., 3rd, Dürst M., Gissmann L., Roman A., Turek L. P. Transcriptional regulation of the human papillomavirus-16 E6-E7 promoter by a keratinocyte-dependent enhancer, and by viral E2 trans-activator and repressor gene products: implications for cervical carcinogenesis. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3745–3753. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02709.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen A. P., Reid R., Campion M., Lörincz A. T. Analysis of the physical state of different human papillomavirus DNAs in intraepithelial and invasive cervical neoplasm. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):606–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.606-612.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Dzarlieva-Petrusevska R. T., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Gissmann L. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of immortalized human primary keratinocytes obtained after transfection with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Kleinheinz A., Hotz M., Gissmann L. The physical state of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA in benign and malignant genital tumours. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1515–1522. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. G., Girardi F., Pfister H. Human papillomavirus 16 DNA in cervical cancers and in lymph nodes of cervical cancer patients: a diagnostic marker for early metastases? Int J Cancer. 1989 Jan 15;43(1):41–44. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima M., Yamakawa Y., Shimano S., Hashimoto M., Sawada Y., Fujinaga K. The physical state of human papillomavirus 16 DNA in cervical carcinoma and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Cancer. 1990 Nov 15;66(10):2155–2161. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19901115)66:10<2155::aid-cncr2820661019>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm R., Karlsen F., Nesland J. M. In situ hybridization with nonisotopic probes using different detection systems. Mod Pathol. 1992 May;5(3):315–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., McDougall J. K. Characterization of primary human keratinocytes transformed by human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1917-1924.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura T., Koi S., Sugase M. Both episomal and integrated forms of human papillomavirus type 16 are involved in invasive cervical cancers. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pater M. M., Pater A. Human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 sequences in carcinoma cell lines of the cervix. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Yasumoto S., Feller M., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Transformation of human fibroblasts and keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1061-1066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., DiPaolo J. A. Integration of human papillomavirus 16 DNA and genomic rearrangements in immortalized human keratinocyte lines. Cancer Res. 1990 Feb 15;50(4):1316–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. C., Rawls W. E., Brinton L. A. Epidemiology of genital papillomaviruses and cervical cancer. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):426–439. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.3.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Phelps W. C., Zhang Y. L., Barbosa M. Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3181–3187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Freese U. K., Gissmann L., Mayer W., Roggenbuck B., Stremlau A., zur Hausen H. Structure and transcription of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical carcinoma cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):111–114. doi: 10.1038/314111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettstein F. O., Stevens J. G. Variable-sized free episomes of Shope papilloma virus DNA are present in all non-virus-producing neoplasms and integrated episomes are detected in some. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):790–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee C., Krishnan-Hewlett I., Baker C. C., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. Presence and expression of human papillomavirus sequences in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):361–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Awady M. K., Kaplan J. B., O'Brien S. J., Burk R. D. Molecular analysis of integrated human papillomavirus 16 sequences in the cervical cancer cell line SiHa. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90478-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]