Abstract
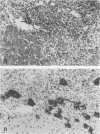
AIMS--To see how useful the application of a bile duct specific cytokeratin antibody (AE1) was in identifying and counting bile ducts in liver allograft biopsy specimens. METHODS--Eighteen liver biopsy specimens showing acute rejection and 17 biopsy specimens plus six hepatectomy specimens showing chronic rejection were studied. Serial sections were cut and stained with haematoxylin and eosin and AE1 antibody. Two pathologists (RFH and KP) examined the sections with respect to a range of histological features. RESULTS--Similar numbers of bile ducts were identified on haematoxylin and eosin sections as on corresponding sections stained by AE1 in cases of acute rejection and end stage chronic rejection. Greater numbers of bile ducts were identified by AE1 during the early stages of chronic rejection, especially when dense portal inflammatory infiltrates were present. These were often incomplete structures or individual cells within portal tracts, and bile ducts subsequently disappeared in all cases. Ductular proliferation was clearly shown by AE1 in acute rejection and the extent seemed to correlate with the severity of rejection present. By contrast, no ductular proliferation was observed in chronic rejection. CONCLUSIONS--Haematoxylin and eosin stained sections are adequate for counting bile ducts in most biopsy specimens from patients with suspected chronic rejection. Immunostaining for biliary cytokeratins using AE1 is of limited use in occasional cases where bile ducts are obscured by inflammatory cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Demetris A. J., Belle S. H., Hart J., Lewin K., Ludwig J., Snover D. C., Tillery G. W., Detre K. Intraobserver and interobserver variation in the histopathological assessment of liver allograft rejection. The Liver Transplantation Database (LTD) Investigators. Hepatology. 1991 Nov;14(5):751–755. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840140502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demetris A. J., Lasky S., Van Thiel D. H., Starzl T. E., Dekker A. Pathology of hepatic transplantation: A review of 62 adult allograft recipients immunosuppressed with a cyclosporine/steroid regimen. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jan;118(1):151–161. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet V. J. Intrahepatic bile ducts under the lens. J Hepatol. 1985;1(5):545–559. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80752-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese D. K., Snover D. C., Sharp H. L., Gross C. R., Savick S. K., Payne W. D. Chronic rejection after liver transplantation: a study of clinical, histopathological and immunological features. Hepatology. 1991 May;13(5):882–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubscher S. G., Buckels J. A., Elias E., McMaster P., Neuberger J. Vanishing bile-duct syndrome following liver transplantation--is it reversible? Transplantation. 1991 May;51(5):1004–1010. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199105000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubscher S. G. Histological findings in liver allograft rejection--new insights into the pathogenesis of hepatocellular damage in liver allografts. Histopathology. 1991 Apr;18(4):377–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Y. S., Thung S. N., Gerber M. A., Chen M. L., Schaffner F. Expression of cytokeratins in normal and diseased livers and in primary liver carcinomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989 Feb;113(2):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J., Wiesner R. H., Batts K. P., Perkins J. D., Krom R. A. The acute vanishing bile duct syndrome (acute irreversible rejection) after orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1987 May-Jun;7(3):476–483. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanuma Y., Ohta G. Histometric and serial section observations of the intrahepatic bile ducts in primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jun;76(6):1326–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguma S., Belle S., Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J. A histometric analysis of chronically rejected human liver allografts: insights into the mechanisms of bile duct loss: direct immunologic and ischemic factors. Hepatology. 1989 Feb;9(2):204–209. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snover D. C., Sibley R. K., Freese D. K., Sharp H. L., Bloomer J. R., Najarian J. S., Ascher N. L. Orthotopic liver transplantation: a pathological study of 63 serial liver biopsies from 17 patients with special reference to the diagnostic features and natural history of rejection. Hepatology. 1984 Nov-Dec;4(6):1212–1222. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spagnolo D. V., Michie S. A., Crabtree G. S., Warnke R. A., Rouse R. V. Monoclonal anti-keratin (AE1) reactivity in routinely processed tissue from 166 human neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Dec;84(6):697–704. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/84.6.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thung S. N., Gerber M. A. Histological features of liver allograft rejection: do you see what I see? Hepatology. 1991 Nov;14(5):949–951. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840140530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thung S. N. The development of proliferating ductular structures in liver disease. An immunohistochemical study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990 Apr;114(4):407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner R. H., Ludwig J., van Hoek B., Krom R. A. Current concepts in cell-mediated hepatic allograft rejection leading to ductopenia and liver failure. Hepatology. 1991 Oct;14(4 Pt 1):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(91)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]