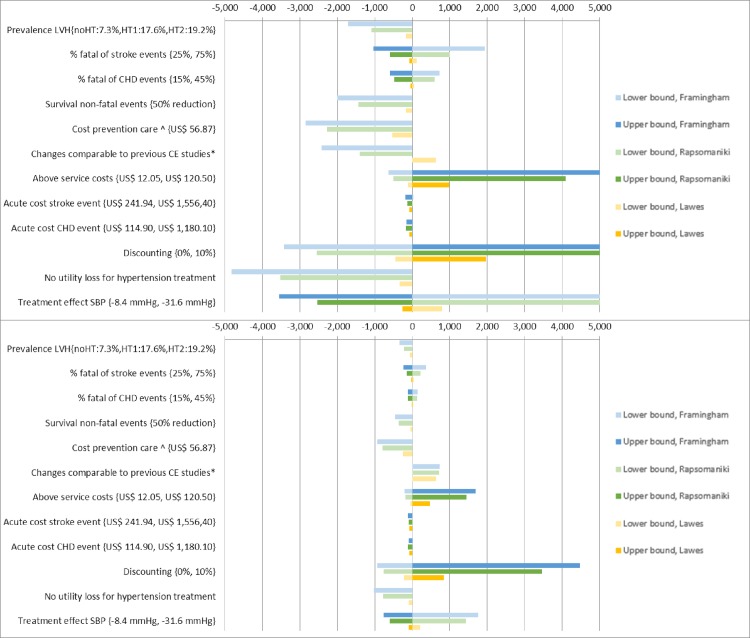
Within Fig 3, Fig 3A and 3B are incorrectly reversed. The authors have provided the correct Fig 3 here.
Fig 3.
3A: One-way sensitivity analysis, risk and HT based strategy. Fig 3B: One-way sensitivity analysis, risk based strategy. Legend Fig 3A and 3B: Presents the change in ICER (incremental costs per DALY averted) compared to the baseline when parameter input is either varied in a high and low bound or when parameter input is varied to an alternative scenario (presented as lower bound). Darker and lighter bars represent the change in ICER when a parameter is varied to a respectively lower value (or alternative scenario) and higher value compared to the baseline estimate. *effect of treatment on SBP: -14.6, coverage of 100% for eligible patients and no disability loss for hypertension treatment. ^based on observed costs in a scenario when limited diagnostic testing and task-shifting from doctors to nurses[24]. Abbreviations: SBP: systolic blood pressure; CHD: coronary heart disease; LVH: left ventricle hypertrophy. noHT: no hypertension; HT1: hypertension stage 1; HT2: hypertension stage 2. All values for the parameters tested as well as resulting ICERs are reported in Tables K and L (S1 File).
There is an error in Table 1. The row “Relative risk reduction (RRR0 per 10 mmHg SBP decrease” was incorrectly omitted. The publisher apologizes for this error.
Table 1. Input parameters for cost-effectiveness analyses.
| Population and risk factor distributions | ||||
| Proportion (SE) | Average (SE) | Distribution | Source # | |
| Age categories | ||||
| 30–44 years old | 0.37 (0.01) | 35.8 (0.15) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| 45–59 years old | 0.34 (0.01) | 50.1 (0.15) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| 60–69 years old | 0.19 (0.01) | 62.5 (0.14) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| 70–79 years old | 0.11 (0.01) | 71.8 (0.17) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| Gender, male | 0.45 (0.01) | - | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| Hypertension severity^ | ||||
| No hypertension | 0.77 (0.01) | 114.0 (0.30) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| Hypertension, stage 1 | 0.13 (0.01) | 142.66 (0.56) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| Hypertension, stage 2 | 0.11 (0.01) | 173.49 (1.36) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| Total Cholesterol | ||||
| TC > 5 mmol/L | 0.08 (0.01) | 5.49 (0.05) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| TC < = 5 mmol/L | 0.92 (0.01) | 3.66 (0.02) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol | ||||
| TC > 5 mmol/L* | 0.08 (0.01) | 1.36 (0.09) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| TC < = 5 mmol/L* | 0.92 (0.01) | 1.08 (0.02) | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| Current daily smoking | 0.12 (0.01) | N.A. | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| Diabetes | 0.04 (0.01) | N.A. | Beta | Kwara HH survey |
| Probabilities and outcomes in model | ||||
| Stroke event | Base Case | Range | Distribution | Source # |
| Probability of stroke event | Framingham risk score per risk profile per year | [26] | ||
| Probability of stroke to be fatal within one year | 0.53 | 0.50–0.57 | Triangular | [30–42] |
| Survival time if stroke fatal within one year | 82.0 days | 77.6–89.6 days | Triangular | [30–42] |
| Survival time if stroke non-fatal within one year | Age- and gender-specific, adapted to Nigeria | [43,44] | ||
| CHD event | Base Case | Range | Distribution | Source # |
| Probability of CHD event | Framingham risk score per risk profile per year | [25] | ||
| Probability of CHD to be fatal within one year | 0.30 | 0.26–0.33 | Triangular | [16,45,46] |
| Survival time if CHD fatal within one year | 49.3 days | 44.3–61.3 days | Triangular | [16,45,46] |
| Survival time if CHD non-fatal within one year | Age- and gender-specific, adapted to Nigeria | [44,47] | ||
| Other death | Distribution | Source # | ||
| Probability of non-CVD mortality per year | Age- and gender-specific table in supplement | [44] | ||
| Hypertension treatment | Base Case | Range | Distribution | Source # |
| Coverage in KSHI program | 29% | - | - | Kwara HH survey |
| SBP decrease–individuals on antihypertensive treatment (mmHg) | -20 | (-31.6–-8.4) | Triangular | Kwara HH survey |
| SBP decrease–screened hypertensive individuals, not on antihypertensive treatment (mmHg) | -2.4 | (-6.0–0) | Triangular | Kwara HH survey |
| Relative risk reduction (RRR) per 10 mmHg SBP decrease | Base Case | Range | Distribution | Source # |
| RRR Stroke–based on Lawes 30–44 years old | 2.38 | 2.13–2.63 | Triangular | [7] |
| RRR Stroke–based on Lawes 45–59 years old | 2 | 1.92–2.04 | Triangular | [7] |
| RRR Stroke–based on Lawes 60–69 years old | 1.56 | 1.52–1.61 | Triangular | [7] |
| RRR Stroke–based on Lawes 70–79 years old | 1.37 | 1.32–1.43 | Triangular | [7] |
| RRR CHD–based on Lawes 30–44 years old | 1.92 | 1.54–2.38 | Triangular | [7] |
| RRR CHD–based on Lawes 45–59 years old | 1.67 | 1.56–1.75 | Triangular | [7] |
| RRR CHD–based on Lawes 60–69 years old | 1.33 | 1.27–1.39 | Triangular | [7] |
| RRR CHD–based on Lawes 70–79 years old | 1.25 | 1.191.32 | Triangular | [7] |
| RRR Stroke–based on Rapsomaniki | 1.16 | 1.14–1.18 | Triangular | Calculated from[48] |
| RRR CHD–based on Rapsomaniki | 1.16 | 1.15–1.18 | Triangular | Calculated from[48] |
| Cost parameters (2012 US$) | ||||
| Base Case | Range | Distribution | Source # | |
| Cost of hypertension care per patient per year | 112 | 101–126 | Triangular | Adapted from [24] |
| Cost of screening per person screened | 5 | 4–6 | Triangular | [49] |
| Above-service delivery costs of insurance program management per patient per year | 24 | - | Triangular | KSHI program management |
| Cost of acute care after a stroke per patient | 380 | 242–1,556 | Triangular | Base Case: UITH data, [24] Range: [16,17,19,35,50–57] |
| Cost of follow up care after a stroke per patient per year | 240 | 206–275 | Triangular | [24] |
| Cost of acute care after CHD event per patient | 181 | 115–1,180 | Triangular | Base Case: UITH data, [24] Range: [16,17,19] |
| Cost of follow up care after CHD event per patient per year | 278 | 235–320 | Triangular | [24] |
| DALY assumptions | ||||
| Base Case | Range | Distribution | ||
| Disability weight during survival period after a fatal stroke (death during first year) | 0.553 | 0.363–0.738 | Triangular | Adapted from [27] |
| Disability weight during survival after a non-fatal stroke | 0.256 | 0.021–0.553 | Triangular | Adapted from [27] |
| Disability weight during survival period after a fatal CHD event (death during first year) | 0.180 | 0.135–0.250 | Triangular | Adapted from [27] |
| Disability weight during survival after a non-fatal CHD event | 0.09 | 0.022–0.234 | Triangular | Adapted from [27] |
| Disability weight while on antihypertensive treatment | 0.031 | 0.017–0.05 | Triangular | [27] |
Reference
- 1.Rosendaal NTA, Hendriks ME, Verhagen MD, Bolarinwa OA, Sanya EO, Kolo PM, et al. (2016) Costs and Cost-Effectiveness of Hypertension Screening and Treatment in Adults with Hypertension in Rural Nigeria in the Context of a Health Insurance Program. PLoS ONE 11(6): e0157925 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0157925 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]