Abstract
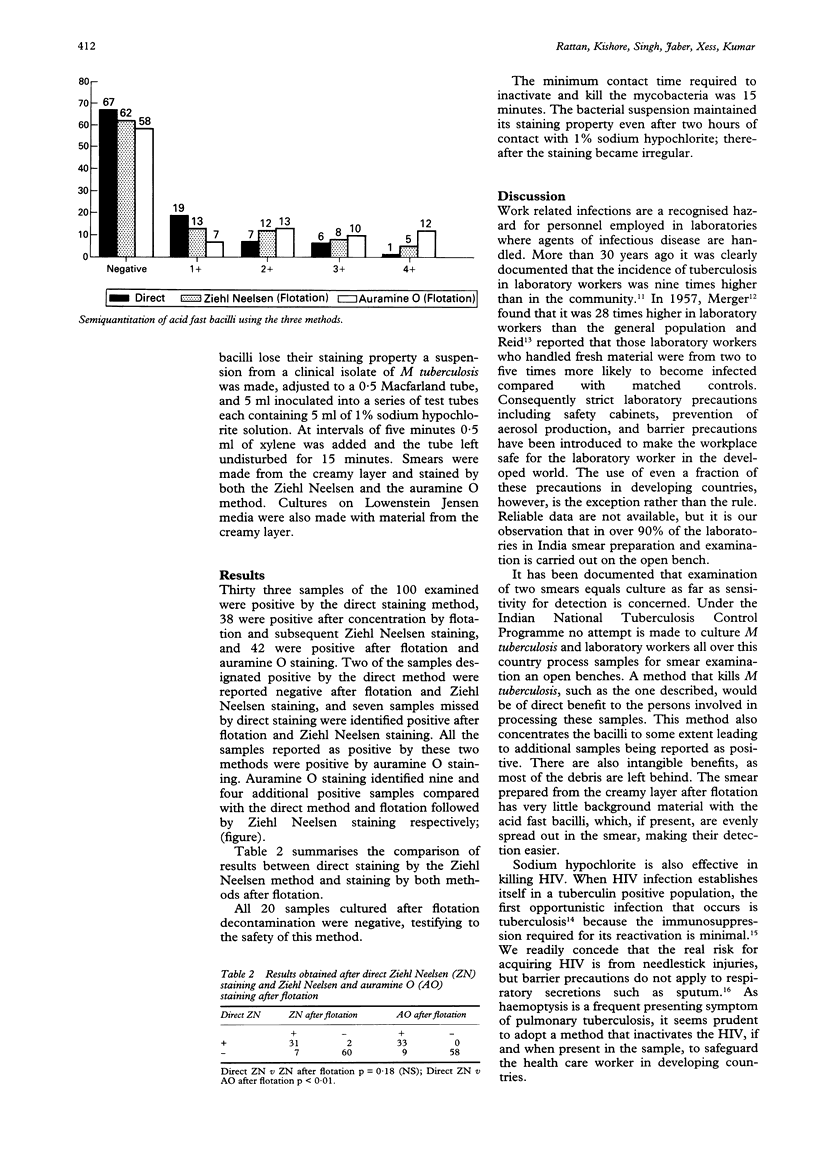
AIMS--To evaluate a safe sputum processing method for detection of tuberculosis in developing countries. METHODS--A sample processing method was developed in which acid fast bacilli were killed with 1% sodium hypochlorite and concentrated by flotation on a layer of xylene before staining by the Ziehl Neelsen or auramine O methods. RESULTS--Best results were obtained by auramine O staining after flotation. Staining by the Ziehl Neelsen method after flotation gave better results than direct Ziehl Neelsen staining without flotation. CONCLUSIONS--The flotation method with Ziehl Neelsen staining offers advantages for smear preparation in the tuberculosis control programmes of developing countries.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. F., Bloch A. B., Davidson P. T., Snider D. E., Jr Tuberculosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 6;324(23):1644–1650. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106063242307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. H. Laboratory-acquired tuberculosis. Tubercle. 1982 Sep;63(3):151–155. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(82)80025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contijo Filho P. P., Fonseca K. S. The flotation method for detection of tubercle bacilli in sputum smears. Tubercle. 1979 Jun;60(2):105–107. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(79)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley S. W., Jarvis W. R., Martone W. J., Snider D. E., Jr Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 1;117(3):257–259. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-3-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Uttamchandani R. B., Daikos G. L., Poblete R. B., Moreno J. N., Reyes R. R., Boota A. M., Thompson L. M., Cleary T. J., Lai S. An outbreak of tuberculosis caused by multiple-drug-resistant tubercle bacilli among patients with HIV infection. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 1;117(3):177–183. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-3-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERGER C. Hazards associated with the handling of pathogenic bacteria. Can J Med Technol. 1956 Dec;18(4):122–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKOL E. X., HORTON R., LINCOLN N. S., STOKES A. M. Incidence of pulmonary tuberculosis among employees of tuberculosis hospitals. Am Rev Tuberc. 1952 Jul;66(1):16–27. doi: 10.1164/art.1952.66.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra A., Rattan A., Kishore K., Jaber M., Gupta A., Malhotra R., Sarma R. K. Universal precautions--a critical review. J Acad Hosp Adm. 1993 Jan;5(1):47–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson M. L., Jereb J. A., Frieden T. R., Crawford J. T., Davis B. J., Dooley S. W., Jarvis W. R. Nosocomial transmission of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A risk to patients and health care workers. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 1;117(3):191–196. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-3-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID D. D. Incidence of tuberculosis among workers in medical laboratories. Br Med J. 1957 Jul 6;2(5035):10–14. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5035.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


