Abstract
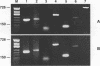
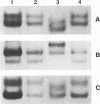
AIM--To establish a simple and reliable polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methodology for random amplification of whole genomic DNA from limited histopathological samples. METHODS--Trace amounts of genomic DNA extracted from fresh tissue and individual lymphoid follicles microdissected from archival paraffin wax tissue sections were amplified using a two-phase PCR protocol with random hexamers as primers (RP-PCR). The randomly amplified DNA samples were used as templates for specific PCR amplifications. To check the fidelity of the RP-PCR, products of the specific PCR amplifications were further analysed by single stranded conformation polymorphism (SSCP) or sequencing. RESULTS--Using a minute fraction of RP-PCR template pool, multiple PCR analyses, including those for beta globin gene, p53 gene (exon 5-6, exon 7, exon 8-9 and exon 7-9), and rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene fragments (VH framework 3 to JH and VH framework 2 to JH) were successfully performed. No artefactual mutations were identified in the products of these specific PCR reactions by SSCP or sequencing when compared with the products from the original DNA. CONCLUSION--This method is simple and reliable, and permits multiple genetic analyses when only a limited amount of tissue is available.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diss T. C., Peng H., Wotherspoon A. C., Isaacson P. G., Pan L. Detection of monoclonality in low-grade B-cell lymphomas using the polymerase chain reaction is dependent on primer selection and lymphoma type. J Pathol. 1993 Mar;169(3):291–295. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert K. A., Kunkel T. A. DNA polymerase fidelity and the polymerase chain reaction. PCR Methods Appl. 1991 Aug;1(1):17–24. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaidano G., Ballerini P., Gong J. Z., Inghirami G., Neri A., Newcomb E. W., Magrath I. T., Knowles D. M., Dalla-Favera R. p53 mutations in human lymphoid malignancies: association with Burkitt lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5413–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson P. G., Wotherspoon A. C., Diss T., Pan L. X. Follicular colonization in B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991 Sep;15(9):819–828. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199109000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan L. X., Diss T. C., Peng H. Z., Isaacson P. G. Clonality analysis of defined B-cell populations in archival tissue sections using microdissection and the polymerase chain reaction. Histopathology. 1994 Apr;24(4):323–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1994.tb00532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenius H., Carter N. P., Bebb C. E., Nordenskjöld M., Ponder B. A., Tunnacliffe A. Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR: general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):718–725. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90147-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Cui X., Schmitt K., Hubert R., Navidi W., Arnheim N. Whole genome amplification from a single cell: implications for genetic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5847–5851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]