Abstract
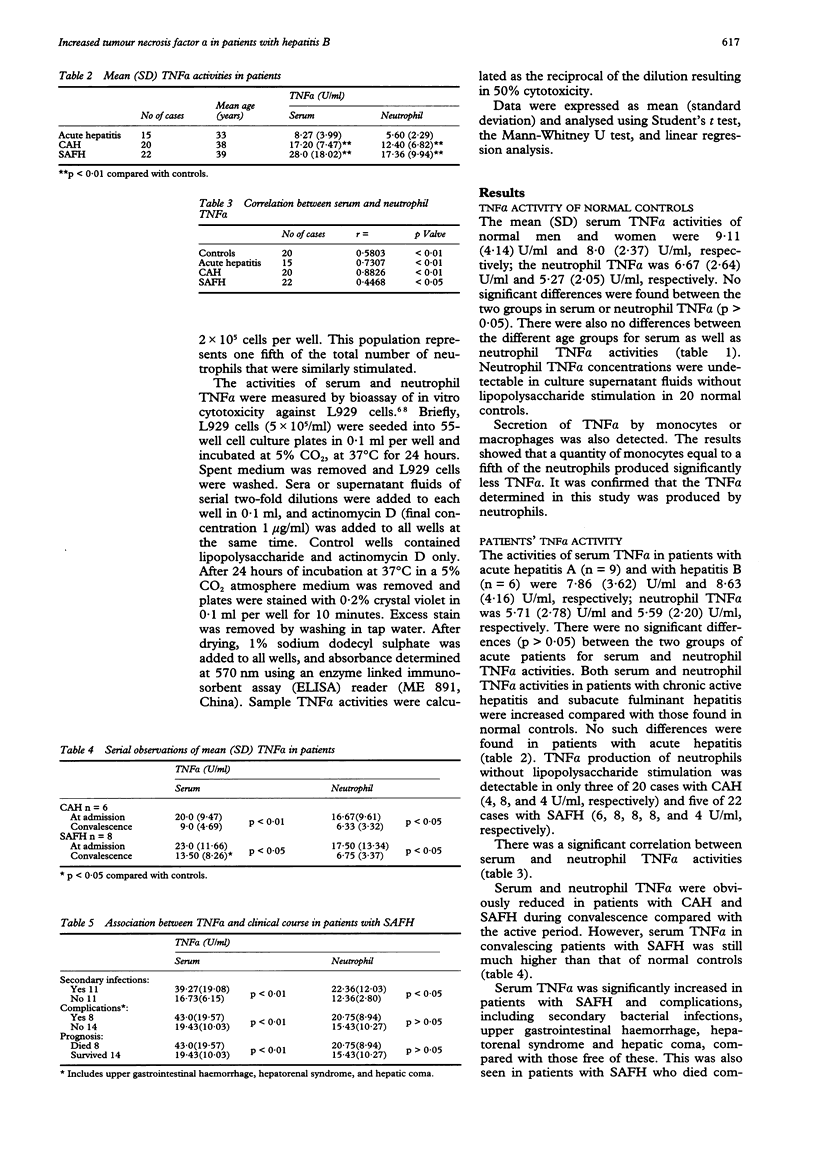
AIMS--To investigate the role of serum and neutrophil tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) in patients with viral hepatitis. METHODS--The activities of serum and neutrophil TNF alpha were measured using a bioassay of in vitro cytotoxicity against L929 cells in 57 patients with viral hepatitis and 20 healthy blood donors. RESULTS--Both serum and neutrophil TNF alpha in patients with chronic active hepatitis (CAH) and subacute fulminant hepatitis (SAFH) increased compared with those in normal controls (p < 0.01). No such differences were seen in patients with acute hepatitis. Serum and neutrophil TNF alpha were obviously reduced in patients with CAH and SAFH during convalescence compared with the active period (p < 0.05; p < 0.01). Furthermore, serum TNF alpha was significantly increased in patients with SAFH and complications compared with those without (p < 0.01), and in patients with SAFH who died compared with those who survived (p < 0.01). Neutrophil TNF alpha was significantly higher in patients with SAFH and secondary bacterial infections (p < 0.05). CONCLUSIONS--Production of serum and neutrophil TNF alpha is increased in patients with CAH and SAFH, suggesting that neutrophil TNF alpha causes liver injury in these patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Levo Y. Does tumor necrosis factor play a role in the pathogenesis of fulminant hepatitis? Med Hypotheses. 1988 Nov;27(3):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(88)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M. J., Bentley I. S., Tanner A. R., Saunders P. K., Millward-Sadler G. H., Wright R. Oxygen-derived free radicals promote hepatic injury in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1114–1122. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubravec D. B., Spriggs D. R., Mannick J. A., Rodrick M. L. Circulating human peripheral blood granulocytes synthesize and secrete tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6758–6761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Fox R. A., Sherlock S. Cellular immunity and hepatitis-associated, Australia antigen liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Apr 1;1(7753):723–726. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Inadequate antibody response to hBAg or suppressor T-cell defect in development of active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1974 Dec 28;2(7896):1543–1545. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer S. M., Carver M. E. Serum-free in vitro bioassay for the detection of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 6;93(2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Graham D., Toy K., Lin L. S., Senyk G., Fendly B. M. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor causes activation of human granulocytes. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):640–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Lethal toxicity of lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor in normal and D-galactosamine-treated mice. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):657–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S., Balkwill F. R. Tumour necrosis factor. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Apr 30;296(6631):1214–1214. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6631.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain C. J., Cohen D. A. Increased tumor necrosis factor production by monocytes in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology. 1989 Mar;9(3):349–351. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto Y., Nouri-Aria K. T., Meager A., Alexander G. J., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Enhanced tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in fulminant hepatic failure. Lancet. 1988 Jul 9;2(8602):72–74. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Williams R. IL-8 as a circulating cytokine: induction by recombinant tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jul;89(1):100–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06885.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slungaard A., Vercellotti G. M., Walker G., Nelson R. D., Jacob H. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin stimulates eosinophil oxidant production and toxicity towards human endothelium. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):2025–2041. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. P., Arroyo V., Gazzard B. G., Moodie H., Williams R. Relation of renal impairment and haemorrhagic diathesis to endotoxaemia in fulminant hepatic failure. Lancet. 1974 Mar 30;1(7857):521–524. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92711-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Kakumu S., Arao M., Tsutsumi Y., Inoue M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 1989 Nov;10(5):769–773. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Kakumu S., Arao M., Tsutsumi Y., Inoue M., Wakita T., Ishikawa T., Mizokami M. Immunohistochemical studies of intrahepatic tumour necrosis factor alpha in chronic liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Apr;43(4):298–302. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.4.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



