Abstract
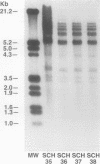
AIMS--To assess a chemiluminescent universal probe for taxonomical and epidemiological investigations of Aeromonas sp isolates. METHODS--Total DNA was extracted from 69 well characterised Aeromonas sp strains and digested with the restriction endonucleases Sma I or Pst I. Following electrophoresis, the resulting fragments were transferred to a nylon membrane where they were hybridised to a commercially available universal probe of 16S + 23S rRNA. The banding patterns (ribotypes) were made visible by enhanced chemiluminescence. RESULTS--Both restriction endonucleases produced heterogeneous ribotypes so that no allocation could be made to any of the control genospecies tested. For A hydrophila and A caviae, however, groups of strains (mostly from the same patient) could be identified by indistinguishable banding patterns. A relatively high proportion (36%) of A sobria strains were non-typable. CONCLUSIONS--Although this universal chemiluminescent probe is user friendly, it is unsuitable for taxonomical investigations of Aeromonas sp. It is useful in epidemiological studies of A hydrophila and A caviae, but is of less value for A sobria.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott S. L., Cheung W. K., Kroske-Bystrom S., Malekzadeh T., Janda J. M. Identification of Aeromonas strains to the genospecies level in the clinical laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1262–1266. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1262-1266.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar N., Eley A. Restriction endonuclease analysis and ribotyping differentiate genital and nongenital strains of Bacteroides ureolyticus. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Sep;30(9):2408–2414. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.9.2408-2414.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altwegg M., Altwegg-Bissig R., Demarta A., Peduzzi R., Reeves M. W., Swaminathan B. Comparison of four typing methods for Aeromonas species. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1988 Jun;6(2):88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altwegg M., Steigerwalt A. G., Altwegg-Bissig R., Lüthy-Hottenstein J., Brenner D. J. Biochemical identification of Aeromonas genospecies isolated from humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):258–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.258-264.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnahan A. M., Behram S., Joseph S. W. Aerokey II: a flexible key for identifying clinical Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2843–2849. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2843-2849.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang B. J., Bolton S. M. Plasmids and resistance to antimicrobial agents in Aeromonas sobria and Aeromonas hydrophila clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1281–1282. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustaferro C. A., Persing D. H. Chemiluminescent universal probe for bacterial ribotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):1039–1041. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.1039-1041.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokka R. P., Janda J. M., Oshiro L. S., Altwegg M., Shimada T., Sakazaki R., Brenner D. J. Biochemical and genetic characterization of autoagglutinating phenotypes of Aeromonas species associated with invasive and noninvasive disease. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):890–894. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Steigerwalt A. G., Schoenmakers B. S., Peeters M. F., Zanen H. C., Brenner D. J. Phenotypic characterization and DNA relatedness in human fecal isolates of Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):132–138. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.132-138.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., van Alphen L., Leenders E., Zanen H. C. Typing of Aeromonas strains by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of cell envelopes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1280–1285. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1280-1285.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinetti Lucchini G., Altwegg M. rRNA gene restriction patterns as taxonomic tools for the genus Aeromonas. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):384–389. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Borman P. A rapid biochemical method for purifying high molecular weight bacterial chromosomal DNA for restriction enzyme analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3631–3631. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Goullet P. Epidemiological complexity of hospital aeromonas infections revealed by electrophoretic typing of esterases. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Feb;98(1):5–14. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800061665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M. H., Cook A. M., Eley A., Spencer R. C. Aeromonas spp as a potential cause of diarrhoea in children. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Nov;45(11):959–963. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.11.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M. H., Cook A. M., Thickett K. J., Eley A., Spencer R. C. Phenotypic methods for speciating clinical Aeromonas isolates. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Dec;45(12):1079–1083. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.12.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]