Abstract
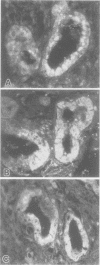
AIM--To determine whether pancreatic enzymes are present in hepatic bile and in intrahepatic bile duct epithelium. METHODS--The activity and proteins of pancreatic enzymes (pancreatic alpha-amylase, lipase, trypsin/trypsinogen) in hepatic bile were investigated using biochemical and western blot analyses in 25 patients with extrahepatic bile duct obstruction. Immunolocalization of enzyme proteins was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in 20 necropsy livers with extrahepatic bile duct obstruction. RESULTS--Western blot analysis showed proteins of pancreatic alpha-amylase, lipase, and trypsin in 19 of 25 (76%), 10 of 25 (40%), and 14 of 25 (56%) patients, respectively. Pancreatic alpha-amylase and lipase activities was present in every bile specimen. Radioimmunoassay showed that trypsin was present in every bile sample. Immunohistochemically, the immunoreactivity of the three enzymes was present in epithelia and in the lumina of intrahepatic large bile ducts, septal bile ducts, and peribiliary glands in all cases. CONCLUSIONS--These results strongly suggest that biliary epithelia of larger intrahepatic ducts produce pancreatic alpha-amylase, lipase, and trypsin, and that these enzymes are secreted into the lumina of intrahepatic bile ducts.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskams T., van den Oord J. J., De Vos R., Desmet V. J. Neuroendocrine features of reactive bile ductules in cholestatic liver disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Nov;137(5):1019–1025. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Nakanuma Y. Lactoferrin and lysozyme in the intrahepatic bile duct of normal livers and hepatolithiasis. An immunohistochemical study. J Hepatol. 1992 May;15(1-2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90028-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Schaffner F., Popper H. Bile ductules in cholestasis: morphologic evidence for secretion and absorption in man. Lab Invest. 1967 Jan;16(1):84–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura H., Nakanuma Y. Secretory component and immunoglobulins in the intrahepatic biliary tree and peribiliary gland in normal livers and hepatolithiasis. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1989 Jun;24(3):308–314. doi: 10.1007/BF02774329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada T., Kida T., Nakanuma Y. Extrahepatic peribiliary glands express alpha-amylase isozymes, trypsin and pancreatic lipase: an immunohistochemical analysis. Hepatology. 1993 Oct;18(4):803–808. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840180409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada T., Nakanuma Y. Development of human intrahepatic peribiliary glands. Histological, keratin immunohistochemical, and mucus histochemical analyses. Lab Invest. 1993 Mar;68(3):261–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada T., Nakanuma Y. Expression of alpha-amylase isoenzymes and trypsin by the proliferating epithelium of large intrahepatic bile ducts and intrahepatic peribiliary glands in hepatolithiasis. Histopathology. 1993 May;22(5):467–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada T., Nakanuma Y. Pancreatic lipase is a useful phenotypic marker of intrahepatic large and septal bile ducts, peribiliary glands, and their malignant counterparts. Mod Pathol. 1993 Jul;6(4):419–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]