Abstract
Aim:
To evaluate the efficacy of platelet rich fibrin (PRF) with or without bone graft [demineralized bone matrix (DBM) graft] in the treatment of intrabony defects based on clinical and radiographic parameters.
Materials and Methods:
Thirty six intrabony defects in 36 patients were randomly divided into three different groups and were treated with group A (PRF with DBM) or group B (PRF alone) or group C [open flap debridement (OFD)]. Clinical parameters such as plaque index (PI), gingival index (GI), probing depth (PD), relative attachment level (RAL), and gingival recession (GR) were assessed at baseline and 9 months postoperatively; radiographic parameters such as linear bone growth (LBG) and percentage in bone fill (%BF) were calculated by using the image analysis software. Comparisons of groups were analyzed using Kruskal–Wallis analysis of variance test. Pair-wise comparison of groups was done by Mann-Whitney U test.
Results:
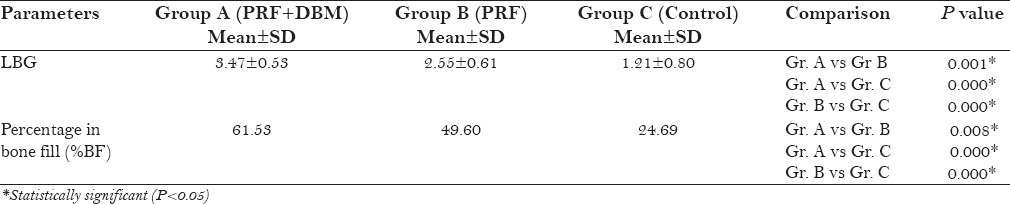
Mean PD reduction and RAL gain were greater in group A (4.25 ± 1.48, 3.92 ± 0.90) and group B (3.82 ± 0.75, 3.27 ± 0.65) than control (3.00 ± 1.21, 2.25 ± 0.62). Furthermore, statistically significant improvement in LBG and %BF was found in group A (3.47 ± 0.53, 61.53 ± 4.54) compared to group B (2.55 ± 0.61, 49.60 ± 14.08) and group C (1.21 ± 0.80, 24.69 ± 15.59).
Conclusions:
The study demonstrated that PRF improves clinical and radiological parameters compared to OFD alone in intrabony defects. Addition of DBM enhances the effects of PRF in RAL gain and radiographic defect fill.
Key words: Chronic periodontitis, clinical trial, periodontal attachment loss, platelet-derived growth factor, regeneration
INTRODUCTION
Various biomaterials have been used for the treatment of intrabony defects and have demonstrated variable results.[1] Recently, biological modifiers demonstrated their ability to stimulate cells which are located in periodontal defects and resulted in proliferation and differentiation of periodontal ligament cells.[2] Platelets are considered as a natural source of these growth factors that play a vital role in enhancing wound healing after periodontal treatment.[3] Platelet rich fibrin (PRF), which belongs to second generation platelet concentrate, was first developed in France by Choukroun et al.[4] The natural fibrin clot in PRF seems to be responsible for slow release of growth factors for an extended period.[5] Because of its strict autologous nature, extended growth factor release, and cost-effectiveness, PRF may be considered as a better treatment option compared to platelet rich plasma (PRP) – a first generation platelet concentrate.[6] Even though numerous studies have shown the role of PRF in bone regeneration, the effect of PRF in combination with bone graft is still remaining inconclusive. The purpose of this clinical study was to evaluate the effectiveness of PRF in the treatment of intrabony defects and to assess the ability of bone graft to enhance the regenerative effects of PRF.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The present randomized, controlled clinical trial was conducted in the Department of Periodontics, from December 2012 to March 2015. The study was performed according to the Helsinki declaration, and ethical clearance (SHDCH/2012-13/336(4) Dated on 21.11.2012) for the study was obtained from the institutional ethics committee. The participants enrolled for the study were informed verbally, and written consent was obtained before the start of the trial. A total of 38 patients were screened from the outpatient department of periodontics.
Each patient contributed one defect per site. In case of multiple defects, site with deepest probing depth was selected. The sample size was calculated based on the formula. 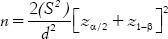 Thirty six intrabony defects were selected (18 males and 18 females, age range: 35-50) based on following inclusion criteria: systemically healthy patients diagnosed with chronic periodontitis based on the international workshop for the classification of periodontal disease,[7] having ≥20 teeth and ≥30% of sites with >4 mm clinical attachment loss (CAL), probing depth (PD) ≥5 mm, and presence of intrabony defect (IBD) ≥3 mm (measured from alveolar crest to the base of the defect on intraoral periapical radiograph). Exclusion criteria were patients with use of tobacco or tobacco-related products; systemic or local application of antibiotics within the previous 6 months; patients with poor oral hygiene (plaque index (PI) ≥3) after the revaluation of cause-related therapy. The present study was conducted for a period of 9 months. After verification of the inclusion criteria, 2 patients were excluded from the screening group as they failed to meet the study protocol. Total 36 patients (sites) were randomly assigned to one of the three treatment regimens, group A, PRF with DBM, group B, PRF alone, and group C, control (OFD) [Figure 1]. Allotment of participants within the groups was performed randomly by creating a randomization list by means of a freeware link (http://www.graphad.com/quickcalcs/randomize1.cfm). The treatment allocation of the patients was prepared and sealed in the numbered opaque envelopes and were opened during surgery immediately after completing the defect debridement. Allocation protocol was unavailable to the periodontal examiner (RS) throughout the study. Patients were masked for allocation to particular group and treatment. All the surgical procedures in three groups were performed by a trained periodontist (NC). The pre and postoperative assessments were performed by another examiner (RS) without knowledge of the nature of intervention.
Thirty six intrabony defects were selected (18 males and 18 females, age range: 35-50) based on following inclusion criteria: systemically healthy patients diagnosed with chronic periodontitis based on the international workshop for the classification of periodontal disease,[7] having ≥20 teeth and ≥30% of sites with >4 mm clinical attachment loss (CAL), probing depth (PD) ≥5 mm, and presence of intrabony defect (IBD) ≥3 mm (measured from alveolar crest to the base of the defect on intraoral periapical radiograph). Exclusion criteria were patients with use of tobacco or tobacco-related products; systemic or local application of antibiotics within the previous 6 months; patients with poor oral hygiene (plaque index (PI) ≥3) after the revaluation of cause-related therapy. The present study was conducted for a period of 9 months. After verification of the inclusion criteria, 2 patients were excluded from the screening group as they failed to meet the study protocol. Total 36 patients (sites) were randomly assigned to one of the three treatment regimens, group A, PRF with DBM, group B, PRF alone, and group C, control (OFD) [Figure 1]. Allotment of participants within the groups was performed randomly by creating a randomization list by means of a freeware link (http://www.graphad.com/quickcalcs/randomize1.cfm). The treatment allocation of the patients was prepared and sealed in the numbered opaque envelopes and were opened during surgery immediately after completing the defect debridement. Allocation protocol was unavailable to the periodontal examiner (RS) throughout the study. Patients were masked for allocation to particular group and treatment. All the surgical procedures in three groups were performed by a trained periodontist (NC). The pre and postoperative assessments were performed by another examiner (RS) without knowledge of the nature of intervention.
Figure 1.
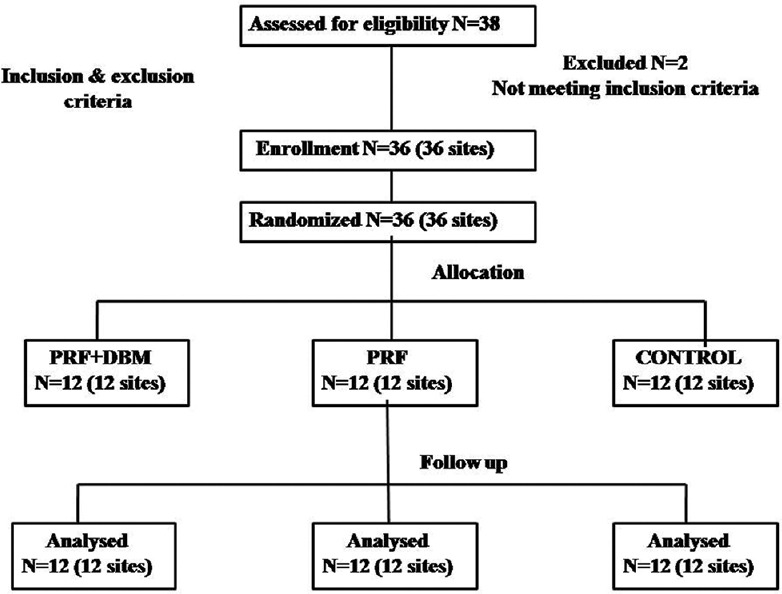
Consolidated standard of reporting trials (CONSORT) flow chart. N: Number of patients, PRF: Platelet. rich fibrin, DBM: Demineralized bone matrix xenograft
Clinical parameters
Clinical measurements were performed using the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) or a fixed reference point, when applicable. All measurements were recorded to the nearest millimetre using University of North Carolina no. 15 (UNC-15, Hu-Friedy, Chicago, IL, USA) periodontal probe. Plaque scores were assessed using Silness and Loe[8] PI and gingival condition was assessed with the help of Loe and Silness[9] gingival index (GI). Gingival recession (GR) was measured as the distance from CEJ to the crest of the receded free gingival margin. Probing depth (PD) was measured as the distance from gingival margin to the base of the pocket. An occlusal stent was prepared with cold cure acrylic resin and a groove was made on the stent in relation to each selected tooth to guide the probe position.[10] Relative attachment level (RAL) was measured from apical border of the stent to the base of the pocket. All clinical parameters were assessed by a single examiner. Examiner calibration was conducted in 7 participants with similar clinical situation with an interval of 48 hours. The examiner calibration was found reproducible if measurements were similar to the mm at the ≥90% level.
Radiographic assessment
Intraoral periapical (IOPA) radiographs were obtained by long cone paralleling technique at baseline and 9 months postsurgery using a Flow RAPD right angle positioning device and a size 2 E speed IOPA X-ray film (Kodak intra oral X-ray film, care stream health India private limited, Mumbai) in an X-ray unit (70 kV, 7 mA). Individually customized bite blocks were prepared by asking the patient to bite on putty index along with holder and were used pre and postoperatively to standardize the position of exposure. These radiographs were scanned and computer assisted image analysis of the radiographs was done with the help of AutoCAD image analysis software (2010, Autodesk, India Pvt. Ltd, Mumbai, India) [Figures 2 and 3]. All radiographic parameters were assessed by the same evaluator who was masked to the surgical intervention performed. The intraexaminer calibration was assessed by performing radiographic measurements in 10 radiographs, not involved in study groups. The anatomical landmarks of the defects were selected based on the criteria set by Schei et al.[11] which include CEJ, alveolar crest (AC), and base of the defect (BD). Defect depth (DD) was assessed by drawing an auxiliary line (AUX 1) parallel to the long axis of the tooth. A second auxiliary line (AUX 2) perpendicular to AUX 1 was drawn from the AC. The DD was measured from the lateral extension of intrabony defect to the point where AUX 2 crossed the root surface to the BD.[12]
Figure 2.
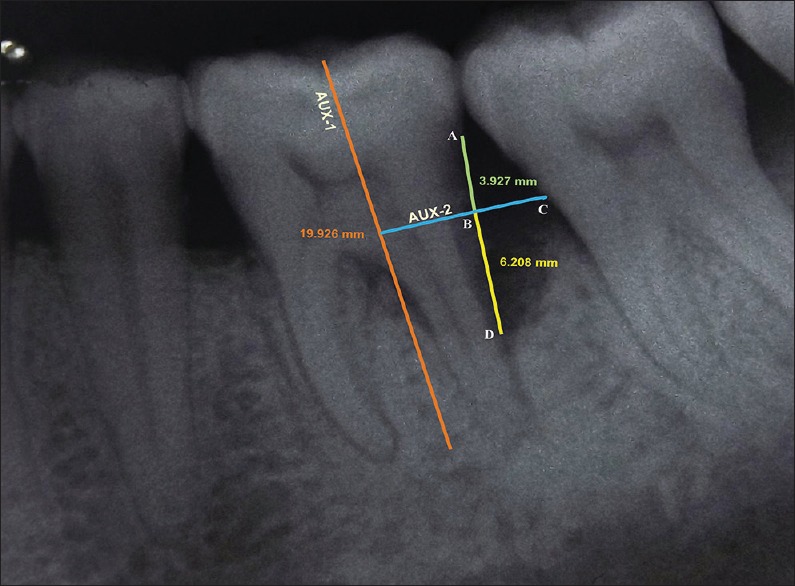
Radiographic appearance at baseline for site treated with PRF + DBM. AUX 1: Auxillary line 1 was drawn in the direction of tooth long axis, A: Cementoenamel junction (CEJ), C: Most coronal extension of the lateral wall of intrabony defect, AUX 2: Auxillary line 2 was drawn perpendicular to the tooth long axis and through point C, D: Base of the defect, B: Point where AUX 2 cross the contour of the root to point
Figure 3.
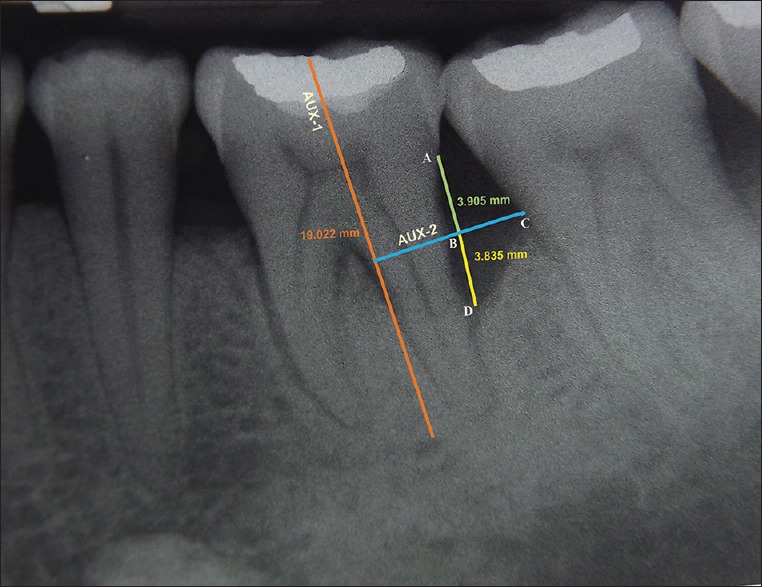
Radiographic appearance at 9 months for site treated with PRF + DBM. AUX 1: Auxillary line 1 was drawn in the direction of tooth long axis, A: Cementoenamel junction (CEJ), C: Most coronal extension of the lateral wall of intrabony defect, AUX 2: Auxillary line 2 was drawn perpendicular to the tooth long axis and through point C, D: Base of the defect, B: Point where AUX 2 cross the contour of the root to point D
The radiographic distance between CEJ to root apex was measured to correct the foreshortening/elongation. If any difference in this measurement existed between baseline and the 9 month radiograph, the measurements were corrected for any distortion. Radiographic parameters evaluated were linear bone growth (LBG) and percentage in bone fill (%BF). LBG was calculated by subtracting the CEJ to the BD value at baseline and 9 months. %BF was calculated by dividing LBG by DD at the baseline.
Surgical therapy
Local anesthesia (2% lidocaine with 1:80000 adrenaline) was administered and bone sounding was done to identify the extension of the defect. Intrasulcuar incisions were given buccally and lingually involving one tooth mesial and distal to the intrabony defect and mucoperiosteal flaps were reflected. Vertical incisions were avoided. After performing meticulous defect debridement, direct measurement of the osseous defect was obtained with UNC-15 periodontal probe.
Plate rich fibrin preparation
The PRF was prepared according to the process protocol developed by Choukroun et al. (2001).[4,13] Immediately before the surgical procedure, 10 ml intravenous blood was drawn by venipuncturing the antecubital vein. Blood was collected in a sterile glass test tube without any anticoagulant, and centrifuged immediately using a centrifuge (REMI, R-4c, Mumbai, India) at 3000 rpm for 12 min. The fibrin clot (middle) layer was removed along with a small RBC layer at the end of PRF clot to collect as many platelets and leukocytes as possible.[14] In the PRF + DBM group the required amount of DBM with a particle size of 250 microns (Osseograft, advanced biotech, Chennai, India) was mixed with PRF which had been minced into small pieces. The mixture was made into a workable consistency and delivered into the defect. In the PRF group the defects were filled with minced PRF only. The control group defects were treated with OFD only. The flaps were secured with interrupted 3-0 black braided silk sutures (Ethicon, Johnson and Johnson Ltd., Somerville, NJ, USA). The surgical area was protected with a non-eugenol pack (Coe Pack, GC, America Inc. Alsp, IL, USA).
Postoperative treatment
The patients were prescribed systemic antibiotic (Amoxicillin 500 mg) for 5 days and analgesics (Ibuprofen 400 mg + Paracetamol 500 mg) three times per day. Patients were instructed to avoid brushing, flossing and chewing in the surgical area for a period of 2-3 weeks. All the patients were instructed to use 0.2% chlorhexidine rinses twice daily for 2 weeks. Sutures were removed 1 week postoperatively.
Statistical analysis
The sample size was set a priori at 12 patients per group with a power of 80% based on the results of previous randomized controlled study.[15] Clinical and radiographic measurements for each group are presented as mean ± SD. The net difference between each pair of measurements (pre and postoperative) was calculated, followed by computation of the difference among treatment groups. Comparisons of groups were analyzed using Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA test. Pair-wise comparison of groups was done by Mann–Whitney U test. Values of P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
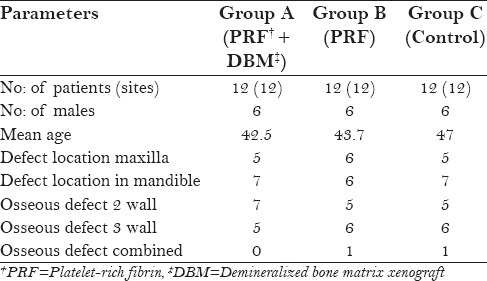
All participants were followed up for a period of 9 months. Postoperative healing of all the control and test sites were uneventful. Participant's age, gender, defect characteristics, and location are presented in [Table 1].
Table 1.
Subject age, gender, osseous defect morphology, and defect location
Clinical parameters
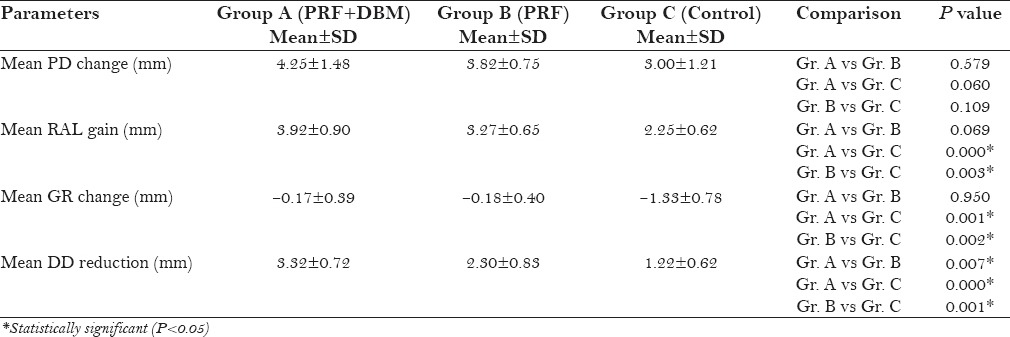
A statistically significant reduction in the PI, GI [Table 2], and PD [Table 3] were observed in all three groups at 9 months postoperatively (P < 0.05). A mean reduction in PD was higher in group A and B compared to group C, however, the results were not statistically significant [Table 4]. All three groups revealed a significant gain (P < 0.05) in RAL [Table 3]. Intergroup comparison showed a significant gain in RAL in PRF + DBM and PRF group compared to the control group [Table 4]. A significant reduction in mean GR was also observed in PRF + DBM and PRF group compared to the control [Table 4].
Table 2.
PI and GI scores in groups (A, B, C) at baseline and 9 months
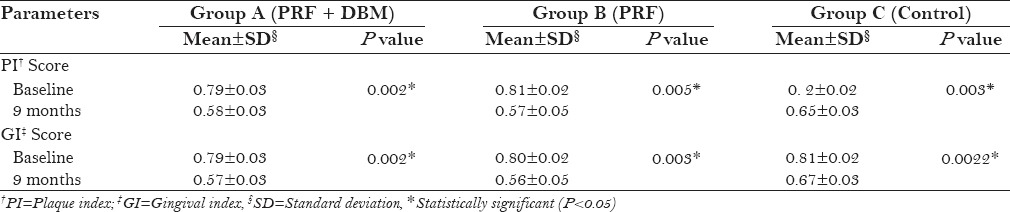
Table 3.
PD, RAL, GR, and DD scores in groups at baseline and 9 months
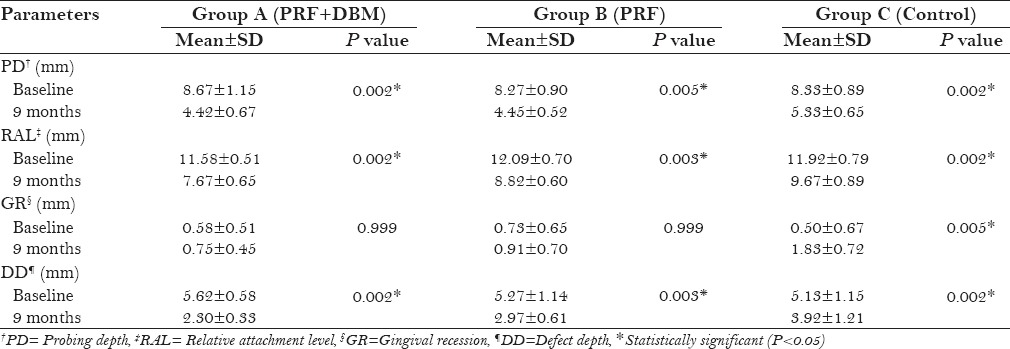
Table 4.
Comparison of groups (A,B,C) with respect to mean changes in clinical parameters and radiographic DD over 9 month period
Radiographic parameters
All groups showed a significant reduction in DD at 9 months postoperatively (P < 0.05) [Table 3]. Inter-group analysis revealed a statistically significant (P < 0.05) mean DD reduction in group A compared to group B and C [Table 4]. The LBG and %BF were significantly higher in the group A compared to that in the group B and C [Table 5]. The postoperative IOPA radiograph at 9 months represents the changes in radiographic parameters [Figure 3].
Table 5.
Comparison of linear bone growth (LBG) and Percentage in bone fill (%BF) at 9 months among groups
DISCUSSION
PRF attracts the attention of researchers and clinicians owing to its dense fibrin matrix, which results in slower and sustained release of growth factors from platelets and leukocytes.[16,17] The presence of leukocytes in platelet concentrates provide an antibacterial effect in the wound;[18] moreover, PRF acts as a source of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which is essential for angiogenesis.[19] Previous studies proved that PRF can be used as a sole regenerative material along with OFD,[6,20,21,22] however, a recent systematic review showed lack of evidence regarding the effect of PRF in combination with grafting materials.[23] In vivo and in vitro studies with DBM showed effective healing, radiographic bone fill, and improvement in clinical parameters.[24,25]
In the present study PD, RAL, and GR were considered to be clinical outcome measures and LBG and %BF as radiographic outcome measures. Improved PD reduction was observed in PRF treated sites (groups A and B) compared to group C. An impressive RAL gain (3.92 ± 0.90), LBG (3.47 ± 0.53) and %BF (61.53 ± 4.54) were observed in PRF + DBM group compared to PRF and control groups. Sites treated with PRF (group A and B) showed less GR compared to control group.
The better PD reduction observed in PRF treated sites (groups A and B) may be related to the elevated concentrations of polypeptide growth factors, which might have enhanced soft tissue healing. The present finding is in accordance with the previous studies by Choukroun et al.[4] and Dohan et al.[5] The significant improvement in RAL, LBG, and %BF in this trial can be attributed to the use of DBM, which maintains the space for tissue formation to occur and osteoconductive property of the graft may act as scaffold for the growth of mineralized tissue.[25] One more positive effect of DBM is the presence of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), which are released during the demineralization process.[26] It is speculated that BMPs in their active state (osteoinductive) promote the effects of growth factors within the platelets, which provide a synergetic effect on the different cell populations of the surgical wound.[27,28] The results of the present trial are in accordance with previous study by Lekovic et al.[29] which showed a defect fill of 4.06 ± 0.87mm on buccal and 3.94 ± 0.73 on lingual sites in PRF + BPBM (Bovine porous bone mineral) compared to PRF group (2.21 ± 0.68 mm on buccal and 2.06 ± 0.64 mm on lingual sites). Agarwal et al.[30] reported that PRF + DFDBA (demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft) showed a mean bone fill of 3.50 ± 0.67 mm compared to DFDBA (2.49 ± 0.64 mm). Clinical attachment level (CAL) gain is considered one of the most important parameter reflecting the soft tissue healing, and LBG and %BF were considered as parameters for bone formation. The results of this study clearly show a significant improvement in CAL gain in sites treated with PRF [Table 4]. Similarly, addition of DBM significantly enhanced the bone formation at 9 months. This supports the significance of growth factors in PRF that may improve the soft and hard tissue healing.[6]
GR observed at 3 months was maintained for a period of 9 months in PRF treated sites. This finding may be explained by additional biological properties of PRF. The 3D fibrin matrix in PRF has mechanical adhesive properties and acts like fibrin glue: which hold and maintain the flap in a stable position. Agarwal et al.[31] reported a complete root coverage (100%) in 33.3% sites treated with coronally advanced flap with PRF using microsurgical approach. The improvement in PD, RAL, LBG, and %BF observed in PRF treated sites of present investigation are along the expected lines and in accordance with a recent systematic review.[23] Hence, the results of this trial add to the current evidence regarding the use of PRF with grafting material. The main limitations of our study are less sample size and inability to perform histological analysis due to ethical reason.
CONCLUSION
Within the limits of this study, it is concluded that treatment of intrabony defect with PRF appears to be associated with improvement in clinical and radiological parameters with uneventful healing. Addition of DBM enhances the clinical effects of PRF, with particular benefits, in terms of %BF in intrabony defects. Considering the autologous nature, minimal cost and time, PRF can be incorporated as a regenerative material in intrabony defects. Further, long-term multicenter randomized, clinical trials with large sample size and histological evaluation of new bone formation are needed to confirm the results of this study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Reynolds MA, Kao RT, Camargo PM, Caton JG, Clem DS, Fiorellini JP, et al. Periodontal regeneration – Intrabony defects: A consensus report from the AAP Regeneration Workshop. J Periodontol. 2015;86:S105–7. doi: 10.1902/jop.2015.140378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang ZS, Feng ZH, Wu GF, Bai SZ, Dong Y, Chen FM, et al. The use of platelet-rich fibrin combined with periodontal ligament and jaw bone mesenchymal stem cell sheets for periodontal tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28126. doi: 10.1038/srep28126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kim TH, Kim SH, Sandor GK, Kim YD. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), and concentrated growth factor (CGF) in rabbit-skull defect healing. Arch Oral Biol. 2014;59:550–8. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2014.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Choukroun J, Adda F, Schoeffler C, Vervelle A. PRF: An opportunity in perio-implantology. Implantodontie. 2001;42:55–62. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dohan DM, de Peppo GM, Doglioli P, Sammartino G. Slow release of growth factors and thrombospondin-1 in Choukrouns platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A gold standard to achieve for all surgical platelet concentrates technologies. Growth Factors. 2009;27:63–9. doi: 10.1080/08977190802636713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pradeep AR, Rao NS, Agarwal E, Bajaj P, Kumari M, Naik SB. Comparative evaluation of autologous platelet-rich fibrin and platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of 3 wall intrabony defects in chronic periodontitis: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2012;83:1499–507. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.110705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Armitage GC. Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann Periodontol. 1999;4:1–6. doi: 10.1902/annals.1999.4.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Silness J, Loe H. Periodontal disease in pregnancy. II. Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condition. Acta Odontol Scand. 1964;22:121–35. doi: 10.3109/00016356408993968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Loe H. The gingival index, the plaque index and the retention index systems. J Periodontol. 1967;38:610–16. doi: 10.1902/jop.1967.38.6.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Isidor F, Karring T, Attstrom R. Reproducibility of pocket depth and attachment level measurements using a flexible splint. J Periodontol. 1984;11:662–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1984.tb01314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schei O, Waerhaug J, Lovdal A, Arno A. Alveolar bone loss as related to oral hygiene and age. J Periodontol. 1959;30:7–16. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eickholz P, Horr T, Klein F, Hassfeld S, Kim T. Radiographic parameters for prognosis of periodontal healing of infrabony defects. Two different definitions of defect depth. J Periodontol. 2004;75:399–407. doi: 10.1902/jop.2004.75.3.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Del Corso M, Diss A, Mouhyi J, Charrier JB. Three-dimensional architecture and cell composition of a Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin clot and membrane. J Periodontol. 2010;81:546–55. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mishra A, Avula H, Pathakota KR, Avula J. Efficacy of modified minimally invasive surgical technique in the treatment of human intrabony defects with or without use of rhPDGF-BB gel- A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2013;40:172–9. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part III: Leucocyte activation: a new feature for platelet concentrates? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101:51–5. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: Platelet-related biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101:45–50. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yang LC, Hu SW, Yan M, Yang JJ, Tsou SH, Lin YY. Antimicrobial activity of platelet-rich plasma and other plasma preparations against periodontal pathogens. J Periodontol. 2015;86:310–8. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.140373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Martinez CE, Smith PC, Palma VA. The influence of platelet-derived products on angiogenesis and tissue repair: A concise update. Front Physiol. 2015;6:290. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mathur A, Bains VK, Gupta V, Jhingran R, Singh GP. Evaluation of intrabony defects treated with platelet-rich fibrin or autogenous bone graft: A comparative analysis. Eur J Dent. 2015;9:100–8. doi: 10.4103/1305-7456.149653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gupta SJ, Jhingran R, Gupta V, Bains VK, Madan R, Rizvi I. Efficacy of platelet-rich fibrin vs. enamel matrix derivative in the treatment of periodontal intrabony defects: A clinical and cone beam computed tomography study. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2014;16:86–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ajwani H, Shetty S, Gopalakrishnan D, Kathariya R, Kulloli A, Dolas RS, et al. Comparative evaluation of platelet-rich fibrin biomaterial and open flap debridement in the treatment of two and three wall intrabony defects. J Int Oral Health. 2015;7:32–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Panda S, Doraiswamy J, Malaiappan S, Varghese SS, Fabbro MD. Additive effect of autologous platelet concentrates in treatment of intrabony defects: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Investig Clin Dent. 2016;7:13–26. doi: 10.1111/jicd.12117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Peker E, Karaca IR, Yildirim B. Experimental evaluation of the effectiveness of demineralized bone matrix and collagenated heterologous bone grafts used alone or in combination with platelet-rich fibrin on bone healing in sinus floor augmentation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31:e24–31. doi: 10.11607/jomi.4414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bigham AS, Dehghani SN, Shafiei Z, Nezhad ST. Xenogenic demineralized bone matrix and fresh autogenous cortical bone effects on experimental bone healing: Radiological, histopathological and biomechanical evaluation. J Orthopaed Traumatol. 2008;9:73–80. doi: 10.1007/s10195-008-0006-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Riley EH, Lane JM, Urist MR, Lyons KM, Lieberman JR. Bone morphogenetic protein-2: Biology and applications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;324:39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kaur S, Grover V, Kaur H, Malhotra R. Evaluation of bone morphogenic proteins in periodontal practice. Indian J Dent. 2016;7:28–37. doi: 10.4103/0975-962X.179379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jain AP, Pundir S, Sharma A. Bone morphogenetic proteins: The anomalous molecules. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2013;17:583–6. doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.119275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lekovic V, Milinkovic I, Aleksic Z, Jankovic S, Stankovic P, Kenney EB, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin and bovine porous bone mineral vs. platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of intrabony periodontal defects. J Periodont Res. 2012;47:409–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2011.01446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Agarwal A, Gupta ND, Jain A. Platelet rich fibrin combined with decalcified freeze-dried bone allograft for the treatment of human intrabony periodontal defects: A randomized split mouth clinical trial. Acta Odontol Scand. 2016;74:36–43. doi: 10.3109/00016357.2015.1035672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Agarwal SK, Jhingran R, Bains VK, Srivastava R, Madan R, Rizvi I. Patient-centered evaluation of microsurgical management of gingival recession using coronally advanced flap with platelet-rich fibrin or amnion membrane: A comparative analysis. Eur J Dent. 2016;10:121–33. doi: 10.4103/1305-7456.175686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


