Abstract
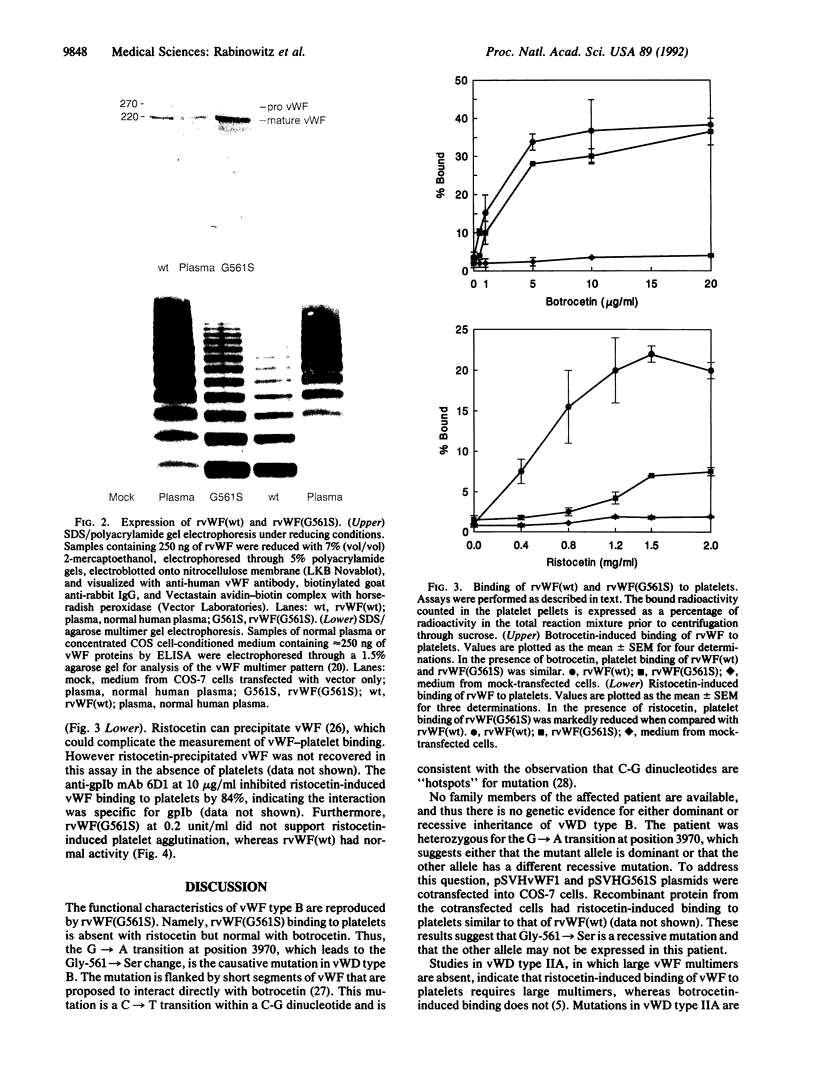
von Willebrand factor (vWF) is a multimeric glycoprotein that mediates the adhesion of platelets to the subendothelium by binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib. For human vWF, this interaction can be induced in vitro by the antibiotic ristocetin or the snake venom protein botrocetin. A missense mutation, Gly-561-->Ser, was identified within the proposed glycoprotein Ib binding domain of vWF in the proband with von Willebrand disease type B, a unique variant characterized by no ristocetin-induced, but normal botrocetin-induced, binding to glycoprotein Ib. The corresponding mutant recombinant protein, rvWF(G561S), formed normal multimers and exhibited the same functional defect as the patient's plasma vWF, confirming that this mutation causes von Willebrand disease type B. These data show that botrocetin and ristocetin cofactor activities of vWF can be dissociated by a point mutation and confirm that these mediators promote vWF binding to platelets by different mechanisms. The normal botrocetin-induced binding and the defective ristocetin-induced binding of rvWF(G561S) suggest that the primary defect in von Willebrand disease type B may be a failure of normal allosteric regulation of the glycoprotein Ib binding function of vWF.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Rose J. K. Incorporation of a charged amino acid into the membrane-spanning domain blocks cell surface transport but not membrane anchoring of a viral glycoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1442–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews R. K., Booth W. J., Gorman J. J., Castaldi P. A., Berndt M. C. Purification of botrocetin from Bothrops jararaca venom. Analysis of the botrocetin-mediated interaction between von Willebrand factor and the human platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8317–8326. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews R. K., Gorman J. J., Booth W. J., Corino G. L., Castaldi P. A., Berndt M. C. Cross-linking of a monomeric 39/34-kDa dispase fragment of von Willebrand factor (Leu-480/Val-481-Gly-718) to the N-terminal region of the alpha-chain of membrane glycoprotein Ib on intact platelets with bis(sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8326–8336. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S., Fricke W. A., Wagner R. H. Botrocetin (venom coagglutinin): reaction with a broad spectrum of multimeric forms of factor VIII macromolecular complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1463–1466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Pachl C., Quiroga M., Rosenberg S., Haigwood N., Nordfang O., Ezban M. The functional domains of coagulation factor VIII:C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12574–12578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney K. A., Nichols W. C., Bruck M. E., Bahou W. F., Shapiro A. D., Bowie E. J., Gralnick H. R., Ginsburg D. The molecular defect in type IIB von Willebrand disease. Identification of four potential missense mutations within the putative GpIb binding domain. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1227–1233. doi: 10.1172/JCI115123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Girolami A., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Interaction of purified type IIB von Willebrand factor with the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib induces fibrinogen binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex and initiates aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7424–7428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Holland L. Z., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. The von willebrand factor domain-mediating botrocetin-induced binding to glycoprotein IB lies between Val449 and Lys728. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):985–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Russell S. R., Roberts J. R., Elder J. H., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor. A reduced and alkylated 52/48-kDa fragment beginning at amino acid residue 449 contains the domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):381–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Usami Y., Titani K., Niinomi K., Nishio K., Takase T., Yoshioka A., Fukui H. Studies on anti-von Willebrand factor (vWF) monoclonal antibody NMC-4, which inhibits both ristocetin- and botrocetin-induced vWF binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):113–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girma J. P., Takahashi Y., Yoshioka A., Diaz J., Meyer D. Ristocetin and botrocetin involve two distinct domains of von Willebrand factor for binding to platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Oct 22;64(2):326–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Firkin B. G. Ristocetin--a new tool in the investigation of platelet aggregation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Oct 31;26(2):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Perkin J., Salem H. H., Firkin B. G. The agglutination of human platelets by botrocetin: evidence that botrocetin and ristocetin act at different sites on the factor VIII molecule and platelet membrane. Br J Haematol. 1984 May;57(1):25–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb02862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Salem H. H., Thomas K. B., Hau L., Perkin J., Coghlan M., Firkin B. G. Variant von Willebrand's disease type B--revisited. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1420–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroner P. A., Kluessendorf M. L., Scott J. P., Montgomery R. R. Expressed full-length von Willebrand factor containing missense mutations linked to type IIB von Willebrand disease shows enhanced binding to platelets. Blood. 1992 Apr 15;79(8):2048–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons S. E., Bruck M. E., Bowie E. J., Ginsburg D. Impaired intracellular transport produced by a subset of type IIA von Willebrand disease mutations. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4424–4430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Worrall N. K., Shelton-Inloes B. B., Sorace J. M., Alevy Y. G., Sadler J. E. Structure of the gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19514–19527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti T., Rösselet S. J., Titani K., Walsh K. A. Identification of disulfide-bridged substructures within human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8099–8109. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier C., Gaucher C., Jorieux S., Parquet-Gernez A., Goudemand M. Evidence for a von Willebrand factor defect in factor VIII binding in three members of a family previously misdiagnosed mild haemophilia A and haemophilia A carriers: consequences for therapy and genetic counselling. Br J Haematol. 1990 Nov;76(3):372–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb06371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Fujimura Y., Shima M., Yoshioka A., Houghten R. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Structure of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17901–17904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio K., Fujimura Y., Niinomi K., Takahashi Y., Yoshioka A., Fukui H., Usami Y., Titani K., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Enhanced botrocetin-induced type IIB von Willebrand factor binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib initiates hyperagglutination of normal platelets. Am J Hematol. 1990 Apr;33(4):261–266. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830330409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines G., Aumann H., Sykes S., Street A. Multimeric analysis of von Willebrand factor by molecular sieving electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulphate agarose gel. Thromb Res. 1990 Nov 1;60(3):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90181-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randi A. M., Rabinowitz I., Mancuso D. J., Mannucci P. M., Sadler J. E. Molecular basis of von Willebrand disease type IIB. Candidate mutations cluster in one disulfide loop between proposed platelet glycoprotein Ib binding sequences. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1220–1226. doi: 10.1172/JCI115122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. S., Shermer R. W., Brinkhous K. M. Venom coagglutinin: an activator of platelet aggregation dependent on von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribba A. S., Lavergne J. M., Bahnak B. R., Derlon A., Piétu G., Meyer D. Duplication of a methionine within the glycoprotein Ib binding domain of von Willebrand factor detected by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis in a patient with type IIB von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1991 Oct 1;78(7):1738–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeghiero F., Castaman G., Dini E. Epidemiological investigation of the prevalence of von Willebrand's disease. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):454–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J. Developing relationships: arterial platelet adhesion, glycoprotein Ib, and leucine-rich glycoproteins. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):5–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. P., Montgomery R. R., Retzinger G. S. Dimeric ristocetin flocculates proteins, binds to platelets, and mediates von Willebrand factor-dependent agglutination of platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8149–8155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto M., Mohri H., McClintock R. A., Ruggeri Z. M. Identification of discontinuous von Willebrand factor sequences involved in complex formation with botrocetin. A model for the regulation of von Willebrand factor binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18172–18178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuley E. A., Gaucher C., Jorieux S., Worrall N. K., Sadler J. E., Mazurier C. Expression of von Willebrand factor "Normandy": an autosomal mutation that mimics hemophilia A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6377–6381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Saffaripour S., Bonfanti R., Sadler J. E., Cramer E. M., Chapman B., Mayadas T. N. Induction of specific storage organelles by von Willebrand factor propolypeptide. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90648-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J., Dent J. A., Azuma H., Sugimoto M., Kyrle P. A., Yoshioka A., Ruggeri Z. M. Identification of a point mutation in type IIB von Willebrand disease illustrating the regulation of von Willebrand factor affinity for the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]