Abstract
Use of circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) as a liquid biopsy has been proposed for potential identification and monitoring of solid tumours. We investigate a next-generation sequencing approach for mutation detection in ctDNA in two related studies using a targeted panel. The first study was retrospective, using blood samples taken from melanoma patients at diverse timepoints before or after treatment, aiming to evaluate correlation between mutations identified in biopsy and ctDNA, and to acquire a first impression of influencing factors. We found good concordance between ctDNA and tumour mutations of melanoma patients when blood samples were collected within one year of biopsy or before treatment. In contrast, when ctDNA was sequenced after targeted treatment in melanoma, mutations were no longer found in 9 out of 10 patients, suggesting the method might be useful for detecting treatment response. Building on these findings, we focused the second study on ctDNA obtained before biopsy in lung patients, i.e. when a tentative diagnosis of lung cancer had been made, but no treatment had started. The main objective of this prospective study was to evaluate use of ctDNA in diagnosis, investigating the concordance of biopsy and ctDNA-derived mutation detection. Here we also found positive correlation between diagnostic lung biopsy results and pre-biopsy ctDNA sequencing, providing support for using ctDNA as a cost-effective, non-invasive solution when the tumour is inaccessible or when biopsy poses significant risk to the patient.
Introduction
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has been known to exist in blood since 1948, and is present in all people to some degree[1,2]. In maternal plasma, cfDNA has proven to be a useful source of fetal genetic material to diagnose certain inherited conditions during pregnancy [3]. In cancer patients, solid tumours often release DNA into the circulation, leading to the suggestion that blood-derived circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) could be a source of “liquid biopsy” and act as a surrogate for traditional tumour biopsy [4]. Because it helps to establish the mutational spectrum of the tumour, analysis of ctDNA has been reported to be of potential value in determining prognosis, monitoring tumour evolution during treatment and detection of relapse [5, 6]. Concordance between tumour and plasma DNA mutations has been reported by several groups, in early and late-stage cancers [7–9].
It is well-documented that solid tumours are not composed of a single oncogenic clone, but have extensive inter- and intra-tumoural genetic heterogeneity [10]. This variation is due in part to genomic instability caused by defects in DNA repair and replication, and in part due to the effects of treatment, when new driver mutations may emerge as treatment-sensitive clones diminish. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) of a targeted panel of cancer genes allows simultaneous detection of a large set of informative mutations from small amounts of material that are usually taken from a single biopsy. Theoretically, ctDNA should be more representative of the spatial heterogeneity of the tumour compared with discrete biopsies. Lung cancer and melanoma exhibit the highest frequency of somatic mutations of the solid cancers and present the greatest opportunities for targeted and personalised therapies.
Previous NGS analysis of ctDNA has detected a wide range of mutant allele frequencies, from 52% [11] down to 2–3% [4, 6]. Structural variants and copy number variations have been measured down to levels of 0.75–0.9% [11, 12]. Other approaches, which rely on the capture of specific recurrent mutations before sequencing, can detect allele frequencies as low as 0.02% [13].
Here we study two aspects of next-generation sequencing in ctDNA: first we identify factors influencing the concordance between mutations in melanoma tumours and circulating DNA. Second, we examine whether ctDNA sequencing can be used in lung cancer diagnosis, by sequencing plasma DNA taken prior to bronchoscopy.
Materials and Methods
Patient samples
This study, under the authority of the Oxford Radcliffe Biobank (ORB), was reviewed and approved by the South Central—Oxford C Research Ethics Committee (REC reference number 09/H0606/5+5), before the study began. Written informed consent was provided by participants (melanoma and suspected lung cancer patients) according to current ORB guidelines. Blood was drawn, stored at room temperature and processed within 6 hours. In the case of lung patients, blood samples were taken a few minutes prior to tumour biopsy.
Sample processing and extraction of circulating nucleic acids
In order to minimise lymphocyte lysis, blood samples were centrifuged at 2060 x g (3000 rpm in Beckman GS-6R centrifuge) for 10 minutes at room temperature without brake within 6 hours of collection [14]. Plasma was transferred to a new tube, mixed, and aliquots were pipetted into microfuge tubes. After 10 min in the centrifuge at 7000 rpm, the supernatants were transferred to new microfuge tubes and stored at -80°C until DNA extraction. Plasma DNA was isolated using Qiagen QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol (QIAGEN Ltd., Manchester, UK). Matching gDNA was extracted from whole blood using Qiagen QIAamp DSP DNA Blood mini kit. DNA quantity was determined using Qubit dsDNA High Sensitivity assay kit on a Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer (ThermoFisher, Paisley, UK).
Preparation of AmpliSeq libraries for sequencing on the Ion Torrent™ PGM®
Sequencing libraries were prepared with the Ion Ampliseq Cancer Hotspot Panel. The panel contains a collection of primers designed to interrogate hotspot regions in genes commonly mutated in cancer. Over the course of this study, the first version of the panel, which targeted 46 genes, was replaced by a new version targeting 50 genes (https://tools.lifetechnologies.com/content/sfs/brochures/Ion-AmpliSeq-Cancer-Hotspot-Panel-Flyer.pdf, ThermoFisher). Libraries were generated according to the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly, multiplex PCR was performed with the Ion Ampliseq library kit 2.0 using approximately 10 ng DNA and the panel primer pool. IonXpress-barcoded adapters were attached to the amplicons by ligation. The libraries were purified using Agencourt AMPure XP magnetic beads (Beckman Coulter Ltd, High Wycombe, UK) and either quantified by qPCR using the Ion Library Quantitation Kit (melanoma samples) or amplified using adapter primers (lung samples). Libraries quantified by qPCR were diluted 1:100 and run in duplicate on an ABI 7500. Amplified libraries were purified again, and then quantified on an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer using the High Sensitivity DNA kit (Agilent Technologies, Stockport, UK). Library templates for sequencing were prepared by emulsion PCR on the One Touch 2 instrument and loaded onto 318 semiconductor chips and the Ion Torrent PGM™ sequencer [15].
Sequence analysis
The analysis was run with Torrent Variant Caller (TVC) v4.4.5, which was reported to be capable of detecting variants at frequencies of 0.5% [16]. We ran a sensitivity study with spiked-in mutation positive controls and confirmed that the detection limit of 0.5% was a suitable threshold (S1 File, S1 Fig, S1 Table). TVC was called in hotspot mode with 5 inputs: a BAM file, a fasta file of hg19 genome reference, a BED file marking targeted regions, a VCF file specifying hotspot locations, and a parameter file. This TVC version and accompanying parameter set have been optimised to detect single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), hotspot insertion-deletions (indels) smaller than 10bp and non-hotspot indels of at least 5 bp and has been validated with over 400 variants (390 SNP, 15 indel).
Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficients were computed using the R function ‘cor’. Permutation-adjusted (n = 10000) p-values were calculated using a two-tailed test in the R function ‘cor.test’.
Competitive Allele-Specific TaqMan PCR (castPCR)
Competitive Allele-Specific TaqMan® PCR (castPCR™) (ThermoFisher) is a quantitative PCR method that detects specific known mutations [17]. A reference assay is included that measures the total amount of the gene. Nine castPCR assays were available for variants we detected by the cancer hotspot panel, and these were tested on plasma DNA as an orthogonal method. Assays were performed using a BioRad CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System. Percent mutation was calculated as follows:
Where dCt (delta Ct) = Ct mutant–Ct reference (Ct is the threshold cycle, where the fluorescent signal crosses a significant threshold determined automatically by the BioRad CFX96).
Results
Good concordance between melanoma ctDNA and primary tumours when samples were collected before treatment or less than one year apart
This study was a retrospective pilot investigation in melanoma patients to confirm that mutations discovered in the primary tumour were also detectable in ctDNA using the Ion Torrent™ platform, and to examine factors that may affect concordance of mutation detection (Fig 1). Patients in this cohort had a confirmed diagnosis of melanoma and their blood samples were collected either before or after treatment.
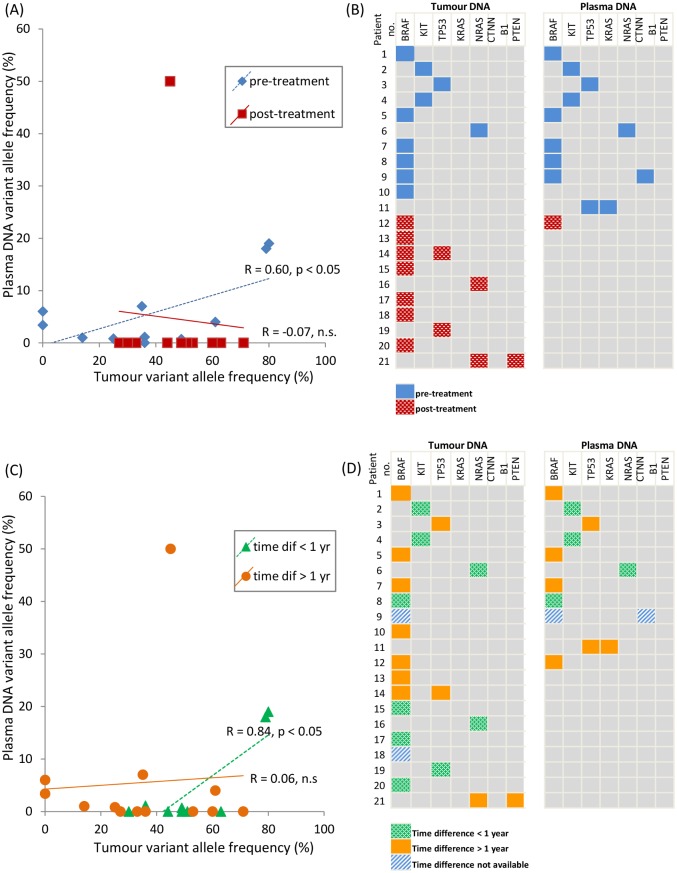
Fig 1. Factors affecting correlation between tumour and plasma DNA variants in melanoma patients.
Tumour and plasma DNA from melanoma patients were sequenced using Ampliseq Cancer Hotspot Panel (8–10 samples per 318 chip), and variant results were compared in relation to two factors, pre- or post-treatment sampling and time difference between sampling of tumour and plasma. (A) Pre- or post-treatment correlation. Blood samples taken before treatment are denoted by blue diamonds, dashed line, and samples taken post-treatment are shown by red squares, solid line; (B) Mutated genes in tumour and plasma DNA, marked in blue if plasma taken pre-treatment, red pattern if plasma was post-treatment; (C) Time difference correlation. Blood samples taken less than a year after biopsy are plotted as green triangles, dashed line, and samples taken more than a year after biopsy are shown as orange circles, solid line; (D) Mutated genes in tumour and plasma DNA, marked in green pattern if time difference between biopsy and blood sampling < 1 year, solid orange if time difference > 1 year (tumour biopsy date not available for patients 9 and 18, marked in blue stripe).
Fig 1, panels A and B, show the effect of treatment time frame on correlation of variant allele frequency between tumour and plasma DNA. Of eleven patients where blood sampling took place before treatment, nine had the same mutation in both ctDNA and primary tumour, and we found a significant positive relationship between the tumour and ctDNA variant allele frequency, Pearsons R(9) = 0.60, p < 0.05 (Panel A, blue diamonds; panel B, solid blue boxes). In contrast, no correlation with tumour variant allele frequency was observed in the ten patients where plasma DNA sampled after treatment took place (Panel A, red squares; Pearsons R(9) = -0.07, n.s.; panel B, red pattern). In patient 9’s plasma DNA (pre-treatment), we detected an additional mutation (CTNNB1 T41A) to the one found in the tumour. In post-treatment samples, the nearly complete absence of mutational findings could be an indication of patients responding to treatment given after tumour biopsy but prior to blood collection for ctDNA extraction. In particular, six of the patients (numbers 13–15, 17, 18, 20) with no mutations detected in ctDNA had previously been given BRAF inhibitors Vemurafenib and Dabrafenib (S2 Table). Patient 12 still carried a BRAF mutation in ctDNA following treatment.
Fig 1, panels C and D, show the effect of a time lag between sampling of tumour and plasma DNA on correlation of mutation allele frequency between the two, in the same set of patients. When blood samples were taken less than a year after biopsy, ctDNA variant allele frequency is significantly correlated with tumour variant allele frequency (Panel C, green dashed line; Pearsons R (7) = 0.84, p < 0.05; panel D, green pattern boxes), whereas samples taken more than a year after biopsy showed no correlation with the tumour (orange solid line; R (11) = 0.06, n.s., and solid orange boxes). It is interesting that no new mutations arose in these patients in the time frame between treatment and sampling, with the exception of patient 11 in which two mutations were found in ctDNA, but none in tumour. S2 Table shows that patient 11’s KRAS G12R ctDNA mutation was present at 6% allele frequency (172/2843 read counts) and TP53 R248Q at 3.4% (388/11654 read counts), which are comfortably above the detection limit of 0.5%. The lack of mutations found in the tumour could result from biopsy sampling of genomically heterogeneous tumour regions or from tumour evolution during the time lag, which was more than two years between tumour and plasma sampling. The depth of coverage of the tumour sequence at the mutation position was 3454 reads for KRAS and 5930 reads for TP53, respectively, and it is highly unlikely with this deep coverage to be due to lack of detection.
Together, this pilot study with melanoma patients demonstrates that ctDNA could be a reliable surrogate for tumour biopsy when sampled in a similar time frame and before treatment. Although it was a retrospective study, the dearth of mutations detected post-treatment suggests that ctDNA sequencing could be an attainable and easy measure of whether patients are responding to therapy.
Prospective study in suspected lung cancer patients confirmed high level of concordance between mutations found in ctDNA and diagnostic biopsy
Based on results of the first study, our second study focused on collecting blood samples prospectively from suspected lung cancer patients just prior to diagnostic tumour biopsy (endobronchial or endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy). The advantage of this is that ctDNA could be sampled at the same time as the tumour biopsy and would be free from any potential contamination by tumour DNA released into the blood as a consequence of the procedure. Furthermore, because most patients were at relatively early stages in the cancer pathway and were treatment-naïve, the collected ctDNA would preserve the original mutational load and allelic frequencies. Among lung cancer patients, there were seven adenocarcinomas, three squamous carcinomas, one carcinoid tumour, and one small cell lung cancer. Sequencing of ctDNA from 12 lung cancer patients identified 22 non-synonymous variants (Table 1), with some of the mutations predicted or known to affect protein function and some of which are actionable, as annotated in the Jackson Laboratory Clinical Knowledgebase, https://ckb.jax.org/ [18] and ClinVar database, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/ [19].
Table 1. Lung cancer ctDNA sequencing.
| ID | Histology | Somatic mutation | Variant | Tumour VAF % | ctDNA VAF% | JAX Clinical Knowledgebase (CKB)2 and ClinVar annotation | Implications for Treatment and CKB Reference Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1178 | Adeno1 | yes | TP53 R273C | 19 | 6.8 | CKB: Hotspot mutation in DNA-binding domain of TP53 (PMID: 22713868); ClinVar: probable pathogenic | Treatment approach: p53 activator, p53 gene therapy (gene-associated clinical trials available) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=3795 |
| no | MET N375S | 37 | 44 | CKB: Lies in extracellular Sema ligand-binding domain, predicted loss of function (PMID: 19723643); ClinVar: benign/ likely benign | May confer resistance to MET targeted agents (PMID: 19723643) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=3356 | ||
| 1530 | Metastatic adeno (brain) | no | MET R988C | 49 | 50 | CKB: Gain of function; no increase in MET phosphorylation, but increased cellular protein phosphorylation and increased proliferation and migration of cultured cells (PMID: 14559814, 20670955, 22973954); ClinVar: conflicting: likely benign(2), uncertain sig(2) | Treatment approach: MET inhibitor (Gene-associated clinical trials available) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=706 |
| yes | MET H1112Y | 26 | 6 | CKB: Gain of function; causes constitutive MET phosphorylation and activation of downstream signaling, and transforming in cell culture (PMID: 15064724, 24061647); not found in ClinVar | Treatment approach: MET inhibitor (Gene-associated clinical trials available) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=1004 | ||
| yes | KRAS G12C | 41 | 8 | CKB: Hotspot mutation, inhibits GTPase activity of KRAS leading to increased activation of downstream signaling pathways promoting tumour formation (PMID: 16051643); ClinVar: pathogenic | Confers resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors; Treatment approach: Pan-MEK inhibitor, Pan-PI3K inhibitor, RAS inhibitor (gene-associated clinical trials ongoing) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=979 | ||
| yes | SMAD4 R361H | 34 | 7 | CKB: Hotspot residue in MH2 domain of SMAD4, with predicted loss of function (PMID: 21763698); ClinVar: pathogenic | Rare in lung cancer and for which there is little evidence for targeted therapies https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=1780 | ||
| 1533 | Metastatic adeno | yes | BRAF D594G | 17 | 2 | CKB: Mutation impairs BRAF kinase activity but paradoxically activates MEK and ERK through CRAF transactivation (PMID: 20141835); ClinVar: pathogenic | Results in BRAF inactivation and insensitivity to BRAF inhibitors; Treatment approach: MEK1, MEK2 and pan-MEK inhibitors https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=897 |
| yes | KIT G510C | 21 | 2 | Not found in CKB or ClinVar | none | ||
| yes | TP53 G244C | 24 | 3 | Not found in CKB or ClinVar | none | ||
| 594 | Adeno | no | KIT V532I | 50 | 52 | Not found in CKB or ClinVar | none |
| no | MET T1010I | 39 | 48 | CKB: Conflicting reports: increase in MET phosphorylation (PMID: 25605252), or no effect (PMID: 20670955); ClinVar: non-pathogenic | none; https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=1388 | ||
| yes | TP53 V172F | 17 | 3 | CKB: Mutation in DNA-binding region of TP53 but uncharacterised so its effect is unknown; not found in ClinVar | none; https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=17312 | ||
| 591 | Metastatic adeno | yes | TP53 R249S | 11 | 0.2 | CKB: Hotspot mutation in DNA-binding domain of TP53 (PMID: 22713868), decreased transactivation activity of TP53, and context-dependent transforming ability in cell culture (PMID: 20212049, PMID: 20538734); ClinVar: non-pathogenic | Treatment approach: p53 activator, p53 gene therapy (gene-associated clinical trials available) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=3231 |
| no | JAK3 V722I | 47 | 54 | CKB: Mutation in protein kinase 1 domain of JAK3, confers gain of function and activation of JAK3/STAT3 pathway (PMID: 23689514); ClinVar: no information | Treatment approach: Pan-JAK inhibitor or JAK3 inhibitor https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=1066 | ||
| 590 | Adeno | yes | CTNNB1 G34V | 22 | not found | CKB: Mutation within ubiquitination recognition motif of CTNNB1 (PMID: 15064718), gain of function due to nuclear accumulation of CTNNB1 in liver cancer (PMID: 9671767); ClinVar: conflicting: pathogenic(1); uncertain sig(1) | Treatment approach: CTNNB1 inhibitor, PDPK1 inhibitor, Tankyrase inhibitor https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=3973 |
| 572 | Adeno | negative | |||||
| 463 | Small cell lung cancer | yes | TP53 G245D | not avail. | 4 | CKB: Hotspot mutation in DNA-binding domain of TP53 (PMID: 22713868), decreased activation of p21, and also confers a gain-of-function (PMID: 22214764); ClinVar: pathogenic | Treatment approach: p53 activator, p53 gene therapy (gene-associated clinical trials available) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=4658 |
| no | TP53 M237I | 9 | CKB: Mutation in DNA-binding domain of TP53 (PMID: 22713868), decreased TP53 transactivation activity in cell culture (PMID: 16492679); ClinVar: pathogenic/likely pathogenic | https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=16637 | |||
| 593 | Squamous cell | yes | CDKN2A C72S | not avail. | 17 | Not found in CKB or ClinVar | none |
| yes | PTEN S59* | 21 | CKB: Results in premature truncation of PTEN protein, predicted loss of function (UniProt.org); not found in ClinVar | Treatment approach: Pan-AKT inhibitor, AKT1 inhibitor, AKT2 inhibitor, AKT3 inhibitor, Pan-PI3K inhibitor (gene-associated clinical trials available) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=4433 | |||
| yes | TP53 M237I | 28 | CKB: Mutation in DNA-binding domain of TP53 (PMID: 22713868), decreased TP53 transactivation activity in cell culture (PMID: 16492679); ClinVar: pathogenic/likely pathogenic | https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=16637 | |||
| no | TP53 R175H | 2 | CKB: Hotspot mutation in DNA-binding domain of TP53 (PMID: 22713868), decreased activation of TP53 targets, also confers gain of function to TP53, with aberrant activation of gene transcription (PMID: 10713666, 22114072); ClinVar: pathogenic | Treatment approach: p53 activator, p53 gene therapy (gene-associated clinical trials available) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=735 | |||
| 466 | Squamous cell | yes | TP53 R282W | not avail. | 2 | CKB: Hotspot mutation in DNA-binding domain of TP53 (PMID: 22713868), decreased activation of TP53 targets, inhibited AMPK signaling, and promoted tumour development in mouse models (PMID: 24857548); ClinVar: conflicting: likely benign(2); pathogenic(2) | Treatment approach: p53 activator, p53 gene therapy (gene-associated clinical trials available) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=4744 |
| 538 | Squamous cell | yes | TP53 Y220C | not avail. | 0.6 | CKB: Hotspot mutation in DNA-binding domain of TP53 (PMID: 17401432), loss of function, decreased TP53 transcriptional activity in cell culture (PMID: 16861262, 23630318); ClinVar: pathogenic | Treatment approach: p53 activator, p53 gene therapy (gene-associated clinical trials available) https://ckb.jax.org/geneVariant/show?geneVariantId=980 |
| 462 | Carcinoid tumour | negative | not avail. | negative |
Blood samples were drawn from patients prior to bronchoscopy. Plasma DNA and genomic DNA from each patient were sequenced using Ampliseq Cancer Hotspot Panel v2, using one plasma DNA:gDNA paired sample per 318 chip. Tumour DNA was sequenced when enough bronchoscopy material was available.
1Adeno, adenocarcinoma.
2CKB website content is for educational and research purposes only.
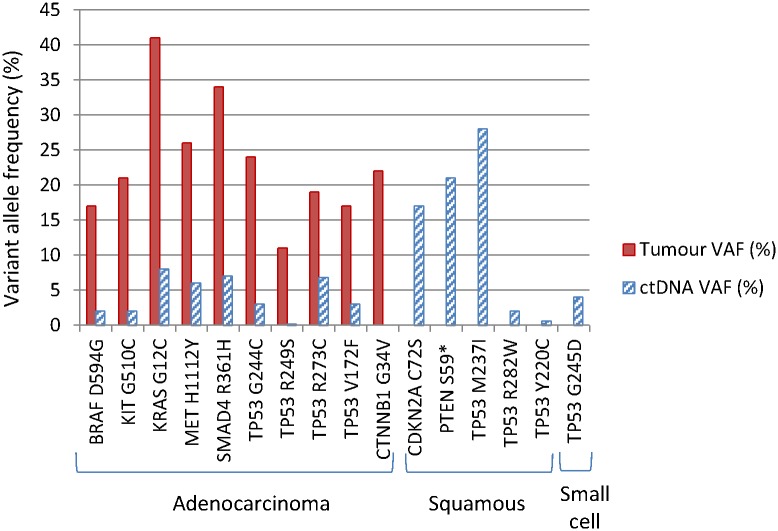
In the ctDNA of lung adenocarcinoma patients, we found mutations in TP53, MET, KRAS, SMAD4, BRAF, KIT, and JAK3 (Table 1). Squamous carcinoma patient ctDNA had several mutations in TP53, as well as in CDKN2A and PTEN. The small cell lung cancer patient plasma DNA had a hotspot mutation in TP53 (G245D). There is significant positive correlation between lung tumour and ctDNA variant allele frequency, Pearsons R(13) = 0.85, p = 0.001.
Fig 2 shows the somatic variants in patients with different types of lung cancer. Sequencing ctDNA confirmed eight out of ten somatic mutations identified from tumour biopsies, and was negative where the tumour was negative. The two remaining mutations were either absent (CTNNB1 G34V, no reads detected) or not present in sufficient read counts for detection (TP53 R249S, could only be detected at <0.5% by looking manually in Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) traces, as listed in Table 1). This suggests that plasma DNA sequencing could be a valuable first-line approach to confirm the diagnosis of lung cancer, but negative findings probably need to be backed up with a biopsy. An additional five patients who were later found not to have cancer, had variants that are annotated as either non-pathogenic in ClinVar database, common SNPs in UCSC genome browser, synonymous variants, or not characterised (S3 Table). All the variants in S3 Table were also found in the patient’s germline DNA (i.e. were not somatic changes).
Fig 2. Somatic variants in lung cancer tumour and plasma DNA.
Variant allele frequency of mutations are shown in solid red bars for tumour and in hatched blue bars for ctDNA, for different types of lung cancer (Adenocarcinoma; Squamous, squamous cell carcinoma; Small cell, small cell lung cancer). Tumour DNA from squamous and small cell lung cancer patients was not available for sequencing. Mutations are denoted as somatic because they were not present in germline DNA from the same patients.
We attempted to validate the variants identified in melanoma and lung ctDNA using castPCR as an orthogonal method (S2 Fig). We detect the mutations with castPCR, but because of limited material, we were unable to run assays in duplicate or triplicate. However, we have previously performed rigorous validation of tumour sequencing with the Cancer Hotspot Panel on the Ion Torrent PGM™, and showed that Hotspot Panel Sequencing was successful in 97% of tumour samples (N = 351) and 100% concordant with known mutations (Hamblin et al., manuscript under review). This complete concordance indicated that the method was suitable for introduction into our routine NHS diagnostic service.
Discussion
Blood was collected from patients with known melanomas for a retrospective pilot study, and we examined factors that may influence whether the confirmed mutations in the tumour were also detectable in plasma DNA. We only observe correlation between tumour and ctDNA variant allele frequency when the blood for ctDNA isolation was collected before treatment had started, or if collected less than one year after the tumour biopsy. With respect to treatment effects, although we did not do a time course study with successive samples taken from the same patient, we did observe a nearly complete absence of mutations in samples that were taken after treatment was started, which is most likely to be explained by the patients responding to targeted treatment. It is interesting to note that no further mutations were seen in all but one of these patient samples. Future longitudinal studies of ctDNA are warranted.
In the study with lung cancer patients, we specified in the standard operating procedure that blood draw for plasma DNA extraction occurred shortly (typically less than an hour) before tumour biopsy. This criterion was important because for several forms of cancer (e.g., breast, prostate, and lung), biopsies have been reported to increase the incidence of tumour cell seeding [20] and tumour cells in the circulation in animal models [21]. We demonstrate that ctDNA findings are in concordance with those found in the tumour for eight out of ten mutations detected. We also show it is possible to detect pathogenic mutations in ctDNA: While no EGFR mutations were detected in the 12 patients with lung cancer, a number of pathogenic variants were identified in oncogenic kinase genes such as KRAS and in tumour suppressor genes such as TP53 or PTEN. In particular, we revealed pathogenic TP53 mutations in ctDNA from all three squamous cell carcinoma patients, which has been shown to be the most commonly mutated gene in squamous lung cancer, as well as mutations in CDKN2A and PTEN [22]. Some of the identified mutations in lung adenocarcinoma affect treatment options in first or subsequent lines of systemic therapy (http://www.mycancergenome.org; https://ckb.jax.org/). For example, the BRAF D594G mutation results in BRAF inactivation and insensitivity to BRAF inhibitors. In the presence of activated RAS, inactivated BRAF can result in hyperactivation of MEK (MAP2K1), and thus MEK inhibitors may be effective in treating patients with D594G mutations, particularly when there is coexistent activation of RAS. The N375S mutation of the MET proto-oncogene confers resistance to MET targeted agents whereas MET R988C mutations in the juxta-membrane domain appear to have no effect on the capability of MET targeted agents to inhibit cMET phosphorylation. Other mutations (JAK V722I, CTNNB1 G34V, SMAD4 R361H) are rare in lung cancer and for which there is only preliminary or no evidence for targeted therapies. Although the lung cancer patients were not selected for specific criteria and the sample size was small, the proportions present of each type are similar to Cancer Research UK statistics for lung cancer incidence by morphology, which on their website are 87% non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC, adenocarcinoma or squamous cell), 12% small cell, and 1% carcinoid (http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/lung-cancer/incidence#heading-Four, accessed July 2016). Among our patients, we observe ten out of twelve (83%) NSCLC, one out of twelve (8%) small cell, and one out of twelve (8%) carcinoid tumour. Therefore our data has good representation of the different types of lung cancer. Others have found that targeted sequencing with the cancer hotspot panel is useful for advanced non-small cell lung cancer [23] and metastatic disease in a variety of tumour types [8]. We extend these results to using the hotspot panel to measure factors affecting mutation detection in melanoma ctDNA and evaluating use in initial diagnosis in lung cancer.
Collectively, these findings support using mutation analysis in ctDNA to provide a tumour profile helpful for diagnostic, predictive and prognostic analysis that does not require invasive procedures. Furthermore, the use of ctDNA also has potential for significant health economic, safety, and logistic benefits, whether as a means of obtaining repeat “liquid biopsies” from patients who are on treatment to allow monitoring of their mutanome, providing an early indication of whether or not patients are responding to targeted treatment, or after relapse of disease (where the standard of care is to undertake re-biopsy of the tumour to determine the presence of new mutations that may be actionable). Targeted therapies are costly and early identification of non-response (prior to symptomatic relapse) could save significant drug costs, as well as prevent unnecessary side effects. Panel ctDNA sequencing on the Ion Torrent PGM™ costs between £300–740 per sample, whereas transbronchial needle aspiration (TBNA) and endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) cost £1365 in 2011, excluding tumour sequencing costs (NICE lung cancer costing report CG121, 2011). Lung cancers are often inaccessible to a bronchoscopically-guided tumour sampling, necessitating CT-guided biopsy that has inherent risks such as pneumothorax. Even in experienced hands, the amount of tumour material obtained by endobronchial or EBUS sampling may be insufficient or unsuitable for analysis. Further, these procedures are costly in terms of human resource, equipment and consumables. Our data suggest that sequencing plasma DNA would be a safer, cost effective yet just as informative a method to employ. Our findings also support the undertaking of further prospective studies of sequential ctDNA and tumour sequencing for patients throughout their treatment pathway. Identification of early disease progression or relapse, assessment of response and use within a screening programme are all potential applications of this relatively simple procedure.
In summary, we reveal two factors that influence concordance of mutation detection between primary tumour and ctDNA sequencing in melanoma: treatment status at time of blood sampling and time lag between sampling of the primary tumour and blood for ctDNA extraction. The findings provide evidence to support the use of plasma DNA sequencing to assess effectiveness of treatment, monitor cancer patients in remission, and provide an early indication of emerging mutations that could be amenable to targeted therapy. Additionally we find good but not perfect (80%) concordance of mutations in lung diagnostic biopsy and contemporaneous ctDNA, suggesting that liquid biopsy analysis could be a valuable first-line approach to confirm the diagnosis of lung cancer, especially when the tumour is inaccessible or when biopsy poses significant risk to the patient.
Supporting Information
(TIF)
We chose castPCR as an orthogonal platform to attempt validation of the Ion Ampliseq sequencing results. Nine castPCR assays were available to assess mutations in melanoma and lung cancer patients who had plasma DNA available for validation (less than the recommended 15–20ng DNA/well for the castPCR assay; assays were run in singlicate). X-axis, patient number and mutation tested; y-axis, percentage mutation. (A) Melanoma patient samples, (B) Lung patient samples. KIT M541L is a UCSC common polymorphism and not included in Table 1, but was assayed for technical validation.
(PDF)
(DOCX)
(XLSX)
Blood samples were taken from melanoma patients who were known to have cancer (some patients were sampled pre-treatment, some were post-treatment). Tumour and plasma DNA were sequenced using Ampliseq Cancer Hotspot Panel (8–10 samples per 318 chip), and variant results were compared. For patients 9–14, ctDNA was also sequenced at higher coverage (using 1 ctDNA:gDNA paired sample per 318 chip).
(DOCX)
Blood samples were drawn from patients prior to bronchoscopy. These patients were subsequently found to be negative for cancer. Plasma DNA and genomic DNA from each were sequenced using Ampliseq Cancer Hotspot Panel v2.
(XLSX)
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to the patients for their participation, and thank the research nurses Julianne Hollidge and Emma-Jayne Muir for their expertise and dedication in collecting and transporting samples. Sequences reported in this paper have been submitted to Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession number SRP066676. The views expressed in this paper are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Data Availability
Sequences reported in this paper have been submitted to Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession number SRP066676.
Funding Statement
This study was supported by grants from: Technology Strategy Board (now called Innovate UK) (TP No: 10809-62174) (JCT and AS), https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/innovate-uk; National Institute for Health Research Oxford Biomedical Research Centre based at Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust and University of Oxford (JCT and AS), http://oxfordbrc.nihr.ac.uk/; The Wellcome Trust (090532/Z/09/Z) (JCT), http://www.wellcome.ac.uk/; Oxford Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre (MRM), http://www.ecmcnetwork.org.uk/. The views expressed in this paper are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Mandel P, Metais P. [Not Available]. Comptes rendus des seances de la Societe de biologie et de ses filiales. 1948;142(3–4):241–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Elshimali YI, Khaddour H, Sarkissyan M, Wu Y, Vadgama JV. The clinical utilization of circulating cell free DNA (CCFDNA) in blood of cancer patients. International journal of molecular sciences. 2013;14(9):18925–58. 10.3390/ijms140918925 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.White HE, Dent CL, Hall VJ, Crolla JA, Chitty LS. Evaluation of a novel assay for detection of the fetal marker RASSF1A: facilitating improved diagnostic reliability of noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. PloS one. 2012;7(9):e45073 10.1371/journal.pone.0045073 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Forshew T, Murtaza M, Parkinson C, Gale D, Tsui DW, Kaper F, et al. Noninvasive identification and monitoring of cancer mutations by targeted deep sequencing of plasma DNA. Science translational medicine. 2012;4(136):136ra68 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003726 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Crowley E, Di Nicolantonio F, Loupakis F, Bardelli A. Liquid biopsy: monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood. Nature reviews Clinical oncology. 2013;10(8):472–84. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.110 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Murtaza M, Dawson SJ, Tsui DW, Gale D, Forshew T, Piskorz AM, et al. Non-invasive analysis of acquired resistance to cancer therapy by sequencing of plasma DNA. Nature. 2013;497(7447):108–12. 10.1038/nature12065 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bettegowda C, Sausen M, Leary RJ, Kinde I, Wang Y, Agrawal N, et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Science translational medicine. 2014;6(224):224ra24 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lebofsky R, Decraene C, Bernard V, Kamal M, Blin A, Leroy Q, et al. Circulating tumor DNA as a non-invasive substitute to metastasis biopsy for tumor genotyping and personalized medicine in a prospective trial across all tumor types. Molecular oncology. 2015;9(4):783–90. 10.1016/j.molonc.2014.12.003 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chang GA, Tadepalli JS, Shao Y, Zhang Y, Weiss S, Robinson E, et al. Sensitivity of plasma BRAF(mutant) and NRAS(mutant) cell-free DNA assays to detect metastatic melanoma in patients with low RECIST scores and non-RECIST disease progression. Molecular oncology. 2016;10(1):157–65. 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.09.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Burrell RA, McGranahan N, Bartek J, Swanton C. The causes and consequences of genetic heterogeneity in cancer evolution. Nature. 2013;501(7467):338–45. 10.1038/nature12625 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chan KC, Jiang P, Zheng YW, Liao GJ, Sun H, Wong J, et al. Cancer genome scanning in plasma: detection of tumor-associated copy number aberrations, single-nucleotide variants, and tumoral heterogeneity by massively parallel sequencing. Clinical chemistry. 2013;59(1):211–24. 10.1373/clinchem.2012.196014 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Leary RJ, Kinde I, Diehl F, Schmidt K, Clouser C, Duncan C, et al. Development of personalized tumor biomarkers using massively parallel sequencing. Science translational medicine. 2010;2(20):20ra14 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Newman AM, Bratman SV, To J, Wynne JF, Eclov NC, Modlin LA, et al. An ultrasensitive method for quantitating circulating tumor DNA with broad patient coverage. Nature medicine. 2014;20(5):548–54. 10.1038/nm.3519 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Page K, Guttery DS, Zahra N, Primrose L, Elshaw SR, Pringle JH, et al. Influence of plasma processing on recovery and analysis of circulating nucleic acids. PloS one. 2013;8(10):e77963 10.1371/journal.pone.0077963 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Merriman B, Ion Torrent Team RD, Rothberg JM. Progress in ion torrent semiconductor chip based sequencing. Electrophoresis. 2012;33(23):3397–417. 10.1002/elps.201200424 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brinza D, Dhingra D, Scafe C, Chien R, Hyland F, editors. A research approach for the detection of somatic mutations at 0.5% frequency from cfDNA and cTc DNA using a multiplex sequencing assay targeting 2000 tumor mutations. [abstract nr 2402]. 106th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research; 2015 2015 Apr 18–22; Philadelphia, PA: AACR.
- 17.Didelot A, Le Corre D, Luscan A, Cazes A, Pallier K, Emile JF, et al. Competitive allele specific TaqMan PCR for KRAS, BRAF and EGFR mutation detection in clinical formalin fixed paraffin embedded samples. Experimental and molecular pathology. 2012;92(3):275–80. 10.1016/j.yexmp.2012.03.001 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Patterson SE, Liu R, Statz CM, Durkin D, Lakshminarayana A, Mockus SM. The clinical trial landscape in oncology and connectivity of somatic mutational profiles to targeted therapies. Human genomics. 2016;10:4 10.1186/s40246-016-0061-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Landrum MJ, Lee JM, Riley GR, Jang W, Rubinstein WS, Church DM, et al. ClinVar: public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D980–5. 10.1093/nar/gkt1113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Robertson EG, Baxter G. Tumour seeding following percutaneous needle biopsy: the real story! Clinical radiology. 2011;66(11):1007–14. 10.1016/j.crad.2011.05.012 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Juratli MA, Sarimollaoglu M, Siegel ER, Nedosekin DA, Galanzha EI, Suen JY, et al. Real-time monitoring of circulating tumor cell release during tumor manipulation using in vivo photoacoustic and fluorescent flow cytometry. Head & neck. 2014;36(8):1207–15. 10.1002/hed.23439 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature. 2012;489(7417):519–25. 10.1038/nature11404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xu S, Lou F, Wu Y, Sun DQ, Zhang JB, Chen W, et al. Circulating tumor DNA identified by targeted sequencing in advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Lett. 2016;370(2):324–31. 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.005 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(TIF)
We chose castPCR as an orthogonal platform to attempt validation of the Ion Ampliseq sequencing results. Nine castPCR assays were available to assess mutations in melanoma and lung cancer patients who had plasma DNA available for validation (less than the recommended 15–20ng DNA/well for the castPCR assay; assays were run in singlicate). X-axis, patient number and mutation tested; y-axis, percentage mutation. (A) Melanoma patient samples, (B) Lung patient samples. KIT M541L is a UCSC common polymorphism and not included in Table 1, but was assayed for technical validation.
(PDF)
(DOCX)
(XLSX)
Blood samples were taken from melanoma patients who were known to have cancer (some patients were sampled pre-treatment, some were post-treatment). Tumour and plasma DNA were sequenced using Ampliseq Cancer Hotspot Panel (8–10 samples per 318 chip), and variant results were compared. For patients 9–14, ctDNA was also sequenced at higher coverage (using 1 ctDNA:gDNA paired sample per 318 chip).
(DOCX)
Blood samples were drawn from patients prior to bronchoscopy. These patients were subsequently found to be negative for cancer. Plasma DNA and genomic DNA from each were sequenced using Ampliseq Cancer Hotspot Panel v2.
(XLSX)
Data Availability Statement
Sequences reported in this paper have been submitted to Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession number SRP066676.