Abstract
A model was developed to account for the recent observations indicating that type I collagen fibrils assembled in vivo grow from symmetrical pointed tips. The essential features of the model are (i) a distinctive structural nucleus forms at each end of a growing fibril and growth of the fibril then proceeds by propagation of the two structural nuclei, (ii) the two structural nuclei have similar spiral or helical conformations, and (iii) assembly of each structural nucleus requires two kinds of specific binding steps defined as 3.4 D-period and 0.4 D-period overlaps, but propagation of the nucleus requires only the 3.4 D-period binding step.
Full text
PDF

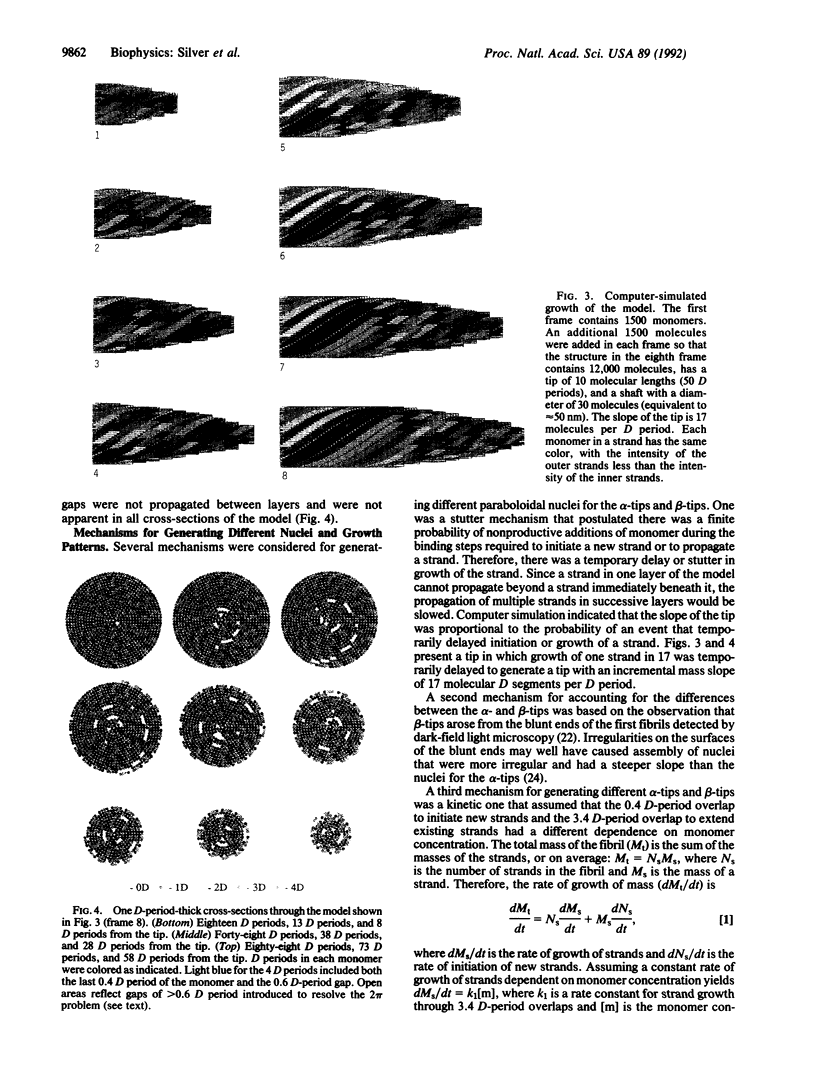
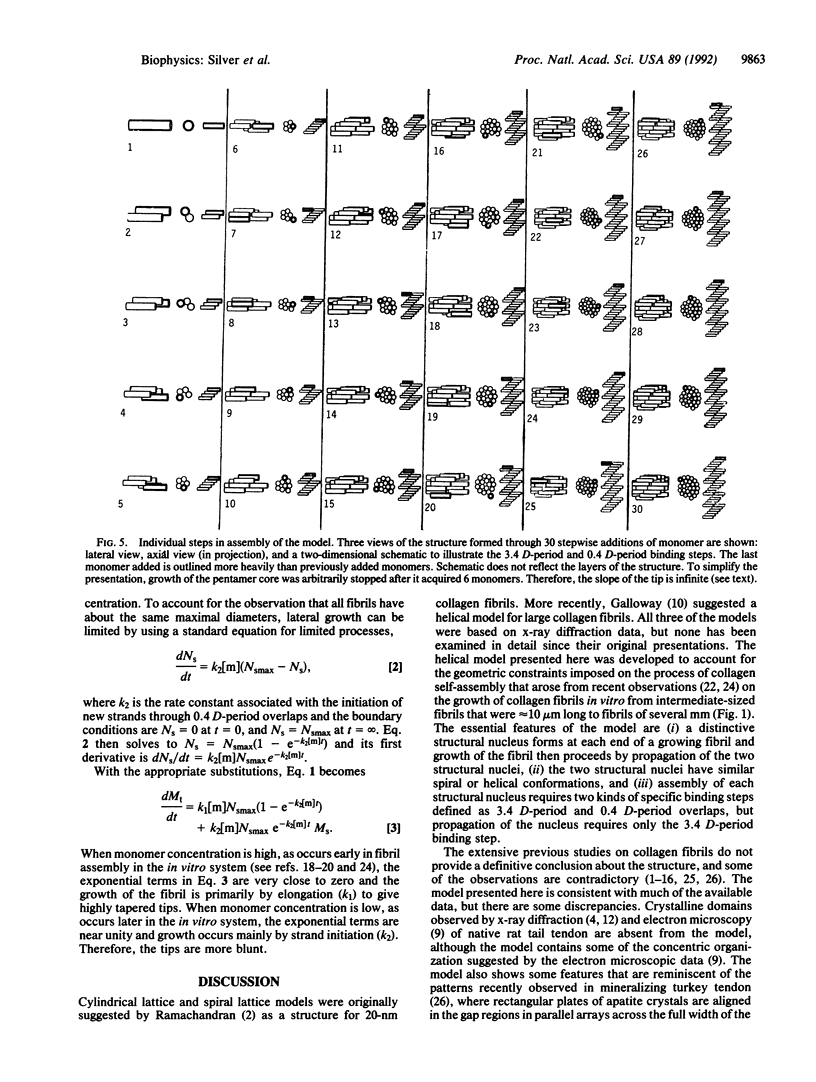

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birk D. E., Zycband E. I., Winkelmann D. A., Trelstad R. L. Collagen fibrillogenesis in situ: fibril segments are intermediates in matrix assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4549–4553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky B., Eikenberry E. F. Characterization of fibrous forms of collagen. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):127–174. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. A. The regulation of size and form in the assembly of collagen fibrils in vivo. Biopolymers. 1989 Aug;28(8):1367–1382. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman R. A., Piez K. A. Collagen fibril formation in vitro. A quasielastic light-scattering study of early stages. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8098–8102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. F., Chapman J. A. Axial mass distributions of collagen fibrils grown in vitro: results for the end regions of early fibrils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 27;87(4):993–999. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(79)80005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. F., Chapman J. A., Prockop D. J., Kadler K. E. Growing tips of type I collagen fibrils formed in vitro are near-paraboloidal in shape, implying a reciprocal relationship between accretion and diameter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9855–9859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Holmes D. F., Cummings C. Crystalline regions in collagen fibrils. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Jesior J. C., Miller A., Berthet-Colominas C., Wolff C. Electron microscopy shows periodic structure in collagen fibril cross sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3567–3571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Kadler K. E., Mould A. P., Hojima Y., Holmes D. F., Cummings C., Chapman J. A., Prockop D. J. Pleomorphism in type I collagen fibrils produced by persistence of the procollagen N-propeptide. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 20;210(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Miller A. Quasi-hexagonal molecular packing in collagen fibrils. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):878–880. doi: 10.1038/282878a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. Y., Miller A. Analysis of structural design features in collagen. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90885-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadler K. E., Hojima Y., Prockop D. J. Assembly of collagen fibrils de novo by cleavage of the type I pC-collagen with procollagen C-proteinase. Assay of critical concentration demonstrates that collagen self-assembly is a classical example of an entropy-driven process. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15696–15701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadler K. E., Hojima Y., Prockop D. J. Collagen fibrils in vitro grow from pointed tips in the C- to N-terminal direction. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):339–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2680339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadler K. E., Hulmes D. J., Hojima Y., Prockop D. J. Assembly of type I collagen fibrils de novo by the specific enzymic cleavage of pC collagen. The fibrils formed at about 37 degrees C are similar in diameter, roundness, and apparent flexibility to the collagen fibrils seen in connective tissue. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;580:214–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara M., Njieha F. K., Prockop D. J. Formation of collagen fibrils in vitro by cleavage of procollagen with procollagen proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8442–8448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piez K. A., Trus B. L. A new model for packing of type-I collagen molecules in the native fibril. Biosci Rep. 1981 Oct;1(10):801–810. doi: 10.1007/BF01114803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanic A. M., Adachi E., Kadler K. E., Hojima Y., Prockop D. J. Copolymerization of pNcollagen III and collagen I. pNcollagen III decreases the rate of incorporation of collagen I into fibrils, the amount of collagen I incorporated, and the diameter of the fibrils formed. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12703–12709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W. Molecular pattern in native collagen. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):157–158. doi: 10.1038/219157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W., Arad T., Weiner S. Three-dimensional ordered distribution of crystals in turkey tendon collagen fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9822–9826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward N. P., Hulmes D. J., Chapman J. A. Collagen self-assembly in vitro: electron microscopy of initial aggregates formed during the lag phase. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 5;190(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





