Abstract
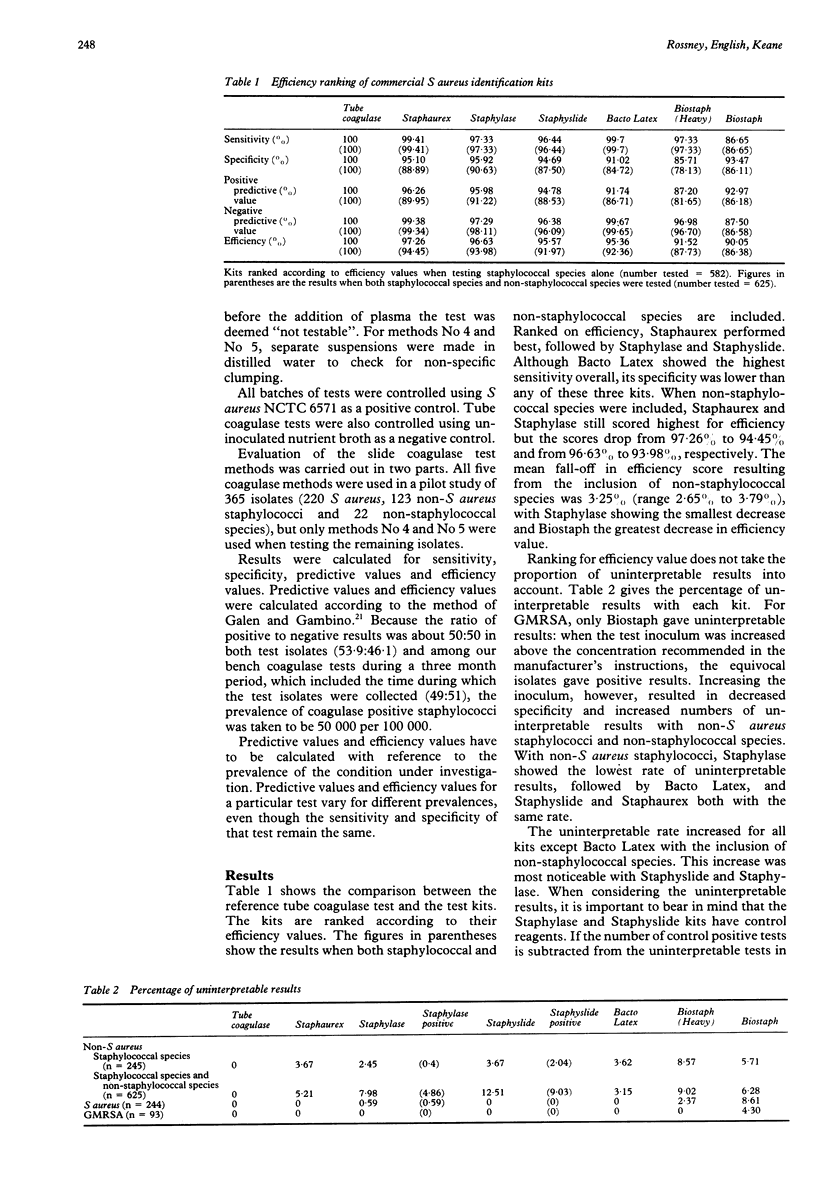
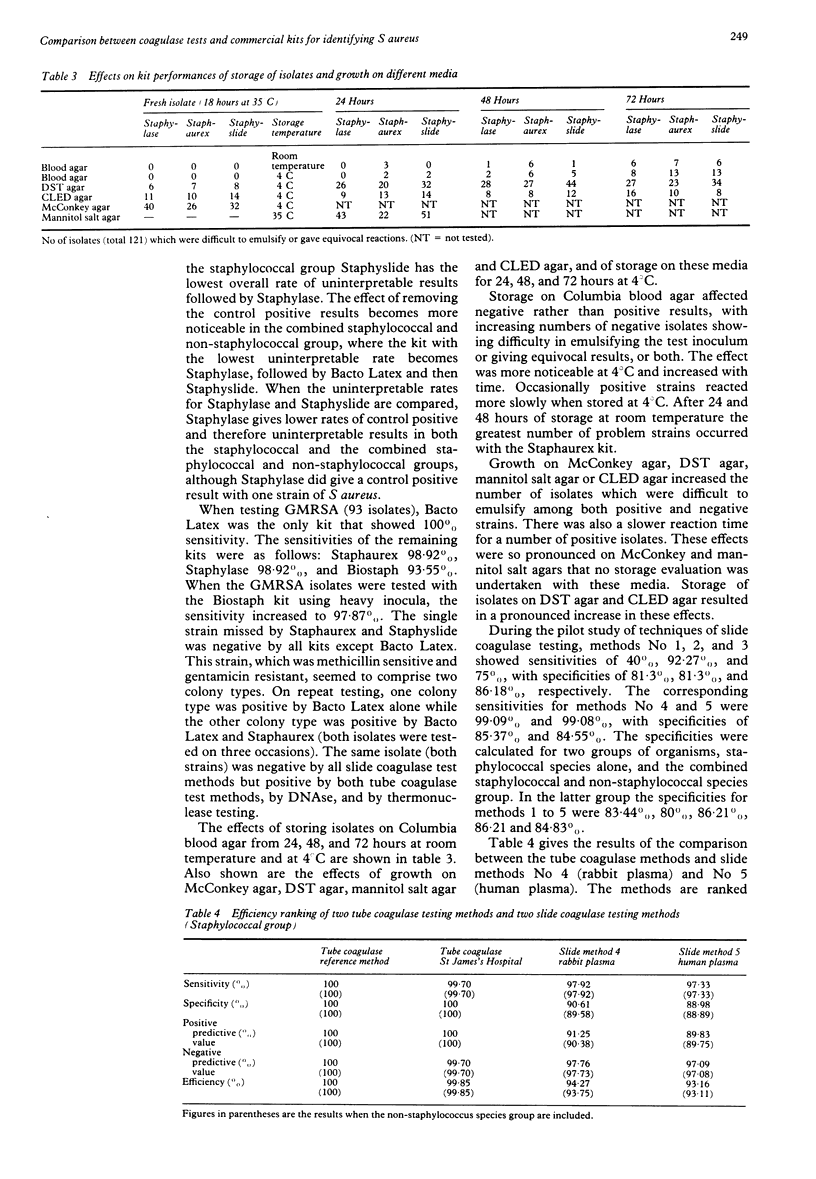
Five commercial Staphylococcus aureus identification kits--Staphaurex (Wellcome), Staphylase (Oxoid), Staphyslide (bioMèrieux), Biostaph (Medlabs) and Bacto Latex (Difco)--were evaluated for the routine identification of S aureus from primary plates in the routine microbiology laboratory. Comparison was made with two methods of tube coagulase testing and five slide methods for detecting clumping factor (slide coagulase testing). Performances were assessed for two groups of organisms, staphylococcal species alone and a combined staphylococcal and non-staphylococcal species group. The effects of growth on selective media and storage of isolates at room temperature and 4 degrees C were investigated. Selective media cannot be recommended, nor can storage of isolates before testing. Ranked according to efficiency value with the combined staphylococcal and non-staphylococcal species group, the kits and coagulase methods performed as follows (the figures in parentheses are the efficiency values for the staphylococcal group alone): tube coagulase reference method 100% (100%), tube coagulase SJH method 99% (99%), Staphaurex 94% (97%), Staphylase 93% (96%), slide coagulase method No 4 93% (94%), slide coagulase method No 5 93% (93%), Bacto Latex 92% (95%), Staphyslide 92% (95%), and Biostaph 87% (91%). It is concluded that a commercial S aureus identification kit should not replace tube coagulase testing for the routine identification of the organism from primary plates and that, even the kits with the best performances, have little advantage over a good slide coagulase test method.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Kogos C., Sanders C. V., Marier R. L. Comparison of rapid identification assays for Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):703–704. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.703-704.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. S., Bormann M. A., Boudreau D. H. Evaluation of various rapid agglutination methods for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):726–729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.726-729.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke A., Tilton R. C. Evaluation of rapid coagulase methods for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):916–919. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.916-919.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer A. W., Grüneberg R. N. Assessment of a new test ("Staphylase') for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. Med Lab Sci. 1988 Jul;45(3):221–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES G. E. Factors influencing the in vitro production of staphylococcal coagulase. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Oct;5(4):687–697. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-4-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson J. I., Marples R. R. Coagulase production by strains of Staphylococcus aureus of differing resistance characters: a comparison of two traditional methods with a latex agglutination system detecting both clumping factor and protein A. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Apr;39(4):371–375. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.4.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essers L., Radebold K. Rapid and reliable identification of Staphylococcus aureus by a latex agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):641–643. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.641-643.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flandrois J. P., Carret G. Study of the staphylococcal affinity to fibrinogen by passive hemagglutination: a tool for the Staphylococcus aureus identification. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981 Dec;251(2):171–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregson D. B., Low D. E., Skulnick M., Simor A. E. Problems with rapid agglutination methods for identification of Staphylococcus aureus when Staphylococcus saprophyticus is being tested. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1398–1399. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1398-1399.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT P. F., MILLS J., YOUNG D. K. THE EARLY EFFECTS OF CHRYSOTILE ASBESTOS DUST ON THE RAT LUNG. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:15–23. doi: 10.1002/path.1700870103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungkind D. L., Torhan N. J., Corman K. E., Bondi J. M. Comparison of two commercially available test methods with conventional coagulase tests for identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):191–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.191-193.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Genigeorgis C., Hoeprich P. D. Metachromatic agar-diffusion methods for detecting staphylococcal nuclease activity. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.585-587.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mifsud A. J., Parker S. C. Staphaurex reappraised: role of protein A in false positive results and recommendations for use. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jul;40(7):808–809. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.7.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. E., Jr, Kloos W. E. Identification of coagulase-positive Staphylococcus intermedius and Staphylococcus hyicus subsp. hyicus isolates from veterinary clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):671–673. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.671-673.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper J., Hadfield T., McCleskey F., Evans M., Friedstrom S., Lauderdale P., Winn R. Efficacies of rapid agglutination tests for identification of methicillin-resistant staphylococcal strains as Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1907–1909. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1907-1909.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A., Jr, Migneault P. C., Nolte F. S. Reliability of latex agglutination tests for identification of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to oxacillin. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):1104–1106. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.1104-1106.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruane P. J., Morgan M. A., Citron D. M., Mulligan M. E. Failure of rapid agglutination methods to detect oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):490–492. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.490-492.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selepak S. T., Witebsky F. G. Inoculum size and lot-to-lot variation as significant variables in the tube coagulase test for Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):835–837. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.835-837.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager M., Drummond M. C. Staphylocoagulase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):92–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weers-Pothoff G., Moolhuijzen C. E., Bongaerts G. P. Comparison of seven coagulase tests for identification of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;6(5):589–591. doi: 10.1007/BF02014257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


