Abstract
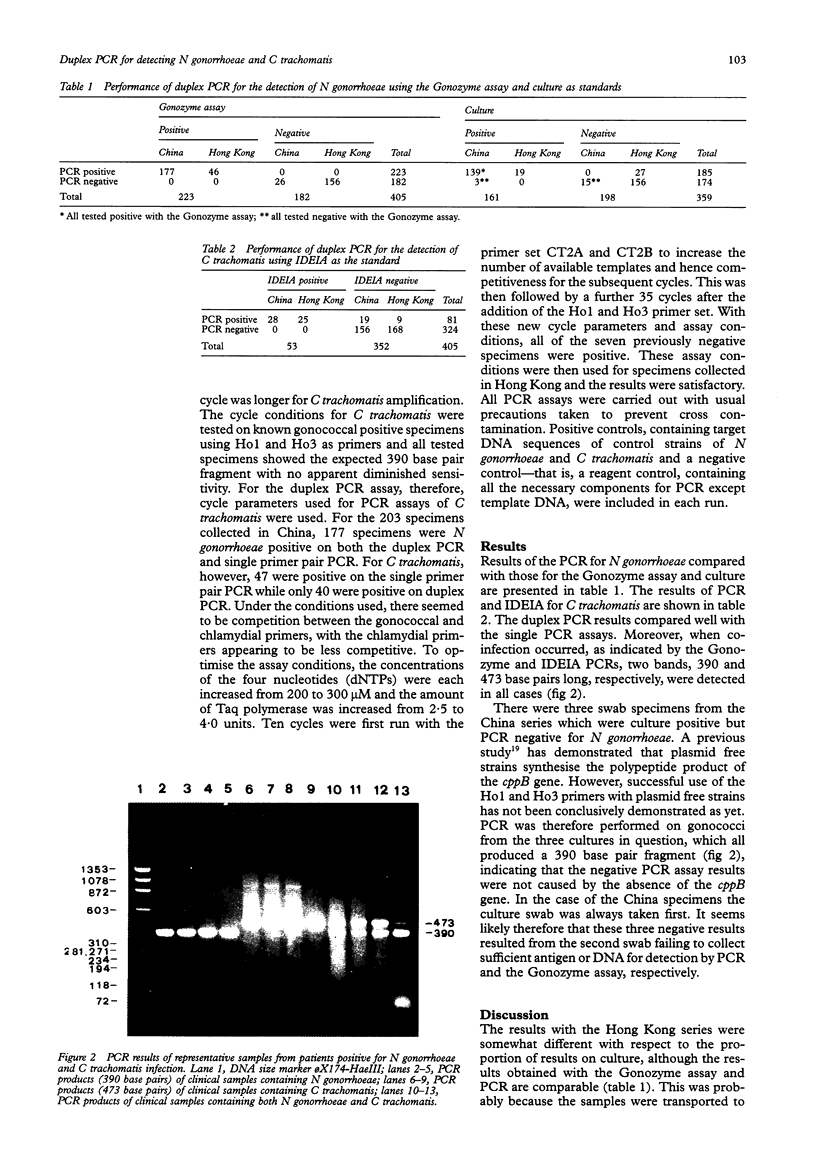
AIMS--To evaluate the use of a duplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay for the simultaneous detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis in clinical samples. METHODS--Genital swab specimens were obtained from both China (203 swabs) and Hong Kong (202 swabs). N gonorrhoeae and C trachomatis were detected in each specimen with a number of tests including enzyme immunoassays (IDEIA) and PCR assays using both single and double primer pairs. The primer pair for N gonorrhoeae was derived from the cppB gene on its cryptic plasmid and the PCR product was 390 base pairs long. For C trachomatis, the PCR product was 473 base pairs long, resulting from amplification of a sequence in the common 7.4 kilobase plasmid present in all serovars. For N gonorrhoeae, PCR results were also compared with those obtained by culture and Gram's smear of the discharges. RESULTS--For the 203 specimens collected in China, similar numbers of positive results (177) were obtained by both Gonozyme and duplex PCR for the detection of N gonorrhoeae. No discrepant results were found among the cultured specimens when Gonozyme and duplex PCR were compared. C trachomatis was detected in 47 specimens by duplex PCR, but was detected in only 28 by IDEIA. Of the 202 Hong Kong specimens, 46 were positive for N gonorrhoeae, detected by both Gonozyme and duplex PCR; 34 were positive for C trachomatis, 25 of which were detected by IDEIA and the remainder by duplex PCR. CONCLUSIONS--The duplex PCR assay is a satisfactory diagnostic tool for the simultaneous detection of N gonorrhoeae and C trachomatis in clinical swab samples. Further evaluation is suggested.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caul E. O., Paul I. D., Milne J. D., Crowley T. Non-invasive sampling method for detecting Chlamydia trachomatis. Lancet. 1988 Nov 26;2(8622):1246–1247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90831-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernesky M., Castriciano S., Sellors J., Stewart I., Cunningham I., Landis S., Seidelman W., Grant L., Devlin C., Mahony J. Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis antigens in urine as an alternative to swabs and cultures. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):124–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claas H. C., Wagenvoort J. H., Niesters H. G., Tio T. T., Van Rijsoort-Vos J. H., Quint W. G. Diagnostic value of the polymerase chain reaction for Chlamydia detection as determined in a follow-up study. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.42-45.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley T., Milne D., Arumainayagam J. T., Paul I. D., Caul E. O. The laboratory diagnosis of male Chlamydia trachomatis infections--a time for change? J Infect. 1992 Jul;25 (Suppl 1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(92)92099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson D., Moi H., Forslin L. Diagnosis of urogenital gonorrhoea by detecting gonococcal antigen with a solid phase enzyme immunoassay (Gonozyme). J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jun;36(6):674–677. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.6.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Wang S. New knowledge of chlamydiae and the diseases they cause. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):87–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho B. S., Feng W. G., Wong B. K., Egglestone S. I. Polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in clinical samples. J Clin Pathol. 1992 May;45(5):439–442. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.5.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirrett S., Reller L. B., Knapp J. S. Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains inhibited by vancomycin in selective media and correlation with auxotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):94–99. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.94-99.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita N., Matsumoto A. Establishment of a particle-counting method for purified elementary bodies of chlamydiae and evaluation of sensitivities of the IDEIA Chlamydia kit and DNA probe by using the purified elementary bodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2911–2916. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2911-2916.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard L., Birkelund S., Christiansen G. Use of polymerase chain reaction for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1254–1260. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1254-1260.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul I. D., Caul E. O. Evaluation of three Chlamydia trachomatis immunoassays with an unbiased, noninvasive clinical sample. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):220–222. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.220-222.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roongpisuthipong A., Lewis J. S., Kraus S. J., Morse S. A. Gonococcal urethritis diagnosed from enzyme immunoassay of urine sediment. Sex Transm Dis. 1988 Oct-Dec;15(4):192–195. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198810000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., McCormack W. M., Smith R. F., Parks R. M., Bailey R., Ohlin A. C. Enzyme immunoassay for diagnosis of gonorrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):57–59. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.57-59.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANG F. F., CHANG H. L., HUANG Y. T., WANG K. C. Studies on the etiology of trachoma with special reference to isolation of the virus in chick embryo. Chin Med J. 1957 Jun;75(6):429–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Lee M. F., Yin S. C., Yang D. M., Cheng S. F. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction, monoclonal antibody based enzyme immunoassay, and cell culture for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in genital specimens. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 Jul-Aug;19(4):193–197. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199207000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]