Abstract
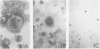
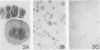
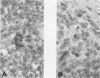
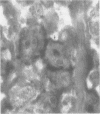
AIMS--To determine the cellular origin of the most potent cytokine present in Hodgkin's disease, transforming growth factor (TGF) beta, the polycellular population of Hodgkin's tissue was studied using in situ hybridisation. METHODS--A biotin labelled oligo-complementary DNA (cDNA) was constructed according to the previously determined sequence for TGF beta 1 cDNA. Forty three frozen and paraffin wax embedded tissue samples replaced by Hodgkin's disease or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, three Reed-Sternberg cell lines, one Ki1 positive lymphoma cell line, and an epithelial cell line were studied for expression of TGF beta 1 messenger RNA (mRNA) as well as secretion of the TGF beta 1 protein and expression of the CD30 epitope. RESULTS--The results obtained with the 24 frozen tissue samples confirmed that the TGF beta antigen is found predominantly in the nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease (NSHD) subtype. Nineteen paraffin wax embedded tissue samples were used to measure the simultaneous expression of CD30 and TGF beta 1 mRNA. The latter was found in eight of eight NSHD samples, two of six mixed cellularity samples, and two of five non-Hodgkin's lymphoma samples. No evidence of fibroblast expression of TGF beta 1 mRNA was noted. CONCLUSIONS--Activated lymphocytes in NSHD express TGF beta 1 mRNA, but binucleate Reed-Sternberg cells and mononuclear Hodgkin's cells are the primary sources of activated TGF beta in Hodgkin's disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burrichter H., Heit W., Schaadt M., Kirchner H., Diehl V. Production of colony-stimulating factors by Hodgkin cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1983 Mar 15;31(3):269–274. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss H. J., Brach M. A., Drexler H. G., Bross K. J., Herrmann F. Interleukin 9 is expressed by primary and cultured Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 15;52(4):1026–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Hsu S. M. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin by cells of Hodgkin's neoplastic cell lines HDLM-1 and KM-H2. Am J Pathol. 1989 Oct;135(4):735–745. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Lin J., Xie S. S., Hsu P. L., Rich S. Abundant expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and -beta 2 by Hodgkin's Reed-Sternberg cells and by reactive T lymphocytes in Hodgkin's disease. Hum Pathol. 1993 Mar;24(3):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90034-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Zhao X., Chakraborty S., Liu Y. F., Whang-Peng J., Lok M. S., Fukuhara S. Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's cell lines HDLM, L-428, and KM-H2 are not actively replicating: lack of bromodeoxyuridine uptake by multinuclear cells in culture. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1382–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Agnarsson B. A., Ellingsworth L. R., Newcom S. R. Immunohistochemical evidence of a role for transforming growth factor beta in the pathogenesis of nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1209–1214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M., Butmarc J., Elovic A., Wong D. Eosinophils are the major source of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):11–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Wakefield L. M., Roberts A. B., Jakowlew S., Alvarez-Mon M., Derynck R., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S. Production of transforming growth factor beta by human T lymphocytes and its potential role in the regulation of T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1037–1050. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer C., Jones D. B., Morrison K., Schlüter C., Feist W., Ulmer A. J., Arnoldi J., Matthes J., Diamantstein T., Flad H. D. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and lymphotoxin production in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):341–351. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz H., Houssiau F. A., Orscheschek K., Renauld J. C., Fliedner A., Herin M., Noel H., Kadin M., Mueller-Hermelink H. K., Van Snick J. Interleukin-9 expression in human malignant lymphomas: unique association with Hodgkin's disease and large cell anaplastic lymphoma. Blood. 1991 Sep 1;78(5):1311–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Utz P. J., Bergstrom S. K., Morgan R., Molina A., Toole J. J., Glader B. E., McFall P., Weiss L. M., Warnke R. SUP-HD1: a new Hodgkin's disease-derived cell line with lymphoid features produces interferon-gamma. Blood. 1989 Dec;74(8):2733–2742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcom S. R., Ansari A. A., Gu L. Interleukin-4 is an autocrine growth factor secreted by the L-428 Reed-Sternberg cell. Blood. 1992 Jan 1;79(1):191–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcom S. R., Kadin M. E., Ansari A. A., Diehl V. L-428 nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's cell secretes a unique transforming growth factor-beta active at physiologic pH. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1915–1921. doi: 10.1172/JCI113810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcom S. R., Kadin M. E., Phillips C. L-428 Reed-Sternberg cells and mononuclear Hodgkin's cells arise from a single cloned mononuclear cell. Int J Cell Cloning. 1988 Nov;6(6):417–431. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530060606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcom S. R., O'Rourke L. Potentiation of fibroblast growth by nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease cell cultures. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):228–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcom S. R., Tagra K. K. High molecular weight transforming growth factor beta is excreted in the urine in active nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6768–6773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcom S. R. The Hodgkin's cell in nodular sclerosis does not release interleukin-1. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Feb;105(2):170–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paietta E., Racevskis J., Stanley E. R., Andreeff M., Papenhausen P., Wiernik P. H. Expression of the macrophage growth factor, CSF-1 and its receptor c-fms by a Hodgkin's disease-derived cell line and its variants. Cancer Res. 1990 Apr 1;50(7):2049–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samoszuk M., Nansen L. Detection of interleukin-5 messenger RNA in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease with eosinophilia. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]