Abstract
Background
Hydrogen cyanamide (HC) and pruning (P) have frequently been used to break dormancy in grapevine floral buds. However, the exact underlying mechanism remains elusive. This study aimed to address the early mode of action of these treatments on accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and expression of related genes in the dormancy breaking buds of grapevine in the summer.
Results
The budbreak rates induced by pruning (P), hydrogen cyanamide (HC), pruning plus hydrogen cyanamide (PHC) and water (control) after 8 days were 33, 53, 95, and 0 %, respectively. Clearly, HC was more effective in stimulating grapevine budbreak and P further enhanced its potency. In situ staining of longitudinal bud sections after 12 h of treatments detected high levels of ROS and nitric oxide (NO) accumulated in the buds treated with PHC, compared with HC or P alone. The amounts of ROS and NO accumulated were highly correlated with the rates of budbreak among these treatments, highlighting the importance of a rapid, transient accumulation of sublethal levels of ROS and RNS in dormancy breaking. Microarray analysis revealed specific alterations in gene expression in dormancy breaking buds induced by P, HC and PHC after 24 h of treatment. Relative to control, PHC altered the expression of the largest number of genes, while P affected the expression of the least number of genes. PHC also exerted a greater intensity in transcriptional activation of these genes. Gene ontology (GO) analysis suggests that alteration in expression of ROS related genes is the major factor responsible for budbreak. qRT-PCR analysis revealed the transient expression dynamics of 12 specific genes related to ROS generation and scavenge during the 48 h treatment with PHC.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that rapid accumulation of ROS and NO at early stage is important for dormancy release in grapevine in the summer, and the identification of the commonly expressed specific genes among the treatments allowed the construction of the signal transduction pathway related to ROS/RNS metabolism during dormancy release. The rapid accumulation of a sublethal level of ROS/RNS subsequently induces cell wall loosening and expansion for bud sprouting.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12870-016-0889-y) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Hydrogen cyanamide, ROS, Dormancy breaking buds, Grapevines, Gene ontology
Background
Grapevine is a perennial crop in temperate climates and perceives short day petoperiod and cool temperatures as signals to onset bud endodromancy to survive winter conditions; subsequently it requires exposure to adequate chilling temperatures for several weeks (or months) to end the dormancy [1–3]. Endodormancy is regulated by the physiological factors inside the affected buds [3, 4]. Abascisic acid (ABA) accumulates during the development of endodormancy in grapevine by suppression of bud meristem activity and its degradation is critical for dormancy release [5]. Furthermore, ethylene is suggested to participate in the degradation of ABA and budbreak by modulating the expression of ABA signaling regulators [5, 6]. Grapevine grown in subtropical regions often exhibits non-uniform or delayed budbreak in early spring due to warm winter that provides inadequate chilling. This represents a major obstacle for the commercial production of table grapes. Hydrogen cyanamide (H2CN2, HC) has been found very effective for breaking the dormancy of floral buds in grapevine [7–9], kiwifruit [10] and apple [11, 12]. In subtropical regions, HC treatment on intact dormant buds in spring is an important grapevine orchard management practice to induce uniform budbreak. In Taiwan, a subtropical region, this treatment is also a common practice in mid-summer for the second grapevine harvest in the winter, where paradormant buds on the pruned canes can be treated with HC to ensure effective budbreak. Paradormancy in the latent buds in the summer is regulated by plant growth regulators originating from other organs, such as auxin from the apical meristem, affecting apical dormancy [3, 4]. Few studies have been focused on the mechanism of paradormancy and its release by HC. An understanding of the biochemical and molecular bases underlying the release of dormancy by HC is critical for commercial production of grapes in subtropical and tropical regions.
HC is commonly used as a nitrogen fertilizer with herbicidal and fungicidal effects. It is readily taken up by plant tissues and rapidly decomposed by cyanamide hydratase to urea, followed by urease to ammonium [13]. Rapid detoxification of the highly toxic ammonia is achieved by the GOGAT pathway to produce arginine, histadine and lysine. However, cyanamide is also a very reactive substance and belongs to the classic nitriles. Nitrile hydratases metabolize nitriles to the corresponding amides glutamine and asparagine. However, at high concentrations it is toxic to plants when the enzymatic breakdown of cyanamide exceeds the ammonia detoxification capacity. Cyanamide is well known for its effect to break dormant buds of fruit trees. The most dramatic physiological effect of cyanamide to plants is its strong inhibition of catalase, caused by the reaction of the nitrile group with the thiols and haematin of the enzyme, and the subsequent increase in H2O2 content [13]. After HC application, cyanide (CN) is released and breaks dormant flower buds in Prunus species [14]. Cyanide is also a co-product of cyanogenic glucoside hydrolysis [6, 15, 16]. Cyanide is toxic to plants by arresting aerobic respiration (e.g. cellular hypoxia) and energy production. Consequently, a shift to anaerobic respiration is induced.
Plants respond to HC or potassium cyanide (KCN, respiration inhibitor) by eliciting the reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as H2O2, as shown in sunflower seeds [15, 17] and in grapevine buds [15, 18]. Hypoxia (8 % O2), and two inhibitors of respiration (e.g. KCN and sodium nitroprusside) also triggers the production of H2O2 and ethylene, which in turn activates the antioxidant systems in grapevine buds through the mediation of the these signaling molecules [19]. Consistently, during germination the seeds develop an anaerobic condition after imbibition due to the rapid consumption of O2 and the barrier imposed by the seed coat for gas exchanges, and the depletion of O2 in seeds is accompanied by an increase in H2O2 and NO levels [20]. Taken together, these results suggest that hypoxia maybe the primary cause that induces budbreak and the increased levels of ROS and NO are the secondary products produced in response to hypoxia. A general model accounting for the major events occurring during artificially induced bud dormancy release has been proposed [5, 7, 19, 21]. In this model, upon HC treatment a respiratory disturbance in mitochondria leads to a transient oxidative stress expressed as an increased level of ROS, decreased activity of TCA cycle and decreased production of ATP and increased production of ethylene. To cope with energy crisis, alternative respiratory pathway, glycolysis, pyruvate metabolism and anaerobic respiration or fermentation is induced. In parallel, various antioxidant systems are upregulated to cope with the transient oxidative burst. However, the underlying mechanism leading to growth resumption remains elusive.
ROS are known to play a key role in cell wall loosening in growing tissues [22, 23] and act as signalling molecules in signal transduction in cells, regulating plant growth and development in response to biotic and abiotic stimuli [24, 25]. In plant cells, ROS production is regulated spatially and temporally from many sources and ROS reactivities take place in various cellular components, such as chloroplast, mitochondria, peroxisome, endoplasmic reticulum, apoplast, plasma membrane and cell wall [24, 26–28], with mitochondria as the major source of ROS production [29, 30]. Accumulation of endogenous ROS in plants can be triggered by many environmental stresses, such as water deficit and salinity [31] and chilling stress [32], especially under high light or in combination with other stresses. Generation of ROS can be catalysed by many enzymes, such as glucose oxidase, xanthine oxidase, peroxidases, oxalate oxidases, amine oxidase, lipoxygenases, quinine reductases and NADPH oxidases [24, 33].
Membrane-bound NADPH oxidases, known as respiratory burst oxidase homologues (RBOHs), serve as important molecular ‘hubs’ during ROS mediated signalling in plants [33]. NADPH oxidases control plant growth and development by making ROS that regulate plant cell expansion through the activation of Ca2+ [34], integrating calcium signalling and protein phosphorylation with increasing ROS production [25]. Also, the bioreactive lipoxygenase (LOX) metabolites stimulate the activity of NADPH oxidases and production of ROS [35]. The major bulk of lipoxygenases (LOXs) is localized in the cytoplasm and vacuole of the plant cell [36]. Expression of LOX is regulated by different forms of stress, such as wounding, water deficiency [37, 38], or pathogen attack [39]. Thus, NADPH oxidases have a dedicated function of generating ROS and act as key signalling nodes integrating multiple signal transduction pathways in plants [40, 41].
ROS in the form of H2O2 is moderately reactive and relatively long-lived that can pass freely through membranes by diffusion and acts as a messenger in the stress signalling response [42, 43]. H2O2 upregulates transcription factors (TFs) and TF-interacting proteins, affecting cell division, stem branching, flowering time and flower development [44]. The gaseous nitrogen reactive species (NRS) NO may serve as an enhancer in the ROS generation network [45, 46]. As a key signalling molecule, NO functions in different intercellular processes, including the expression of defense-related genes against pathogens and apoptosis/program cell death (PCD), maturation and senescence, stomatal closure, dormancy release during seed germination, root development and induction of ethylene emission. Recent studies showed that NO can be produced in plants by enzymatic and non-enzymetic systems. The major NO-producing enzymes in plants are nitrate reductase in a NADH-dependent reaction and several arginine-dependent nitric oxide synthase-like (NOS) activities in different cellular compartments [20, 47]. Other potential enzymatic sources of NO include NO synthase, xanthine oxidoreductase, peroxidase, cytochrome P450, and some hemeproteins.
To control ROS levels under oxidative stress, organisms induce a variety of antioxidant enzymes and compounds to scavenge ROS and RNS in the cells. Within a cell, the superoxide dismutases (SODs) in various cellular organelles constitute the first line of defense against ROS [48]. Other defense enzymes, including catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), guaiacol peroxidase (GPX), glutathione reductase (GR), monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDHAR), and dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR), protect their cellular constituents by scavenging the harmful ROS and thus maintaining the normal cellular redox state [49]. The antioxidant compounds ascorbate and glutathione serve as cofactors in some of these scavenging reactions. Earlier studies showed that HC inhibits grapevine bud catalase gene expression during the first 4 days of treatment, but induces transcripts for the enzymes pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) and alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) [50]. In grapevine buds, HC also upregulates oxidative stress-related genes, such as thioredoxin h (Trxh), glutathione S-transferase (GST), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione reductase (GR), and hypoxia related genes, such as sucrose synthase (SuSy) [51, 52]. After exposure to HC, peroxidase activity in a number of plants is increased. Peroxidases utilize different organic electron donors to reduce H2O2. Natural chilling also leads to similar induction of these genes during the last stage of the dormancy cycle of grape buds [53]. Class 1 nonsymbiotic hemoglobin is involved in scavenging of NO [20, 54–57]. Its expression is increased during hypoxic stress, application of respiratory chain inhibitors (e.g. cyanide) and high level of nitrate.
Accumulation of excessive ROS (e.g. H2O2) and RNS (e.g., NO) in turn induces the activation of alternative electron-transport pathway to prevent accumulation of excessive ROS, and the expression of alternative oxidase gene (AOX1a) is also known to respond to various stresses in plants [58]. The expression of AOX1 affects both ROS and RNS generation and accumulation through the respiratory chain in mitochondria [59–61]. Expression of AOX is up-regulated in grapevine buds by HC treatment [7], but HC treatment increased H2O2 production in grapevine buds [18]. Clearly, a complicate regulatory network controlling ROS metabolism exists in plant cells. Moreover, as many genes exist in a gene family whether all members in the family are affected by the same stimuli is not known. Thus, how HC exactly affects the ROS regulatory network during grapevine dormancy release remains unclear.
To gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanism of the release of paradormancy in the summer grapevine buds by P and HC, this study aimed to follow the changes of endogenous ROS and NO levels in the intact dormancy breaking buds by cytochemical staining and identify the candidate genes being significantly altered by microarray analysis. GO categories that are related to ROS-generating, ROS-scavenging, and NO detoxification were identified as key early factors in grapevine dormant bud break. The expression dynamics of these factors during the early stages of budbreak support the importance of a rapid accumulation of ROS and RNS with a concomitant activation of related genes for budbreak.
Results
Budbreak rate
After 8 days, the budbreak rates of dormant grapevine buds treated with P (pruning), HC (1 % or 12.5 mM hydrogen cyanamide), PHC (P + HC) and water (as a control) were 33.3, 53.3, 95.3 and 0 %, respectively (Fig. 1a). Obviously, HC alone was more effective in promoting dormant budbreak than P. The effect of HC on breaking dormant buds was further enhanced by P. A combined P and HC (PHC) treatment gave rise to the highest dormant budbreak, showing a synergetic interaction between P and HC. During the treatment with PHC, the breaking buds enlarged and sprouted rapidly between 96 and 192 h (Fig. 1b). Anatomical examination before and after PHC treatment showed an active growth resumption of floral meristem starting at 12 h (Fig. 1C-c). Four to five leaf primordia were visible at 12 h and the inflorescence meristem began to develop at 48 h (Fig. 1C-e), and the inflorescence primodia became well developed with complete floral meristem at 96 h post treatment (Fig. 1C-f).
Fig. 1.
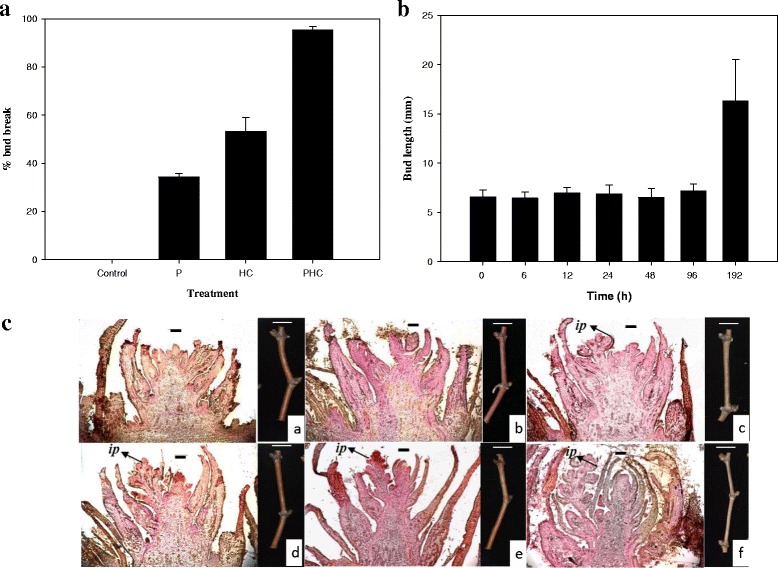
Morphological and anatomical changes in grapevine buds during dormancy break. Percentages of budbreak after 192 h of treatment with P, HC, PHC, or water as a control (n = 10, bar: standard deviation) (A). Changes in bud length after PHC treatment at 0, 6, 12, 24, 48, 96 and 192 h (n = 10, bar: standard error) (B). Longitudinal sections of grapevine floral bud development during release of dormancy after PHC treatment: (a) 0 h, (b) 6 h, (c) 12 h, (d) 24 h, (e) 48 h and (f) 96 h. ip: inflorescence primordium (C). Bar: 200 μm
In situ detection of H2O2, O2•- and NO
The accumulation of H2O2 in the grapevine buds during the treatments was first quantitatively determined by measuring the Fe-H2O2 complex in the buds [62]. For all four treatments, H2O2 increased rapidly and almost linearly, reaching its maximum level after 12 h and decreased slightly thereafter (Fig. 2), and the averaged amounts on a fresh weight basis were 1.38, 12.24, 22.06, and 29.31 μg/g for the control, P, HC, and PHC treatments, respectively. The accumulation of H2O2, O2•- and NO was subsequently examined by staining in situ in the bud longitudinal sections after 12 h of treatment. A similar pattern of accumulation among these treatments for H2O2, O2•- and NO was also observed, with the highest levels detected in the PHC treated buds and the lowest levels in the control buds. When the sections were incubated with specific scavengers of ROS or inhibitor of NO, no staining occurred, showing a low background as in the control sections. The results confirmed the specificity of the in situ staining of these reactive species. Thus, H2O2, O2•- and NO significantly accumulated in the sections of buds treated with PHC, followed by HC and P (Fig. 3). The results suggest that intensive H2O2, O2•- and NO production took place in the treated dormant buds at the early stage of budbreak. These levels are positively correlated with the percentages of budbreak (Fig. 1a).
Fig. 2.
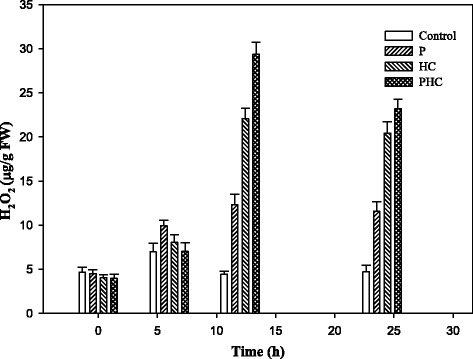
Levels of H2O2 in the control, P, HC and PHC treated buds. Hydroperoxide was assayed by the ferric-xylenol orange (Fe-XO) complex [62]. After incubation in the dark for 30 min, the absorbance was read at 560 nm with 100 μM xylenol orange as blank
Fig. 3.
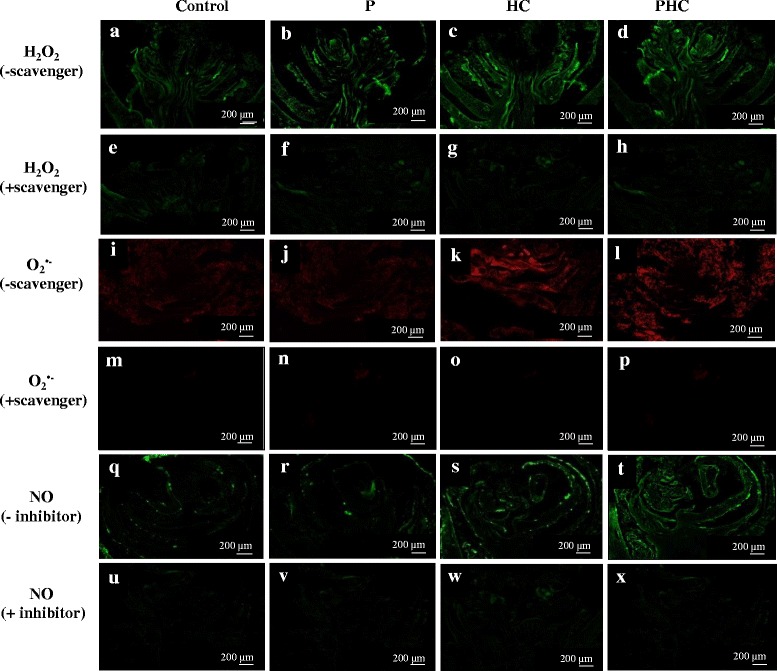
In situ detection of H2O2, O2 •- and NO at early stages of grapevine budbreak. Visualization of H2O2 by fluorescence microscopy using DCF-DA assay in grapevine bud sections after 12 h of treatment: H2O as a control (a), P (b), HC (c) and PHC (d). For negative control, grapevine bud sections were incubated with 1 mM sodium pyruvate, an H2O2 scavenger: control (e), P (f), HC (g) and PHC (h). Visualization of O2 •- by reaction with 10 μM dihydroethidium (DHE) in grapevine bud sections: control (i), P (j), HC (k) and PHC (l). For negative control, grapevine bud sections were incubated in 1 mM tetramethylpiperdinooxy, an O2 •- scavenger: control (m), P (n), HC (o) and PHC (p). Visualization of nitric oxide (NO) by DAF-2DA assay in grapevine bud sections: control (q), P (r), HC (s) and PHC (t). For negative control, grapevine bud sections were incubated in 10 μM carboxy-PTIO, an NO inhibitor: control (u), P (v), HC (w) and PHC (x). Bar: 200 μm
Microarray analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and clustering of expressed genes
To gain insights into the early mode of molecular action during grapevine budbreak transcriptomic profiles in buds treated with P, HC and PHC for 24 h were examined by microarray using Agilent 44 K Gene Expression Array with specific probes for grapevine genes. An earlier time course study showed that the numbers of up- and down-regulated genes in grapevine buds treated with HC reached the peak around 24 h post-treatment [7]. Clustering of the expressed genes into functional categories in the buds treated with P, HC, and PHC were based on GenSpring analysis, and the changes in transcript abundance were identified by M/A plot. A larger distribution of transcript abundance was found in the buds treated with PHC, followed by HC and P (Additional file 1), consistent with its strong potency on dormancy release. However, it must be pointed out that transcriptional activation of some genes that occurred within 24 h of treatment may have not been identified.
Identification of common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) among treatments
Analysis by GenSpring indicated that a total of 965, 1662 and 3783 genes showed significantly up-regulated expression and a total of 287, 1511 and 3261 genes showed significantly down-regulated expression by P, HC and PHC treatments, respectively (Fig. 4a, b). Clearly, alteration in expression of many genes is involved in dormant budbreak in grapevine and many more genes were up-regulated than down-regulated by these treatments, similar to that reported in grape after treatment with HC [7]. 239 up-regulated and 106 down-regulated genes were common for all three treatments, indicating similar molecular events occurred in these buds (Additional file 2). Among the commonly up-regulated genes with a greater than a log2-fold change in expression are those coding for TF factors (e.g. 7 bHLHs, 2 WRKYs, EGL, ERF073, NAM-B1, OFP5 and HEC2) and functional genes coding for protein kinase, peroxidase, ion oxygenase, amine oxidase, PR proteins, dirigent proteins, expansin and extension (Table 1). The expression of some genes related to degradation of cyanamide (e.g. bifunctional nitrilase and nitrile hydratase), synthesis of pigments (e.g. stilbene, anthocyanidin) and metabolism of growth regulators (e.g. ethylene, salicylic acid, brassinosteroid, auxin and cytokinin) was also upregulated. In particular, the hypoxia related gene coding for sucrose synthase (SuSy) was significantly up-regulated by all three treatments, especially by PHC. Among the commonly down-regulated genes are those coding for TFs (e.g. ERF016, ERF010-like, DET010-like, NAC18, NAC29, NAC100, FUS3, MYB24, A-7a-like, ABI5, GATA 24-like, ATHB-2, ATHB40) and functional genes coding for chloroplast chaperone danJ11, PR proteins, protein kinase, ubiquitin ligase, cytochrome P-450 and peroxidase 10 and 25. These genes are generally related to stress responses in hormonal action, ROS metabolism, and transition to growth resumption process.
Fig. 4.
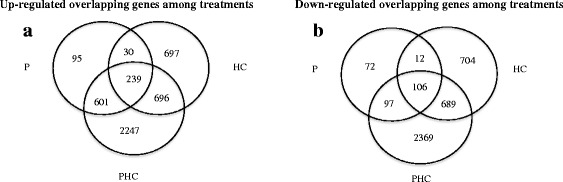
Venn diagrams to show the overlap of significantly up- and down-regulated genes among different treatments. Comparison of significantly up- (a) and down–regulated genes (b) among P, HC and PHC treatments after 24 h of treatment. Microarray data analyses yielded 6410 significantly up- and 5059 significantly down-regulated genes by the 3 treatments with at least two fold changes (p < 0.05, n = 3)
Table 1.
Functions of important transcription factors and proteins
| TFs or proteins | Function | References |
|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated | ||
| 1. bHLH | bHLHs have a range of different roles in plant cell and tissue development as well as plant metabolism. | [68] |
| 2. WRKY | Regulators involved in various develop006Dental and physiological process, especially in coping with diverse biotic (e.g. wounding, salicylic acid, cold, and salinity) and abiotic (e.g. methyl jasmonate (MeJA) stresses. | [66, 99] |
| 3. ERF | Plays a crucial role in plant growth and development and in response to biotic and abiotic stress conditions in plant. It’s also involved in fruit ripening and stress processes. | [67] |
| 4. NAM-B1 | Acts in tissue specific manner to regulate monocarpic senescence and grain filling, and it’s related to carbohydrate metabolism in stems and the grain, and associated with the grain protein content in Fennoscandian wheat. | [69, 70] |
| 5. Protein kinase | Protein kinases are universal signal transduction modules in eukaryotes, including yeasts, animals and plants. | [73] |
| 6. Peroxidase | Peroxidases as key players during the whole life cycle of a plant, and particularly in cell wall modifications, and in roles that can be antagonistic depending on the developmental stage. | [74] |
| 7. Amine oxidase | Cell wall maturation and lignification during development as well as with wound-healing and cell wall reinforcement during pathogen invasion. | [26] |
| 8. NADPH oxidase | A plasma membrane NADPH oxidase produces ROS in planta or in elicited cells during incompatible interaction | [100] |
| 9. PR proteins | The class 1 pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins are thought to be involved in plant defense responses against infection by pathogens, such as fungi or viruses. | [75, 76] |
| 10. Expansin | Expansins are involved in enhancing growth by mediating cell wall loosening. | [77, 98] |
| 11. Extensin | Extensins are involved in defense and in the control of extension growth by differential expressing under stress and non-stress conditions. Extensin genes are developmentally regulated and induced by wounding, methyl jasmonate, abscisic and salicylic acid. | [78–80] |
| Down-regulated | ||
| 1. NAC | NAC has a variety of important functions in plant development, and also in abiotic stress responses. | [101] |
| 2. FUS3 | A positive regulator of seed responses to ABA and mediates osmotic stress responses during seed development. | [81, 102] |
| 3. MYB | Regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in the grape via expression of the UFGT gene (UDP glucose: flavonoid -3-O-glucosyltransferase). | [85, 103] |
| 4. ABI5 | Insensitive to ABA in seed germination, with an earlier flowering phenotype. | [82] |
| 5. GATA-like | GATA DNA motifs have been implicated in light-dependent and nitrate-dependent control of transcription. | [86] |
| 6. ATHB | ATHB10 regulates root hair development, ATHB8 promotes vascular cell differentiation and positively modulates the activity of procambial and cambial cells to differentiate, ATHB2 and ATHB4 genes are strongly induced by far-red-rich light. | [83, 84, 104] |
| 7. Chaperone dnaJ | Regulation of the heat shock response by serving as an important pathway for the folding of newly synthesized polypeptides. | [87, 88] |
| 8. Ubiquitin ligase | Ubiquitin ligase is an important part of cellular regulation in Arabidopsis, suggesting a major role for protein degradation in control of plant life. | [89, 105] |
Classification of up- and down- regulated genes involved in ROS/NO metabolism
GO categories by ErmineJ analysis of ROS related genes that were up- or down-regulated in molecular function 24 h post-treatment were listed in Table 2. Many ROS- and NO-related genes showed significant alteration in expression. We identified clear overlaps of the molecular functions among the up- and down-regulated genes in response to P, HC and PHC treatments. GO terms in which their gene expression levels altered significantly (by at least two fold) by the treatments were listed in Additional file 3. PHC induced more up- and down-regulated genes than HC and P treatments. Also, there are genes commonly regulated by all three treatments. Among the ROS-generating genes, the two respiratory burst oxidase homolog genes related to GO:0043167 (ion binding), VvRBOHE and VvRBOHA, were down-regulated by PHC, while only VvRBOHA was down-regulated by HC. However, VvRBOHE was upregulated by P and HC.
Table 2.
Number of genes that were expressed in each treatment, as identified by GO categories
| ROS-/NO-related genes | GO category | Gene family | No. of gene up/down regulated | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | HC | PHC | |||
| ROS-related genes | |||||
| ROS-generating genes | GO:0043167 ion binding |
Respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein (VvRBOH) | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/2 |
| GO:0004601 peroxidase activity |
Peroxidase (VvPOD) | 10/1 | 10/14 | 15/10 | |
| ROS-scavenging genes | GO:0016209 antioxidant activity |
Alpha-dioxygenase 1 (VvDOX1) | 1/0 | 1/0 | 0/0 |
| Glutathione peroxidase (VvGPX) | 0/0 | 0/1 | 1/1 | ||
| Catalase isozyme 1-like (VvCAT) | 0/0 | 0/2 | 0/2 | ||
| Cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase (VvAPX) | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/2 | ||
| Superoxide dismutase [Fe], chloroplastic (VvFSD) | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | ||
| Alternative oxidase 2, mitochondrial (VvAOX2) | 0/0 | 1/0 | 1/0 | ||
| ROS-specific transcription factors | GO:00037000 transcription factor |
Heat Stress transcription factor (VvHSF) | 0/1 | 2/2 | 3/6 |
| Ethylene response element binding factor (VvERF) | 4/3 | 8/6 | 8/9 | ||
| WRKY transcription factor (VvWRKY) | 1/0 | 9/4 | 7/7 | ||
| NO-related gene | |||||
| NO-scavenging | GO:0005488 Binding |
Hemoglobin-2 (VvHB2) | 0/0 | 1/0 | 1/0 |
These were significantly up/down regulated genes related to ROS/NO metabolism in grapevine buds treated with P, HC and PHC following the GO categories by ErmineJ analysis
The ROS-scavenging peroxidases related to GO:0004601 exist in a big gene family, and many of VvPOD genes were up-/down-regulated, especially by HC and PHC (10/14, and 15/10). Obviously, most of the POD genes were upregulated and they are assumed to play a key role in the reduction of H2O2 in grapevine buds treated with HC [13]. For other ROS-scavenging genes in GO:0016209 (antioxidant activity), the expressions of five gene families have been up- or down-regulated by the three treatments. For example, one alpha-dioxygenase gene (VvDOX1) was up-regulated by P and HC, but not by PHC. Gene coding for glutathione peroxidase (VvGPX2) was up-regulated by PHC whereas another (VvGPX8) gene was down-regulated by HC and PHC. After 24 h of treatment, two catalase isozyme 1-like genes (VvCAT) were down-regulated by both HC and PHC. In addition, VvAPX coding for cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase was down-regulated by both HC and PHC, and VvFSD coding for chloroplastic superoxide dismutase (SOD) [Fe] was down-regulated by PHC whereas VvFSD3 was up-regulated by PHC. The expression of VvAOX that codes for alternative oxidase in mitochondria was up-regulated by both HC and PHC. For NO related genes, the expression of hemoglobin-2 gene (VvHB2) in binding (GO:0005488) was significantly up-regulated by both HC and PHC. The expression of the genes in the three ROS related transcription factor gene families (GO:0003700), namely heat stress transcription factor (VvHSF), ethylene response element binding factor (VvERF) and WRKY transcription factor (VvWRKY), was also differentially altered. The numbers of VvHSF genes up-/down-regulated by P, HC, and PHC were 0/1, 2/2, and 3/6, respectively, while the numbers of VvERF genes up-/down-regulated expressed by these treatments were 4/3, 8/6, and 8/9, respectively. Many of the VvWRKY genes were also up-/down-regulated, especially by HC and PHC (9/4 and 7/7), compared to P (1/0). These results indicate that more genes are altered in their expression at a higher intensity by PHC and the expressions of different genes in the same GO category are differentially regulated by these treatments.
Expression dynamics of ROS/NO-related genes during PHC treatment
Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to confirm the alteration in expression of 12 selected DEGs identified by cDNA microarray and profile the expression dynamics of these genes during the 48 h of PHC treatment using eIF4A as a reference gene as its expression did not change substantially [1]. The DEGs included 2 genes coding for ROS-generating (VvRBOHE, VvRBOHA), 9 genes coding for ROS-scavenging (VvPOD72, and VvPOD12, VvDOX1, VvGPX2, VvAPX3, VvFSD3, VvFSD, VvAOX2, VvCAT1) and one gene coding for NO-scavenging (VvHB2) (Table 3). The expression profiles of these 12 genes during the 48 h treatment showed different tempos, with most of their expression peaked at 6 or 12 h, indicating a transient nature. A similar trend in gene expression was also reported in detached grapevine canes treated with HC or heat shock (HS) [7]. Two of the ROS-generating respiratory burst oxidase homologue genes, VvRBOHE and VvRBOHA, and the scavenging peroxidase gene VvPOD12 were down-regulated by more than two folds throughout the first 48 h of treatment. In significant contrast, the expression of the peroxidase gene VvPOD72 started to increase after 6 h of treatment and reached its maximum expression at 12 h (14.8 fold), but dropped off to normal levels thereafter, consistent with the results obtained by microarray (Table 3). Thus, VvPOD72 and several other members of the peroxidase family (Table 2) played an important role in early ROS metabolism by scavenging H2O2 upon PHC treatment, which synchronized with the new meristem growth (Fig. 5a).
Table 3.
List of genes that were used to profile their expression dynamics by qRT-PCR
| Gene Locus ID | Gene description | Normalized Fold (Log2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | HC | PHC | ||
| GSVIVT00016386001 | Vitis vinifera respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein E (VvRBOHE) | 0.30 ± 0.21 | 1.11 ± 0.18 | −1.22 ± 0.06 |
| GSVIVT00002525001 | Vitis vinifera respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein A (VvRBOHA) | −0.64 ± 0.06 | −1.53 ± 0.29 | −1.96 ± 0.16 |
| GSVIVT00031598001 | Vitis vinifera peroxidase 72 (VvPOD72) | 1.59 ± 0.77 | 2.09 ± 1.18 | 4.19 ± 0.18 |
| GSVIVT00031723001 | Vitis vinifera peroxidase 12 (VvPOD12) | −0.79 ± 0.05 | −0.74 ± 0.25 | −1.71 ± 0.13 |
| GSVIVT00020782001 | Vitis vinifera alpha-dioxygenase 1 (VvDOX1) | 1.83 ± 1.16 | 2.82 ± 0.55 | 0.13 ± 0.25 |
| GSVIVT00001920001 | Vitis vinifera glutathione peroxidase 2 (VvGPX2) | 0.34 ± 0.39 | 0.28 ± 0.45 | 1.10 ± 0.54 |
| GSVIVT00004080001 | Vitis vinifera catalase isozyme 1-like (VvCAT1) | −0.35 ± 0.17 | −1.52 ± 0.02 | −1.57 ± 0.15 |
| GSVIVT00036747001 | Vitis vinifera cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase (VvAPX3) | −0.47 ± 0.24 | −1.05 ± 0.09 | −1.75 ± 0.04 |
| GSVIVT00007083001 | Vitis vinifera superoxide dismutase [Fe] 3, chloroplastic (VvFSD3) | 0.40 ± 0.17 | 0.17 ± 0.10 | 1.82 ± 0.11 |
| GSVIVT00014163001 | Vitis vinifera superoxide dismutase [Fe], chloroplastic (VvFSD) | 0.50 ± 0.13 | 0.33 ± 0.22 | −1.60 ± 0.17 |
| GSVIVT00003173001 | Vitis vinifera alternative oxidase 2, mitochondrial (VvAOX2) | 0.44 ± 0.16 | 2.43 ± 0.37 | 1.07 ± 0.18 |
| GSVIVT00036443001 | Vitis vinifera hemoglobin-2 (VvHB2) | −0.52 ± 0.43 | 4.41 ± 0.34 | 3.08 ± 0.43 |
These include twelve differentially expressed genes related to ROS/NO metabolism in grapevine buds treated with P, HC or PHC for 24 h, as revealed by microarray analysis
Fig. 5.
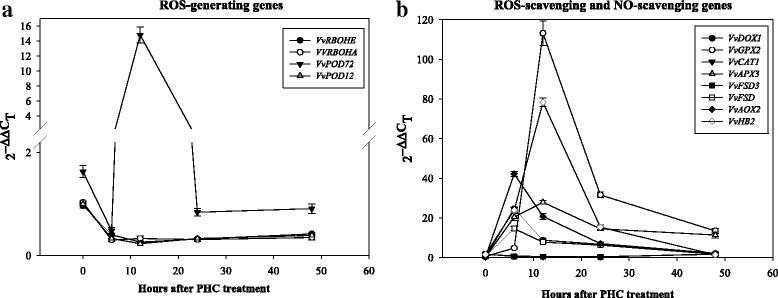
Changes in transcript abundance of 12 up- and down-regulated ROS/NO-related genes during 48 h treatment with PHC, as analyzed by qRT-PCR. These include 4 ROS-generating genes (VvRBOHE, VvRBOHA, VvPOD72, VvPOD12) (a), and 7 ROS-scavenging genes (VvDOX1, VvGPX2, VvCAT1, VvAPX3, VvFSD3, VvFSD, VvAOX2) and one NO-scavenging gene (VvHB2) (b). The selection of these genes was based on their relative expression levels obtained by the microarray analysis (Table 3)
For other ROS-scavenging genes, the alpha-dioxygenase VvDOX1 showed a rapid increase (24.6 fold) in transcript as early as 6 h post treatment and declined gradually throughout the treatment. A small increase (4.8 fold) in the glutathione peroxidase VvGPX2 transcript was detected as early as 6 h, but its expression accelerated rapidly thereafter and reached its maximum expression (113.2 fold) at 12 h, but dropped off to 31.6 and 13.4 fold at 24 and 48 h, respectively. For the ascorbate peroxidase gene VvAPX3, a rapid increase of transcript (20.4 fold) was detected as early as 6 h and reached its maximum expression (27.8 fold) at 12 h and slowly declined to 14.5 and 11.4 fold at 24 and 48 h, respectively. Interestingly, VvFSD3 and VvFSD, both coding for chloroplastic superoxide dismutases (SODs), showed different expression patterns: VvFSD3 expression decreased progressively from 0.6 fold at 6 h to 0.4 fold at 24 h after treatment but increased to 1.8 folds after 48 h of treatment, whereas the expression of VvFSD showed a rapid increase as early as 6 h (14.6 fold) but declined gradually to a normal level at 48 h. The mitochondrial alternative oxidase VvAOX2 also showed a rapid increase in expression (42.2 fold) as early as 6 h but declined gradually to a normal level at 48 h. It is also noticeable that the expression of the peroxisomal catalase isozyme-like VvCAT1 was first down-regulated, decreasing progressively from 0.7 fold at 6 h to 0.5 fold at 24 h, but increased to 1.8 fold after 48 h of treatment. The initial downregulation of catalase expression may have contributed to the rapid accumulation of H2O2 [13], but its subsequent rise in expression may have prevented the buildup of a lethal level of H2O2. A rapid increase in the hemoglobin-2 (VvHB2) transcript was detected at 6 h (23.9 fold) and it reached its maximum expression (78.3 fold) at 12 h, but its transcript level dropped off from 15.33 at 24 h to 1.39 fold at 48 h, similar to that reported in an earlier study [7]. This result suggests that the intensive expression of hemoglobin 2 is triggered by the treatment at very early stage of the treatment and may be important in scavenging NO. Taken together, these results suggest that the two NADPH oxidases, VvRBOHE and VvRBOHA, may not be a key player in ROS generation, while VvPOD72, VvDOX1, VvGPX2, VvAPX3 and VvHB2 are important for ROS and NO scavenging, respectively (Fig. 5b). Overall, these results are in agreement with those obtained by microarray analysis after 24 h of treatment with HC (Table 2, Additional file 3).
Discussion
HC has been frequently used to break endodormancy of floral buds in grape and several studies have been conducted to address its physiological and molecular basis [4, 8, 9, 13, 63]. However, study on its application to release paradormancy of grape floral buds in the summer has received very little attention. This study aimed to address the early mode of action of PHC, a combination of pruning and HC, with intact grape canes on its effective alleviation of bud dormancy in hot summer that results in uniform budbreak and floral development without chilling requirement. PHC induced budbreak much more rapidly and efficiently than P or HC alone, indicating a synergetic interaction between P and HC treatments (Fig. 1a). Compared to the long period of time required for budbreak by chilling [64], the rapid induction of budbreak by PHC observed in this study may in part be due to the nature of dormancy and the warm temperatures in the summer which accelerate metabolism and growth. Large amounts of H2O2, O2•- and NO accumulated rapidly in the buds upon the treatments, especially by PHC (Fig. 3); and the amount of H2O2 in the buds increased almost linearly in the buds, reaching its maximum level within 12 h (Fig. 2). Moreover, the ROS levels accumulated are closely correlated with the percentage of budbreak among these treatments, and this strong, transient oxidative burst coincides with growth resumption in the buds (Fig. 1). Similarly, previous studies also showed that grape buds respond to HC and KC by eliciting ROS, such as H2O2 [18, 19, 65]. Thus, a combination of P and HC is most effective in eliciting rapid accumulation of ROS and release of the paradormant buds in summer grapevine.
To provide insights into the molecular basis of HC effect on breaking dormant buds in grapevine, we conducted transcriptomic analysis during budbreak. Our transcriptomic profile provided a clear link between gene expression and ROS accumulation during the early stage of budbreak. Upon PHC treatment expression of a number of specific genes was altered rapidly to accommodate the metabolic activities required for budbreak and growth resumption. As expected, the numbers of significantly up-/down-regulated genes were highest in PHC treated buds, compared to HC and P treated buds (Fig. 4a, b). Moreover, PHC exerted a higher intensity of regulation, relative to other treatments. Although P, HC and PHC induced dormant budbreak at varying degrees, many transcription factor (TF) and functional genes were commonly induced or suppressed by these treatments (Table 1). These genes/proteins must play important roles in budbreak response. Many of the upregulated TFs, such as WRKYs [66] and ERF (ethylene response factor) [67], are known to be involved in biotic and abiotic stress responses, whereas some other TFs, such as bHLH and NAM-B1, are related to cell and tissue development. For example, bHLHs exhibit a range of different roles in plant cell and tissue development [68], and NAM-B1 acts in a tissue specific manner to regulate monocarpic senescence and grain filling [69, 70]. Consistently, ethylene biosynthesis is reported to increase in grape buds in response to HC and HS treatments and plays a key role in dormancy release by activating ERFs [7], and the high levels of ethylene accumulated in the submerged tissues promote shoot elongation [71] and parenchyma formation [72].
Many of the upregulated functional genes, such as protein kinase, peroxidase, amine oxidase, PR proteins, expansin and extension, are related to plant defense responses and cellular growth. For example, protein kinases are universal signal transduction modules in eukaryotes [73]. Amine oxidase that catalyzes the oxidative de-amination of polyamines and production of H2O2 has been correlated with cell wall maturation and lignification during development as well as wound-healing and cell wall reinforcement during pathogen invasion [26]. Peroxidases that catalyze the reduction of H2O2 are known to be involved in cell wall loosening [74]. Thus, these two enzymes may be the key players of ROS metabolism in the cell wall during dormant budbreak in grapevine, as exerted by PHC. PR proteins are thought to be involved in plant defense responses [75] and response to infection by pathogens [76]. In addition, expansin is related to cell wall loosening [77], while extensins expressed under stress and non-stress conditions (e.g. wounding, methyl jasmonate, abscisic acid and salicylic acid) [78, 79] are related to defense and control of extension growth [80]. Thus, these commonly induced TF and functional genes in stress response, oxidative burst, hormonal regulation, and reprogramming of cellular developmental and physiological processes must play important roles in the ROS regulatory network leading to dormancy breaking and bud sprouting in grapevine. Earlier microarray analyses with detached grapevine canes also suggest that HC and HS break the dormant buds through the link between sublethal stress, mitochondrial activity, temporary hypoxic conditions, ethylene metabolism, ROS scavenging activity and cell enlargement during bud dormancy release [7, 52].
Among the down-regulated TFs, NAC is known to be involved in biotic and abiotic stress response, FUS3 controls multiple elementary processes during seed development [81], ABI5 is related to insensitivity to ABA in seed germination and during embryogenesis [82], and ATHB regulates root hair development and promotes procambial and cambial vascular cell differentiation [83, 84]. In addition, MYB regulates proanthocyanidian biosynthesis in grapes [85], and GATA-like has been implicated in light-dependent and nitrate-dependent control of transcription [86]. Among the down-regulated functional genes, chaperone dnaJ regulates heat shock response [87] for proper folding of newly synthesized polypeptides [88] and ubiquitin ligases is an important part of cellular regulation in Arabidopsis [89]. Most of these responses may reflect temporary impairment of normal metabolic activities under the oxidative stress conditions.
Expression dynamics of ROS metabolism related genes
PHC triggered a rapid generation and accumulation of ROS and NO peaked at 12 h (Figs. 1b, 2 and 3), with a concomitant transcriptional activation of related genes peaked at 6–12 h post-treatment (Figs. 4 and 5). ROS levels are controlled by a network of generating and scavenging enzyme systems. For ROS generation, PHC highly induced POD72, but suppressed RBOHE, RBOHA and POD12 at the early stages of treatment. Besides amine oxidase (Table 1), these results emphasize the importance of POD72 and other peroxidase members in ROS generation in cell wall during paradormant bud break in the summer grapevine. Consistently, previous results also suggest that peroxidase activity is increased largely in grapevine buds upon fulfilment of chilling requirement [64] and it may play an important role in consumption or release of ROS and in cell wall modification [74]. In response to oxidative burst genes coding for the various antioxidant systems, e.g. GPX2, CAT1, APX3, AOX2, DOX1 and HB2, were also rapidly turned on in the dormancy breaking buds to scavenge ROS and NO. As reported earlier, after 12–24 h of HC treatment, GR, GST and APX genes are upregulated in grapevine buds [7]. GPX and APX catalyze the reduction of hydrogen peroxide to water by using glutathione and ascorbate, respectively, as a specific electron donor [90]. In addition, glutathione is a strong detoxifying agent and has been shown to bind HC directly on its free thiol groups [91].
In Arabidopsis, α-DOX fatty acid dioxygenase protects oxidative stress and cell death [92]. AOX1 is known to be induced by H2O2 and NO [93] and its expression is induced by both HS and HC application in grapevine buds during 96 h of treatment [7] and it may contribute to the reduction of both ROS and RNS generation through the respiratory chain in mitochondria [47]. Therefore, our results are in agreement with the earlier observations that detoxifying mechanisms are correlated with the temporary oxidative stress and H2O2 may act as a signal in the release of endodormancy in grapevine buds by HC [50]. Taken together, these results support a common mode of ROS regulatory network and its modulation in grapevine dormancy break. For detoxification of RNS, the expression of grapevine HB2 gene peaked at 6 h post-treatment by PHCN (Fig. 5b). Similarly, the expression of HB was markedly up-regulated in the HC treated buds in an earlier study with grape [7]. Besides being an O2 carrier, HB serves as an electron carrier during the conversion of NO to NO3 in various tissues [20, 54–57]. Therefore, VvHB2 may play a key role in preventing accumulation of excessive NO and its toxicity in grape buds during budbreak.
Working model integrating physiological and molecular events during paradormancy release by PHC in grapevine buds
Earlier studies suggest a general model accounting for the major events occurring during artificially induced bud dormancy release [4, 5, 7, 13, 19, 21, 45]. Cellular hypoxia is considered the primary cause that induces budbreak while the increased levels of ROS and NO are the secondary products produced in response to hypoxia. Disturbance in mitochondria leads to a transient oxidative stress expressed as an increased level of ROS, decreased activity of TCA cycle and decreased production of ATP and increased production of ethylene. Alternative respiratory pathway, glycolysis, pyruvate metabolism and anaerobic respiration or fermentation is subsequently induced to cope with energy crisis. Our results are in general consistent with this model. However, there are unique features derived from this study that may be attributed to the nature of the plant material used. These studies mainly addressed the release of endodomancy by HC in the spring, while the present study was focused on the release of paradormncy of grapevine buds in the hot summer. For example, ABA is known to accumulate during the development of endodormancy in grapevine by suppression of bud meristem activity and its degradation mediated by ethylene is critical for dormancy release [5]. It is unlikely that well-irrigated grapevines in the summer accumulate ABA in the paradormant buds. In this study, pruning resulted in a budbreak rate of 33 % (Fig. 1a), which is consistent with paradormancy in the latent buds in the summer as regulated by plant growth regulators originating from other organs (e.g., auxin from the apical meristem), affecting apical dormancy [3, 4]. However, the hormone ethylene is clearly involved in growth resumption in both types of dormancy.
Based on our results and the literature, we propose a working model to integrate the early physiological and molecular events underlying the release of paradormancy by PHC in grapevine buds (Fig. 6). Upon PHC treatment, the release of cyanide [6, 14–16] rapidly disturbed aerobic respiration and resulted in cellular hypoxia, and the inhibition of catalase by cyanide promoted H2O2 accumulation. ROS (O2•-, H2O2,.OH) and RNS (NO) were also rapidly produced by NADPH oxidase/amine oxidase and NADH dependent nitrate reductase/arginine-nitric oxide synthase, respectively. The gaseous NO in turn served as an enhancer in the ROS regulatory network [46]. To prevent the accumulation of lethal levels of ROS/RNS and PCD, the expression of specific genes involved in various metabolic activities (e.g., AOX, SuSy) and antioxidant systems (e.g., FSD, POD72, APX3, GPX2, CAT1, HB2, and pigments) were induced. H2O2 and.OH activated Ca2+ channels and initiated signal transduction through protein kinase activity, leading to expression of specific stress-responsive TFs (e.g., HSFs, WRKYs, ERFs, HLHs, NAM-B1) to regulate ROS producing and scavenging pathways and cellular metabolism [40]. Apoplastic.OH in the presence of H2O2 and O2•- interacted with cell wall component leading to modification of cell wall structure for expansion growth [94]. Whereas the ROS produced in the cytosol or transported from the apoplast served as signal molecules [15, 17] and triggered the expression of stress-induced specific TFs for the expression of related downstream functional genes responsible for dormancy breaking and growth resumption (e.g., hormone metabolism, expansin, extension) in grapevine buds. The accumulation of ethylene in the buds promoted cell elongation and chlorenchyma formation by activating related ERFs.
Fig. 6.
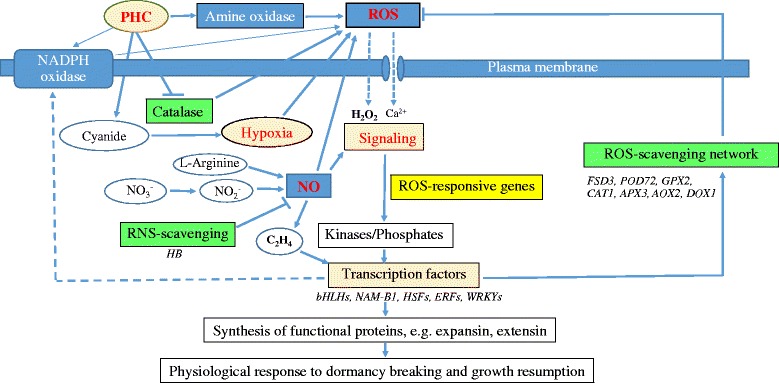
Proposed mechanistic model for paradormancy release by PHC in grapevine buds. Upon application, HC causes immediate cellular hypoxia through the action of released cyanide on aerobic respiration and inhibition of catalase activity and induces H2O2 production. ROS (O2 •-, H2O2,.OH) and RNS (NO) are rapidly produced possibly by several enzymatic systems, such as NADPH oxidase, amine oxidase, nitrate reductase and arginine-nitric oxide synthase. H2O2 and ethylene act as signaling molecules activating genes involved in antioxidant defense systems. The antioxidant machinery and related pathways (e.g. FSD, POD, DOX, GPX, APX, AOX, HB, etc.) are upregulated to maintain ROS and RNS at sublethal levels to avoid PCD. H2O2 in the cell wall induces cell wall loosening and expansion. H2O2 also functions in anabolic, signaling and defense pathways and in the synthesis of the other ROSs,.OH in the presence of H2O2 and O2 •- exerts a wall loosening effect, and H2O2 also drives peroxidase-mediated cross-linking of structural cell wall components. In the signal transduction pathway, ROS triggers the expression of ROS responsive genes. H2O2 and.OH activate Ca2+ channels and initiate a signal transduction and activate protein kinase activity, which in turn activates different transcription factors to regulate ROS scavenging and ROS producing pathways. Finally, these transcription factors control the downstream functional gene expression responsible for dormancy release and growth resumption in grapevine buds. The accumulation of ethylene in the buds promotes cell elongation and parenchyma formation by activating related ERFs
It’s clear that the buildup of a sublethal level of ROS and RNS is a common denominator for bud dormancy release in grapevine in response to natural chilling, HS, P and HC treatments. Enhanced expression of the antioxidant enzymes GST, APX, GR, GPX, AOX and expansin is also reported by HC and HS treatment [7, 51, 52] and during the last stage of chilling requirement in grapevine [53, 64]. Also, genes related to ABA, auxin, ethylene and salicylic acid metabolism are commonly regulated by these treatments. The interplay among these growth regulators leads to cell expansion and division and growth resumption. Thus, judged from the fact that a repertoire of the similar genes is commonly induced by HC, HS, P and natural chilling in a temporary nature, this ROS/NRS regulatory network is essential for the release of bud dormancy in grape and possibly other plants as well.
Conclusion
In summary, PHC effectively releases paradormancy in grapevine buds in the summer with a rapid accumulation of ROS and RNS and a concomitant transcriptional activation of related genes. Our transcriptional profiling links the rapid transcriptional activation of specific ROS related genes and accumulation of various ROS and RNS underlying the early physiological process during dormant bud break as affected by PHC. The key up-/down-regulated genes identified are all related to ROS metabolism in three important GO categories: peroxidase activity, antioxidant activity and transcription factor. Most of these genes exhibited a peak expression 6–12 h post-treatment, coinciding with the maximum accumulation of ROS at 12 h. The ROS scavenging activities mediated by various antioxidant systems avoid the buildup of lethal levels of ROS and RNS to trigger PCD. The sublethal levels of ROS in turn trigger cell wall loosening and the expression of genes (e.g. expansin, extensin) necessary for cell expansion and extension required for new bud growth as regulated by related hormones (e.g. ethylene). As the overall response to a number of dormancy releasing treatments is remarkably similar, this simplified working model of ROS regulatory network may describe the important molecular and biochemical events during budbreak in grapes and other species as well.
Methods
Plant material
The grapevine buds used in this experiment were collected in late August from the mature canes of 5-year-old plants (V. vinifera. x V. labruscana Bailey cv. Kyoho) grown in the research vineyard of the Taichung District Agricultural Research and Extension Station (Taichung DARES, 24°00’N, 120°53’E, elevation19 M), Changhua County, Taiwan. The day/night temperature in Taichung in Changhua was 27–34 °C/22–27 °C. Plants were fertilized on a regular basis and irrigated with drips on open orchard.
Dormancy release by different treatments
In late August, uniform grapevine canes (with ca. 25 buds) were identified and divided into three blocks of randomized complete blocks for four treatments: water (as control; CK), pruning (P), 1 % (w/v or 12.5 mM) HC (H2CN2, 50 % stock, Dormex, SKW, Trostberg, Germany) and a combination of P and HC (PHC). All treatments were applied to the 8th dormant buds from the base of cane. Control buds were sprayed with water until dripping, while buds for HC treatment was sprayed with 1 % (w/v) HC until dripping without pruning. For P treatment, the canes were pruned at 2 cm apart from the 8th node, and for PHC treatment the buds on the 8th node of the pruned canes were sprayed immediately with 1 % (v/v) HC until dripping. After 24 h of treatments, buds on ten single-nodes in each treatment were sampled in 3 replications, frozen immediately in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until RNA extraction. Freshly harvested buds before and after treatments were also used for microscopic examination, H2O2 assay, and in situ detection of H2O2, O2•- and NO. Rates of budbreak were assessed in 30 buds/treatment after 8 days of treatment.
Microscopic observation of bud development after treatments
Grapevine buds were collected before and after 6, 12, 24, 48 and 96 h of treatments and fixed in FAA solution for 2 h, washed three times with 1X PBS buffer (13.7 mM NaCl, 0.27 mM KCl, 1 mM Na2HPO4, and 0.18 mM KH2PO4) and embedded into OCT (optimal cutting temperature) compound (Cryomatrix, Thermo Scientific). Longitudinal sections (10 μm thick) were cut with a microtome (Microm HM550, Thermo Scientific), mounted on glass slides, dehydrated at 60 °C for 1 h, and then stained with filtered 0.1 % Harris Hematoxylin solution (HHS, Sigma) for 10 min. Samples were rinsed in cool running double distilled H2O for 5 min, followed by 70 % and 100 % EtOH dehydration before dipping in 0.5 % Erosin (1.5 g dissolved in 300 mL of 95 % EtOH). Finally, the samples were equilibrated in xylene solution before mounting and covering with Leica CV mount. Images of sections were captured with a light microscopy (Axio Imager 2, Carl Zeiss).
Ferric xylenol orange assay of H2O2
Frozen grapevine buds (0.10 g) harvested before and during treatments were ground to fine powder in liquid N2 and then suspended in 2 mL of 80 % ethanol. After centrifugation, 100 μL supernatant was mixed with 1 mL of reaction solution containing 25 mM H2SO4, 100 μM xylenol orange, and 250 μM ferrous ammonium sulphate, following the protocol for hydroperoxide assay with the ferric-xylenol orange (Fe-XO) complex [62]. After incubation in the dark for 30 min, the absorbance was read at 560 nm with 100 μM xylenol orange as blank.
In situ H2O2, O2•- and NO detection by fluorescence microscopy
For in situ staining of H2O2, O2•- and NO, dormant grapevine buds treated with P, HC, PHC and water (as a control) for 12 h were sectioned (10 μm thickness) and stained for H2O2, O2•- and NO with 25 μM 2’, 7’-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCF-DA, Calbiochem, San Diego, CA, USA) [95], 10 μM dihydroethidium (DHE, Calbiochem, San Diego, CA, USA) [96], and 10 μM 4,5-diaminonaphthalene (DAF-2DA, Calbiochem, San Diego, CA, USA) prepared in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), respectively. For negative controls, sections were incubated sequentially with 1 mM sodium pyruvate (H2O2 scavenger), 1 mM tetramethylpiperdinooxy (O2•- scavenger), and 1 mM carboxy-PTIO; 2-(4-Carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide potassium salt (NO inhibitor), respectively. The bud sections were subsequently washed twice in 1X PBS buffer (13.7 mM NaCl, 0.27 mM KCl, 1 mM Na2HPO4, and 0.18 mM KH2PO4) for 15 min each and then embedded in 30 % polyacrylamide blocks. The sections were mounted on glass slides and images captured with a fluorescence microscope (Axio Imager 2, Carl Zeiss).
RNA extraction and microarray analysis
Frozen grapevine buds were ground to fine powder in liquid N2 and RNA was extracted following the protocol of a previous study [97]. Total RNA was purified by RNeasy plant mini columns (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s guide, and RNA quality was verified by 2100 Bioanalyzer RNA 6000 nano chip (Santa Clara, CA. USA). The RINs (RNA Integrity Number) for the RNA samples ranged from 8.6 to 10.0, indicative of low degradation.
Probes and gene expression microarray
The whole genome mRNA sequences of grape were downloaded in FASTA format from http://www.genoscope.cns.fr/externe/Download/Projets/Projet_ML/data/8X/annotation/Vitis_ vinifera_mRNA v1.fa and saved into a text file. Sequences in text format were downloaded to the eArray web design application from Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) for probe design. One probe per target was designed in the sense orientation with a 3ʹ bias, using base composition methodology as recommended by the manufacturer for gene expression arrays. The best probes were used for generating a custom microarray arranged in a 4 × 44 K format, using a randomized lay-out. Each array included 30,128 probes (i.e., 30,128 genes, each gene with 1 probe), 60 bp in length, 1264 positive (spike-in) controls and 153 negative control probes distributed across the array. Positive controls were used as a quality control of the cRNA synthesis, labelling and hybridization steps, whereas negative controls were included to estimate fluorescence background and background variance.
Microarray analyses
Microarray experiment procedures were carried out following the manufacturer’s protocols. Briefly, 1 μg of total RNA was amplified by an Agilent Quick Amp Labeling Kit (Agilent Technologies, USA) and labeled with Cy3-CTP or Cy5-CTP (Agilent Technologies, USA). During the in vitro transcription process the treatment sample RNA was labeled by Cy5 and the control sample RNA was labeled by Cy3. 0.825 μg of Cy-labeled cRNA was fragmented to an average size of about 50–100 nucleotides by incubation with fragmentation buffer (Agilent Technologies, USA) at 60oC for 30 min. Correspondingly fragmented labeled cRNA is then pooled and hybridized to Agilent Whole Grape Genome 4x44K oligo microarray (Agilent Technologies, USA) at 65 °C for 17 h. After washing and drying by nitrogen gun blowing, microarrays were scanned with an Agilent microarray scanner (Agilent Technologies, USA) at 535 nm for Cy3 and 625 nm for Cy5. Scanned images were analyzed by Feature Extraction software 10.5 (Agilent Technologies, USA) to quantify signal and background intensity for each feature, and the data were normalized by rank-consistency-filtering LOWESS method. Finally, the GenSpring (Agilent Technologies, USA) software was used to identify significant differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The raw data is available at the Gene Expression Omnibus (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/info/linking.html) under the accession GSE86163.
Differentially expressed gene annotation and functional categorization
A cutoff value of 2-fold change (i.e. the absolute value of log2 ≥ 1) was adopted to identify genes that were differentially expressed and considered as potential candidate genes involved in the response to treatments. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis for gene information annotation and functional category distribution frequency was performed using the ErmineJ (version 3.0.2) software (max class size = 1500, min class size = 5) [98]. GO terms were assigned according to the gene ontology (www.go_daily-termdb.rdf.xml.gz) and the DBgrapego gene annotation analysis (http://www.genoscope.cns.fr/externe/Download/Projets/Projet_ML/data/8X/annotation/prot2go.filtered).
Quantification of gene expression by quantitative RT- PCR (qRT-PCR)
For qRT-PCR quantitation of gene transcripts upon PHC treatment, grapevine canes were pruned to the 8th dormant buds from the base and the 8th dormant buds were immediately treated with 1 % (w/v) HC. Total RNA was extracted at 0, 6, 12, 24, 48 h post-treatment. For each time point, three replicates of bud samples were harvested for RNA extraction. First strand cDNAs was synthesized from 2 μg of total RNA using High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (P/N4368814, ABI, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Based on the results of microarray analysis, twelve grape genes, including five, six and one genes coding for ROS-generating, ROS-scavenging and NO-scavenging enzymes, respectively, were selected for quantification of gene expression by qRT-PCR. The forward and reverse primers for candidate and reference genes (Additional file 4) were designed using the primer Express® Software v2.0 (ABI, USA). A set of primers was designed for the eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF4A, accession #CO168508) [64], which served as a reference gene. qRT-PCR was performed using ABI PRISM 7500 Sequence Detection System (ABI, USA). One μL of synthesized cDNA was diluted five folds with water and used as template. Each assay was replicated three times. The amplification of target genes was monitored every cycle by SYBR-Green fluorescence (ABI, USA). PCR amplification begun with an initial denaturing step at 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of amplification at 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 60s, 1 cycle of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 60 s, 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 15 s.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the supports of the Ph.D. Program of Agriculture Science, National Chiayi University.
Funding
This research was supported in part by the Council of Agriculture (TW) grant 105AS-9.8.3-FD-Z1, and the Ministry of Science and Technology (TW) grant 104-2221-E-415 -022.
Availability of data and materials
The raw data is available at the Gene Expression Omnibus (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/info/linking.html) under the accession GSE86163.
Authors’ contributions
YFY and SB planned and designed the study, and SB performed the experiments and analyzed the results and drafted the manuscript. CSC assisted in management of plant material and supervision of the study. HFC assisted in microarray analysis. MSBK assisted data analysis and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ABI5
Abscisic insensitive
- ADH
Alcohol dehydrogenase
- AOX
Alternative oxidase
- APX
Ascorbate peroxidase
- Carboxy-PTIO
2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide potassium salt
- CAT
Catalase
- DAF-2DA
4,5-diaminonaphthalene
- DCF-DA
2’,7́-dichlorofluorescin diacetate
- DEGs
Differentially expressed genes
- DHAR
Dehydroascorbate reductase
- DHE
Dihydroethidium
- ERF
Ethylene responsive factor
- FAA
Formalin-acetic acid-alcohol
- Fe-XO
Ferric-xylenol orange
- GO
Gene ontology
- GPX
Guaiacol peroxidase
- GR
Glutathione reductase
- GST
Glutathione S-transferase
- HCN
Hydrogen cyanamide
- KCN
Potassium cyanide
- LOXs
Lipoxygenases
- MDHAR
Monodehydroascorbate reductase
- NO
Nitric oxide
- NOS
Nitric oxide synthase-like
- NOXs
NADPH oxidases
- OCT
Optimal cutting temperature
- P
Pruning
- PBS
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCD
Program cell death
- PDC
Pyruvate decarboxylase
- PHCN
Pruning plus hydrogen cyanamide
- qRT-PCR
quantitative RT-PCR
- RBOHs
Respiratory burst oxidase homologues
- RNS
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- SNP
Sodium nitroprusside
- SODs
Superoxide dismutases
- SuSy
Sucrose synthase
- TFs
Transcription factors
- Trxh
Thioredoxin h
- VvAOX
Vitis vinifera alternative oxidase 2
- VvAPX3
Vitis vinifera ascorbate peroxidase 3
- VvCAT1
Vitis vinifera catalase isozyme 1-like
- VvDOX1
Vitis vinifera alpha-dioxygenase
- VvERF
Vitis vinifera ethylene response element transcription factor
- VvFSD
Vitis vinifera superoxide dismutase
- VvFSD3
Vitis vinifera superoxide dismutase 3
- VvGPX2
Vitis vinifera glutathione peroxidase 2
- VvHB2
Vitis vinifera hemoglobin-2
- VvHSF
Vitis vinifera heat stress transcription factor
- VvPOD12
Vitis vinifera peroxidase 12
- VvPOD72
Vitis vinifera peroxidase 72
- VvRBOHA
Vitis vinifera respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein A
- VvRBOHE
Vitis vinifera respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein E
- VvWRKY
Vitis vinifera WRKY transcription factor
Additional files
Changes in transcript abundance and clustering of significant differentially expressed genes. Changes in transcript abundance (M/A plot) from the top to bottom, relative mRNA abundance in P (A), HC (B) and PHC (C). The Y- and X-axis show M (log2 (Normalized Expressions Ratio) (by rank consistency-filtering LOWESS method) and A (log2 (gBGSubSignal x rBGSubSignal)1/2, representing the average signal of the two channels for each gene) obtained from microarray data, respectively. (DOCX 109 kb)
239 up- and 106 down-regulated genes that were common regulated by P, HC and PHC treatments. (XLSX 34 kb)
Gene expression levels in ROS-related GO categories. The expression levels of significantly up-/down-regulated genes in the categories of ROS-generating, ROS-scavenging, ROS-specific transcription factors and NO-scavenging in grapevine buds treated with P, HC and PHC for 24 h, as revealed by ErmineJ analysis. (XLSX 20 kb)
List of primers used for qRT-PCR. (DOCX 16 kb)
Contributor Information
Boonyawat Sudawan, Email: s0961473@mail.ncyu.edu.tw.
Chih-Sheng Chang, Email: changcs@mail.coa.gov.tw.
Hsiu-fung Chao, Email: hfchao@mail.tndais.gov.tw.
Maurice S. B. Ku, Email: mku@mail.ncyu.edu.tw
Yung-fu Yen, Email: yfyen@mail.ncyu.edu.tw.
References
- 1.Dokoozlian N, Williams L, Neja R. Chilling exposure and hydrogen cyanamide interact in breaking dormancy of grape buds. HortSci. 1995;30:1244–1247. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dokoozlian N. Chilling temperature and duration interact on the budbreak of ‘Perlette’ grapevine cuttings. HortSci. 1999;34:1–3. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lang G. Dormancy: a new universal terminology. HortSci. 1987;22:817–820. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Or E. Grape Bud dormancy release − the molecular aspect. In: Roubelakis-Angelakis KA, editor. Grapevine molecular physiology & biotechnology. Dordrecht: Springer; 2009. pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zheng C, Halaly T, Acheampong AK, Takebayashi Y, Jikumaru Y, Kamiya Y, Or E. Abscisic acid (ABA) regulates grape bud dormancy, and dormancy release stimuli may act through modification of ABA metabolism. J Exp Bot. 2015;66(5):1527–1542. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Oracz K, El-Maarouf-Bouteau H, Bogatek R, Corbineau F, Bailly C. Release of sunflower seed dormancy by cyanide: cross-talk with ethylene signalling pathway. J Exp Bot. 2008;59(8):2241–2251. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ophir R, Pang X, Halaly T, Venkateswari J, Lavee S, Galbraith D, Or E. Gene-expression profiling of grape bud response to two alternative dormancy-release stimuli expose possible links between impaired mitochondrial activity, hypoxia, ethylene-ABA interplay and cell enlargement. Plant Mol Biol. 2009;71(4-5):403–423. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9531-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shulman Y, Nir G, Fanberstein L, Lavee S. The effect of cyanamide on the release from dormancy of grapevine buds. Sci Hort. 1983;19:97–104. doi: 10.1016/0304-4238(83)90049-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Or E, Vilozny I, Eyal Y, Ogrodovitch A. The transduction of the signal for grape bud dormancy breaking induced by hydrogen cyanamide may involve the SNF-like protein kinase GDBRPK. Plant Mol Biol. 2000;43(4):483–494. doi: 10.1023/A:1006450516982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Linsley-Noakes G. Improving flowering of kiwifruit in climatically marginal areas using hydrogen cyanamide. Sci Hort. 1989;38:247–259. doi: 10.1016/0304-4238(89)90072-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Petri J, Stuker H. Effect of mineral oil and hydrogen cyanamide concentrations on apple dormancy, cv. Gala. Acta Hortic. 1996;395:161–168. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jackson J, Bepete M. The effect of hydrogen cyanamide (Dormex) on flowering and cropping of different apple cultivars under tropical conditions of sub-optimal winter chilling. Sci Hort. 1995;60:293–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4238(94)00707-M. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Amberger A. Cyanamide in plant metabolism. Int J Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013;5(1):1–10. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sanchez-Perez R, Del Cueto J, Dicenta F, Martinez-Gomez P. Recent advancements to study flowering time in almond and other Prunus species. Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:334. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Oracz K, El-Maarouf-Bouteau H, Kranner I, Bogatek R, Corbineau F, Bailly C. The mechanisms involved in seed dormancy alleviation by hydrogen cyanide unravel the role of reactive oxygen species as key factors of cellular signaling during germination. Plant Physiol. 2009;150(1):494–505. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.138107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bogatek R, Gawronska H, Oracz K. Involvement of oxidative stress and ABA in CN-mediated elimination of embryonic dormancy in apple. In: Nicolas G, Bradford KJ, Come D, Pritchard HW, editors. The biology of seeds: recent research advances. Oxon: CABI Publishing; 2003. pp. 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Oracz K, El-Maarouf Bouteau H, Farrant JM, Cooper K, Belghazi M, Job C, Job D, Corbineau F, Bailly C. ROS production and protein oxidation as a novel mechanism for seed dormancy alleviation. Plant J. 2007;50(3):452–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Perez F, Vergara R, Rubio S. H2O2 is involved in the dormancy-breaking effect of hydrogen cyanamide in grapevine buds. Plant Growth Regul. 2008;55:149–155. doi: 10.1007/s10725-008-9269-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vergara R, Parada F, Rubio S, Perez FJ. Hypoxia induces H2O2 production and activates antioxidant defence system in grapevine buds through mediation of H2O2 and ethylene. J Exp Bot. 2012;63(11):4123–4131. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bykova NV, Hu J, Ma Z, Igamberdiev AU. The role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in bioenergetics, metabolism, and signaling during seed germination. In: Gupta JK, Igamberdiev UA, editors. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species signaling and communication in plants. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2015. pp. 177–195. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Perez FJ, Vergara R, Or E. On the mechanism of dormancy release in grapevine buds: a comparative study between hydrogen cyanamide and sodium azide. Plant Growth Regul. 2009;59(2):145–152. doi: 10.1007/s10725-009-9397-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liszkay A, van der Zalm E, Schopfer P. Production of reactive oxygen intermediates (O(2)(.-), H(2)O(2), and (.)OH) by maize roots and their role in wall loosening and elongation growth. Plant Physiol. 2004;136(2):3114–3123. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.044784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Potikha TS, Collins CC, Johnson DI, Delmer DP, Levine A. The involvement of hydrogen peroxide in the differentiation of secondary walls in cotton fibers. Plant Physiol. 1999;119(3):849–858. doi: 10.1104/pp.119.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mittler R. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2002;7(9):405–410. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Suzuki N, Miller G, Morales J, Shulaev V, Torres MA, Mittler R. Respiratory burst oxidases: the engines of ROS signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2011;14(6):691–699. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2011.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cona A, Rea G, Angelini R, Federico R, Tavladoraki P. Functions of amine oxidases in plant development and defence. Trends Plant Sci. 2006;11(2):80–88. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2005.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Navrot N, Rouhier N, Gelhaye E, Jacquot J. Reactive oxygen species generation and antioxidant systems in plant mitochondria. Physiol Plantarum. 2007;129:185–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00777.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Karuppanapandian T, Moon J-C, Kim C, Manoharan K, Kim W. Reactive oxygen species in plants: their generation, signal transduction, and scavenging mechanisms. Aust J Crop Sci. 2011;5:709–725. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Moller IM. PLANT MITOCHONDRIA AND OXIDATIVE STRESS: electron transport, NADPH turnover, and metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 2001;52:561–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Noctor G, De Paepe R, Foyer CH. Mitochondrial redox biology and homeostasis in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2007;12(3):125–134. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R. Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ. 2010;33(4):453–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Einset J, Nielsen E, Connolly E, Bones A, Sparstad T, Winge P, Zhu J. Membrane-trafficking RabA4c involved in the effect of glycine betaine on recovery from chilling stress in Arabidopsis. Physiol Plantarum. 2007;130:511–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2007.00920.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Marino D, Dunand C, Puppo A, Pauly N. A burst of plant NADPH oxidases. Trends Plant Sci. 2012;17(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2011.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Foreman J, Demidchik V, Bothwell JH, Mylona P, Miedema H, Torres MA, Linstead P, Costa S, Brownlee C, Jones JD, et al. Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase regulate plant cell growth. Nature. 2003;422(6930):442–446. doi: 10.1038/nature01485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cho KJ, Seo JM, Kim JH. Bioactive lipoxygenase metabolites stimulation of NADPH oxidases and reactive oxygen species. Mol Cells. 2011;32(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/s10059-011-1021-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Porta H, Rocha-Sosa M. Plant lipoxygenases. Physiological and molecular features. Plant Physiol. 2002;130(1):15–21. doi: 10.1104/pp.010787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Brash AR. Lipoxygenases: occurrence, functions, catalysis, and acquisition of substrate. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(34):23679–23682. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.34.23679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Porta H, Rueda-Benitez P, Campos F, Colmenero-Flores JM, Colorado JM, Carmona MJ, Covarrubias AA, Rocha-Sosa M. Analysis of lipoxygenase mRNA accumulation in the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) during development and under stress conditions. Plant Cell Physiol. 1999;40(8):850–858. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a029614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Melan MA, Dong X, Endara ME, Davis KR, Ausubel FM, Peterman TK. An Arabidopsis thaliana lipoxygenase gene can be induced by pathogens, abscisic acid, and methyl jasmonate. Plant Physiol. 1993;101(2):441–450. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Karkonen A, Kuchitsu K. Reactive oxygen species in cell wall metabolism and development in plants. Phytochemistry. 2015;112:22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jiang F, Zhang Y, Dusting GJ. NADPH oxidase-mediated redox signaling: roles in cellular stress response, stress tolerance, and tissue repair. Pharmacol Rev. 2011;63(1):218–242. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.002980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Halliwell B. Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J Neurochem. 2006;97(6):1634–1658. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Moller IM, Jensen PE, Hansson A. Oxidative modifications to cellular components in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2007;58:459–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Balazadeh S, Jaspert N, Arif M, Mueller-Roeber B, Maurino VG. Expression of ROS-responsive genes and transcription factors after metabolic formation of H(2)O(2) in chloroplasts. Front Plant Sci. 2012;3:234. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F. Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2004;9(10):490–498. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hancock JT, Neill SJ, Wilson ID. Nitric oxide and ABA in the control of plant function. Plant Sci. 2011;181(5):555–559. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.del Rio LA, Corpas FJ, Barroso JB. Nitric oxide and nitric oxide synthase activity in plants. Phytochemistry. 2004;65(7):783–792. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Alscher RG, Erturk N, Heath LS. Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants. J Exp Bot. 2002;53(372):1331–1341. doi: 10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Das K, Roychoudhury A: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front Environ Sci 2014;2(53):1–13.
- 50.Or E, Vilozny I, Fennell A, Eyal Y, Ogrodovitch A. Dormancy in grape buds: isolation and characterization of catalase cDNA and analysis of its expression following chemical induction of bud dormancy release. Plant Sci. 2002;162:121–130. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00542-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Keilin T, Pang X, Venkateswari J, Halaly T, Crane O, Keren A, Ogrodovitch A, Ophir R, Volpin H, Galbraith D. Digital expression profiling of a grape-bud EST collection leads to new insight into molecular events during grape-bud dormancy release. Plant Sci. 2007;173:446–457. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2007.07.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Halaly T, Pang X, Batikoff T, Crane O, Keren A, Venkateswari J, Ogrodovitch A, Sadka A, Lavee S, Or E. Similar mechanisms might be triggered by alternative external stimuli that induce dormancy release in grape buds. Planta. 2008;228(1):79–88. doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0720-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pacey-Miller T, Scott K, Ablett E, Tingey S, Ching A, Henry R. Genes associated with the end of dormancy in grapes. Funct Integr Genomics. 2003;3(4):144–152. doi: 10.1007/s10142-003-0094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Dordas C, Rivoal J, Hill RD. Plant haemoglobins, nitric oxide and hypoxic stress. Ann Bot 2003. 91 Spec No:173-178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 55.Igamberdiev AU, Seregelyes C, Manac’h N, Hill RD. NADH-dependent metabolism of nitric oxide in alfalfa root cultures expressing barley hemoglobin. Planta. 2004;219(1):95–102. doi: 10.1007/s00425-003-1192-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wittenberg JB, Bolognesi M, Wittenberg BA, Guertin M. Truncated hemoglobins: a new family of hemoglobins widely distributed in bacteria, unicellular eukaryotes, and plants. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(2):871–874. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100058200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Perazzolli M, Dominici P, Romero-Puertas MC, Zago E, Zeier J, Sonoda M, Lamb C, Delledonne M. Arabidopsis nonsymbiotic hemoglobin AHb1 modulates nitric oxide bioactivity. Plant Cell. 2004;16(10):2785–2794. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.025379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Clifton R, Millar AH, Whelan J. Alternative oxidases in Arabidopsis: a comparative analysis of differential expression in the gene family provides new insights into function of non-phosphorylating bypasses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1757(7):730–741. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Brookes PS, Levonen AL, Shiva S, Sarti P, Darley-Usmar VM. Mitochondria: regulators of signal transduction by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;33(6):755–764. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00901-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Clifton R, Lister R, Parker KL, Sappl PG, Elhafez D, Millar AH, Day DA, Whelan J. Stress-induced co-expression of alternative respiratory chain components in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol. 2005;58(2):193–212. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-5514-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Huang X, von Rad U, Durner J. Nitric oxide induces transcriptional activation of the nitric oxide-tolerant alternative oxidase in Arabidopsis suspension cells. Planta. 2002;215(6):914–923. doi: 10.1007/s00425-002-0828-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gay C, Collins J, Gebicki JM. Hydroperoxide assay with the ferric-xylenol orange complex. Anal Biochem. 1999;273(2):149–155. doi: 10.1006/abio.1999.4208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cirami R, Furkaliev D. Effect of time of pruning and hydrogen cyanamide on growth and development of glasshouse-grown cardinal grapes. Aust J Exp Agric. 1991;31:273–278. doi: 10.1071/EA9910273. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mathiason K, He D, Grimplet J, Venkateswari J, Galbraith DW, Or E, Fennell A. Transcript profiling in Vitis riparia during chilling requirement fulfillment reveals coordination of gene expression patterns with optimized bud break. Funct Integr Genomics. 2009;9(1):81–96. doi: 10.1007/s10142-008-0090-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Perez F, Burgos B. Alterations in the pattern of peroxidase isoenzymes and transient increases in its activity and in H2O2 levels take place during the dormancy cycle of grapevine buds: the effect of hydrogen cyanamide. Plant Growth Regul. 2004;43:213–220. doi: 10.1023/B:GROW.0000046003.33194.ac. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Guo C, Guo R, Xu X, Gao M, Li X, Song J, Zheng Y, Wang X. Evolution and expression analysis of the grape (Vitis vinifera L.) WRKY gene family. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(6):1513–1528. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Licausi F, Giorgi FM, Zenoni S, Osti F, Pezzotti M, Perata P. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in Vitis vinifera. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:719. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Heim MA, Jakoby M, Werber M, Martin C, Weisshaar B, Bailey PC. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in plants: a genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity. Mol Biol Evol. 2003;20(5):735–747. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Borrill P. The NAM-B1 transcription factor and the control of grain composition in wheat. UK: University of East Anglia; 2014.
- 70.Hagenblad J, Asplund L, Balfourier F, Ravel C, Leino MW. Strong presence of the high grain protein content allele of NAM-B1 in Fennoscandian wheat. Theor Appl Genet. 2012;125(8):1677–1686. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-1943-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kende H, van der Knaap E, Cho HT. Deepwater rice: a model plant to study stem elongation. Plant Physiol. 1998;118(4):1105–1110. doi: 10.1104/pp.118.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Peeters AJ, Cox MC, Benschop JJ, Vreeburg RA, Bou J, Voesenek LA. Submergence research using Rumex palustris as a model; looking back and going forward. J Exp Bot. 2002;53(368):391–398. doi: 10.1093/jexbot/53.368.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Group M. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci. 2002;7(7):301–308. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02302-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Passardi F, Penel C, Dunand C. Performing the paradoxical: how plant peroxidases modify the cell wall. Trends Plant Sci. 2004;9(11):534–540. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Riviere MP, Marais A, Ponchet M, Willats W, Galiana E. Silencing of acidic pathogenesis-related PR-1 genes increases extracellular beta-(1- > 3)-glucanase activity at the onset of tobacco defence reactions. J Exp Bot. 2008;59(6):1225–1239. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kitajima S, Sato F. Plant pathogenesis-related proteins: molecular mechanisms of gene expression and protein function. J Biochem. 1999;125(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Cosgrove DJ. Loosening of plant cell walls by expansins. Nature. 2000;407(6802):321–326. doi: 10.1038/35030000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Yoshiba Y, Aoki C, Iuchi S, Nanjo T, Seki M, Sekiguchi F, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K. Characterization of four extensin genes in Arabidopsis thaliana by differential gene expression under stress and non-stress conditions. DNA Res. 2001;8(3):115–122. doi: 10.1093/dnares/8.3.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Merkouropoulos G, Barnett DC, Shirsat AH. The Arabidopsis extensin gene is developmentally regulated, is induced by wounding, methyl jasmonate, abscisic and salicylic acid, and codes for a protein with unusual motifs. Planta. 1999;208(2):212–219. doi: 10.1007/s004250050552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Wilson L, Fry J. Extensin-a major cell wall glycoprotein. Plant Cell Environ. 1986;9:239–260. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Parcy F, Valon C, Kohara A, Misera S, Giraudat J. The ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE3, FUSCA3, and LEAFY COTYLEDON1 loci act in concert to control multiple aspects of Arabidopsis seed development. Plant Cell. 1997;9(8):1265–1277. doi: 10.1105/tpc.9.8.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wang Y, Li L, Ye T, Lu Y, Chen X, Wu Y. The inhibitory effect of ABA on floral transition is mediated by ABI5 in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot. 2013;64(2):675–684. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Di Cristina M, Sessa G, Dolan L, Linstead P, Baima S, Ruberti I, Morelli G. The Arabidopsis Athb-10 (GLABRA2) is an HD-Zip protein required for regulation of root hair development. Plant J. 1996;10(3):393–402. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1996.10030393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Baima S, Possenti M, Matteucci A, Wisman E, Altamura MM, Ruberti I, Morelli G. The arabidopsis ATHB-8 HD-zip protein acts as a differentiation-promoting transcription factor of the vascular meristems. Plant Physiol. 2001;126(2):643–655. doi: 10.1104/pp.126.2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Koyama K, Numata M, Nakajima I, Goto-Yamamoto N, Matsumura H, Tanaka N. Functional characterization of a new grapevine MYB transcription factor and regulation of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in grapes. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(15):4433–4449. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Reyes JC, Muro-Pastor MI, Florencio FJ. The GATA family of transcription factors in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2004;134(4):1718–1732. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.037788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Schroder H, Langer T, Hartl FU, Bukau B. DnaK, DnaJ and GrpE form a cellular chaperone machinery capable of repairing heat-induced protein damage. EMBO J. 1993;12(11):4137–4144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Langer T, Lu C, Echols H, Flanagan J, Hayer MK, Hartl FU. Successive action of DnaK, DnaJ and GroEL along the pathway of chaperone-mediated protein folding. Nature. 1992;356(6371):683–689. doi: 10.1038/356683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Stone SL, Hauksdottir H, Troy A, Herschleb J, Kraft E, Callis J. Functional analysis of the RING-type ubiquitin ligase family of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005;137(1):13–30. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.052423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Shi WM, Muramoto Y, Ueda A, Takabe T. Cloning of peroxisomal ascorbate peroxidase gene from barley and enhanced thermotolerance by overexpressing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 2001;273(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00566-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Fuchigami L, Nee C-C. Degree growth stage model and rest-breaking mechanisms in temperate woody perennials. HortSci. 1987;22:836–845. [Google Scholar]
- 92.De Leon IP, Sanz A, Hamberg M, Castresana C. Involvement of the Arabidopsis alpha-DOX1 fatty acid dioxygenase in protection against oxidative stress and cell death. Plant J. 2002;29(1):61–62. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Gray GR, Maxwell DP, Villarimo AR, McIntosh L. Mitochondria/nuclear signaling of alternative oxidase gene expression occurs through distinct pathways involving organic acids and reactive oxygen species. Plant Cell Rep. 2004;23(7):497–503. doi: 10.1007/s00299-004-0848-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Voegele A, Graeber K, Oracz K, Tarkowska D, Jacquemoud D, Tureckova V, Urbanova T, Strnad M, Leubner-Metzger G. Embryo growth, testa permeability, and endosperm weakening are major targets for the environmentally regulated inhibition of Lepidium sativum seed germination by myrigalone A. J Exp Bot. 2012;63(14):5337–5350. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Tarpey MM, Wink DA, Grisham MB. Methods for detection of reactive metabolites of oxygen and nitrogen: in vitro and in vivo considerations. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004;286(3):R431–444. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00361.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Yamamoto Y, Kobayashi Y, Devi SR, Rikiishi S, Matsumoto H. Aluminum toxicity is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and the production of reactive oxygen species in plant cells. Plant Physiol. 2002;128(1):63–72. doi: 10.1104/pp.010417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Chang S, Puryear J, Cairney J. A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine trees. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 1993;11:113–116. doi: 10.1007/BF02670468. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Choi D, Lee Y, Cho HT, Kende H. Regulation of expansin gene expression affects growth and development in transgenic rice plants. Plant Cell. 2003;15(6):1386–1398. doi: 10.1105/tpc.011965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Jiang Y, Duan Y, Yin J, Ye S, Zhu J, Zhang F, Lu W, Fan D, Luo K. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the Populus WRKY transcription factor family and analysis of their expression in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(22):6629–6644. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Elmayan T, Simon-Plas F. Regulation of plant NADPH oxidase. Plant Signal Behav. 2007;2(6):505–507. doi: 10.4161/psb.2.6.4609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Nakashima K, Takasaki H, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1819(2):97–103. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Tsai AY, Gazzarrini S. Overlapping and distinct roles of AKIN10 and FUSCA3 in ABA and sugar signaling during seed germination. Plant Signal Behav. 2012;7(10):1238–1242. doi: 10.4161/psb.21549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Kobayashi S, Ishimaru M, Hiraoka K, Honda C. Myb-related genes of the Kyoho grape (Vitis labruscana) regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis. Planta. 2002;215(6):924–933. doi: 10.1007/s00425-002-0830-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Carabelli M, Sessa G, Baima S, Morelli G, Ruberti I. The Arabidopsis Athb-2 and -4 genes are strongly induced by far-red-rich light. Plant J. 1993;4(3):469–479. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1993.04030469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Mazzucotelli E, Belloni S, Marone D, De Leonardis A, Guerra D, Di Fonzo N, Cattivelli L, Mastrangelo A. The e3 ubiquitin ligase gene family in plants: regulation by degradation. Curr Genomics. 2006;7(8):509–522. doi: 10.2174/138920206779315728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data is available at the Gene Expression Omnibus (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/info/linking.html) under the accession GSE86163.


