Abstract
Ultrathin metal layers can be highly active carbon dioxide electroreduction catalysts, but may also be prone to oxidation. Here we construct a model of graphene confined ultrathin layers of highly reactive metals, taking the synthetic highly reactive tin quantum sheets confined in graphene as an example. The higher electrochemical active area ensures 9 times larger carbon dioxide adsorption capacity relative to bulk tin, while the highly-conductive graphene favours rate-determining electron transfer from carbon dioxide to its radical anion. The lowered tin–tin coordination numbers, revealed by X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy, enable tin quantum sheets confined in graphene to efficiently stabilize the carbon dioxide radical anion, verified by 0.13 volts lowered potential of hydroxyl ion adsorption compared with bulk tin. Hence, the tin quantum sheets confined in graphene show enhanced electrocatalytic activity and stability. This work may provide a promising lead for designing efficient and robust catalysts for electrolytic fuel synthesis.
 Ultrathin metal layers can be highly active carbon dioxide electroreduction catalysts but may also be prone to oxidation. Here, the authors report the fabrication of reactive tin quantum nanosheets confined in graphene and demonstrate their enhanced electrocatalytic activity and stability.
Ultrathin metal layers can be highly active carbon dioxide electroreduction catalysts but may also be prone to oxidation. Here, the authors report the fabrication of reactive tin quantum nanosheets confined in graphene and demonstrate their enhanced electrocatalytic activity and stability.
The excessive utilization of fossil fuels provoked the increasing energy crisis and the worsening global climate, which triggered tremendous attention at CO2 capture, storage and utilization1,2,3. To address these issues, electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 into hydrocarbon fuels is considered as a promising strategy1,2,3, among which metal electrodes, benefiting from high electronic conductivity, show considerable catalytic activities toward CO2 electroreduction4,5,6. Nevertheless, the practical applications of these metal electrodes are greatly impeded by the very low energetic efficiencies, which could be primarily ascribed to their extremely low amount of catalytically active sites7. Very recently, our study demonstrates that the ultrathin layers of metallic Co exhibit roughly 26 times higher CO2 reduction activity relative to bulk Co (ref. 2), profiting from the former's ultralarge fraction of metal atoms exposed on the surface. In spite of such a significant advantage, not all metals could be easily fabricated into ultrathin layers for substantially promoting CO2 reduction performances. For some metals with higher chemical reactivity, while exposing ultrahigh amount of surface atoms, they tend to be very unstable at ambient conditions and will be oxidized in a non-controlled manner1,5,6,8, which would lead to the loss of electronic conductivity and consequently cause a rapid decay in the cyclability. As such, developing a new strategy for stabilizing the ultrathin layers of highly reactive metals is highly imperative for both fundamental research and practical application in CO2 electroreduction.
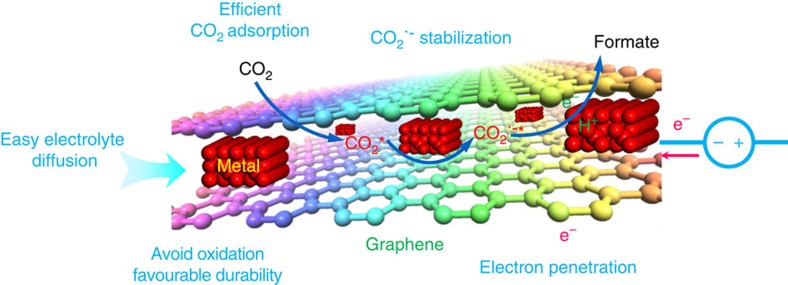
Motivated by the above consideration, we construct a material model of ultrathin metal layers confined in graphene, in which the protection of graphene could avoid the oxidation of the highly reactive metals at ambient atmosphere (Fig. 1). The metal ultrathin layers could not only serve as a ‘spacer' to favour electrolyte diffusion into the matrix of graphene9, but also afford abundant surface atoms to act as the active sites for efficient CO2 adsorption10,11, hence providing the prerequisite to involve the following reduction reactions. That is to say, in our designed sandwich-like structure, there is enough space between the graphene layers and hence the electrolyte can freely diffuse into/out the deep matrix of graphene. In this case, CO2 could diffuse into the graphene layers through dissolving in the electrolyte and simultaneously the products could also be transported out of the graphene layers by virtue of the freely flowing electrolyte. Moreover, the highly-conductive graphene endures fast electron penetration to the metal ultrathin layers12, which hence favours the rate-determining electron transfer from CO2 to CO2− intermediate. In addition, as revealed by X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy (XAFS) in our previously systematic studies13,14, the exposed surface metal atoms would possess lowered coordination number compared with interior atoms, in which the low-coordinated metal atoms with many dangling bonds could help to stabilize the CO2− intermediate, hence lowering the overall activation energy barrier and remarkably improving the catalytic activity. Furthermore, the intimate contact between ultrathin metal layers and graphene in a sandwich-like fashion could ensure excellent long-term stability.
Figure 1. Scheme.
Schematic illustration depicts the several advantages of ultrathin metal layers confined in graphene for CO2 electroreduction into hydrocarbon fuels.
Results
Characterizations of Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene
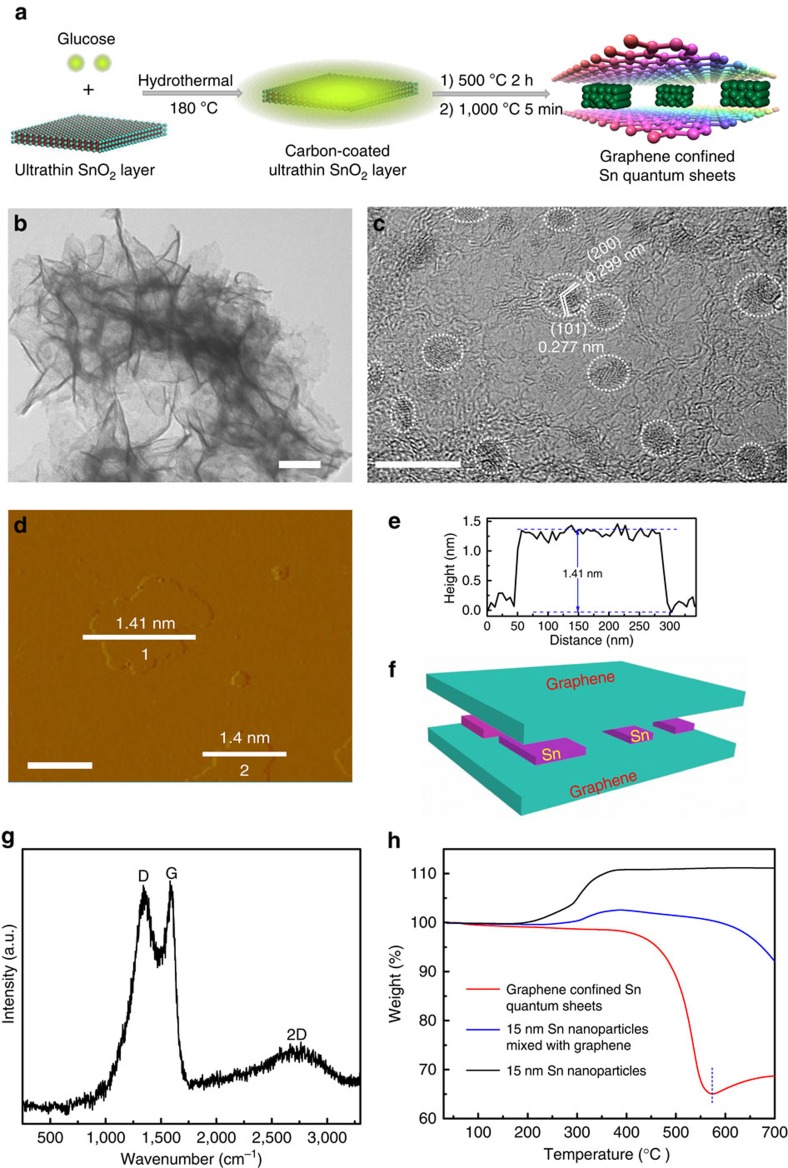
Of note, the low cost and environmentally benign Sn is not only one of the most active metals, but also possesses selective reduction of CO2 to formate5,8,15, which enables it to be a highly reactive metal candidate for investigating the corresponding CO2 reduction performances. Therefore, it is highly warranted for controllably synthesizing Sn ultrathin layers in the confined space of graphene. Herein, metallic Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene were first successfully synthesized through a spatially confined reduction strategy (Fig. 2a). The as-prepared ultrathin SnO2 layers16 were initially coated with amorphous carbon through a hydrothermal method. Hence, after subsequent temperature-programmed calcination for the carbon-coated ultrathin SnO2 layers, the amorphous carbon turned into graphene, while the ultrathin SnO2 layers simultaneously reduced into monodispersed Sn quantum sheets in the confined space of graphene, benefiting from the short calcination time and rapid subsequent cooling in an inert atmosphere of Ar gas.
Figure 2. Formation process and characterizations of the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene.
(a) Scheme illustration for the formation of Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene, (b) TEM image, (c) HRTEM image, (d–f) AFM image, the corresponding height profile and scheme illustration and (g) micro-Raman spectrum of the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene. (h) TG analysis of Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene. The scale bars in (b–d) are 100, 10 and 200 nm, respectively. The inset circles in (c) denote the presence of Sn quantum sheets.
With regard to the precise characterization of ultrathin Sn layers, it encounters many great difficulties since the lack of long-range order in the third dimensionality causes the typical X-ray diffraction technique unable to identify the spatial atomic distribution, while the XPS spectrum is only a surface-sensitive spectroscopic technique7. In this regard, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) image and synchrotron radiation XAFS spectroscopy were utilized to characterize the phase and atomic structure of the synthetic Sn quantum sheets. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image in Fig. 2b shows the extremely thin sheet-like morphology of graphene, in which the Raman bands at around 1,352, 1,593 and 2,700 cm−1 demonstrated the formation of graphene (Fig. 2g)17. In addition, HRTEM image in Fig. 2c also shows that abundant two-dimensional (2D) sheets nearly monodispersed on the graphene, while the interplanar spacing of 0.299 and 0.277 nm as well as the corresponding dihedral angle of 61.4° could index them to be tetragonal Sn. It should be noted that the Sn quantum sheets were encapsulated in graphene rather than exposed on the outer surface (Fig. 2f), which could be further implied by the thermogravimetric (TG) result in Fig. 2h. The TG analysis in air showed a rapid weight loss between 390 and 570 °C, corresponding to the decomposition of gaphene, and a weight increase at above 570 °C, owing to the oxidation of metallic Sn, which indicated that the protection of graphene enabled the Sn quantum sheets to be stable in air up to 570 °C. Contrastingly, both the synthetic 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and their mixture with graphene showed a weight increase at above ca. 200 °C (see Methods for details), indicating that the metallic Sn is easily oxidized without the protection of graphene interlayer. As a result, the presence of graphene interlayer not only avoided the oxidation of metallic Sn, but also prevented the aggregation of quantum sized Sn sheets. Moreover, as revealed by the atomic force microscopic image and the corresponding height profiles in Fig. 2d–e, the sandwich-like structure possessed an average thickness of ca. 1.4 nm, which indicated that the thickness of either Sn or graphene layer was much less than 1.4 nm. Accordingly, the above results demonstrated the formation of monodisperse Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene.
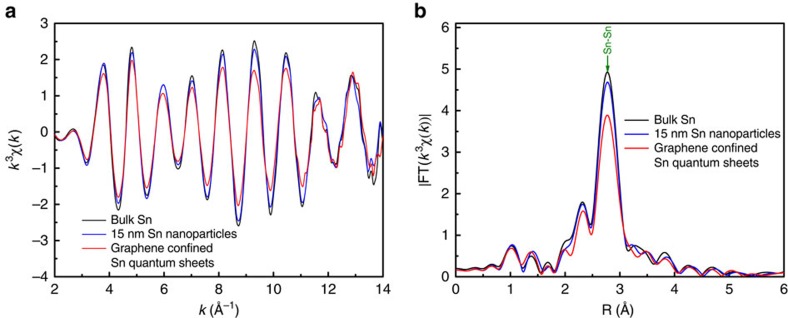
To further identify the phase and unravel the local atomic arrangements of the synthetic Sn quantum sheets, synchrotron radiation XAFS measurements were performed. As shown in Fig. 3a,b, the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene exhibited a strong FT peak of Sn–Sn metallic bonding at ca. 2.77 Å, while they did not possess the peaks for Sn4+–O at ca. 1.45 Å and Sn–O–Sn at above 3 Å, which undoubtedly confirmed that the Sn quantum sheets were well protected from oxidation through spatially confining in the graphene. In addition, their Sn K-edges k3χ(k) oscillation curves in Fig. 3a show obvious differences relative to the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk counterpart (Supplementary Figs 1–3), which suggested their distinct local atomic arrangement further verified by their R-space curves in Fig. 3b. According to the high-quality extended XAFS spectra, least-squares fittings were further conducted and the obtained quantitative results are shown in Table 1. For the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene, the coordination numbers of Sn–Sn reduced from 2 and 4 to 1.4 and 2.7, while their disorder degrees increased significantly as compared with the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk counterpart. This suggested that the reduced size resulted in many dangling bonds as well as a noticeable distortion on the surface of Sn quantum sheets, which would contribute to their high catalytic activity along with excellent stability7,13,14. Altogether, both the HRTEM and XAFS results disclosed that the synthetic Sn quantum sheets were free of oxidation under the effective umbrella of graphene.
Figure 3. Synchrotron radiation XAFS measurements.
(a) Sn K-edge extended XAFS oscillation function k3χ(k), (b) the corresponding Fourier transforms FT(k3χ(k)) for the graphene confined Sn quantum sheets, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn, respectively.
Table 1. EXAFS curve-fitting results.
| Sample | Path | N | R (Å) | σ2 (10−3Å2) | ΔE0 (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk Sn | Sn–Sn1 | 4.0 | 3.02 | 9.1 | 3.6 |
| Sn–Sn2 | 2.0 | 3.18 | 10.5 | 3.6 | |
| 15 nm Sn nanoparticles | Sn–Sn1 | 4.0 | 3.02 | 9.7 | 4.0 |
| Sn–Sn2 | 2.0 | 3.18 | 12.0 | 4.0 | |
| Graphene confined Sn quantum sheets | Sn–Sn1(surface) | 2.7 | 3.01 | 10.8 | 4.3 |
| Sn–Sn1(interior) | 4.0 | 3.02 | 9.3 | 4.3 | |
| Sn–Sn2(surface) | 1.4 | 3.17 | 14.0 | 4.3 | |
| Sn–Sn2(interior) | 2.0 | 3.18 | 10.7 | 4.3 |
EXAFS, extended X-ray absorption fine structure.
Structural parameters around Sn atoms extracted from EXAFS curve-fitting for the graphene confined Sn quantum sheets, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn, respectively.
Electroreduction of CO2 into hydrocarbon fuels
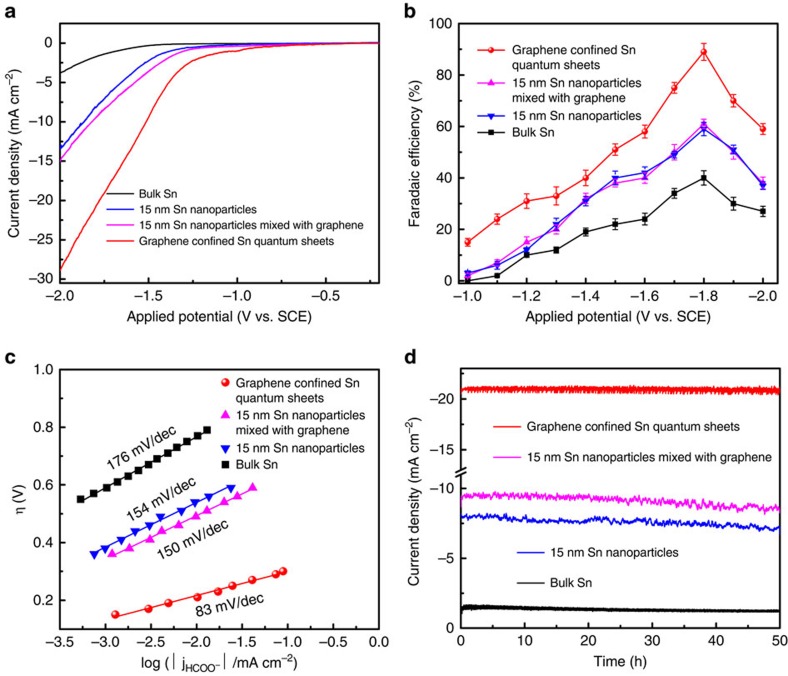
Benefiting from the lowered coordination number, obvious structure distortion as well as surface conductive graphene, the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene were expected to give substantially promoted CO2 electroreduction performances in comparison with the Sn nanoparticles as well as the bulk counterpart. To verify the higher activity of the unique sandwich-like 2D structure, CO2 reduction activities for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn were determined in CO2-saturated 0.1 M NaHCO3 solution. As revealed by linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) in Fig. 4a, the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene exhibited the highest catalytic activity among the above four samples. For instance, the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene displayed a current density of 21.1 mA cm−2 at −1.8 V versus SCE, which was roughly 2, 2.5 and 13 times larger than that of the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn, respectively. In addition, the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene exhibited an onset potential of −0.85 V versus SCE, which was much positive relative to other three samples (Fig. 4a). This strongly demonstrated the simple addition of graphene could only slightly mend the catalytic activity, while the formation of unique sandwich construction can help to remarkably promote the activity.
Figure 4. CO2 electroreduction performances.
(a) Linear sweep voltammetric curves in the CO2-saturated 0.1 M NaHCO3 aqueous solution, (b) Faradaic efficiencies for formate at each applied potentials for 4 h, (c) Tafel plots for producing formate, (d) Chrono-Amperometry results at the potentials of −1.8 V versus SCE for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn. The error bars in b represent the standard deviations of five independent measurements of the same sample.
To analyse the electroreduction products, stepped-potential electrolyses at each given potential for 4 h were performed to periodically quantify the liquid products by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and the gas products by an Agilent Technologies 7890B gas chromatograph2. As revealed by the faradaic efficiency for formate production in Fig. 4b, one can clearly observe that the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene behaved obviously higher faradaic efficiency relative to other three samples in the whole applied potentials. At the potential of −1.8 V versus SCE, the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene attained a maximum faradaic efficiency of 89%, which was roughly 1.45, 1.5 and 2 times higher than that of the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn, denoting the superior activity of their unique structure. In addition, the faradaic efficiency for gas products in Supplementary Fig. 4 reveal that the main gas products are the H2, while CO accounted for the remaining products. Of note, the above four samples achieved the maximum formate faradaic efficiency at the similar potentials, which could be ascribed to the mass transport limitation of CO2 as well as the competitive H2 evolution reaction8,18. To obtain further insights into these electrocatalysts, their Tafel plots were investigated and presented in Fig. 4c. The resulting Tafel slope of the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene was 83 mV dec−1, much smaller than that of the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn, respectively. The smaller Tafel slope of the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene is very advantageous for practical applications, since it will lead to a much faster increment of CO2 reduction rate with increasing overpotential10. Besides the activity of CO2 electroreduction, electrochemical stability is another significant criterion to evaluate an advanced electrocatalyst. Hence, continuous CO2 reduction was performed at −1.8 V versus SCE for 50 h in order to probe the durability of the above electrocatalysts. The Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene did not show any obvious decay in the current densities, while their Faradaic efficiency for producing formate was always larger than 85% during the long test period of 50 h, indicative of their very favourable stability (Fig. 4d). Contrastingly, all the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn exhibited relatively poor long-term stability. Therefore, the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene have sufficient potential as a promising catalyst for electrocatalytic CO2 conversion with a superior formate production rate as well as a prolonged stability.
Discussion
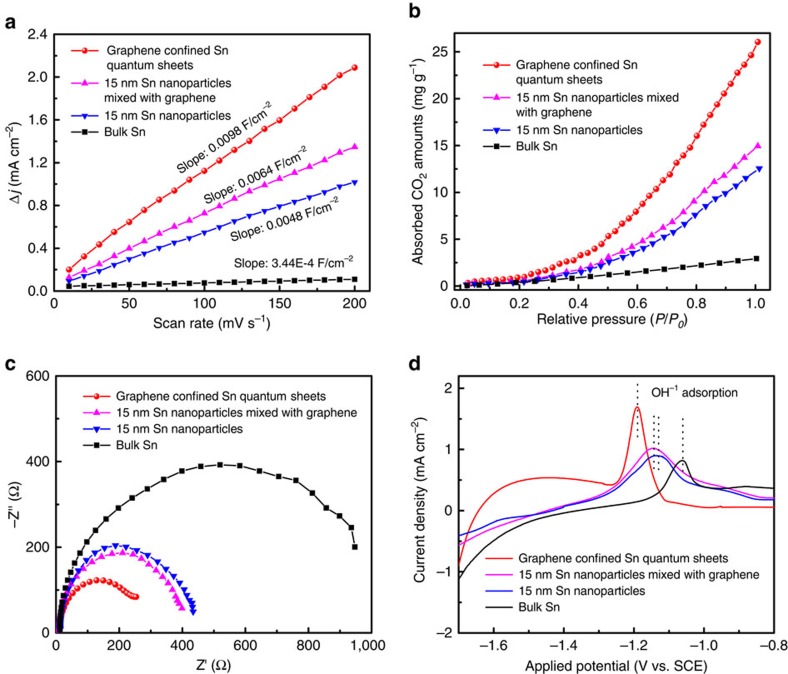
With regard to the notable enhancement of catalytic activity for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene, the increase in electrochemical active surface area (ECSA) may be one of the main contributors since larger ECSA could afford more catalytically active sites2. According to the measured double-layer capacitance in Fig. 5a, the ECSA for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene was estimated to be roughly 1.5, 2 and 28 times higher than that of the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn. The increased ECSA for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene suggested their remarkably larger amount of active sites, which endowed them with increased CO2 adsorption capacity, verified by the corresponding CO2 adsorption isotherms in Fig. 5b. For instance, the amount of CO2 adsorption capacity for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene could reach 26.1 mg g−1 at 1 atm, which is roughly 1.75, 2 and 9 times higher than that of the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk counterpart. Compared with the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles, the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene possessed a slightly increased CO2 adsorption amount, which suggested that the graphene played a limited role in increasing the CO2 adsorption. Thus, the 28 times higher ECSA for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene, largely coming from the high surface area graphene, only led to ca. 9 times higher CO2 adsorption capacity relative to bulk Sn, and hence only resulted in 13 times higher current density. Moreover, the lowered Sn–Sn coordination number for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene, revealed by XAFS fitting results in Fig. 3, further indicated their higher intrinsic catalytic activity, which could be further demonstrated by their Tafel slope lowered from 176 to 83 mV dec−1 relative to bulk Sn in Fig. 4c. Moreover, the presence of highly-conductive graphene could enhance the overall electronic conductivity, which was confirmed by their lowest interfacial charge-transfer resistance in Fig. 5c, hence ensuring fast electron transfer to CO2 for forming CO2− radiacal anion intermediate. Of note, the first electron transfer step of CO2 + e → CO2− is generally regarded as the rate-determining step1,2,4,5,6, in which stabilization of the CO2− intermediate plays a fundamental role in CO2 reduction into formate. To testify the binding affinity of CO2− on the four samples, adsorption of OH− as a surrogate for CO2− was conducted by oxidative LSV scans under a N2-bubbled 0.1 M NaOH electrolyte. The results in Fig. 5d revealed that the potential for surface OH− adsorption on the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene was 0.05, 0.06 and 0.13 V lower than that of the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn. This illustrated the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene possessed stronger adsorption affinity of OH−, and hence they could efficiently stabilize the CO2− intermediate8,19, finally facilitating formate production. Therefore, the above results strongly demonstrated that the simple addition of graphene could only slight improve the CO2 reduction performances, while the graphene interlayer confined Sn quantum sheets could fully optimize the crucial processes during CO2 electroreduction into formate.
Figure 5. Advantages of the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene.
(a) Charging current density differences plotted against scan rates; (b) CO2 adsorption isotherms; (c) Nyquist plots; (d) single oxidative LSV scans in N2-saturated 0.1 M NaOH for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn.
In conclusion, we first put forward an ideal material model of ultrathin metal layers confined in graphene, in which the protection of graphene could avoid the oxidation of the highly reactive metals in air. As an example, highly reactive metallic Sn quantum sheets, confined in few-layered graphene, are first successfully synthesized through a spatially confined reduction strategy. Synchrotron radiation XAFS results disclose that Sn–Sn coordination numbers for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene reduce from 2 and 4 to 1.4 and 2.7 compared with that of bulk counterpart, which implies the former's higher intrinsic catalytic activity, further demonstrated by their lowered Tafel slope from 176 to 83 mV dec−1. The remarkably increased ECSA for the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene could afford larger amount of active sites to efficiently adsorb CO2, further confirmed by their 1.75, 2 and 9 times higher CO2 adsorption capacity compared with the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn. The lowest interfacial charge-transfer resistance, benefiting from the highly-conductive graphene, facilitates the rate-limiting electron transfer from CO2 to CO2− intermediate. In addition, compared to the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn, the 0.05, 0.06 and 0.13 V lowered potential of OH− adsorption indicate that the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene possess the strongest adsorption affinity of CO2− intermediate, and hence they efficiently stabilize the CO2− intermediate, thus definitely lowering the overall reaction barrier. As an outcome, the Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene display a current density of 21.1 mA cm−2 at −1.8 V versus SCE, which is roughly 2, 2.5 and 13 times larger than that of the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, 15 nm Sn nanoparticles and bulk Sn. Also, the formate Faradaic efficiency for Sn quantum sheets confined in graphene is always larger than 85% during the long test period of 50 h. Thus, the present work demonstrates that the unique structure of highly reactive metal quantum sheets confined in graphene could fully optimize CO2 electroreduction performances.
Methods
Synthesis of Sn quantum sheets confined in grapheme
In a typical synthesis, 10 mg ultrathin SnO2 layers, synthesized according to our previous work (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10,569), were dispersed in 40 ml 0.03 M aqueous glucose solution under mild stirring for 30 min. Then the above mixture was transferred into a 50 ml Teflon-lined autoclave, sealed and heated at 180 °C for 10 h. After the initial hydrothermal method, the ultrathin SnO2 layers were homogenerously encapsulated in the carbon layer. Then, the carbon-coated ultrathin SnO2 layers were initially annealed at 500 °C for 2 h, and then immediately annealed at 1,000 °C for 5 min, and hence cooled down rapidly (within 1 min) to room temperature under the protection of argon atmosphere. During this temperature-programed process, the amorphous carbon turned into graphene, while the ultrathin SnO2 layers simultaneously reduced into monodispersed Sn quantum sheets in the confined space of graphene, thus forming a sandwich-like structure. By contrast, for the synthesis of 15 nm Sn nanoparticles mixed with graphene, the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles, synthesized according to the ref. of Nanotechnology, 2011, 22, 22,5701, were physically mixed with the commercial graphene under mild stirring for 1 h. Then, the 15 nm Sn nanoparticles could be dispersed on the surface of graphene.
Synthesis of bulk Sn
In a typical synthesis, 50 mg ultrathin SnO2 layers, synthesized according to ref. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10,569, were annealed at 500 °C for 5 h in H2 atmosphere and then cooled down to room temperature. The obtained powders were collected for further characterization.
Characterization
TEM images and high-resolution TEM image were performed by using a JEOL-2010 TEM with an acceleration voltage of 200 kV. The Sn K-edge XAFS was measured at the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Factory and the National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, China. Thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) of the as-synthesized samples were carried out on a Shimadzu TA-50 thermal analyser at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 from room temperature to 700 °C in air. The liquid products were quantified by nuclear magnetic resonance (Bruker AVANCE AV III 400) spectroscopy. CO2 adsorption isotherms measurements for all the synthetic samples were carried out by using an automatic microporous physical and chemical gas adsorption analyser (ASAP 2020M+C).
Electrochemical measurements
Electrochemical measurements were implemented in a three-electrode system at an electrochemical station (CHI660E). The working electrode was glassy carbon electrode. The platinum gauze and the saturated calomel electrode (SCE) reference electrode served as counter and the reference electrodes, respectively. In a typical prepared procedure of the working electrode, 3 μl of the homogeneous ink, which was prepared by dispersing 5 mg sample and 40 μl Nafion solution (5 wt%) in 1 ml water-ethanol solution with volume ratio of 3:1, was loaded onto a glassy carbon electrode with 3 mm diameter. For CO2 reduction experiments, LSV with a scan rate of 20 mV s−1 was carried out in CO2-saturated 0.1 M NaHCO3 solution (60 ml) (The NaHCO3 electrolyte was purged with CO2 for 30 min prior to the measurement.). ECSA was determined by measuring the capacitive current associated with double-layer charging from the scan-rate dependence of CVs. The Cdl was estimated by plotting the Δj (ja−jc) at −0.75 V versus SCE against the scan rate, where the Δj could be acquired by Cyclic voltammetry measurement under the potential windows of −0.8∼−0.7 V versus SCE (0.1 M NaHCO3 solution).
EXAFS experimental details
Sample of 20 mg was homogeneously mixed with 100 mg graphite and hence pressed into circular pellets with a diameter of 10 mm for further extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) measurement under ambient conditions. Then, the XAFS measurements were performed at BL14W1 station in Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, China. The storage rings of SSRF were operated at 3.5 GeV with the maximum current of 210 mA. Si(311) double-crystal monochromator crystals were used to monochromatize the X-ray beam. The energy resolution at Sn K-edge was about 2 eV. XAFS data were collected in transmission in the energy range from −200 below to 1,000 eV above the Sn K-edge. The detuning was done by 30% to remove harmonics.
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information files and from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Additional information
How to cite this article: Lei, F. et al. Metallic tin quantum sheets confined in graphene toward high-efficiency carbon dioxide electroreduction. Nat. Commun. 7:12697 doi: 10.1038/ncomms12697 (2016).
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Figures 1-4
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Nature Science Foundation (21422107, 21331005, 91422303, 11321503, 11422547), the National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB932302), Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS (CX2340000100), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities No. WK2340000063, WK2340000073 and Scientific Research Grant of Hefei Science Center of CAS (2016HSC-IU002, 2015HSC-UE006, 2015HSC-UP015).
Footnotes
Author contributions Y.X., Y.S., T.Y., F.L. and W.L. conceived the idea and co-wrote the paper. F.L., J.X., K.L. and L.L.carried out the sample synthesis, characterization and CO2 reduction meansurement. Y.S., F.L. and B.P. discussed the catalytic process. W.L., T.Y. and S.W. performed and analysed the XAFS data. All the authors discussed the results, commented on and revised the manuscript.
References
- Li C. W., Ciston J. & Kanan M. W. Electroreduction of carbon monoxide to liquid fuel on oxide-derived nanocrystalline copper. Nature 508, 504–507 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao S. et al. Partially oxidized atomic cobalt layers for carbon dioxide electroreduction to liquid fuel. Nature 529, 68–71 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. A. et al. Ionic liquid-mediated selective conversion of CO2 to CO at low overpotentials. Science 334, 643–644 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Li C. W. & Kanan M. W. Aqueous CO2 reduction at very low overpotential on oxide-derived Au nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 19969–19972 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H. & Kanan. M. W. Tin oxide dependence of the CO2 reduction efficiency on tin electrodes and enhanced activity for tin/tin oxide thin-film catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 1986–1989 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. W. & Kanan M. W. CO2 reduction at low overpotential on Cu electrodes resulting from the reduction of thick Cu2O Films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 7231–7234 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. F., Gao S. & Xie Y. Atomically-thick two-dimensional crystals: electronic structure regulation and energy device construction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 530–546 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S., Kang P. & Meyer T. J. Nanostructured Tin Catalysts for Selective Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Formate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 1734–1737 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. et al. N-doped graphene film-confined nickel nanoparticles as a highly efficient three-dimensional oxygen evolution electrocatalyst. Energy Environ. Sci 6, 3693–3699 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- Gao S. et al. Ultrathin Co3O4 layers realizing optimized CO2 electroreduction to formate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 698–702 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang L. et al. Single unit cell bismuth tungstate layers realizing robust solar CO2 reduction to methanol. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 13971–13974 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng J. et al. Enhanced electron penetration through an ultrathin graphene layer for highly efficient catalysis of the hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 2100–2104 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. F. et al. Fabrication of flexible and freestanding zinc chalcogenide single layers. Nat. Commun 3, 1057 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. F. et al. Pits confined in ultrathin cerium(IV) oxide for studying catalytic centers in carbon monoxide oxidation. Nat. Commun. 4, 2899 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina-Ramos J. et al. Efficient conversion of CO2 to CO using tin and other inexpensive and easily prepared post-transition metal catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 5021–5027 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. F. et al. Atomically thin tin dioxide sheets for efficient catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 10569–10572 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X. K. et al. Sandwich-like LiFePO4/graphene hybrid nanosheets: in situ catalytic graphitization and their high-rate performance for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 11534–11538 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- Humar B. et al. Renewable and metal-free carbon nanofibre catalysts for carbon dioxide reduction. Nat. Commun. 4, 2819 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- Won D. H. et al. Rational design of a hierarchical tin dendrite electrode for efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2. Chemsuschem 8, 3092–3098 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Figures 1-4
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information files and from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.