Abstract
We have isolated a lymphoid cell line, MDS, from the pleural exudate of a patient with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. The cells are biphenotypic, containing various T-cell and myeloid markers, and are surface negative for CD4 and CD8 but have low CD4 mRNA. The cells grow in suspension with a doubling time of 15 hr, have been karyotyped as trisomy 21, are negative for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), and are tumorigenic in the nude mouse. We have isolated two stable HIV-1-producing cell lines, MDS-T, by transfecting MDS cells with pHXBc2, and MDS-I, by infecting MDS cells with HIV-1IIIB. In 24 hr, 1 x 10(5) MDS-T or MDS-I cells produce 46 ng of p24 per ml and reverse transcriptase that is capable of incorporating 0.2 pmol of [32P]TTP into oligo(dT).poly(A). Ultrastructural studies showed numerous mature viral particles in MDS-T and MDS-I cells that are capable of infecting T cells. HIV-1 infection could be inhibited by 25% in the MDS cells with the anti-CD4 antibody Leu 3a. For over a year MDS-T and MDS-I cells have been producing high concentrations of HIV-1 in culture. A subclone derived from the MDS cells behaves like the parent cells when transfected or infected with HIV-1. In contrast to other T-cell lines, neither phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate nor tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulated the replication of HIV-1, whereas bromoadenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate or interferon alpha caused 50% and 80% inhibition of reverse transcriptase production, respectively. These chronically infected T-cell lines are a useful model system to study the effect of anti-HIV agents and cellular factors required for HIV-1 replication.
Full text
PDF


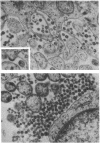
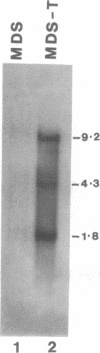
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee R., Karpen S., Siekevitz M., Lengyel G., Bauer J., Acs G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces a kappa B sequence-specific DNA-binding protein in human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells. Hepatology. 1989 Dec;10(6):1008–1013. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casareale D., Stevenson M., Sakai K., Volsky D. J. A human T-cell line resistant to cytopathic effects of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):40–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90434-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:219–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Justement J., Kinter A., Schnittman S., Orenstein J., Poli G., Fauci A. S. Characterization of a promonocyte clone chronically infected with HIV and inducible by 13-phorbol-12-myristate acetate. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1117–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Sarin P. S., Gelmann E. P., Robert-Guroff M., Richardson E., Kalyanaraman V. S., Mann D., Sidhu G. D., Stahl R. E., Zolla-Pazner S. Isolation of human T-cell leukemia virus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):865–867. doi: 10.1126/science.6601823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Hartshorn K. L., Rota T. R., Andrews C. A., Kaplan J. C., Schooley R. T., Hirsch M. S. Recombinant human interferon alfa-A suppresses HTLV-III replication in vitro. Lancet. 1985 Mar 16;1(8429):602–604. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92144-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman A. D., Banapour B., Levy J. A. Characterization of the AIDS-associated retrovirus reverse transcriptase and optimal conditions for its detection in virions. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):326–335. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeuchi K., Kim S., Byrn R. A., Goldring S. R., Groopman J. E. Infection of nonlymphoid cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 or type 2. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4226–4231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4226-4231.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Changing concepts in HIV infection: challenges for the 1990s. AIDS. 1990 Nov;4(11):1051–1058. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199011000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Hoffman A. D., Kramer S. M., Landis J. A., Shimabukuro J. M., Oshiro L. S. Isolation of lymphocytopathic retroviruses from San Francisco patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):840–842. doi: 10.1126/science.6206563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Mysteries of HIV: challenges for therapy and prevention. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):519–522. doi: 10.1038/333519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Potter S. J., Steimer K., Dina D., Levy J. A. Molecular cloning of AIDS-associated retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):760–763. doi: 10.1038/312760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrachi Y., Sternas L., Volsky D. J. The establishment of rodent cell lines persistently producing HIV-1. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90071-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn R. J., Marx P. A., Yamamoto J. K., Gardner M. B. Ultrastructural comparison of the retroviruses associated with human and simian acquired immunodeficiency syndromes. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):194–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa G. J., Zaia J. A., Spallone P. A., Stephens D. A., Kaplan B. E., Wallace R. B., Rossi J. J. Direct detection of HIV-1 RNA from AIDS and ARC patient samples. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):287–295. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E., Sporborg C., Harrison A., Martin M. L., Feorino P. Morphology and immunoelectron microscopy of AIDS virus. Arch Virol. 1985;85(3-4):189–196. doi: 10.1007/BF01314230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Orenstein J. M., Kinter A., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S. Interferon-alpha but not AZT suppresses HIV expression in chronically infected cell lines. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):575–577. doi: 10.1126/science.2470148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Read-Connole E., Gallo R. C. T4 positive human neoplastic cell lines susceptible to and permissive for HTLV-III. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1472–1473. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91666-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Z. F., Fauci A. S. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of HIV infection: cytokine induction of HIV expression. Immunol Today. 1990 May;11(5):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90070-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Josephs S. F., Dukovich M., Peffer N., Wong-Staal F., Greene W. C. Activation of the HIV-1 LTR by T cell mitogens and the trans-activator protein of HTLV-I. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2825351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaishnav Y. N., Wong-Staal F. The biochemistry of AIDS. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:577–630. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]