Significance
Usually diagnosed in young men, testicular germ cell tumors (TGCTs) originate from abnormalities in germ cells during fetal development. Testicular cancer is a complex disease combining multiple genetic variants and environmental factors. The discovery of unconventional inheritance for TGCT risk both in humans and mice highlighted the major contribution of epigenetic mechanisms. The current work identifies two TGCT modifiers, the RNA-binding proteins apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme complex 1 (APOBEC1) complementation factor (A1CF) and Argonaute 2 (AGO2), respectively involved in RNA editing and RNA silencing. These results help us better understand the epigenetic control of germ-cell fate, urogenital development, and gamete functions.
Keywords: A1CF, AGO2, testicular cancer, parent-of-origin effects, epigenetic inheritance
Abstract
Testicular tumors, the most common cancer in young men, arise from abnormalities in germ cells during fetal development. Unconventional inheritance for testicular germ cell tumor (TGCT) risk both in humans and mice implicates epigenetic mechanisms. Apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme complex 1 (APOBEC1) cytidine deaminase and Deadend-1, which are involved in C-to-U RNA editing and microRNA-dependent mRNA silencing, respectively, are potent epigenetic modifiers of TGCT susceptibility in the genetically predisposed 129/Sv inbred mouse strain. Here, we show that partial loss of either APOBEC1 complementation factor (A1CF), the RNA-binding cofactor of APOBEC1 in RNA editing, or Argonaute 2 (AGO2), a key factor in the biogenesis of certain noncoding RNAs, modulates risk for TGCTs and testicular abnormalities in both parent-of-origin and conventional genetic manners. In addition, non-Mendelian inheritance was found among progeny of A1cf and Ago2 mutant intercrosses but not in backcrosses and without fetal loss. Together these findings suggest nonrandom union of gametes rather than meiotic drive or preferential lethality. Finally, this survey also suggested that A1CF contributes to long-term reproductive performance. These results directly implicate the RNA-binding proteins A1CF and AGO2 in the epigenetic control of germ-cell fate, urogenital development, and gamete functions.
The germline is the only cell lineage that transmits genetic and epigenetic information across generations. Early in mammalian development, primordial germ cells (PGCs) escape a somatic fate to become unipotent precursors of gametes, the highly specialized cells that give rise to the totipotent zygote upon fertilization (1). Various molecular mechanisms regulate pluripotency by modulating gene expression and protein activity throughout development (2). Failure of pluripotency control can lead to infertility, carcinoma in situ, gamete dysfunctions, and unusual modes of inheritance. Carcinoma in situ anomalously express markers of pluripotency and can give rise to testicular germ cell tumors (TGCTs) (3–7). Studying the genetics, epigenetics, and biology of germ cells (GCs) and TGCTs can provide unique insights about GC development, pluripotency control, tumorigenesis, and unconventional inheritance.
TGCTs are the third most heritable cancer and are the most common cancers in young men 15–35 y old (8). Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in humans identified susceptibility loci such as KIT ligand (KITL), Sprouty 4 (SPRY4), Bcl2 antagonist killer (BAK1), Doublesex- and Mab3-related transcription factor (DMRT1), Deleted in azoospermia RNA-binding protein (DAZL), PRDM transcriptional regulator (PRDM14), the telomerase reverse transcriptase TERT, and its cofactor AFT7IP (9–15). Individually and collectively, however, these susceptibility genes account for only a modest portion of inherited risk. Many genes and inherited factors remain to be discovered, their functions in normal development characterized, and the ways that dysfunction leads to TGCTs investigated (16, 17).
Risk for TGCTs is strongly associated with various testicular abnormalities (TAs) such as undescended testis (cryptorchism) and testicular atrophy (18–23). This association, sometimes referred to as “testicular dysgenesis syndrome,” suggests shared genetic and environmental origins for TGCTs and abnormalities in urogenital development (24–26).
Studies of human pathologies such as TGCTs occasionally reveal unusual modes of inheritance such as parent-of-origin (PofO) effects, which are implicated when phenotypes are transmitted preferentially through either the maternal or paternal germline (27). Such inheritance is associated with several human conditions (28–30). PofO effects include a four- to sixfold elevated risk of TGCTs among sons of affected versus unaffected fathers (31, 32), inheritance of SPRY4 risk through the maternal but not paternal germline (15), and gender-specific inheritance of methylation in TGCT families (33). Studying the molecular bases of unconventional inheritance and their associations with pathologies such as TGCTs is challenging in humans because of the need to obtain multigeneration families and to resolve heterogeneity and stratification in study populations. Animal models, with their defined genetics and controlled husbandry, can resolve some of these challenges.
Unlike other inbred strains, males of the 129/Sv family of mouse strains have a strong genetic predisposition to spontaneous TGCTs (Mouse Tumor Biology Database, tumor.informatics.jax.org/mtbwi/index.do) (3, 34). Interestingly, these TGCTs share many characteristics with pediatric TGCTs and nonseminomas in humans, including embryonic origin, heterogeneous cell and tissue composition, and abnormal expression of pluripotency markers (7, 35–37). Genetic studies with 129/Sv males have identified many susceptibility genes such as Kitl, the RNA-binding protein (RBP) Deadend homolog 1 (Dnd1), apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme complex 1 (Apobec1) cytidine deaminase, and the transcriptional factors Trp53 and Dmrt1 (3, 38–44). The association between Kitl mutations and TGCT susceptibility in mice was later demonstrated in humans, where inherited KITL variants show the strongest association with TGCTs of any GWAS locus (9, 10, 12, 15).
Unusual modes of inheritance such as PofO and transgenerational epigenetic effects are readily characterized with mouse TGCT models (45, 46). For instance, Slgb/+ heterozygous mutant males that carry a Kitl deletion transmit strong protection to wild-type male offspring (47). In addition, an engineered loss-of-function Apobec1 mutation shows contrasting effects on TGCT risk among Apobec1KO/+ male offspring depending on whether the Apobec1KO allele is inherited paternally (enhanced risk) or maternally (reduced risk) (41). Maternal Apobec1KO/+ heterozygosity also acts in a PofO and transgenerational manner to reduce risk among wild-type male offspring for several generations (41).
Atypical patterns of inheritance can also result from transmission ratio distortion (TRD), which occurs when allelic transmission to offspring departs significantly from Mendelian expectations (48). Examples have been described in mice, flies, and other species, although evidence for strong TRD in humans is weak (49–52). TRD may arise at different stages of male and female gametogenesis (meiotic drive), at fertilization (gamete competition), and during embryonic development (preferential lethality). Mechanisms underlying such events may be allele-, sex-, or strain-specific (50, 52). In mice, TRD also has been reported in intercrosses with mutant heterozygotes for TGCT-susceptibility genes such as Dnd1tm1Na (hereafter referred to as “Dnd1KO”) (53) and a combination of maternal Apobec1KO/+ and paternal Dnd1Ter/+ heterozygosity (41). Together, these results suggest that susceptibility genes for TGCTs may also affect gamete functions in ways that bias genetic transmission.
Jablonka and Lamb (54) proposed that anomalies in the epigenetic regulation of the germline could lead to TRD and infertility. The present study tested the role of two epigenetic factors, namely APOBEC1 complementation factor (A1CF), the RNA-binding cofactor for APOBEC1 in C-to-U RNA editing (55, 56), and Argonaute 2 (AGO2, also known as “EIF2C2”), a key factor of microRNA (miRNA)- and siRNA-mediated gene silencing, on TGCT susceptibility. The DND1 protein shares sequence similarity with A1CF (40). Consequently, DND1 could affect TGCT susceptibility through effects on mRNA editing. Indeed, APOBEC1 is a potent TGCT modifier of parental effects, gametic transmission, and transgenerational epigenetic inheritance (41). Interestingly, A1cfKO/+ heterozygous matings also show strong TRD (57). A1CF and APOBEC1 therefore may have similar effects on TGCTs and TRDs. Here we tested the consequences of partial A1CF deficiency on the susceptibility to TGCTs, TAs, and TRDs as well as on epigenetic inheritance in genetically predisposed 129/Sv mice.
In parallel, previous work showed that DND1 directly binds the 3′ UTR of specific mRNAs, thereby blocking access of miRNAs to their targets in TGCT cell lines (58). DND1 associates with several pluripotency transcripts such as OCT4, NANOG, and lineage defect LIN28 (59). If DND1 contributes to TGCT susceptibility by interfering with miRNA functions, genes directly involved in miRNA biogenesis should have similar effects. AGO2 regulates miRNA and endogenous siRNA functions (60). To determine whether miRNA and siRNA pathways are directly implicated in teratocarcinogenesis and related aspects of GC biology, we tested the effects of partial AGO2 deficiency on susceptibility to TGCTs, TAs, and TRDs and on PofO effects in 129/Sv mice.
We found that both A1cf and Ago2 reduce the risk for TGCTs in both PofO and conventional manners, regulate TA susceptibility, and show TRD, albeit in somewhat different manners. Together, these results support the role of epigenetics on mRNA availability for translation as well as the link between unconventional inheritance and biased fertilization.
Results
Study Design.
The purpose of this survey was to test the impact of A1cf and Ago2 hemizygosity on parental versus conventional inheritance of TGCT susceptibility, transmission ratios, and reproductive performance over three backcross generations. For both mutants, a combination of reciprocal backcrosses and intercrosses was used to assess inheritance of TGCT and TA risk. A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ mutant mice were generated from related 129-derived targeted ES cell lines (57, 61) and then were backcrossed to inbred 129/Sv control mice. A total of 1,589 offspring males, including 361 from 129/Sv control crosses, 1,010 from separate A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ reciprocal backcrosses, and 218 males from separate A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ intercrosses, were examined for TGCTs and TAs (Tables 1 and 2 and Table S1). Conventional (Mendelian) inheritance was inferred in cases in which maternal and paternal inheritance affected offspring phenotypes similarly. By contrast, a PofO effect was inferred in cases in which offspring phenotype depended on parental sex and genotype.
Table 1.
Occurrence of TGCT-affected males in the 129/Sv control strain and in A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ reciprocal backcrosses and intercrosses
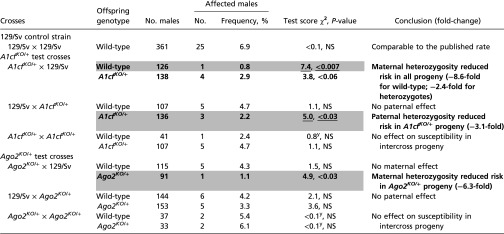 |
A total of 1,589 offspring males, including 361 from 129/Sv control crosses, 1,010 from separate A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ reciprocal backcrosses, and 218 males from separate A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ intercrosses, were examined for TGCTs and TAs (Tables 1 and 2 and Table S1). Conventional (Mendelian) inheritance was inferred in cases where maternal and paternal inheritance affected offspring phenotypes similarly. By contrast, a PofO effect was inferred in cases where offspring phenotype depended on parental sex and genotype. χ2 goodness-of-fit tests were used to compare the occurrence of TGCT-affected heterozygous and wild-type males with the 7% baseline in the 129/Sv inbred strain (34, 41, 62, 63). χ2 (χ2) and P values are indicated for each test result (df = 1). Results below the pointwise 0.05 threshold are highlighted in bold font with a gray background. We treated the six tests for each mutant (A1cf and Ago2) as a ”family” of tests. Results that showed family-wide significance at an FDR of 0.1 are underlined. Fold-change refers to results for each mutant test cross versus the 129/Sv control strain. Results highlighted in bold (no gray, no underlining) represent a strong trend with substantial fold-change. NS indicates results that did not pass the threshold of statistical significance. y indicates Yate’s correction was applied to the test.
Table 2.
Effect of A1cfKO and Ago2KO on occurrence of atrophy and cryptorchism in backcross and intercross progeny
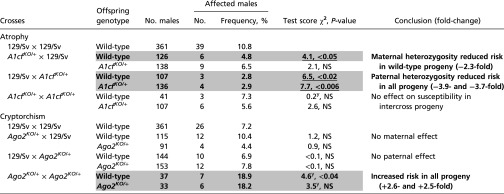 |
Comparison of results for A1cfKO/+, Ago2KO/+ and respective wild-type sibling males in reciprocal backcrosses and intercrosses with results for males in the 129/Sv control strain. χ2 contingency test with an FDR assessment. Bold, underlining, and shading are as in Table 1. See Table 1 for additional information. Complete data are supplied in Table S1. NS, not significant.
Table S1.
Occurrence of males with cryptorchism, atrophy, and other TAs in 129/Sv control cross and in A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ reciprocal backcrosses and intercrosses
| Cross | Offspring genotype | No. of males | Cryptorchism | Atrophy | Miscellaneous | Total TAs | ||||
| No. | Frequency, % | No. | Frequency, % | No. | Frequency, % | No. | Frequency, % | |||
| 129/Sv control strain | ||||||||||
| 129/Sv × 129/Sv | 361 | 26 | 7.2 | 39 | 10.8 | 1 | 0.3 | 66 | 18.3 | |
| A1cfKO/+ test crosses | ||||||||||
| A1cfKO/+ × 129/Sv | Wild-type | 126 | 6 | 4.8 | 6 | 4.8 | 1 | 0.8 | 13 | 10.3 |
| A1cfKO/+ | 138 | 10 | 7.2 | 9 | 6.5 | 1 | 0.7 | 20 | 14.5 | |
| 129/Sv × A1cfKO/+ | Wild-type | 107 | 13 | 12.1 | 3 | 2.8 | 1 | 0.9 | 17 | 15.9 |
| A1cfKO/+ | 136 | 8 | 5.9 | 4 | 2.9 | 1 | 0.7 | 13 | 9.6 | |
| A1cfKO/+ × A1cfKO/+ | Wild-type | 41 | 2 | 4.9 | 3 | 7.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 12.2 |
| A1cfKO/+ | 107 | 6 | 5.6 | 6 | 5.6 | 0 | 0.0 | 12 | 11.2 | |
| Ago2KO/+ test crosses | ||||||||||
| Ago2KO/+ × 129/Sv | Wild-type | 115 | 12 | 10.4 | 8 | 7.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 20 | 17.4 |
| Ago2KO/+ | 91 | 4 | 4.4 | 13 | 14.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 17 | 18.7 | |
| 129/Sv × Ago2KO/+ | Wild-type | 144 | 10 | 6.9 | 16 | 11.1 | 2 | 1.4 | 27 | 18.8 |
| Ago2KO/+ | 153 | 12 | 7.8 | 17 | 11.1 | 1 | 0.7 | 30 | 19.6 | |
| Ago2KO/+ × Ago2KO/+ | Wild-type | 37 | 7 | 18.9 | 2 | 5.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 9 | 24.3 |
| Ago2KO/+ | 33 | 6 | 18.2 | 5 | 15.2 | 0 | 0.0 | 11 | 33.3 | |
PofO Effects on TGCT Susceptibility.
Growing evidence of PofO effects on TGCT risk in both humans (15, 31, 32) and mice (41, 47, 63) suggests that epigenetic mechanisms influence tumorigenesis. Here, we asked whether A1cf and Ago2 contribute to TGCT susceptibility in a conventional or a PofO manner.
129/Sv.
Because the occurrence of TGCT-affected males in the present survey (6.9%) (Table 1) was consistent with previous reports (34, 41, 62, 63), the 7% long-term average was used to analyze A1cf and Ago2 results.
A1cf.
Partial deficiency for A1cf had both conventional and PofO effects, depending on parental and offspring genotype (Table 1). Maternal but not paternal heterozygosity significantly reduced risk in wild-type male offspring (8.6-fold, P < 0.007). By contrast, conventional effects were found in A1cfKO/+ heterozygous offspring with both maternal and paternal heterozygosity, in which risk was strongly reduced (2.4- and 3.1-fold, P < 0.06 and <0.03, respectively). TGCT occurrence among A1cfKO/+ intercross progeny did not differ significantly from the 129/Sv baseline.
Ago2.
A protective PofO effect was found in Ago2KO/+ backcrosses in which the occurrence of affected Ago2KO/+ heterozygous males was reduced significantly with maternal but not paternal heterozygosity (6.3-fold, P < 0.03) (Table 1). No other backcross or intercross results differed significantly from 129/Sv.
Thus, both A1cf and Ago2 affected TGCT risk, depending on parental sex and offspring genotype. As with Apobec1KO/+ heterozygosity (41), maternalA1cfKO/+ heterozygosity reduced risk among all male offspring, whereas paternal heterozygosity led to conventional genetic effects, albeit in a different direction (reduced risk) than results for Apobec1 (increased risk).
PofO Effects on TA Susceptibility.
In humans, cryptorchism is relatively common (3–5%); atrophy and agonadism are less common (0.2%) (64). We investigated whether partial deficiency of A1cf or Ago2 affected TA incidence in the same crosses in which the TGCT survey was conducted.
129/Sv.
The occurrence of cryptorchid as well as atrophic testes (including agonadism) among 129/Sv males (18.3%) (Table S1) was consistent with the 18% rate previously reported (65).
A1cf.
A strong paternal effect was found in A1cfKO/+ backcrosses in which heterozygous male offspring showed a 3.7-fold reduced risk for atrophy (P < 0.006) (Table 2). By contrast, a conventional effect for atrophy was observed among wild-type offspring with occurrence strongly reduced (2.3- and 3.9-fold, P < 0.05 and P < 0.02, respectively). TA occurrence among A1cfKO/+ intercross progeny did not differ significantly from the 129/Sv rate (Table 2). Cryptorchism occurred at comparable frequencies in all A1cfKO/+ crosses and 129/Sv (Table S1).
Ago2.
Partial deficiency of Ago2 did not significantly affect the occurrence of cryptorchism or atrophy in Ago2KO/+ backcross progeny (Table S1). However, wild-type and heterozygous intercross progeny showed a 2.6- and 2.5-fold increased risk for cryptorchid testes compared with 129/Sv mice (Table 2).
Thus, both A1cf and Ago2 affected the occurrence of TAs in 129/Sv mice but did so in contrasting ways: A1cf significantly reduced the risk of atrophy in backcross progeny in both conventional and PofO manners, whereas Ago2KO/+ heterozygosity increased the risk of cryptorchism in wild-type and heterozygous mutant intercross progeny.
Cooccurrence of TGCTs and TAs.
In humans, individuals with a cryptorchid testis have an elevated risk of developing additional urogenital conditions including reduced fertility, testicular atrophy, and TGCTs (18, 21). An estimated 10% of testicular tumors are associated with cryptorchid testis (18). In all crosses, we found males with cryptorchid or atrophic testes that also had a TGCT, referred to hereafter as “cryptorchid TGCT” and “atrophic TGCT” cases, respectively. However, because such cases were rare in A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ crosses, we restricted the analysis to the 129/Sv strain (Table S2).
Table S2.
Cooccurrence of cryptorchid or atrophic testes and TGCTs in the same testis of 129/Sv controls
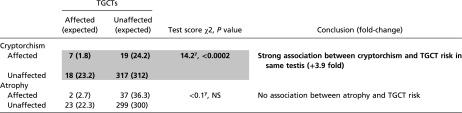 |
Interestingly, we found the joint occurrence of cryptorchism and TGCTs was increased 3.9-fold over the expectations for independent risks (P < 0.0002) (Table S2). In fact, 27% of cryptorchid cases also had a TGCT. The association between cryptorchism and TGCT in the same testis is consistent with observations in humans (19, 20). By contrast, atrophy and TGCTs occurred independently (Table S2). Also, TGCTs with contralateral atrophy were rare, and cryptorchism was never associated with contralateral TGCTs; this finding is consistent with the low risk for TGCTs in scrotal testes with a contralateral cryptorchid testis in humans (66).
Risk for Male Offspring of Affected Males.
In humans, sons of a father with a TGCT or a cryptorchid testis have an elevated risk for TGCTs and for cryptorchism (four- to sixfold and four- to fivefold, respectively) (31, 32, 67). In our study, the presence of paternal TAs was not associated with altered risk for TGCTs or TAs among progeny (see Table S4). Therefore, we pooled the results for sons of male parents with healthy testes together with those of sons of male parents affected with a TA. This pool, hereafter referred to as “healthy breeders,” was then used to test the effect of filial relations on TGCT risk.
Table S4.
Association of parent–offspring relationship with TA and TGCT risk
| Strain | Male parent genotype | Female parent genotype | Male offspring genotype | Phenotype of male parent | No. of males | Cryptorchism | Atrophy | Total TAs | |||
| No. | Frequency, % | No. | Frequency, % | No. | Frequency, % | ||||||
| Comparison between TA-breeders and healthy breeders | |||||||||||
| 129/Sv control strain | With TA | 91 | 7 | 7.7 | 7 | 7.7 | 5 | 5.5 | |||
| Wild-type | Wild-type | Wild-type | None | 270 | 19 | 7.0 | 32 | 11.9 | 20 | 7.4 | |
| A1cf | Wild-type | A1cfKO/+ | Wild-type | With TA | 4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| None | 122 | 6 | 4.9 | 6 | 4.9 | 1 | 0.8 | ||||
| A1cfKO/+ | With TA | 3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | |||
| None | 135 | 10 | 7.4 | 9 | 6.7 | 4 | 3.0 | ||||
| A1cfKO/+ | Wild-type | No breeder with TA-affected male parent | |||||||||
| Ago2 | Wild-type | Ago2KO/+ | Wild-type | With TA | 40 | 5 | 12.5 | 5 | 12.5 | 1 | 2.5 |
| None | 75 | 7 | 9.3 | 3 | 4.0 | 4 | 5.3 | ||||
| Ago2KO/+ | With TA | 37 | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 10.8 | 0 | 0.0 | |||
| None | 54 | 4 | 7.4 | 9 | 16.7 | 1 | 1.9 | ||||
| Ago2KO/+ | Wild-type | Wild-type | With TA | 45 | 2 | 4.4 | 3 | 6.7 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| None | 99 | 8 | 8.1 | 13 | 13.1 | 6 | 6.1 | ||||
| Ago2KO/+ | With TA | 46 | 2 | 4.3 | 3 | 6.5 | 0 | 0.0 | |||
| None | 107 | 10 | 9.3 | 14 | 13.1 | 5 | 4.7 | ||||
| Comparison between TGCT-breeders and healthy breeders | |||||||||||
| 129/Sv control strain | With TGCT | 19 | 2 | 10.5 | 3 | 15.8 | 0 | 0.0 | |||
| Wild-type | Wild-type | Wild-type | None | 361 | 26 | 7.2 | 39 | 10.8 | 25 | 6.9 | |
| A1cf | Wild-type | A1cfKO/+ | Wild-type | With TGCT | 21 | 1 | 4.8 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 4.8 |
| None | 126 | 6 | 4.8 | 6 | 4.8 | 1 | 0.8 | ||||
| A1cfKO/+ | With TGCT | 30 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 3.3 | 0 | 0.0 | |||
| None | 138 | 10 | 7.2 | 9 | 6.5 | 4 | 2.9 | ||||
| A1cfKO/+ | Wild-type | Wild-type | With TGCT | 16 | 2 | 12.5 | 1 | 6.3 | 0 | 0.0 | |
| None | 107 | 13 | 12.1 | 3 | 2.8 | 5 | 4.7 | ||||
| A1cfKO/+ | With TGCT | 14 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 14.3 | 3 | 21.4 | |||
| None | 136 | 8 | 5.9 | 4 | 2.9 | 3 | 2.2 | ||||
| Ago2 | Wild-type | Ago2KO/+ | Wild-type | With TGCT | 6 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 16.7 | 0 | 0.0 |
| None | 115 | 12 | 10.4 | 8 | 7.0 | 5 | 4.3 | ||||
| Ago2KO/+ | With TGCT | 12 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 16.7 | 2 | 16.7 | |||
| None | 91 | 4 | 4.4 | 13 | 14.3 | 1 | 1.1 | ||||
| Ago2KO/+ | Wild-type | No breeder with TGCT-affected male parent | |||||||||
Occurrence of males affected with a TA or a TGCT in 129/Sv controls and in A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ heterozygous and wild-type sibling males of reciprocal backcrosses in breeders with a TA-affected or a TGCT-affected male parent and breeders with a male parent with healthy testes.
Although results are anecdotal because of the modest number of breeders with TGCT-affected parental males (referred to hereafter as “TGCT breeders”) (Table S3), the similarity with evidence from humans is striking. The first example involves progeny of an affected A1cfKO/+ breeder male: 21.4% of A1cfKO/+ male offspring developed a TGCT, whereas only 2.2% of the progeny of healthy breeders were affected—a 9.7-fold difference (P < 0.006) (Table S3). The second example involves progeny of a TGCT-affected 129/Sv control male mated with Ago2KO/+ females. TGCT risk among Ago2KO/+ male offspring of this cross increased 15.2-fold compared with progeny of healthy breeders (P < 0.04) (Table S3). If validated in a larger study, these results suggest that the action of a paternally inherited factor depends on offspring genotype, because in both examples, increased risk was found in mutant heterozygous offspring but not in their wild-type siblings (Table S3).
Table S3.
TGCT risk in progeny of TGCT-affected male parents
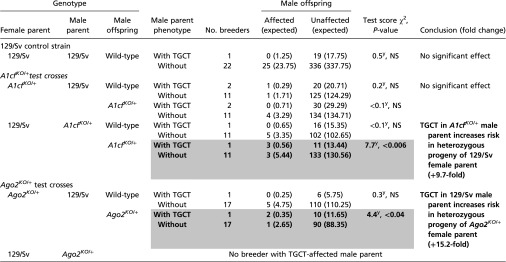 |
Occurrence of 129/Sv control and A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ and respective wild-type sibling males affected with a TGCT in breeders with a TGCT-affected male parent and breeders with a male parent with healthy testes. Note that the number of breeders is repeated for each of the three informative crosses because wild-type and heterozygous siblings share the same parents. χ2 contingency test. y indicates Yate’s correction was applied to the test. Bold is as in Table 1. See Table 1 for additional information. Complete data are given in Table S4.
No significant differences in TA occurrence were detected between the 118 male offspring of TGCT breeders and the progeny of healthy breeders (Table S4).
Laterality.
Human TGCTs are generally unilateral (21), with no obvious side preference (68). By contrast, mouse TGCTs present a 2:1 left:right bias (3, 34, 65) that is accentuated in some strains such as Dnd1Ter (34, 69, 70). However, A1cf and Ago2 partial deficiencies did not affect laterality (Table S5). Bilateral cases were rare (3, 21, 65, 70). Cryptorchism and atrophy occurred predominantly on the left side without a significant difference between 129/Sv and the other strains, also confirming previous reports (3, 34, 65). Bilateral TAs were infrequent (Table S5), whereas in humans 15% of all cryptorchid testes are bilateral (64). Thus, both TGCTs and TAs in mice are primarily unilateral with a strong left-preference that is largely unaffected by partial loss of A1cf or Ago2 function.
Table S5.
Laterality for cryptorchid testes, atrophic testes, and TGCTs in 129/Sv controls and A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ heterozygous and wild-type sibling males of reciprocal backcrosses and intercrosses
| Crosses | Offspring | Genotype | Cryptorchism | Atrophy | TGCTs | |||||||||
| No. unilateral | % left | No. left | No. bilateral | No. unilateral | % left | No. left | No. bilateral | No. unilateral | % left | No. left | No. bilateral | |||
| 129/Sv control strain | ||||||||||||||
| 129/Sv × 129/Sv | Wild-type | 26 | 24 | 92 | 0 | 37 | 37 | 100 | 1 | 24 | 15 | 63 | 1 | |
| A1cfKO/+ test crosses | ||||||||||||||
| A1cfKO/+ × 129/Sv | Wild-type | 6 | 5 | 83 | 0 | 6 | 5 | 83 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| A1cfKO/+ | 10 | 10 | 100 | 0 | 9 | 9 | 100 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 80 | 0 | ||
| 129/Sv × A1cfKO/+ | Wild-type | 13 | 13 | 100 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 100 | 0 | |
| A1cfKO/+ | 8 | 6 | 75 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 100 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 50 | 1 | ||
| A1cfKO/+ × A1cfKO/+ | Wild-type | 2 | 2 | 100 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ND | 1 | |
| A1cfKO/+ | 6 | 6 | 100 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 100 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 60 | 0 | ||
| Ago2KO/+ test crosses | ||||||||||||||
| Ago2KO/+ × 129/Sv | Wild-type | 12 | 11 | 92 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 100 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 80 | 0 | |
| Ago2KO/+ | 4 | 4 | 100 | 0 | 13 | 13 | 100 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 129/Sv × Ago2KO/+ | Wild-type | 10 | 10 | 100 | 0 | 14 | 13 | 93 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 83 | 0 | |
| Ago2KO/+ | 12 | 10 | 83 | 0 | 17 | 17 | 100 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 50 | 0 | ||
| Ago2KO/+ × Ago2KO/+ | Wild-type | 7 | 6 | 86 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 100 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 50 | 0 | |
| Ago2KO/+ | 6 | 5 | 83 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 80 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 100 | 0 | ||
TRD.
Transmission of alternative alleles from heterozygotes is usually Mendelian, but exceptions are known at selected loci in several species (49–51). For example, a fivefold excess of heterozygotes over expectations is found in A1cfKO/+ intercrosses (57) and was confirmed in the current survey (P < 0.002) (Table 3). We also observed TRD in Ago2KO/+ crosses, with only 50% of the expected number of Ago2KO/+ heterozygotes among progeny of both intercrosses (P < 0.0002) (Table 3 and Table S6) and backcrosses with maternal but not paternal Ago2KO heterozygosity (P < 0.02) (Table 3). Interestingly, the genotypic bias was stronger for females in A1cfKO/+ intercrosses (P < 0.003) and for males in Ago2KO/+ intercrosses (P < 0.0006) (Table S6), suggesting that sex chromosomes may be involved. In all cases, litter sizes were similar among backcross and intercross matings, suggesting that embryonic lethality was not responsible for distorting transmission.
Table 3.
A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ transmission in backcrosses and intercrosses
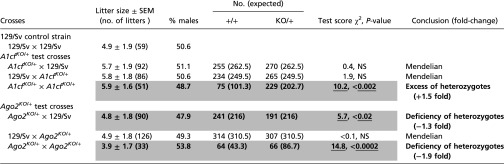 |
Genotypic transmission in progeny compared with Mendelian expectations (1:1) for A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ backcrosses and (1:2) for intercrosses. Sexes are similarly represented (not shown); only combined data are presented. χ2 goodness-of-fit test. Bold, underlining, and shading are as in Table 1. Complete data are given in Table S6.
Table S6.
A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ transmission in backcrosses and intercrosses in inbred versus mixed-background mice
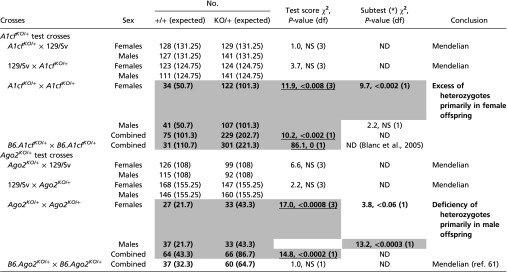 |
Underlining and bold are as in Table 1. ND, not done.
In cases of positive test results, a subtest was performed for each sex subgroup to determine which contrast contributed most.
Gametogenesis and Reproduction.
TRD may arise during gametogenesis, at fertilization, or during embryogenesis. We therefore examined morphological and histological features of oogenesis, spermatogenesis, and reproductive performance of A1cf and Ago2 mutant mice.
Oogenesis.
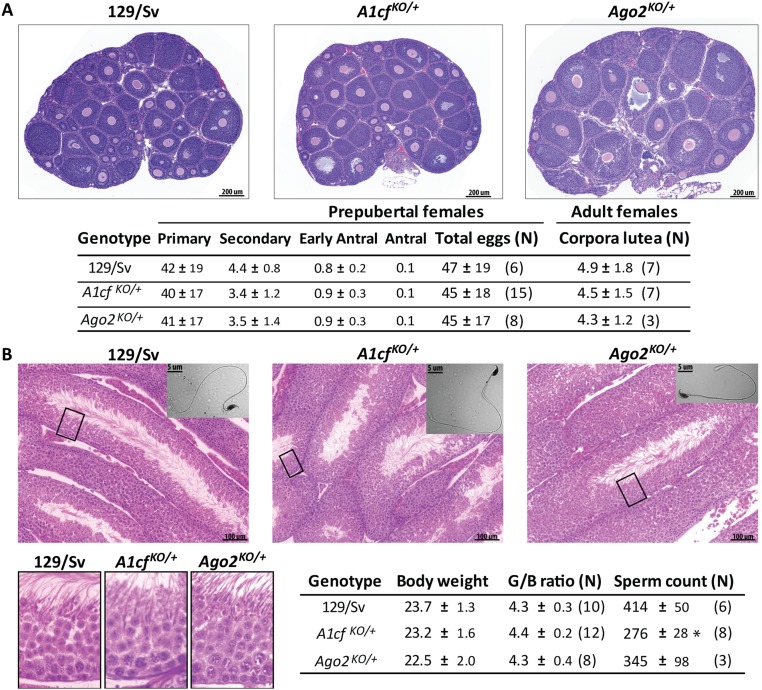
Given that puberty (and therefore first ovulation) occurs at ∼29 d of age (71), the total number of eggs present at birth and fixed for the lifetime can be reliably assessed in females at weaning. On average in prepubertal A1cfKO/+, Ago2KO/+, and 129/Sv ovaries, we counted 45–47 eggs/mm2 (Fig. S1A). However, two (of 15) A1cfKO/+ ovaries had dramatically more eggs (141 eggs/mm2; P ∼ 0), suggesting heterogeneity in reproductive performance among A1cfKO/+ females, although no outlier litter sizes were noted. Oocyte maturation was assessed with emphasis on primary, secondary, early antral, and antral follicles, but no significant differences were observed (Fig. S1A). The number of corpora lutea in adult ovaries did not vary substantially, suggesting quantitatively normal ovulation in the three strains. Overall histology also appeared normal (Fig. S1A).
Fig. S1.
Effect of A1cfKO and Ago2KO on oogenesis and spermatogenesis. (A) Histology (Upper) and total number of eggs (no. of eggs/mm2 ± SD, including different maturation stages) in prepubertal (P21) 129/Sv control, A1cf KO/+, and Ago2KO/+ ovaries, and number of corpora lutea in adult (P70) ovaries (Lower). N, total number of ovaries examined. (B) Histology of testis (Upper and Lower Left) and average body weight (in milligrams ± SD) with G/B ratio ± SD and total number of sperm (no. of sperm × 106/mL ± SEM) of 129/Sv control, A1cfKO/+, and Ago2KO/+ adult (P70) males (Lower Right). N, total number of males examined. The asterisk indicates that the test value exceeds the 129/Sv value by more than the SEM. (Magnification: B, Upper, 40×; B, Lower Left (boxed area of Upper), 10×.)
Spermatogenesis.
Testis weight is an established proxy measure of spermatogenesis and male fertility (72, 73). The average body weight of adult A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ males (23.2 and 22.5 g, respectively) did not differ significantly from that of 129/Sv controls (23.7 g) (Fig. S1B). 129/Sv males showed a gonad/body mass (G/B) ratio of 4.3 that was not significantly affected by partial deficiency of A1cf or Ago2 (4.3 and 4.4, respectively). Histological analysis of A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ testes revealed no obvious abnormalities. Mature spermatozoa in the three strains had normal morphology (Fig. S1B), although A1cfKO/+ adult males produced fewer mature sperm (276 × 106 sperm/mL) than 129/Sv and Ago2KO/+ adult males (414 and 345 × 106 sperm/mL, respectively) (Fig. S1B).
Reproduction.
The number of pups per litter at weaning, the age at first litter, litter intervals, and persistence of productivity are commonly used to characterize reproductive performance (74). Mating and culling times were set up blinded to genotype. No significant differences in parental age at mating, death, or at first and last litters were observed among strains. The litter interval between mating and the first litter did not differ significantly among strains (Table 4). Most breeders appeared to be still productive at the time they were killed, making an estimate of the reproductive lifespan for each strain impossible. Nonetheless, the reproductive capacity of 129/Sv controls was declining at the time of death, with one less pup in the last litter than in the first litter (Table 4), as expected in aging laboratory mice (75) and suggesting that the end of breeding productivity for our strains was imminent.
Table 4.
Reproductive performance in 129/Sv control cross and A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ backcrosses
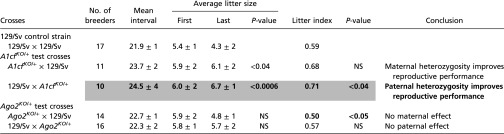 |
Mean interval (days) between mating and first litter, average size of first and last litters, and litter index are compared in 129/Sv control cross and A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ backcrosses. t tests. Only significant results are presented. Bold, shading, and underlining are as in Table 1.
Interestingly, although the size of first litters did not differ significantly among strains (Table 4), the number of pups in the last litters was significantly higher in A1cf backcrosses: +1.8 (P < 0.04) and +2.4 pups (P < 0.0006) with maternal and paternal heterozygosity, respectively (Table 4), compared with 129/Sv control cross and Ago2 backcrosses (Table 4). Consequently, average litter sizes were increased by approximately one pup in all A1cf crosses (Table 3) compared with 129/Sv control cross and Ago2 backcrosses and despite the early lethality of A1cfKO/KO homozygotes in intercross (57). By contrast, Ago2 intercrosses lost one pup on average per litter (Table 3), in accordance with the early embryonic lethality of Ago2KO/KO homozygotes (61).
Furthermore, litter indexes were similar in 129/Sv control crosses (0.59) (Table 4) and Ago2 backcrosses (0.50 and 0.57 with maternal and paternal heterozygosity, respectively) (Table 4) but were markedly increased in A1cf backcrosses (0.68 and 0.71 with maternal and paternal heterozygosity, respectively) (Table 4).
Thus, no obvious quantitative or histological evidence for the effects of partial deficiency of A1cf and Ago2 on oogenesis and spermatogenesis was found in 129/Sv mice. Heterozygous males and females were fully fertile with seemingly normal gonads and GCs, despite a reduced number of A1cfKO/+ adult sperm. Surprisingly, however, A1cfKO/+, but not Ago2KO/+, heterozygosity improved the reproductive performance of the aging 129/Sv inbred strain.
Expression of A1cf in Developing and Mature 129/Sv Gonads.
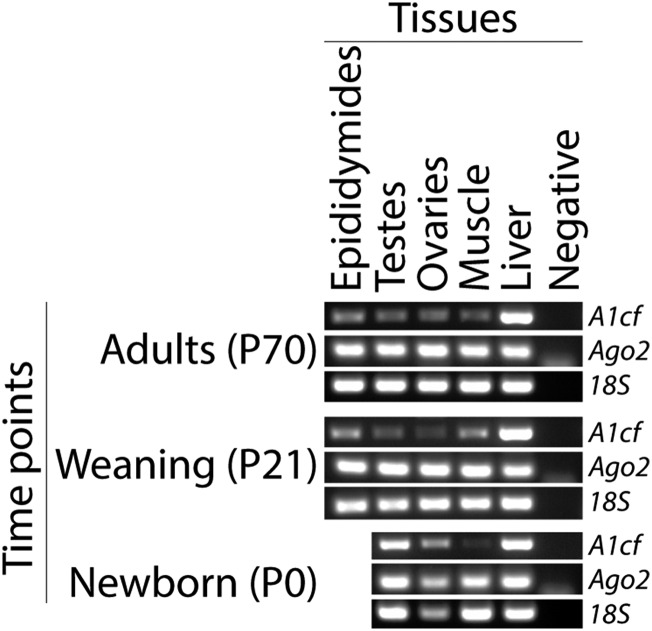
A1CF is highly expressed in the kidney, liver, and small intestine of adult mice and humans and also in heart, spinal cord, and lung of mouse embryos at embryonic day 12.5 (E12.5) (57, 76, 77). A1CF transcripts also were detected in gonads of adult humans (77). Here, the presence of A1cf transcripts was confirmed in 129/Sv muscle and liver (76) at birth [postnatal day 0 (P0)], P21, and P71 (Fig. S2). A1cf transcripts also were detected in 129/Sv testes, epididymides, and ovaries at all time points (Fig. S2).
Fig. S2.
A1cf transcript expression and structure in mouse. Relative levels of A1cf transcript and, for comparison, Ago2 transcript and 18S ribosomal RNA (internal control) in epididymides, testes, and ovaries and in muscle and liver (referents for low and high levels of A1cf, respectively) of adult (P70), weaning (P21), and newborn (P0) 129/Sv females and males. A negative control is included for each set of primers.
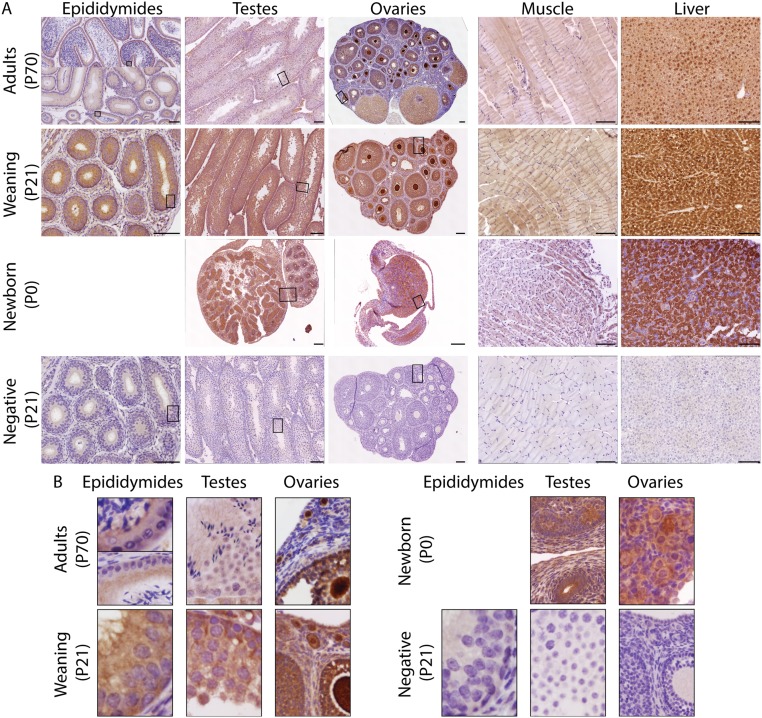
A1CF protein expression then was investigated in the same tissues and at the same time points (Fig. S3). Staining in the liver was strong in both cytoplasm and nucleus at P0 and P21 but was largely circumscribed within nucleus of hepatocytes in adults, in accordance with previous studies (76, 78). Similarly, weak expression of A1CF in muscle (76) was confirmed at all time points in our study (Fig. S3). Therefore, liver and muscle served as references to assess A1CF expression in test samples (epididymides, testes, and ovaries). In epididymides and testes from 129/Sv mice, A1CF staining was strong in the cytoplasm but was weak in the nuclei of somatic cells at P0 and P21. In adult males, expression was reduced globally with a major cytoplasmic localization in spermatozoa and surrounding somatic cells of both tissues. Finally, A1CF staining was strong in both cellular compartments of oocytes in newborn pups and was weak in surrounding somatic cells. Staining then became saturated in eggs at all stages of maturation in weaning and adult 129/Sv females and remained relatively strong in surrounding somatic cells within the follicles of P21 and P70 ovaries.
Fig. S3.
The presence of A1CF protein in 129/Sv gonads. (A) The presence of A1CF protein in epididymides, testes, and ovaries and in muscle and liver (referents for low and high expressions of A1CF, respectively) of 129/Sv females and males at P0, P21, and P70. The same image is used for testes and epididymides at P0. Negative (isotype control) is presented only for P21 samples. (Magnification: 40×.) (Scale bars, 100 μm.) (B) Boxed areas in A are magnified 10×.
By contrast, AGO2 is widely and ubiquitously expressed in mouse embryos and adults (79–81), as it is in adult humans (Human Protein Atlas, www.proteinatlas.org/). As expected, strong expression of Ago2 was found in all tissues tested from birth to adulthood (Fig. S2).
In summary, A1CF is strongly expressed at birth in 129/Sv germ and somatic cells of the testes and declines with age. By contrast, A1CF expression increased in maturing eggs from birth to adulthood. These results suggest that A1CF, and especially maternal A1CF, may play a role in gametogenesis, fertilization, and early embryogenesis, either directly or through their downstream actions as RBPs.
Discussion
Inherited genetic and epigenetic information controls fundamental biological processes and phenotypic variation across generations. Genetic and epigenetic anomalies in the germline can lead to testicular cancer, infertility, and unusual modes of inheritance (3–6, 15, 21, 41, 54). The discovery that Apobec1, Dnd1, and Eif2s2 are potent modifiers of TGCT susceptibility with both conventional and transgenerational effects highlights the emerging role of RNA editing, miRNA regulation, and RNA availability on GC transformation and epigenetic inheritance (38–41, 63, 82). To explore this issue more deeply, we tested two hypotheses about the role of RNA biology in control of the GC lineage. If RNA editing is indeed involved, as results for APOBEC1 suggest (41), then the A1CF RBP that guides APOBEC1 to specific mRNAs for editing should show similar effects on TGCT risk and epigenetic inheritance. Similarly, if miRNA regulation is critical, as DND1 results suggest (38–40, 63), then AGO2, which regulates mRNA stability based on miRNA and siRNA targeting, should also affect TGCT risk in both conventional and epigenetic manners. As phenotypic outcomes, we focused on TGCT risk, TA abnormalities, and TRDs.
TGCT Risk.
A1cf.
A1CF is the RNA-binding cofactor for the APOBEC1 cytidine deaminase in RNA editing (55, 56, 83) and shares sequence similarity with DND1 and several other RBPs (40, 84, 85). We found that, like APOBEC1 (41) and DND1 (40), A1CF regulates TGCT susceptibility with both conventional and PofO effects, consistent with a role for RNA editing in teratocarcinogenesis.
Partial deficiency of A1cf and Apobec1 has similar PofO effects on TGCT susceptibility. Maternal heterozygosity for either of these genes reduced risk among all male offspring, regardless of their genotype (Table 1). By contrast, paternal heterozygosity had disparate consequences on TGCT risk (Table 1), i.e., an increased risk for Apobec1 and a reduced risk for A1cf (Table 1 and ref. 41), suggesting that A1CF and APOBEC1 have distinct context-dependent functions. This hypothesis is supported by the full viability and fertility of APOBEC1-deficient mice (86, 87), whereas A1CF deficiency leads to early embryonic lethality (57).
Furthermore, A1CF was found at varying levels in nucleus and cytoplasm of GCs from birth and throughout adulthood (Fig. S3). Its presence in nuclei as well as cytoplasm suggests that A1CF, like many other RBPs, has multiple functions (84, 85). Given its sequence homology with DND1 (40), A1CF, like DND1, may transport RNAs from nucleus to cytoplasm, in particular to perinuclear P-bodies under stress conditions, and may control access of specific miRNAs to their mRNA targets and perhaps contribute to other aspects of translation arrest (58, 88).
Ago2.
AGO2 is an RBP essential for oogenesis (89, 90) and early embryogenesis (61, 91) but is dispensable for spermatogenesis in mice (92). Our study revealed an additional function for AGO2 on GC fate with a strong PofO effect on TGCTs. Indeed, maternal but not paternal Ago2KO heterozygosity reduced risk among heterozygous male offspring (Table 1). This maternal effect may result from monoallelic expression because Ago2 has characteristics of imprinted genes with a CpG island located within its promotor (−554 to −47 bp from ATG, per CpG islands prediction) that contributes to maternal inheritance in mouse brain and intestinal stem cells (93, 94). However, such monoallelic expression remains to be demonstrated in the mouse germline.
AGO2 is a key factor for siRNA- and miRNA-mediated silencing events that control many downstream pathways (60). miRNA deregulation is an important contributor to tumorigenesis and tumor progression (17, 95). Altered levels of the lethal defect Let-7 miRNA family and LIN28, both regulating pluripotency in growing oocytes and early embryos (96), are characteristics of GC tumors (seminomas and nonseminomas) in humans (17, 95). Interestingly, the TGCT modifier DND1 has been reported to regulate LIN28 transcription (59) that in turn directly controls the expression of the Let-7 family (97–99), supporting the link between miRNAs, pluripotency, and TGCT risk.
Furthermore, siRNAs regulate the expression of transposable elements (TEs) after fertilization and later in primordial GCs (PGCs) (100–102). TEs are heritable mobile genetic elements that can contribute to diseases such as cancer (100, 103). Indeed, altered methylation levels of TEs are commonly found in human tumors such as TGCTs (seminomas and nonseminomas) (33, 104–106). TE regulation is also under the control of RNA editors (ADARs, APOBECs) such as the potent TGCT modifier APOBEC1 (107), emphasizing the role of TEs in TGCT risk and suggesting a functional link between AGO2 siRNAs and APOBEC1-A1CF in teratocarcinogenesis.
Filial relationships.
In humans, offspring risk is significantly elevated if the father is affected with a TGCT (seminoma or nonseminoma) (31, 32), but the genetic, epigenetic, and environmental basis for this unusual relationship is uncertain and difficult to investigate in humans. Surprisingly, in our mouse survey we found two examples in maternal Ago2KO/+ and paternal A1cfKO/+ backcrosses (Table S3). Among offspring of affected males, susceptibility was increased in Ago2KO/+ and A1cfKO/+ heterozygous offspring but not in their wild-type siblings. These results suggest that factors in the affected paternal germline potentiate the effects of TGCT modifiers such as maternal Ago2KO and paternal A1cfKO when inherited in the subsequent generation.
These paternal factors may act epigenetically to control DNA methylation. Aberrant DNA methylation is associated with familial TGCT susceptibility in humans (33, 108). DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) are known to be essential for the progression and aggressiveness of tumors such as TGCTs (109–111). In our filial TGCT cases, paternal TGCTs might express factors that indirectly alter the methylation pattern at the promotors of TEs, miRNAs, and siRNAs (33, 112, 113), inherited elements that are direct targets of TGCT modifiers such as AGO2, DND1, and APOBEC1 (58, 60, 107). The modifiers might interpret these inherited epigenetic factors in heterozygous offspring of affected parent males, resulting in an increased susceptibility compared with the wild-type siblings or heterozygous offspring of healthy male parents. Association of TE methylation status with the father–son relationship and TGCT risk in humans supports this hypothesis (33). A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ mouse models could help characterize the molecular aspects of familial TGCT cases.
Together, these results show that A1CF and AGO2 are two potent TGCT modifiers, suggesting a crucial role of RNA editing and RNA silencing as well as for miRNAs, siRNAs, and TEs in tumor formation and risk inheritance. More importantly, our study suggests that maternal factors (i.e., the maternal effect of AGO2) strongly contribute to TGCT susceptibility in the subsequent generations and that the TGCT fate of GCs may already be settled in mature eggs. At the same time, factors in affected male parents contribute to increased risk among genetically predisposed offspring.
TA Risk, Reproductive Performance, and TRD.
GCs and surrounding somatic cells (Leydig and Sertoli cells) interact from the earliest stages of the development in the urogenital ridge, ensuring normal development of both cell types (114, 115). For instance, Leydig cells control testis descent and indirectly control spermatogenesis (through interaction with Sertoli cells) (114, 115). Sertoli cells support GC migration, proliferation, and differentiation. Absence of proper cell–cell interactions leads to various gonadal abnormalities such as TGCTs, cryptorchism, and atrophy, suggesting a common developmental etiology (23–25, 114, 115). Although several signaling pathways have been characterized (115), the genetic, epigenetic, and molecular origins of such developmental abnormalities remain unclear. Our results offer insights with the identification of two factors, A1CF and AGO2, that epigenetically modulate phenotypes of the testicular dysgenesis syndrome.
TA risk.
A1cfKO/+ heterozygosity reduced the risk for both TGCTs and testicular atrophy but not for cryptorchism, but with distinct PofO effects. Maternal A1cfKO/+ heterozygosity affected atrophy risk in only one offspring genotype, whereas all progeny showed reduced TGCT risk (Table 2). Conversely, paternal A1cfKO/+ heterozygosity affected the risk for atrophy in all progeny, whereas only one offspring genotype had reduced TGCT risk (Table 2). By contrast, Ago2KO/+ heterozygosity increased the occurrence of cryptorchism, but not atrophy, only in intercrosses, whereas TGCT risk was reduced specifically in maternal Ago2KO/+ backcrosses. Interestingly, as observed in humans (18, 21–23), a strong association was also found between cryptorchism and TGCTs in 129/Sv controls, with cooccurrence fourfold greater than independent occurrence (Table S2).
Reproductive performance.
A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ heterozygotes had histologically normal gonads, although A1cfKO/+ males had lower sperm counts, which have been associated with reduced fecundity (116). However, fertility was similar in Ago2 test and 129/Sv control crosses. By contrast, the A1cfKO strain showed an increased reproductive performance with age and an increased litter index. Therefore, A1cfKO/+ heterozygosity led to shortened litter intervals and extended reproductive lifespan.
TRD.
Distorted genotypic transmission results in an atypical inheritance of specific genetic variants (117). The literature and our study reveal several RBPs, such as DND1, Pumilio1 (PUM1), and DEAD box helicase1 (DDX1) (53, 118, 119), in addition to A1CF and AGO2, which show TRD in mice (Table 3) (57, 61). TRD either favors (A1cfKO, Ddx1KO, Pum1KO) or disfavors (Ago2KO, Dnd1KO) heterozygotes relative to wild-type (53, 57, 118, 119).
TRD may arise during gametogenesis, at fertilization, or during embryonic development, but in general the mechanisms are poorly understood (118). With rare exceptions, all ovulated eggs are fertilized. Therefore, the number of ovulated eggs, which is determined before mating, dictates litter size. For the A1cfKO and Ago2KO strains, complete embryonic lethality of homozygotes (57, 61) should reduce the litter sizes among intercrosses by 25% compared with backcrosses. However, the normal litter size in A1cf intercrosses suggests that genotype ratios differed significantly from Mendelian expectations without embryo loss of either wild types or heterozygotes. By contrast, the reduced litter size in Ago2 intercrosses is consistent with the loss of homozygotes but not with reduced viability of heterozygotes; otherwise the average litter size for Ago2 intercrosses would have been reduced by 50% compared with the backcrosses. Litter size and related measures of reproductive performance are not often reported but are essential for critically evaluating the consequences of genetic variants on meiosis, gametogenesis, and embryonic viability.
Conclusion
To ensure the viability and fertility of later generations, various molecular mechanisms monitor the germline for anomalies in DNA repair, DNA replication, cell-cycle control, and unpaired chromosomes (6, 120–123). Gametes must have the proper genetic constitution with few mutations or chromosome aberrations and appropriate epigenetic features (124, 125). Pluripotency must be rigorously controlled in the unipotent germline. When surveillance and pluripotency controls fail, infertility, embryonic lethality, gonadal dysgenesis, tumors, and TRD can ensue. Interestingly, many of these abnormalities are found in Dnd1 (40, 53), Pum1 (119, 126), Ddx1 (118, 127), Prdm9 (122), and A1cf and Ago2 mutants (Tables 1–4). These genes, which encode factors controlling RNA availability for translation, reveal the essential role of RNA biology and epigenetics in fundamental aspects of germline surveillance.
Materials and Methods
The Pacific Northwest Diabetes Research Institute Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all studies and procedures. We used two mutants, A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+, and two kinds of crosses: reciprocal backcrosses to the 129/Sv wild-type mice and intercrosses. All killed males were examined for TGCTs and TAs (128). The χ2 contingency and goodness-of-fit tests were used as appropriate to test relations between TAs, TGCTs, genotype, and paternal phenotype. Previously described methods were used to test for departures from Mendelian expectations of genotype segregation among intercross progeny (129). In all cases, the significance threshold was set at 0.05. To minimize the risk of false positives with multiple comparisons, we computed the false-discovery rate (FDR) (130), set at 0.1, for the six comparisons in each “gene family” of tests. Finally, fold-change was used as a measure of effect size. Emphasis was given to results that were statistically significant after estimation of the FDR and to some rare exceptions with strong effects (fold change >2). All methods are described in SI Materials and Methods and in refs. 131–133.
To control for substrain effects on the TGCT risk in the 129/Sv strain and mutant substrains, we backcrossed both mutants to 129/Sv and surveyed offspring for TGCTs over three generations (N1–N3). Any genetic difference between substrains that was not linked to either theA1cfKO or Ago2KO mutants should be lost at a rate of 0.5 per generation, with a probability of persisting over the three backcross generations in any given family line of 0.125. With multiple families for each mutant, the probability of a significant background effect is negligible. However, to test directly for possible substrain effects, we examined the occurrence of affected mice for each mutant for backcross generations N1–N3. The χ2 contingency tests did not detect significant changes across generations (thresholds P < 0.05, FDR <0.1; see Table S7).
Table S7.
Occurrence of TGCT-affected males per generation in A1cfKO/+ and Ago2KO/+ reciprocal backcrosses
| Crosses | Offspring genotype | No. generation | No. males | Affected males | Test score χ2, P-value | |
| No. | Frequency, % | |||||
| A1cfKO/+ test crosses | ||||||
| A1cfKO/+ × 129/Sv | Wild-type | 1 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 1.4y, NS |
| 2 | 81 | 1 | 1.2 | |||
| 3 | 17 | 0 | 0 | |||
| A1cfKO/+ | 1 | 32 | 2 | 6.2 | 0.4y, NS | |
| 2 | 89 | 2 | 2.2 | |||
| 3 | 17 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 129/Sv × A1cfKO/+ | Wild-type | 1 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0.6y, NS |
| 2 | 44 | 1 | 2.3 | |||
| 3 | 53 | 4 | 7.5 | |||
| A1cfKO/+ | 1 | 22 | 1 | 4.5 | 0.7y, NS | |
| 2 | 52 | 2 | 3.8 | |||
| 3 | 62 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Ago2KO/+ test crosses | ||||||
| Ago2KO/+ × 129/Sv | Wild-type | 1 | 46 | 0 | 0 | 1.5y, NS |
| 2 | 45 | 3 | 6.7 | |||
| 3 | 24 | 2 | 8.3 | |||
| Ago2KO/+ | 1 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 0.5y, NS | |
| 2 | 44 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 3 | 20 | 1 | 5 | |||
| 129/Sv × Ago2KO/+ | Wild-type | 1 | 51 | 2 | 3.9 | 0.1y, NS |
| 2 | 93 | 4 | 4.3 | |||
| Ago2KO/+ | 1 | 50 | 1 | 2 | <0.1y, NS | |
| 2 | 103 | 4 | 3.9 | |||
The χ2 contingency tests were used to compare occurrence of TGCT-affected males in each generation. χ2 and P values are indicated for each test result (df = 2). NS indicates results that did not pass the threshold of statistical significance. y indicates Yate’s correction was applied to the test.
SI Materials and Methods
Mice.
Wild-type control 129S1/SvImJ mice (JR002448; hereafter referred to as “129/Sv mice”) were obtained from the Jackson Laboratory. We generated 129/Sv-A1cfKO mutant mice (hereafter referred to as “A1cfKO mice”) from an A1cf-targeted ES cell line derived from 129X1/SvJ mice in which a GFP and phosphoglycerate kinase I (PGK)-neomycin cassette replaced exon 2 that contains the initiator ATG in the A1cf gene (57). We also generated 129/Sv-Ago2Gt(XE344)Byg/Mmucd mice (hereafter referred to as “Ago2KO mice”) from the mutant ES cell line XE344 derived from 129P2/OlaHsd mice originally created by Bay Genomics (61). A gene-trap vector, pGT1Lxf, was inserted downstream of exon 1 in the Ago2 gene. In both cases, targeted clones were injected into blastocysts to generate chimeras at the Transgenic Resources Program of the University of Washington, Seattle. Three A1cfKO and five Ago2KO chimeras were obtained. The A1cfKO strain is on a mixed 129X1/SvJ and 129/Sv background and is available at the Jackson Laboratory (https://www.jax.org/) under the stock no. 027924. The Ago2KO strain is on a mixed 129P1/OlaHsd and 129/Sv background and is available at the Mutant Mouse Resource and Research Center, University of California, Davis, under the stock no. 037123-UCD. Mice were maintained in the Pacific Northwest Diabetes Research Institute (PNDRI) animal facility on a 12:12-h light:dark cycle with chow (Animal Specialties PicoLab diet 5053) and water supplied ad libitum and with irradiated corn cob bedding (Harlan Teklad). The PNDRI Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all studies and procedures. Two kinds of crosses were used with A1cfKO and Ago2KO heterozygous mice: (i) reciprocal backcrosses to 129/Sv wild-type mice [three generations for each mutant; mice from each generation (N1–N3) were included in the survey], and (ii) heterozygous mutant intercrosses. A1cfKO and Ago2KO homozygous embryos both die early during development (57, 61).
Genotyping.
DNA was extracted from ear punches by incubation in Hot Shot lysis buffer [0.2 mM EDTA (pH 8), 25 mM NaOH] at 95 °C for 30 min (adapted from ref. 131) and then amplified using KAPA2G Fast genotyping PCR kit (Kapa Biosystems, catalog no. KK5621). PCR experiments were carried out with either an MJ Research PTC-200 or a T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad), using similar conditions for both genes, apart for the annealing temperature: 3 min at 95 °C, 30 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 55 °C for 15 s, and 72 °C for 10 s for A1cf and 95 °C for 15 s, 57 °C for 15 s, and 72 °C for 10 s for Ago2. A set of three primers was used to distinguish wild-type and mutant alleles as previously described (57, 61). PCR products were analyzed with 2% (wt/vol) agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide.
Histology.
Mice were killed with CO2 inhalation, and tissue samples were harvested with blinded genotype. All males were examined for tumors and other urogenital abnormalities including cryptorchidism and atrophy (testicular atrophy or agonadism) (128). Testes of uncertain phenotype were examined histologically. Each phenotype was scored for laterality. For males with healthy testes, testes and body weights were recorded, and the G/B ratio was calculated. Testes were preserved in modified Davidson’s buffer [31.7 mL glacial EtOH, 22.2 mL formaldehyde 37% (vol/vol), 11 mL acetic acid, and distilled water for a total volume of 100 mL] for 24 h. Ovaries and other samples were preserved in 4% (wt/vol) paraformaldehyde (Affymetrix catalog no. 19943) for 48 h. Fixed samples were sent to the Histopathology Core at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, for paraffin embedding, sectioning (6 microns), and staining with H&E.
Egg Count.
Left ovaries were collected from prepubertal (at weaning) 129/Sv control, A1cfKO/+, and Ago2KO/+ heterozygous females of reciprocal backcrosses. The number of oocytes was counted as a total egg number/mm2 in every third section over a total of 10 sections per ovary with at least three ovaries per genotype (Fig. S1A). The stage of each egg was scored distinguishing primary, secondary, early antral, antral, and preovulatory follicles by their size (<50 μm, 50–150 μm, 150–250 μm, 250–400 μm, and at least 400 μm, respectively) and by their morphology as described previously (133). No preovulatory follicles were found. The area of each section was estimated using grid and geometric approximation.
Sperm.
Mature sperm were isolated from epididymides of adult (>70-d-old) 129/Sv control, A1cfKO/+, and Ago2KO/+ heterozygous males of reciprocal backcrosses. At least three epididymides per genotype were separately minced and incubated in minimum essential medium (Gibco by Life Technology, no. 11095-072) at 37 °C for 1 h. Diluted (1/10) mature sperm was then quantified as the number of sperm × 106/mL with a Petroff–Hauser Counting chamber (Fig. S1B).
Reproductive Performance.
The following traits were examined (adapted from ref. 74):
Average litter size. Litter size was calculated as the mean number of weaned pups. Breeders failing to produce a litter were excluded. Preweaning mortality was not systematically recorded but was found at a low and similar rate among all strains.
Litter interval. The litter interval was measured as the time (days) between mating and first litters. Because our breeding scheme was based on trio matings, the intervals between subsequent litters could not be measured reliably.
Litter index. The litter index measures the persistency with which animals continue to breed and was calculated as the mean of the total number of litters produced from the initial mating to the last litter, divided by the theoretical total number of litters that should be obtained during the same interval (the mean litter interval of each strain was used as reference to calculate this theoretical number). For example, a trio of 129/Sv mice giving three litters over a period of 100 d should give theoretically a total of nine litters [i.e., 2(100/21.9) because the mean interval for 129/Sv strain in our study was 21.9 d and each mating had two females for one male]. Therefore, the litter index of this example is 0.33.
Total RNA Extraction and PCR Analysis.
RNA was extracted from testes, epididymides, ovaries, muscle, and liver of at least three 129/Sv males and females at different time points (newborn, P0; weaning, P21; and adult, P70 or older) by the guanidinium thiocyanate/phenol/chloroform extraction protocol (132). First-strand cDNA was generated from 1 μg of total RNA using random primers and Omniscript Reverse Transcriptase (Qiagen). cDNA (1/50th of the final PCR volume) was then amplified using the KAPA2G Fast genotyping PCR kit (KAPABIOSYSTEMS, catalog no. KK5621). PCR experiments were carried out with either an MJ Research PTC-200 or a T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad) using similar conditions for both genes: 3 min at 95 °C and at least 30 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 15 s, and 72 °C for 10 s. Primer pairs designed with the National Center for Biotechnology Information primer design tool (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/index.cgi?LINK_LOC=reset) and separated by at least one intron were A1cf, forward 5′-CTGCCAGGAAGAATTCAGTTG-3′ and reverse 5′-CCGGGTGTACCTAACATAACT-3′; Ago2, forward 5′-CCGTTCTTGCTTCTCCTGCTC-3′ and reverse 5′-GCCTGTAGTTTGATTGTTCTCCC-3′; and 18S ribosomal RNA, forward 5′-GACTCAACACGGGAAACCTC-3′ and reverse 5′-AGACAAATCGCTCCACCAAC-3′, producing 345-bp, 109-bp, and 120-bp PCR products, respectively.
Immunohistochemistry.
Fixed testes, epididymides, ovaries, muscle, and liver from at least three 129/Sv males and females taken at the same time points as RNA extraction were sent to the Histopathology Core at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center for sectioning and immunohistochemistry. Tissue sections were incubated with a purified rabbit polyclonal antibody against A1CF (dilution 1:500; Abcam, no. ab99955) in a high stringency diluent and then with an anti-rabbit HRP polymer (Leica PowerVision PV6119). Tissue staining was developed with diaminobenzidine (DAB) and counterstained with hematoxylin (Biocare NM-HEM-M). For each experimental set, one negative control was stained in parallel with an isotype control (rabbit IgG) at 1 μg/mL on serial sections used for the antibody tests.
Imaging.
All photographs and microscans were taken with Leica Application Suite X (LASX) software and a Leica microscope (type DM6000B), camera (DMC 2900, C-mount 0.70×), and objective HCX PL Fluotar 40×/0.75 dry.
Statistics.
The χ2 contingency and goodness-of-fit tests were used as appropriate to test relations between TAs, TGCTs, genotype, and paternal phenotype. For the goodness-of-fit test, the expected frequency of affected males was 7% for TGCTs (34, 41, 62, 63) or TAs, the frequency observed in the 129/Sv controls. Yate’s correction was applied when the observed number was less than five, and a “y” was added as superscript to the χ2 value to highlight these cases. Previously described methods were used to test for departures from Mendelian expectations of genotype segregation among intercross progeny (129). In all cases, the significance threshold was set at 0.05. To minimize the risk of false positives with multiple comparisons, we computed the FDR (130), set at 0.1, for the six comparisons in each gene family of tests. Finally, fold-change was used as a measure of effect size. Emphasis was given to results that were statistically significant after estimation of the FDR and the rare exceptions that nonetheless show strong effect sizes (fold change >2).
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Richard D. Palmiter for assistance during the chimera development and Dr. Steve Schwartz (Hutchinson Cancer Research Center) for discussing several analytical issues. This work was supported by National Cancer Institute Grant CA75056 and NIH Pioneer Award DP1HD075624 (to J.H.N.) and by NIH Grants HL-38180, DK-52574, and DK-56260 (to N.O.D.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1604773113/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Lawson KA, Hage WJ. Clonal analysis of the origin of primordial germ cells in the mouse. Ciba Found Symp. 1994;182:68–84, discussion 84–91. doi: 10.1002/9780470514573.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lesch BJ, Dokshin GA, Young RA, McCarrey JR, Page DC. A set of genes critical to development is epigenetically poised in mouse germ cells from fetal stages through completion of meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(40):16061–16066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315204110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stevens LC. Origin of testicular teratomas from primordial germ cells in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1967;38(4):549–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bustamante-Marín X, Garness JA, Capel B. Testicular teratomas: An intersection of pluripotency, differentiation and cancer biology. Int J Dev Biol. 2013;57(2-4):201–210. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.130136bc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Saitou M, Yamaji M. Primordial germ cells in mice. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4(11):a008375. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Heaney JD, et al. Germ cell pluripotency, premature differentiation and susceptibility to testicular teratomas in mice. Development. 2012;139(9):1577–1586. doi: 10.1242/dev.076851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rijlaarsdam MA, Looijenga LH. An oncofetal and developmental perspective on testicular germ cell cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;29:59–74. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vasdev N, Moon A, Thorpe AC. Classification, epidemiology and therapies for testicular germ cell tumours. Int J Dev Biol. 2013;57(2-4):133–139. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.130031nv. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kanetsky PA, et al. Common variation in KITLG and at 5q31.3 predisposes to testicular germ cell cancer. Nat Genet. 2009;41(7):811–815. doi: 10.1038/ng.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rapley EA, et al. UK Testicular Cancer Collaboration A genome-wide association study of testicular germ cell tumor. Nat Genet. 2009;41(7):807–810. doi: 10.1038/ng.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Turnbull C, et al. UK Testicular Cancer Collaboration Variants near DMRT1, TERT and ATF7IP are associated with testicular germ cell cancer. Nat Genet. 2010;42(7):604–607. doi: 10.1038/ng.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kratz CP, et al. Variants in or near KITLG, BAK1, DMRT1, and TERT-CLPTM1L predispose to familial testicular germ cell tumour. J Med Genet. 2011;48(7):473–476. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ruark E, et al. UK Testicular Cancer Collaboration (UKTCC) Identification of nine new susceptibility loci for testicular cancer, including variants near DAZL and PRDM14. Nat Genet. 2013;45(6):686–689. doi: 10.1038/ng.2635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chung CC, et al. Meta-analysis identifies four new loci associated with testicular germ cell tumor. Nat Genet. 2013;45(6):680–685. doi: 10.1038/ng.2634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Karlsson R, et al. Investigation of six testicular germ cell tumor susceptibility genes suggests a parent-of-origin effect in SPRY4. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(16):3373–3380. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Skakkebaek NE, et al. Male reproductive disorders and fertility trends: Influences of environment and genetic susceptibility. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(1):55–97. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00017.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rijlaarsdam MA, et al. Identification of known and novel germ cell cancer-specific (embryonic) miRs in serum by high-throughput profiling. Andrology. 2015;3(1):85–91. doi: 10.1111/andr.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.McGlynn KA, Cook MB. Etiologic factors in testicular germ-cell tumors. Future Oncol. 2009;5(9):1389–1402. doi: 10.2217/fon.09.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Walsh TJ, Dall’Era MA, Croughan MS, Carroll PR, Turek PJ. Prepubertal orchiopexy for cryptorchidism may be associated with lower risk of testicular cancer. J Urol. 2007;178(4 Pt 1):1440–1446, discussion 1446. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.05.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wood HM, Elder JS. Cryptorchidism and testicular cancer: Separating fact from fiction. J Urol. 2009;181(2):452–461. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.10.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Greene MH, et al. Familial testicular germ cell tumors in adults: 2010 summary of genetic risk factors and clinical phenotype. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17(2):R109–R121. doi: 10.1677/ERC-09-0254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ferguson L, Agoulnik AI. Testicular cancer and cryptorchidism. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2013;4:32. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jørgensen A, et al. Pathogenesis of germ cell neoplasia in testicular dysgenesis and disorders of sex development. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;45:124–137. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Skakkebaek NE, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Main KM. Testicular dysgenesis syndrome: An increasingly common developmental disorder with environmental aspects. Hum Reprod. 2001;16(5):972–978. doi: 10.1093/humrep/16.5.972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dalgaard MD, et al. A genome-wide association study of men with symptoms of testicular dysgenesis syndrome and its network biology interpretation. J Med Genet. 2012;49(1):58–65. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lawaetz AC, Almstrup K. Involvement of epigenetic modifiers in the pathogenesis of testicular dysgenesis and germ cell cancer. Biomol Concepts. 2015;6(3):219–227. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2015-0006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lawson HA, Cheverud JM, Wolf JB. Genomic imprinting and parent-of-origin effects on complex traits. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14(9):609–617. doi: 10.1038/nrg3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kong A, et al. DIAGRAM Consortium Parental origin of sequence variants associated with complex diseases. Nature. 2009;462(7275):868–874. doi: 10.1038/nature08625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cassidy SB, Schwartz S, Miller JL, Driscoll DJ. Prader-Willi syndrome. Genet Med. 2012;14(1):10–26. doi: 10.1038/gim.0b013e31822bead0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mabb AM, Judson MC, Zylka MJ, Philpot BD. Angelman syndrome: Insights into genomic imprinting and neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Trends Neurosci. 2011;34(6):293–303. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2011.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hemminki K, Li X. Familial risk in testicular cancer as a clue to a heritable and environmental aetiology. Br J Cancer. 2004;90(9):1765–1770. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Valberg M, et al. A hierarchical frailty model for familial testicular germ-cell tumors. Am J Epidemiol. 2014;179(4):499–506. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwt267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mirabello L, Savage SA, Korde L, Gadalla SM, Greene MH. LINE-1 methylation is inherited in familial testicular cancer kindreds. BMC Med Genet. 2010;11:77. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stevens LC, Little CC. Spontaneous testicular teratomas in an inbred strain of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1954;40(11):1080–1087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.11.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Metcalfe PD, et al. Pediatric testicular tumors: Contemporary incidence and efficacy of testicular preserving surgery. J Urol. 2003;170(6 Pt 1):2412–2415, discussion 2415–2416. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000097383.09743.f9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nielsen JE, et al. A novel double staining strategy for improved detection of testicular carcinoma in situ cells in human semen samples. Andrologia. 2012;44(2):78–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2010.01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cao D, et al. RNA-binding protein LIN28 is a marker for testicular germ cell tumors. Hum Pathol. 2011;42(5):710–718. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2010.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Noguchi T, Noguchi M. A recessive mutation (ter) causing germ cell deficiency and a high incidence of congenital testicular teratomas in 129/Sv-ter mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985;75(2):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sakurai T, Katoh H, Moriwaki K, Noguchi T, Noguchi M. The ter primordial germ cell deficiency mutation maps near Grl-1 on mouse chromosome 18. Mamm Genome. 1994;5(6):333–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00356550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Youngren KK, et al. The Ter mutation in the dead end gene causes germ cell loss and testicular germ cell tumours. Nature. 2005;435(7040):360–364. doi: 10.1038/nature03595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nelson VR, Heaney JD, Tesar PJ, Davidson NO, Nadeau JH. Transgenerational epigenetic effects of the Apobec1 cytidine deaminase deficiency on testicular germ cell tumor susceptibility and embryonic viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(41):E2766–E2773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207169109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Rotter V, et al. Mice with reduced levels of p53 protein exhibit the testicular giant-cell degenerative syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90(19):9075–9079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Raymond CS, Murphy MW, O’Sullivan MG, Bardwell VJ, Zarkower D. Dmrt1, a gene related to worm and fly sexual regulators, is required for mammalian testis differentiation. Genes Dev. 2000;14(20):2587–2595. doi: 10.1101/gad.834100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Carouge D, Nadeau J. 2012 Mouse models of testicular cell tumors. Germ Cell Tumor, ed Matin A (IntechOpen), pp 75–106. Available at www.intechopen.com/about-open-access.html. Accessed March 30, 2012.
- 45.Xin F, Susiarjo M, Bartolomei MS. Multigenerational and transgenerational effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals: A role for altered epigenetic regulation? Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;43:66–75. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.05.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schaefer S, Nadeau JH. The genetics of epigenetic inheritance: Modes, molecules, and mechanisms. Q Rev Biol. 2015;90(4):381–415. doi: 10.1086/683699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Heaney JD, Lam MY, Michelson MV, Nadeau JH. Loss of the transmembrane but not the soluble kit ligand isoform increases testicular germ cell tumor susceptibility in mice. Cancer Res. 2008;68(13):5193–5197. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Crow JF. The ultraselfish gene. Genetics. 1988;118(3):389–391. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sugimoto M. Developmental genetics of the mouse t-complex. Genes Genet Syst. 2014;89(3):109–120. doi: 10.1266/ggs.89.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bidwell CA, et al. New insights into polar overdominance in callipyge sheep. Anim Genet. 2014;45(Suppl 1):51–61. doi: 10.1111/age.12132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gell SL, Reenan RA. Mutations to the piRNA pathway component aubergine enhance meiotic drive of segregation distorter in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 2013;193(3):771–784. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.147561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Yang L, et al. Parental effect of DNA (Cytosine-5) methyltransferase 1 on grandparental-origin-dependent transmission ratio distortion in mouse crosses and human families. Genetics. 2008;178(1):35–45. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.081562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zechel JL, et al. Contrasting effects of Deadend1 (Dnd1) gain and loss of function mutations on allelic inheritance, testicular cancer, and intestinal polyposis. BMC Genet. 2013;14:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Jablonka E, Lamb MJ. The inheritance of acquired epigenetic variations. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(4):1094–1103. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyv020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lellek H, et al. Purification and molecular cloning of a novel essential component of the apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme-complex. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(26):19848–19856. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001786200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lellek H, Welker S, Diehl I, Kirsten R, Greeve J. Reconstitution of mRNA editing in yeast using a Gal4-apoB-Gal80 fusion transcript as the selectable marker. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(26):23638–23644. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203517200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Blanc V, et al. Targeted deletion of the murine apobec-1 complementation factor (acf) gene results in embryonic lethality. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(16):7260–7269. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.16.7260-7269.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kedde M, et al. RNA-binding protein Dnd1 inhibits microRNA access to target mRNA. Cell. 2007;131(7):1273–1286. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhu R, Iacovino M, Mahen E, Kyba M, Matin A. Transcripts that associate with the RNA binding protein, DEAD-END (DND1), in embryonic stem (ES) cells. BMC Mol Biol. 2011;12:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-12-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Suh N, Blelloch R. Small RNAs in early mammalian development: From gametes to gastrulation. Development. 2011;138(9):1653–1661. doi: 10.1242/dev.056234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Morita S, et al. One Argonaute family member, Eif2c2 (Ago2), is essential for development and appears not to be involved in DNA methylation. Genomics. 2007;89(6):687–696. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Stevens LC, Hummel KP. A description of spontaneous congenital testicular teratomas in strain 129 mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1957;18(5):719–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lam MY, Heaney JD, Youngren KK, Kawasoe JH, Nadeau JH. Trans-generational epistasis between Dnd1Ter and other modifier genes controls susceptibility to testicular germ cell tumors. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16(18):2233–2240. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Giwercman A, Giwercman YL. 2000. Epidemiology of Male Reproductive Disorders (Endotext) Available at www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279020/. Accessed August 23, 2013.
- 65.Youngren KK, Nadeau JH, Matin A. Testicular cancer susceptibility in the 129.MOLF-Chr19 mouse strain: Additive effects, gene interactions and epigenetic modifications. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12(4):389–398. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Akre O, Pettersson A, Richiardi L. Risk of contralateral testicular cancer among men with unilaterally undescended testis: A meta analysis. Int J Cancer. 2009;124(3):687–689. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Elert A, Jahn K, Heidenreich A, Hofmann R. [The familial undescended testis] Klin Padiatr. 2003;215(1):40–45. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-36894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Stone JM, Cruickshank DG, Sandeman TF, Matthews JP. Laterality, maldescent, trauma and other clinical factors in the epidemiology of testis cancer in Victoria, Australia. Br J Cancer. 1991;64(1):132–138. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bustamante-Marin XM, Cook MS, Gooding J, Newgard C, Capel B. Left-biased spermatogenic failure in 129/svj dnd1ter/+ mice correlates with differences in vascular architecture, oxygen availability, and metabolites. Biol Reprod. 2015;93(3):78. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.115.128850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Rivers EN, Hamilton DW. Morphologic analysis of spontaneous teratocarcinogenesis in developing testes of strain 129/Sv-ter mice. Am J Pathol. 1986;124(2):263–280. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kumar D, Boehm U. Genetic dissection of puberty in mice. Exp Physiol. 2013;98(11):1528–1534. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2013.071928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Garcia JM, et al. Ghrelin prevents cisplatin-induced testicular damage by facilitating repair of dna double strand breaks through activation of p53 in mice. Biol Reprod. 2015;93(1):24. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.115.129759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Turner LM, Harr B. Genome-wide mapping in a house mouse hybrid zone reveals hybrid sterility loci and Dobzhansky-Muller interactions. eLife. 2014;3:3. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Festing M. Some aspects of reproductive performance in inbred mice. Lab Anim. 1968;2:89–100. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Finn CA. Reproductive capacity and litter size in mice: Effect of age and environment. J Reprod Fertil. 1963;6:205–214. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0060205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Dür S, Krause K, Pluntke N, Greeve J. Gene structure and expression of the mouse APOBEC-1 complementation factor: Multiple transcriptional initiation sites and a spliced variant with a premature stop translation codon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1680(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2004.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mehta A, Kinter MT, Sherman NE, Driscoll DM. Molecular cloning of apobec-1 complementation factor, a novel RNA-binding protein involved in the editing of apolipoprotein B mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(5):1846–1854. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.5.1846-1854.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Blanc V, Sessa KJ, Kennedy S, Luo J, Davidson NO. Apobec-1 complementation factor modulates liver regeneration by post-transcriptional regulation of interleukin-6 mRNA stability. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(25):19184–19192. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Cheloufi S, Dos Santos CO, Chong MM, Hannon GJ. A dicer-independent miRNA biogenesis pathway that requires Ago catalysis. Nature. 2010;465(7298):584–589. doi: 10.1038/nature09092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Liu J, et al. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science. 2004;305(5689):1437–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.1102513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lü J, et al. Differential expression of components of the microRNA machinery during mouse organogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;334(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.05.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Heaney JD, Michelson MV, Youngren KK, Lam MY, Nadeau JH. Deletion of eIF2beta suppresses testicular cancer incidence and causes recessive lethality in agouti-yellow mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18(8):1395–1404. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Blanc V, Kennedy S, Davidson NO. A novel nuclear localization signal in the auxiliary domain of apobec-1 complementation factor regulates nucleocytoplasmic import and shuttling. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(42):41198–41204. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302951200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Gerstberger S, Hafner M, Tuschl T. A census of human RNA-binding proteins. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(12):829–845. doi: 10.1038/nrg3813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Gerstberger S, Hafner M, Ascano M, Tuschl T. Evolutionary conservation and expression of human RNA-binding proteins and their role in human genetic disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;825:1–55. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1221-6_1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hirano K, Min J, Funahashi T, Davidson NO. Cloning and characterization of the rat apobec-1 gene: A comparative analysis of gene structure and promoter usage in rat and mouse. J Lipid Res. 1997;38(6):1103–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Nakamuta M, et al. Complete phenotypic characterization of apobec-1 knockout mice with a wild-type genetic background and a human apolipoprotein B transgenic background, and restoration of apolipoprotein B mRNA editing by somatic gene transfer of Apobec-1. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(42):25981–25988. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.42.25981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Slanchev K, et al. Control of Dead end localization and activity--implications for the function of the protein in antagonizing miRNA function. Mech Dev. 2009;126(3-4):270–277. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2008.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Kaneda M, Tang F, O’Carroll D, Lao K, Surani MA. Essential role for Argonaute2 protein in mouse oogenesis. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2009;2(1):9. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-2-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Stein P, et al. Essential Role for endogenous siRNAs during meiosis in mouse oocytes. PLoS Genet. 2015;11(2):e1005013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Lykke-Andersen K, et al. Maternal Argonaute 2 is essential for early mouse development at the maternal-zygotic transition. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19(10):4383–4392. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-02-0219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Hayashi K, et al. MicroRNA biogenesis is required for mouse primordial germ cell development and spermatogenesis. PLoS One. 2008;3(3):e1738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Court F, et al. Genome-wide allelic methylation analysis reveals disease-specific susceptibility to multiple methylation defects in imprinting syndromes. Hum Mutat. 2013;34(4):595–602. doi: 10.1002/humu.22276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Kaaij LT, et al. DNA methylation dynamics during intestinal stem cell differentiation reveals enhancers driving gene expression in the villus. Genome Biol. 2013;14(5):R50. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-5-r50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Murray MJ, Nicholson JC, Coleman N. Biology of childhood germ cell tumours, focussing on the significance of microRNAs. Andrology. 2015;3(1):129–139. doi: 10.1111/andr.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Büssing I, Slack FJ, Grosshans H. let-7 microRNAs in development, stem cells and cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14(9):400–409. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2008.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Viswanathan SR, Daley GQ, Gregory RI. Selective blockade of microRNA processing by Lin28. Science. 2008;320(5872):97–100. doi: 10.1126/science.1154040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Viswanathan SR, et al. Lin28 promotes transformation and is associated with advanced human malignancies. Nat Genet. 2009;41(7):843–848. doi: 10.1038/ng.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Murray MJ, et al. CCLG LIN28 Expression in malignant germ cell tumors downregulates let-7 and increases oncogene levels. Cancer Res. 2013;73(15):4872–4884. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Goodier JL, Kazazian HHJ., Jr Retrotransposons revisited: The restraint and rehabilitation of parasites. Cell. 2008;135(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Banisch TU, Goudarzi M, Raz E. Small RNAs in germ cell development. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012;99:79–113. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387038-4.00004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Hajkova P, et al. Epigenetic reprogramming in mouse primordial germ cells. Mech Dev. 2002;117(1-2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(02)00181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.McCLINTOCK B. The origin and behavior of mutable loci in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1950;36(6):344–355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.36.6.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Aporntewan C, et al. Hypomethylation of intragenic LINE-1 represses transcription in cancer cells through AGO2. PLoS One. 2011;6(3):e17934. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Ushida H, et al. Methylation profile of DNA repetitive elements in human testicular germ cell tumor. Mol Carcinog. 2012;51(9):711–722. doi: 10.1002/mc.20831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Amatruda JF, et al. DNA methylation analysis reveals distinct methylation signatures in pediatric germ cell tumors. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:313. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Knisbacher BA, Levanon EY. DNA and RNA editing of retrotransposons accelerate mammalian genome evolution. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1341:115–125. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Mirabello L, Kratz CP, Savage SA, Greene MH. Promoter methylation of candidate genes associated with familial testicular cancer. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2012;3(3):213–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Minami K, et al. DNMT3L is a novel marker and is essential for the growth of human embryonal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(10):2751–2759. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Jin B, et al. Linking DNA methyltransferases to epigenetic marks and nucleosome structure genome-wide in human tumor cells. Cell Reports. 2012;2(5):1411–1424. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.10.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Wongtrakoongate P. Epigenetic therapy of cancer stem and progenitor cells by targeting DNA methylation machineries. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(1):137–148. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Chen BF, Gu S, Suen YK, Li L, Chan WY. microRNA-199a-3p, DNMT3A, and aberrant DNA methylation in testicular cancer. Epigenetics. 2014;9(1):119–128. doi: 10.4161/epi.25799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Cheung HH, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling reveals novel epigenetically regulated genes and non-coding RNAs in human testicular cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010;102(2):419–427. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Sharpe RM, Maddocks S, Kerr JB. Cell-cell interactions in the control of spermatogenesis as studied using Leydig cell destruction and testosterone replacement. Am J Anat. 1990;188(1):3–20. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001880103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.van der Zwan YG, Biermann K, Wolffenbuttel KP, Cools M, Looijenga LH. Gonadal maldevelopment as risk factor for germ cell cancer: Towards a clinical decision model. Eur Urol. 2015;67(4):692–701. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Bonde JP, et al. [Semen quality and fertility in a population-based follow-up study] Ugeskr Laeger. 1999;161(47):6485–6489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Werren JH. Selfish genetic elements, genetic conflict, and evolutionary innovation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(Suppl 2):10863–10870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102343108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Hildebrandt MR, Germain DR, Monckton EA, Brun M, Godbout R. Ddx1 knockout results in transgenerational wild-type lethality in mice. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9829. doi: 10.1038/srep09829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Zhang C, Zhu T, Chen Y, Xu EY. Loss of preimplantation embryo resulting from a Pum1 gene trap mutation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;462(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Shiu PK, Raju NB, Zickler D, Metzenberg RL. Meiotic silencing by unpaired DNA. Cell. 2001;107(7):905–916. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00609-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Sun S, et al. Xist imprinting is promoted by the hemizygous (unpaired) state in the male germ line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(47):14415–14422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519528112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Bhattacharyya T, et al. Mechanistic basis of infertility of mouse intersubspecific hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(6):E468–E477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219126110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Cook MS, Coveney D, Batchvarov I, Nadeau JH, Capel B. BAX-mediated cell death affects early germ cell loss and incidence of testicular teratomas in Dnd1(Ter/Ter) mice. Dev Biol. 2009;328(2):377–383. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.01.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Holliday R, Jeggo PA. Mechanisms for changing gene expression and their possible relationship to carcinogenesis. Cancer Surv. 1985;4(3):557–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Plasschaert RN, Bartolomei MS. Genomic imprinting in development, growth, behavior and stem cells. Development. 2014;141(9):1805–1813. doi: 10.1242/dev.101428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Chen D, et al. Pumilio 1 suppresses multiple activators of p53 to safeguard spermatogenesis. Curr Biol. 2012;22(5):420–425. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.01.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Tanaka K, Okamoto S, Ishikawa Y, Tamura H, Hara T. DDX1 is required for testicular tumorigenesis, partially through the transcriptional activation of 12p stem cell genes. Oncogene. 2009;28(21):2142–2151. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Zhu R, Matin A. Tumor loci and their interactions on mouse chromosome 19 that contribute to testicular germ cell tumors. BMC Genet. 2014;15:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-15-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Nakouzi GA, Nadeau JH. Does dietary folic acid supplementation in mouse NTD models affect neural tube development or gamete preference at fertilization? BMC Genet. 2014;15:91. doi: 10.1186/s12863-014-0091-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Klipper-Aurbach Y, et al. Mathematical formulae for the prediction of the residual beta cell function during the first two years of disease in children and adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Med Hypotheses. 1995;45(5):486–490. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(95)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Truett GE, et al. Preparation of PCR-quality mouse genomic DNA with hot sodium hydroxide and tris (HotSHOT) Biotechniques. 2000;29(1):52–54, 54. doi: 10.2144/00291bm09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Myers M, Britt KL, Wreford NG, Ebling FJ, Kerr JB. Methods for quantifying follicular numbers within the mouse ovary. Reproduction. 2004;127(5):569–580. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.00095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]