Abstract
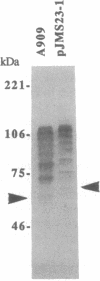
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is the leading cause of neonatal sepsis and meningitis in the United States. The surface-associated C protein alpha antigen of GBS is thought to have a role in both virulence and immunity. We previously cloned the C protein alpha antigen structural gene (named bca for group B, C protein, alpha) into Escherichia coli. Western blots of both the native alpha antigen and the cloned gene product demonstrate a regularly laddered pattern of heterogeneous polypeptides. The nucleotide sequence of the bca locus reveals an open reading frame of 3060 nucleotides encoding a precursor protein of 108,705 Da. Cleavage of a putative signal sequence of 41 amino acids yields a mature protein of 104,106 Da. The 20,417-Da N-terminal region of the alpha antigen shows no homology to previously described protein sequences and is followed by a series of nine tandem repeating units that make up 74% of the mature protein. Each repeating unit is identical and consists of 82 amino acids with a molecular mass of 8665 Da, which is encoded by 246 nucleotides. The size of the repeating units corresponds to the observed size differences in the heterogeneous ladder of alpha C proteins expressed by GBS. The C-terminal region of the alpha antigen contains a membrane anchor domain motif that is shared by a number of Gram-positive surface proteins. The large region of identical repeating units in bca defines protective epitopes and may play a role in generating phenotypic and genotypic diversity of the alpha antigen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. E., McDonald G. A., Jones D. C., Regnery R. L. A protective protein antigen of Rickettsia rickettsii has tandemly repeated, near-identical sequences. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2760–2769. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2760-2769.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Trifonov E. N. A computer algorithm for testing potential prokaryotic terminators. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4411–4427. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleat P. H., Timmis K. N. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Ibc protein genes of group B streptococci: binding of human immunoglobulin A to the beta antigen. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1151–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1151-1155.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey D. C., Alderete J. F. The phenotypically variable surface protein of Trichomonas vaginalis has a single, tandemly repeated immunodominant epitope. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2083–2088. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2083-2088.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi R. H., Wang L. F. Multiple procaryotic ribonucleic acid polymerase sigma factors. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Sep;50(3):227–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.3.227-243.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enea V., Ellis J., Zavala F., Arnot D. E., Asavanich A., Masuda A., Quakyi I., Nussenzweig R. S. DNA cloning of Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite gene: amino acid sequence of repetitive epitope. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.6204384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:321–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R. Nucleotide sequence of a glucosyltransferase gene from Streptococcus sobrinus MFe28. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4271–4278. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4271-4278.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P. Surface-localized protein antigens of group B streptococci. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S363–S366. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Hollingshead S. K., Scott J. R. Structure, function, and genetics of streptococcal M protein. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S356–S359. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Pancholi V., Schneewind O. Conservation of a hexapeptide sequence in the anchor region of surface proteins from gram-positive cocci. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1603–1605. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haanes E. J., Cleary P. P. Identification of a divergent M protein gene and an M protein-related gene family in Streptococcus pyogenes serotype 49. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6397–6408. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6397-6408.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Rekik M., Bairoch A., Neidle E. L., Ornston L. N. Potential DNA slippage structures acquired during evolutionary divergence of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus chromosomal benABC and Pseudomonas putida TOL pWW0 plasmid xylXYZ, genes encoding benzoate dioxygenases. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7540–7548. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7540-7548.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedén L. O., Frithz E., Lindahl G. Molecular characterization of an IgA receptor from group B streptococci: sequence of the gene, identification of a proline-rich region with unique structure and isolation of N-terminal fragments with IgA-binding capacity. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1481–1490. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerlström P. G., Chhatwal G. S., Timmis K. N. The IgA-binding beta antigen of the c protein complex of Group B streptococci: sequence determination of its gene and detection of two binding regions. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):843–849. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. R., Ferrieri P. Group B streptococcal Ibc protein antigen: distribution of two determinants in wild-type strains of common serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):506–510. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.506-510.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Akerström B., Vaerman J. P., Stenberg L. Characterization of an IgA receptor from group B streptococci: specificity for serum IgA. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2241–2247. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopilato J., Bortner S., Beckwith J. Mutations in a new chromosomal gene of Escherichia coli K-12, pcnB, reduce plasmid copy number of pBR322 and its derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):285–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00430440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff L. C., Hori S., Michel J. L., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Phenotypic diversity in the alpha C protein of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2638–2644. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2638-2644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff L. C., Michel J. L., Kasper D. L. A monoclonal antibody identifies a protective C-protein alpha-antigen epitope in group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):204–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.204-210.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J. L., Madoff L. C., Kling D. E., Kasper D. L., Ausubel F. M. Cloned alpha and beta C-protein antigens of group B streptococci elicit protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2023–2028. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2023-2028.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag D. K., Huang H. V., Berg D. E. Bidirectional chain-termination nucleotide sequencing: transposon Tn5seq1 as a mobile source of primer sites. Gene. 1988 Apr 15;64(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90487-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Ferrieri P. The relation of the Ibc protein antigen to the opsonization differences between strains of type II group B streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):672–681. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Kim Y. K., Ferrieri P. Effect of differences in antibody and complement requirements on phagocytic uptake and intracellular killing of "c" protein-positive and -negative strains of type II group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1243–1251. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1243-1251.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Mejia J. S., Ortega-Barria E., Matzilevich D., Prioli R. P. The Trypanosoma cruzi neuraminidase contains sequences similar to bacterial neuraminidases, YWTD repeats of the low density lipoprotein receptor, and type III modules of fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):179–191. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Wessels M. R., Heggen L. M., Kasper D. L. Transposon mutagenesis of type III group B Streptococcus: correlation of capsule expression with virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7208–7212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneewind O., Friedrich K., Lütticken R. Cloning and expression of the CAMP factor of group B streptococci in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2174–2179. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2174-2179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroza T., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the Streptococcus mutans fructosyltransferase gene and flanking regions. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):810–816. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.810-816.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels M. R., Rubens C. E., Benedí V. J., Kasper D. L. Definition of a bacterial virulence factor: sialylation of the group B streptococcal capsule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8983–8987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wren B. W. A family of clostridial and streptococcal ligand-binding proteins with conserved C-terminal repeat sequences. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):797–803. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Briles D. E. Structural properties and evolutionary relationships of PspA, a surface protein of Streptococcus pneumoniae, as revealed by sequence analysis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):601–609. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.601-609.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Eichel-Streiber C., Sauerborn M. Clostridium difficile toxin A carries a C-terminal repetitive structure homologous to the carbohydrate binding region of streptococcal glycosyltransferases. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90348-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Eichel-Streiber C., Sauerborn M. Clostridium difficile toxin A carries a C-terminal repetitive structure homologous to the carbohydrate binding region of streptococcal glycosyltransferases. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90348-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Abrahmsén L. Species-specific variation in signal peptide design. Implications for protein secretion in foreign hosts. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]