Abstract
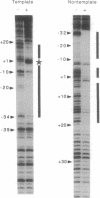
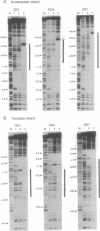
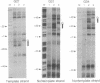
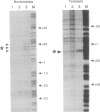
The structure of the elongation complex of vaccinia RNA polymerase halted at discrete template positions was examined by DNase I footprinting. The leading edge of the footprint bore a constant relationship to the catalytic template position, being 22-24 nucleotides (nt) in advance on the nontemplate strand and 17 nt on the template strand. DNase hypersensitivity of the nontemplate strand at the leading edge suggested that the DNA might be distorted as it entered the polymerase molecule. The region of DNA unwinding at the transcription bubble extended at least 12 nt 5' from the catalytic center, as indicated by the reactivity of adenosine residues to diethylpyrocarbonate. Cu-phenanthroline-hypersensitive sites located 13 nt 5' and 4 nt 3' of the growing point appeared to demarcate the margins of the bubble. Strand asymmetry of chemical modification within the bubble was consistent with an RNA-DNA hybrid of no more than 10 base pairs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Events during eucaryotic rRNA transcription initiation and elongation: conversion from the closed to the open promoter complex requires nucleotide substrates. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1940–1946. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Li J., Moss B. Promoter DNA contacts made by the vaccinia virus early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15539–15544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. DNA-dependent ATPase activity associated with vaccinia virus early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10761–10765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Yuen L., Shuman S., Moss B. Purification of a factor required for transcription of vaccinia virus early genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10754–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpousis A. J., Gralla J. D. Interaction of RNA polymerase with lacUV5 promoter DNA during mRNA initiation and elongation. Footprinting, methylation, and rifampicin-sensitivity changes accompanying transcription initiation. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamper H. B., Hearst J. E. A topological model for transcription based on unwinding angle analysis of E. coli RNA polymerase binary, initiation and ternary complexes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler J., Shuman S. A freeze-frame view of eukaryotic transcription during elongation and capping of nascent mRNA. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):983–986. doi: 10.1126/science.1546295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler J., Shuman S. Stability of ternary transcription complexes of vaccinia virus RNA polymerase at promoter-proximal positions. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7644–7654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler J., Shuman S. Ternary complex formation by vaccinia virus RNA polymerase at an early viral promoter: analysis by native gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2982–2989. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2982-2989.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainz M., Roberts J. Structure of transcription elongation complexes in vivo. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):838–841. doi: 10.1126/science.1536008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krummel B., Chamberlin M. J. RNA chain initiation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Structural transitions of the enzyme in early ternary complexes. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7829–7842. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krummel B., Chamberlin M. J. Structural analysis of ternary complexes of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Deoxyribonuclease I footprinting of defined complexes. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90918-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn S. C., Luse D. S. RNA polymerase II elongation complexes paused after the synthesis of 15- or 35-base transcripts have different structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1508–1522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger W., Schickor P., Heumann H. A cinematographic view of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase translocation. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2745–2754. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. A., Kane C. M., Chamberlin M. J. Footprinting analysis of mammalian RNA polymerase II along its transcript: an alternative view of transcription elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Gamper H., Van Houten B., Hearst J. E. Interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with DNA in an elongation complex arrested at a specific psoralen crosslink site. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):277–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigman D. S. Chemical nucleases. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9097–9105. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Crothers D. M. Intermediates in transcription initiation from the E. coli lac UV5 promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]