Abstract
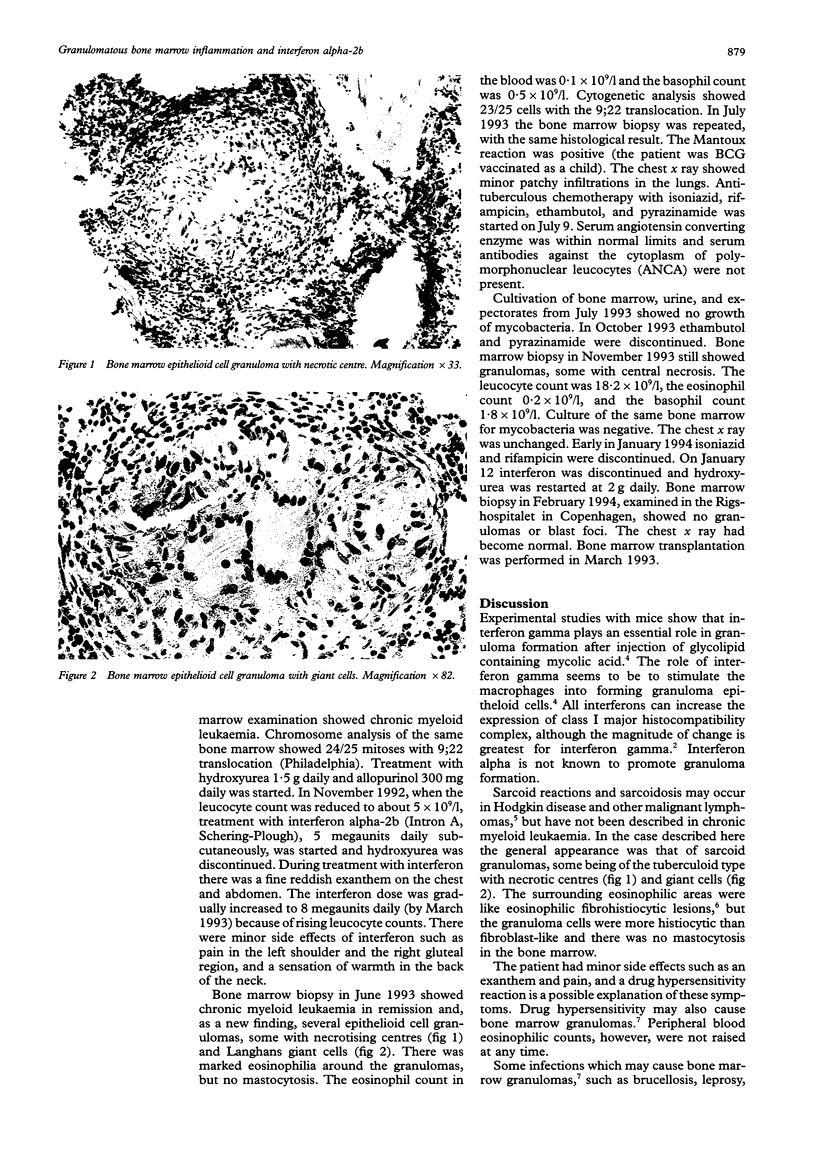
A patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia developed bone marrow granulomas during treatment with interferon alpha-2b. Some granulomas had necrotic centres and giant cells and there was marked eosinophilia surrounding them. The granulomas disappeared when the interferon treatment was discontinued. Mycobacteriosis was ruled out. The most likely explanation for the granuloma formation was drug hypersensitivity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano M., Nakane A., Minagawa T. Endogenous gamma interferon is essential in granuloma formation induced by glycolipid-containing mycolic acid in mice. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2872–2878. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2872-2878.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brincker H. Sarcoid reactions and sarcoidosis in Hodgkin's disease and other malignant lymphomata. Br J Cancer. 1972 Apr;26(2):120–123. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorr R. T. Interferon-alpha in malignant and viral diseases. A review. Drugs. 1993 Feb;45(2):177–211. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199345020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendra J. R., Pickens S., Singh A. K., Singh K. Bone marrow necrosis at transformation of chronic granulocytic leukaemia treated with interferon. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Sep;45(9):830–831. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.9.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloke O., Niederle N., Qiu J. Y., Wandl U., Moritz T., Nagel-Hiemke M., Hawig I., Opalka B., Seeber S., Becher R. Impact of interferon alpha-induced cytogenetic improvement on survival in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1993 Mar;83(3):399–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1993.tb04663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]