Abstract
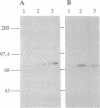
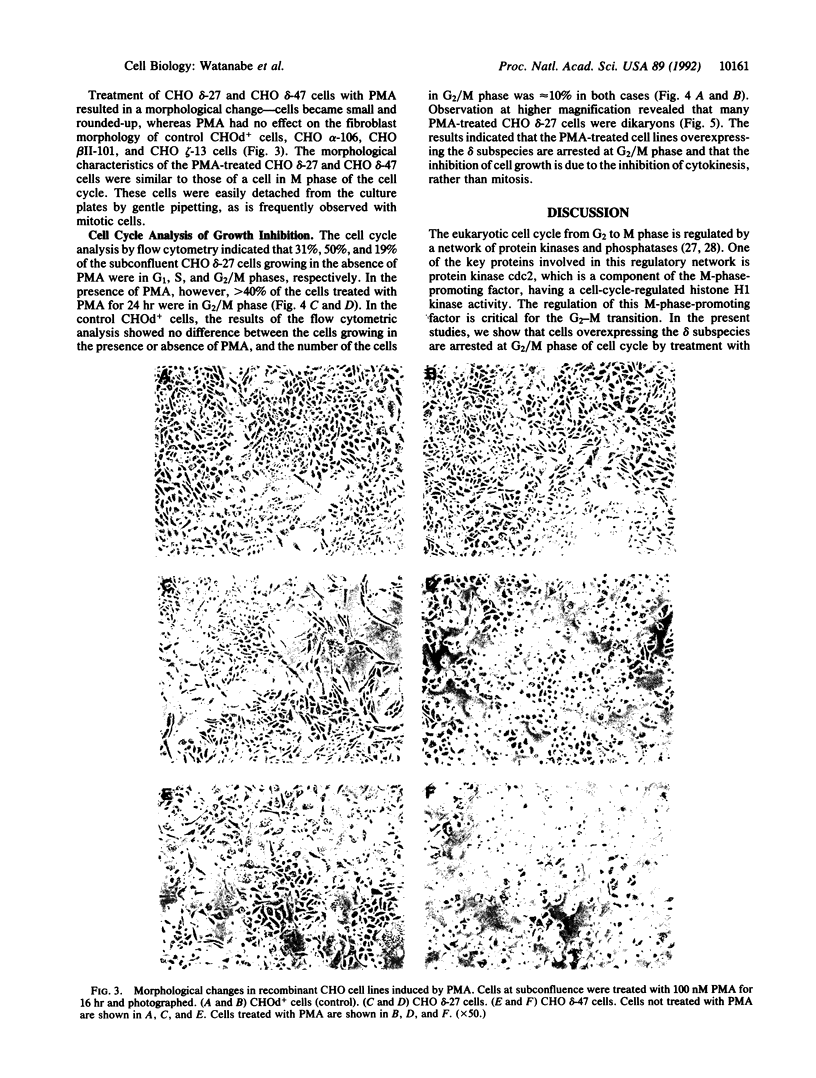
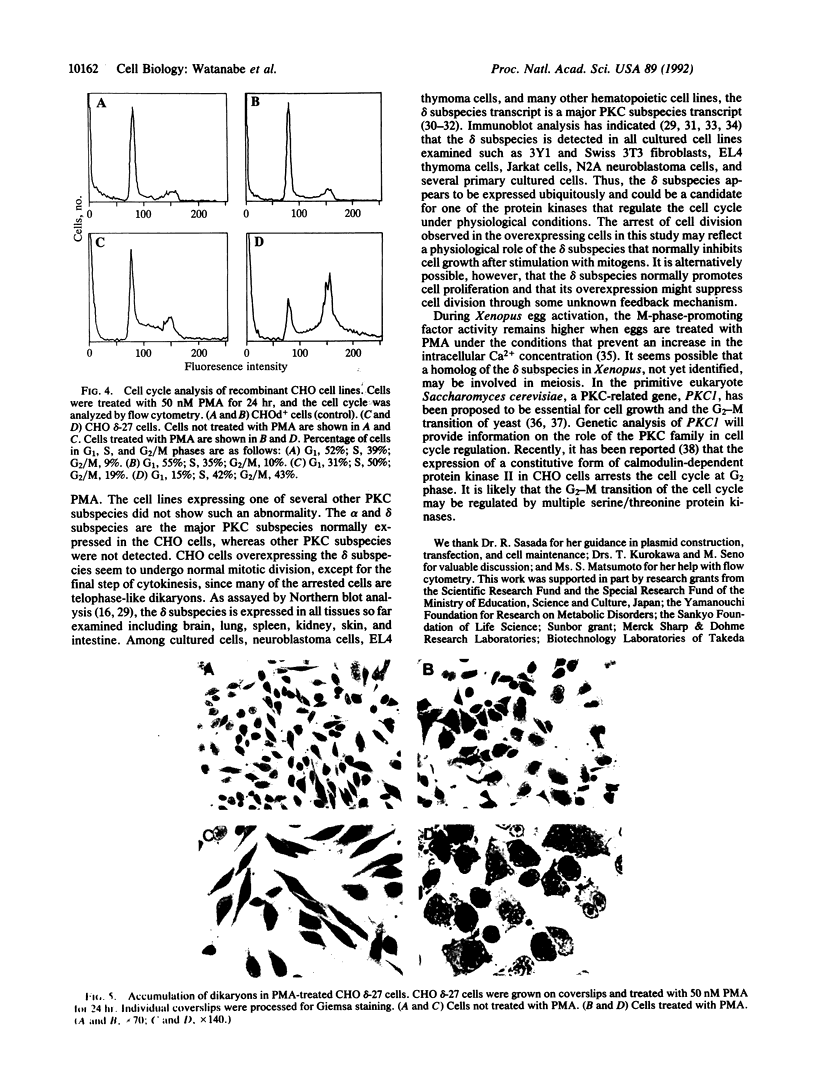
Several lines of CHO cells stably overexpressing protein kinase C (PKC) subspecies to various extents were established by the DNA-mediated transfer. Upon treatment with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, the growth of the cells expressing the PKC-delta subspecies was markedly inhibited, whereas cell lines expressing PKC-alpha, PKC-beta II, and PKC-zeta subspecies were not significantly affected. Flow cytometric analysis indicated that all cell lines overexpressing PKC-delta subspecies accumulated in G2/M phase in response to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. In these arrested cells, dikaryons were predominant, implying that phorbol ester-induced inhibition of cell division is specific to telophase. These results suggest PKC-delta subspecies may play a role in the normal cell cycle progression.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacher N., Zisman Y., Berent E., Livneh E. Isolation and characterization of PKC-L, a new member of the protein kinase C-related gene family specifically expressed in lung, skin, and heart. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):126–133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bement W. M., Capco D. G. Parallel pathways of cell cycle control during Xenopus egg activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R. N-myc disrupts protein kinase C-mediated signal transduction in neuroblastoma. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1119–1125. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borner C., Filipuzzi I., Weinstein I. B., Imber R. Failure of wild-type or a mutant form of protein kinase C-alpha to transform fibroblasts. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):78–80. doi: 10.1038/353078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi P. M., Tchou-Wong K. M., Weinstein I. B. Overexpression of protein kinase C in HT29 colon cancer cells causes growth inhibition and tumor suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4650–4657. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldar H., Zisman Y., Ullrich A., Livneh E. Overexpression of protein kinase C alpha-subtype in Swiss/3T3 fibroblasts causes loss of both high and low affinity receptor numbers for epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13290–13296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Donoghue D. J. Protein kinases and protooncogenes: biochemical regulators of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2293–2302. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes J., Weissmann C. Constitutive, long-term production of human interferons by hamster cells containing multiple copies of a cloned interferon gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):687–706. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homan E. C., Jensen D. E., Sando J. J. Protein kinase C isozyme expression in phorbol ester-sensitive and -resistant EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5676–5681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Hsiao W. L., O'Brian C. A., Murphy J. P., Kirschmeier P., Weinstein I. B. Overproduction of protein kinase C causes disordered growth control in rat fibroblasts. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):343–354. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao W. L., Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Weinstein I. B. Cells that overproduce protein kinase C are more susceptible to transformation by an activated H-ras oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2641–2647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley S. C., Parker P. J., Fabbro D., Jaken S. Differential regulation of protein kinase C isozymes by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in GH4C1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23761–23768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibersperger H., Gschwendt M., Gernold M., Marks F. Immunological demonstration of a calcium-unresponsive protein kinase C of the delta-type in different species and murine tissues. Predominance in epidermis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14778–14784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Bartlett-Heubusch E. Mutants in the S. cerevisiae PKC1 gene display a cell cycle-specific osmotic stability defect. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1221–1229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Fields F. O., Kunisawa R., Bishop J. M., Thorner J. A candidate protein kinase C gene, PKC1, is required for the S. cerevisiae cell cycle. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90360-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megidish T., Mazurek N. A mutant protein kinase C that can transform fibroblasts. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):807–811. doi: 10.1038/342807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mischak H., Bodenteich A., Kolch W., Goodnight J., Hofer F., Mushinski J. F. Mouse protein kinase C-delta, the major isoform expressed in mouse hemopoietic cells: sequence of the cDNA, expression patterns, and characterization of the protein. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):7925–7931. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Kubo K., Saido T. C., Akita Y., Osada S., Kuroki T., Ohno S., Suzuki K. Structure and properties of a ubiquitously expressed protein kinase C, nPKC delta. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):931–940. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Kaibuchi K., Arai K. A protein kinase C cDNA without the regulatory domain is active after transfection in vivo in the absence of phorbol ester. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):831–836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogita K., Miyamoto S., Yamaguchi K., Koide H., Fujisawa N., Kikkawa U., Sahara S., Fukami Y., Nishizuka Y. Isolation and characterization of delta-subspecies of protein kinase C from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1592–1596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Igarashi K., Kikkawa U., Ogita K., Nishizuka Y. Nucleotide sequences of cDNAs for alpha and gamma subspecies of rat brain protein kinase C. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5199–5200. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Igarashi K., Kuno T., Tanaka C., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Phorbol ester binding to protein kinase C requires a cysteine-rich zinc-finger-like sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4868–4871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C zeta subspecies from rat brain: its structure, expression, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Kikkawa U., Ogita K., Fujii T., Kurokawa T., Asaoka Y., Sekiguchi K., Ase K., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Expression and properties of two types of protein kinase C: alternative splicing from a single gene. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1116–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.3576226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osada S., Mizuno K., Saido T. C., Akita Y., Suzuki K., Kuroki T., Ohno S. A phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC eta, a new member of the protein kinase C family predominantly expressed in lung and skin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22434–22440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Kour G., Marais R. M., Mitchell F., Pears C., Schaap D., Stabel S., Webster C. Protein kinase C--a family affair. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;65(1-2):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persons D. A., Wilkison W. O., Bell R. M., Finn O. J. Altered growth regulation and enhanced tumorigenicity of NIH 3T3 fibroblasts transfected with protein kinase C-I cDNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):447–458. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planas-Silva M. D., Means A. R. Expression of a constitutive form of calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II leads to arrest of the cell cycle in G2. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):507–517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05081.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasada R., Onda H., Igarashi K. The establishment of IL-2 producing cells by genetic engineering. Cell Struct Funct. 1987 Apr;12(2):205–217. doi: 10.1247/csf.12.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]