Abstract
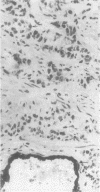
AIM--To assess the value of vimentin and cytokeratin (CK) intermediate filament proteins (IFPs) in distinguishing between nodular hyperplasia and carcinoma of the prostate and in predicting prognosis in prostatic cancer. METHODS--Fifteen carcinomas and 49 cases of nodular hyperplasia were studied using frozen sections and monoclonal antibodies to CK and vimentin IFPs. RESULTS--There was no statistically significant difference in vimentin expression between nodular hyperplasia and carcinoma. The luminal epithelium in both also reacted with antibodies which detect CK8, 18 and 19. CK 7 expression was found in 57% of cases of nodular hyperplasia and was not identified in any carcinoma. There was a reaction with antibodies to CK1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 11, and 13 in only a minority of cases. There was no statistically significant difference in vimentin and CK reactivity in high and low grade carcinomas. CONCLUSION--Neither vimentin nor CK expression assists in establishing whether a prostatic lesion is benign or malignant or in predicting the biological behaviour of a prostatic carcinoma.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azumi N., Battifora H. The distribution of vimentin and keratin in epithelial and nonepithelial neoplasms. A comprehensive immunohistochemical study on formalin- and alcohol-fixed tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Sep;88(3):286–296. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/88.3.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P., Ray V., Shaw M., Rubenstein M., Guinan P. An immunohistologic characterization of human prostatic atypical hyperplasia. Urol Res. 1990;18(3):193–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00295846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daher N., Bove N., Bara J., Abourachid H. Value of different markers in prostatic carcinomas. An immunohistological study. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;243A:507–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domagala W., Lubinski J., Weber K., Osborn M. Intermediate filament typing of tumor cells in fine needle aspirates by means of monoclonal antibodies. Acta Cytol. 1986 May-Jun;30(3):214–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitz W. F., Debruyne F. M., Vooijs G. P., Herman C. J., Ramaekers F. C. Intermediate filament proteins as tissue specific markers in normal and malignant urological tissues. J Urol. 1986 Oct;136(4):922–931. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)45133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Miettinen M., Virtanen I. Antibodies to intermediate filaments in surgical pathology. Arch Geschwulstforsch. 1986;56(4):283–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong A. S., Gilham P., Milios J. Cytokeratin and vimentin intermediate filament proteins in benign and neoplastic prostatic epithelium. Histopathology. 1988 Oct;13(4):435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1988.tb02059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mørk C., van Deurs B., Petersen O. W. Regulation of vimentin expression in cultured human mammary epithelial cells. Differentiation. 1990 Apr;43(2):146–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle R. B. Intermediate filaments: a review of the basic biology. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988;12 (Suppl 1):4–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Tsubura A., Okamura A., Senzaki H., Naka Y., Komatz Y., Morii S. Keratin profiles in normal/hyperplastic prostates and prostate carcinoma. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1992;421(2):157–161. doi: 10.1007/BF01607049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):372–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purnell D. M., Heatfield B. M., Anthony R. L., Trump B. F. Immunohistochemistry of the cytoskeleton of human prostatic epithelium. Evidence for disturbed organization in neoplasia. Am J Pathol. 1987 Feb;126(2):384–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F., van Niekerk C., Poels L., Schaafsma E., Huijsmans A., Robben H., Schaart G., Vooijs P. Use of monoclonal antibodies to keratin 7 in the differential diagnosis of adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):641–655. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaafsma H. E., Ramaekers F. C., van Muijen G. N., Lane E. B., Leigh I. M., Robben H., Huijsmans A., Ooms E. C., Ruiter D. J. Distribution of cytokeratin polypeptides in human transitional cell carcinomas, with special emphasis on changing expression patterns during tumor progression. Am J Pathol. 1990 Feb;136(2):329–343. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood E. R., Berg L. A., Mitchell N. J., McNeal J. E., Kozlowski J. M., Lee C. Differential cytokeratin expression in normal, hyperplastic and malignant epithelial cells from human prostate. J Urol. 1990 Jan;143(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39903-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommers C. L., Walker-Jones D., Heckford S. E., Worland P., Valverius E., Clark R., McCormick F., Stampfer M., Abularach S., Gelmann E. P. Vimentin rather than keratin expression in some hormone-independent breast cancer cell lines and in oncogene-transformed mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 1;49(15):4258–4263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srigley J. R., Dardick I., Hartwick R. W., Klotz L. Basal epithelial cells of human prostate gland are not myoepithelial cells. A comparative immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study with the human salivary gland. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):957–966. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanholm H., Nielsen B., Starklint H. Keratin patterns in prostatic hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma. APMIS Suppl. 1988;4:100–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W. Evolution and expression of vitellogenin genes. Trends Genet. 1988 Aug;4(8):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Niekerk C. C., Jap P. H., Ramaekers F. C., van de Molengraft F., Poels L. G. Immunohistochemical demonstration of keratin 7 in routinely fixed paraffin-embedded human tissues. J Pathol. 1991 Oct;165(2):145–152. doi: 10.1002/path.1711650210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]