Abstract
Ethanol is the major metabolic product of glucose fermentation by the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica under the anaerobic conditions found in the lumen of the colon. Here an internal peptide sequence determined from a major 39-kDa amoeba protein isolated by isoelectric focusing followed by SDS/PAGE was used to clone the gene for the E. histolytica NADP(+)-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase (EhADH1; EC 1.1.1.2). The EhADH1 clone had an open reading frame that was 360 amino acids long and encoded a protein of approximately 39 kDa (calculated size). EhADH1 showed a 62% amino acid identity with the tetrameric NADP(+)-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase of Thermoanaerobium brockii. In contrast, EhADH1 showed a 15% amino acid identity with the closest human alcohol dehydrogenase. EhADH1 contained 18 of the 22 amino acids conserved in other alcohol dehydrogenases, including glycines involved in binding NAD(P)+ as well as histidine and cysteine residues involved in binding the catalytic zinc ion. Like the T. brockii alcohol dehydrogenase, EhADH1 lacked a 23-amino acid stretch present in other alcohol dehydrogenases that includes four cysteines that bind a second noncatalytic zinc ion. An EhADH1-glutathione-S-transferase fusion protein showed the expected NADP(+)-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase and NADPH-dependent acetaldehyde reductase activities. The enzymatic activities of the EhADH1 fusion protein were inhibited by pyrazole and 4-methylpyrazole.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deetz J. S., Luehr C. A., Vallee B. L. Human liver alcohol dehydrogenase isozymes: reduction of aldehydes and ketones. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6822–6828. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman U., Meraz M. A., Rausser S., Agabian N., Meza I. Characterization of an immuno-dominant variable surface antigen from pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):879–888. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Samma J. P., Wallén L., Brändén C. I., Akeson A., Jones T. A. Structure of a triclinic ternary complex of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase at 2.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 15;146(4):561–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
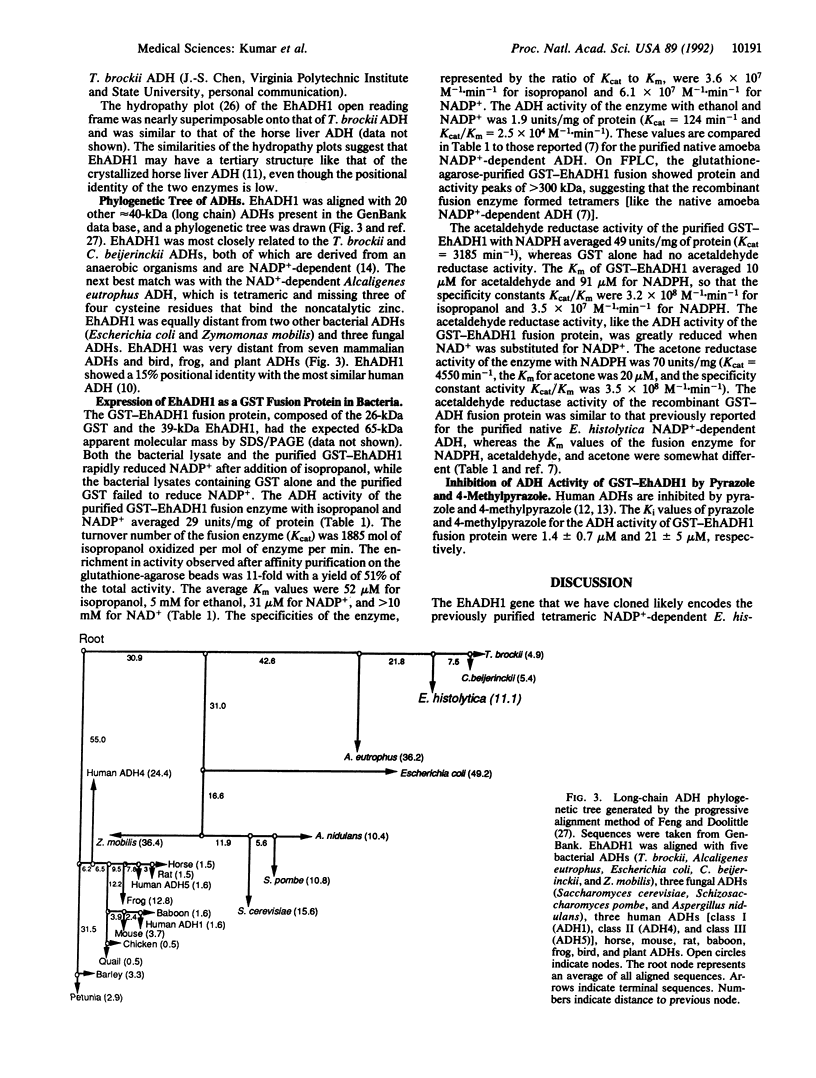
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horjales E., Eklund H., Brändén C. I. Comparison of computer modelling and X-ray results of the binding of a pyrazole derivative to liver alcohol dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 20;197(4):685–694. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90475-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber M., Garfinkel L., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of an Entamoeba histolytica ferredoxin gene. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Oct;31(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H. Alcohol dehydrogenases, aldehyde dehydrogenases, and related enzymes. Alcohol. 1985 Jan-Feb;2(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(85)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Persson B., Jeffery J. Characteristics of alcohol/polyol dehydrogenases. The zinc-containing long-chain alcohol dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 1;167(2):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy T. E., Gawinowicz M. A., Barzilai A., Kandel E. R., Sweatt J. D. Sequencing of proteins from two-dimensional gels by using in situ digestion and transfer of peptides to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes: application to proteins associated with sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7008–7012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Wu X. W., Gibbs R. A., Cook R. G., Muzny D. M., Caskey C. T. Generation of cDNA probes directed by amino acid sequence: cloning of urate oxidase. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1288–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.3344434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T. K., Theorell H. Human liver alcohol dehydrogenase: inhibition by pyrazole and pyrazole analogs. Acta Chem Scand. 1969;23(3):892–902. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.23-0892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo H. S., Chang C. J. Purification and properties of NADP-linked, alcohol dehydrogenase from Entamoeba histolytica. J Parasitol. 1982 Jun;68(3):372–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Palomo A., Martínez-Báez M. Selective primary health care: strategies for control of disease in the developing world. X. Amebiasis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5(6):1093–1102. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.6.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. Energy metabolism of protozoa without mitochondria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:465–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. Reductive activation of nitroimidazoles in anaerobic microorganisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 1;35(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90552-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretz M., Burstein Y. Amino acid sequence of alcohol dehydrogenase from the thermophilic bacterium Thermoanaerobium brockii. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 8;28(16):6549–6555. doi: 10.1021/bi00442a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. E. Metabolism of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903. Adv Parasitol. 1984;23:105–142. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60286-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]