Abstract
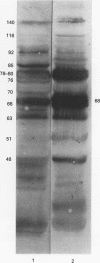
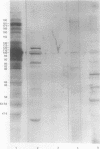
AIM--To improve the diagnosis of culture negative endocarditis by diagnosing cases due to streptococci and enterococci. METHODS--Serum samples were immunoblotted against extracts of the commonest streptococci and enterococci. They were selected from patients with a cardiac murmur, persistent pyrexia and at least three negative blood cultures. The presence of patterns of endocarditis species specific antigenic bands was measured and correlated with clinical outcome. RESULTS--Negative serology was found in 28 patients where the diagnosis of endocarditis was rejected or, if proved, staphylococcal, yeast, Gram negative, systemic lupus erythematosus, due to Q fever or Chlamydia psittaci or nonbacterial thrombotic. Positive serology was found in 27 of the 34 patients where the response to antibiotics suggested streptococcal or enterococcal infection. In 22 of these there was objective evidence of endocarditis. Positive serology was also found in three of four further patients with vegetations at necropsy. CONCLUSION--The identification of patterns of antibody response on immunoblotting can be used to make a specific diagnosis of streptococcal or enterococcal endocarditis in the absence of positive blood cultures.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitchison E. J., Lambert P. A., Smith E. G., Farrell I. D. Serodiagnosis of Streptococcus faecalis endocarditis by immunoblotting of surface protein antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):211–215. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.211-215.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beighton D., Hardie J. M., Whiley R. A. A scheme for the identification of viridans streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Dec;35(6):367–372. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-6-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks W., Burnie J. P. Cloning and sequencing the endocarditis immunodominant antigen of Streptococcus sobrinus strain MUCOB 263. J Med Microbiol. 1994 May;40(5):330–337. doi: 10.1099/00222615-40-5-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Clark I. Diagnosing endocarditis with the cloned 112 kDa antigen of Enterococcus faecalis. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Oct 24;123(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Holland M., Matthews R. C., Lees W. Role of immunoblotting in the diagnosis of culture negative and enterococcal endocarditis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Oct;40(10):1149–1158. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.10.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannady P. B., Jr, Sanford J. P. Negative blood cultures in infective endocarditis: a review. South Med J. 1976 Nov;69(11):1420–1424. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197611000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I., Burnie J. P. Immunoblotting and culture positive endocarditis. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Feb;44(2):152–156. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain M. J., Waltman W. D., 2nd, Turner J. S., Yother J., Talkington D. F., McDaniel L. S., Gray B. M., Briles D. E. Pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA) is serologically highly variable and is expressed by all clinically important capsular serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3293–3299. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3293-3299.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Lukes A. S., Bright D. K. New criteria for diagnosis of infective endocarditis: utilization of specific echocardiographic findings. Duke Endocarditis Service. Am J Med. 1994 Mar;96(3):200–209. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(94)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P. A. Laboratory aspects of infective endocarditis. Br J Biomed Sci. 1993 Sep;50(3):249–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjerulf A., Tvede M., Høiby N. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis used for bacteriological diagnosis in patients with endocarditis. APMIS. 1993 Oct;101(10):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1993.tb00175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. C., Burnie J. P., Howat D., Rowland T., Walton F. Autoantibody to heat-shock protein 90 can mediate protection against systemic candidosis. Immunology. 1991 Sep;74(1):20–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCartney A. C. Changing trends in infective endocarditis. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Nov;45(11):945–948. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.11.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazin G. J., Saul S., Thompson M. E. Blood culture positivity: suppression by outpatient antibiotic therapy in patients with bacterial endocarditis. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Feb;142(2):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesanti E. L., Smith I. M. Infective endocarditis with negative blood cultures. An analysis of 52 cases. Am J Med. 1979 Jan;66(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P., Armstrong D. Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis in patients with malignant neoplastic diseases. Am J Med. 1973 Jan;54(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Wu H. Y., White P. L., Kilian M., Henrichsen J. Serum antibody responses to Streptococcus mutans antigens in humans systemically infected with oral streptococci. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1992 Dec;7(6):321–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1992.tb00630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanson D. C., Hince C. An immunofluorescent method for detecting antibodies against viridans streptococci in Streptococcus viridans endocarditis. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Mar;31(3):292–293. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.3.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanson D. C., Kirk N., Humphrey R. Clinical evaluation of a fluorescent antibody test for the serological diagnosis of streptococcal endocarditis. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jan;38(1):92–98. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. I., Baron E. J., Tenenbaum M. J., Kaplan M. H., Greenspan J., Facklam R. R., Tyburski M. B., Goldman M. A., Kanzer B. F., Pizzarello R. A. Viridans streptococcal endocarditis: clinical, microbiological, and echocardiographic correlations. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):597–603. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunkel A. R., Kaye D. Endocarditis with negative blood cultures. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 30;326(18):1215–1217. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204303261809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Reyn C. F., Levy B. S., Arbeit R. D., Friedland G., Crumpacker C. S. Infective endocarditis: an analysis based on strict case definitions. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Apr;94(4 Pt 1):505–518. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-4-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner A. S., Cobbs C. G., Kaye D., Hook E. W. Studies on the bacteremia of bacterial endocarditis. JAMA. 1967 Oct 16;202(3):199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkin B. A., Lillemoe K. D., Cameron J. L., Effron P. N., Magnuson T. H., Pitt H. A. The triad of Streptococcus bovis bacteremia, colonic pathology, and liver disease. Ann Surg. 1990 Jun;211(6):786–792. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199006000-00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., George M., Bouvet A., Roberts R. B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of antibodies to nutritionally variant streptococci in patients with endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):116–121. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]