Abstract
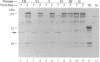
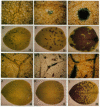
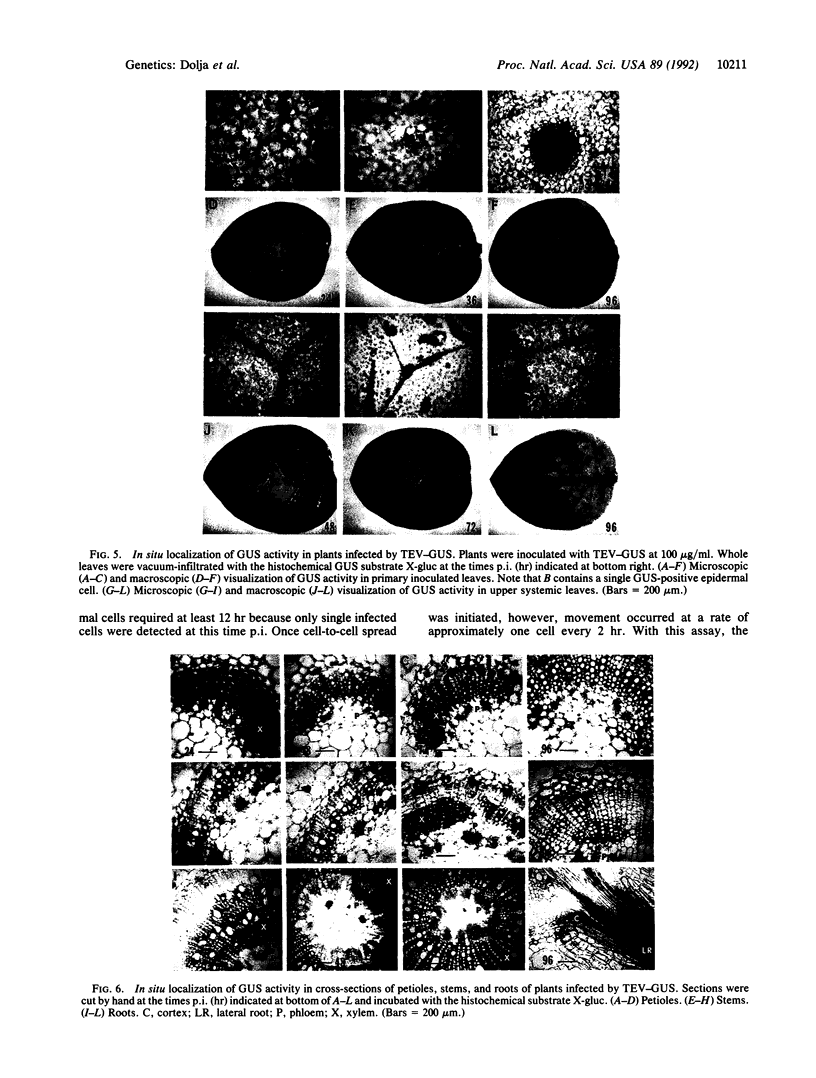
Infectious RNA transcripts were generated from full-length cDNA clones of the tobacco etch potyvirus genome containing an insertion of the bacterial beta-glucuronidase (GUS) gene between the polyprotein-coding sequences for the N-terminal 35-kDa proteinase and the helper component-proteinase. The recombinant virus was able to spread systemically in plants and accumulated to a level comparable with wild-type tobacco etch potyvirus. Proteolytic processing mediated by the 35-kDa proteinase and helper component-proteinase resulted in production of an enzymatically active GUS-helper component-proteinase fusion protein. A virus passage line that retained the GUS insert after numerous plant-to-plant transfers, as well as a line that sustained a deletion of the GUS sequence, was recovered. Use of an in situ histochemical GUS assay in time-course experiments allowed the visualization of virus activity in single, mechanically inoculated leaf epidermal cells, in neighboring epidermal and mesophyll cells, in phloem-associated cells after long-distance transport, and in cells surrounding vascular tissues of organs above and below the site of inoculation. This system represents a powerful tool to study plant virus replication, short- and long-distance virus movement, and virus-host interactions. Additionally, we show that potyviruses may serve as highly efficient, autonomously replicating vectors for the expression of foreign genes in plants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bujarski J. J., Ahlquist P., Hall T. C., Dreher T. W., Kaesberg P. Modulation of replication, aminoacylation and adenylation in vitro and infectivity in vivo of BMV RNAs containing deletions within the multifunctional 3' end. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1769–1774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04425.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Cary S. M., Parks T. D., Dougherty W. G. A second proteinase encoded by a plant potyvirus genome. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):365–370. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Dougherty W. G. A viral cleavage site cassette: identification of amino acid sequences required for tobacco etch virus polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Dougherty W. G. Small nuclear inclusion protein encoded by a plant potyvirus genome is a protease. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2540–2548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2540-2548.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Freed D. D. Cap-independent enhancement of translation by a plant potyvirus 5' nontranslated region. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1590-1597.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Freed D. D., Oh C. S. Expression of potyviral polyproteins in transgenic plants reveals three proteolytic activities required for complete processing. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1347–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deom C. M., Lapidot M., Beachy R. N. Plant virus movement proteins. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90403-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donson J., Kearney C. M., Hilf M. E., Dawson W. O. Systemic expression of a bacterial gene by a tobacco mosaic virus-based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7204–7208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R., Janda M., Ahlquist P. Bacterial gene inserted in an engineered RNA virus: efficient expression in monocotyledonous plant cells. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1294–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4743.1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi R. L., Joshi V., Ow D. W. BSMV genome mediated expression of a foreign gene in dicot and monocot plant cells. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2663–2669. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavankal G., Rhoads R. E. In vitro cleavage at or near the N-terminus of the helper component protein in the tobacco vein mottling virus polyprotein. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):721–731. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90543-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshi T., Watanabe Y., Saito T., Sugimoto A., Maeda T., Okada Y. Function of the 30 kd protein of tobacco mosaic virus: involvement in cell-to-cell movement and dispensability for replication. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2557–2563. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty I. T., French R., Jones R. W., Jackson A. O. Identification of barley stripe mosaic virus genes involved in viral RNA replication and systemic movement. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3453–3457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogue G. P., Hall T. C. The requirement for a 5' stem-loop structure in brome mosaic virus replication supports a new model for viral positive-strand RNA initiation. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):674–684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.674-684.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo M. A., Freed D. D., Carrington J. C. Nuclear transport of plant potyviral proteins. Plant Cell. 1990 Oct;2(10):987–998. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.10.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riechmann J. L., Laín S., García J. A. Highlights and prospects of potyvirus molecular biology. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jan;73(Pt 1):1–16. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorrer K., Parks T. D., Scheffler B., Bevan M., Dougherty W. G. Autocatalytic activity of the tobacco etch virus NIa proteinase in viral and foreign protein sequences. J Gen Virol. 1992 Apr;73(Pt 4):775–783. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-4-775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamatsu N., Ishikawa M., Meshi T., Okada Y. Expression of bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in tobacco plants mediated by TMV-RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):307–311. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verchot J., Herndon K. L., Carrington J. C. Mutational analysis of the tobacco etch potyviral 35-kDa proteinase: identification of essential residues and requirements for autoproteolysis. Virology. 1992 Sep;190(1):298–306. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91216-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]