Abstract
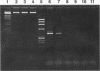
A method was developed for the preparation of genomic DNA from clotted blood that is usually discarded after extraction, for other laboratory tests. The method, which involves proteinase K digestion, salt/chloroform extraction and 90% ethanol precipitation of DNA from clotted blood, is rapid, simple, and easy because it does not impose an extra burden on the patient.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- McCusker J., Dawson M. T., Noone D., Gannon F., Smith T. Improved method for direct PCR amplification from whole blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6747–6747. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllenbach R., Lagoda P. J., Welter C. An efficient salt-chloroform extraction of DNA from blood and tissues. Trends Genet. 1989 Dec;5(12):391–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panaccio M., Lew A. PCR based diagnosis in the presence of 8% (v/v) blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1151–1151. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]