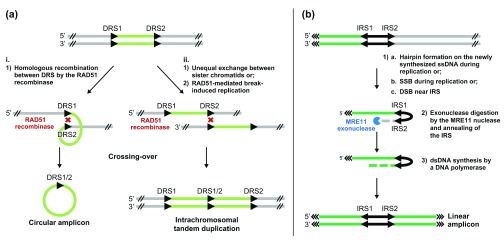
Figure 1. Potential mechanisms for gene amplification in Leishmania.
( a) The RAD51 recombinase mediates homologous recombination between direct repeated sequences (DRS) and leads to (i) extrachromosomal circular amplicon or (ii) intrachromosomal tandem duplication by unequal sister chromatid exchange or RAD51-mediated break-induced replication. Black arrows represent DRS. ( b) The MRE11 nuclease processes DNA ends after single-strand break (SSB), double-strand break (DSB), or hairpin formation during replication and leads to extrachromosomal linear amplification. Black arrows represent inverted repeated sequences (IRS). The green segments represent the amplified DNA regions. dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; ssDNA, single-stranded DNA.