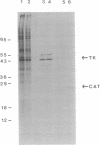
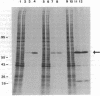
Abstract
Genetic and biochemical studies have revealed that the 5' noncoding region of poliovirus mediates translation of the viral mRNA by an unusual mechanism involving entry of ribosomes in internal sequences of mRNA molecules. We have found that mRNAs bearing the 5' noncoding region of poliovirus were translated at an enhanced rate in poliovirus-infected mammalian cells at a time when translation of cellular mRNAs was not yet inhibited. This translational enhancement of the polioviral 5' noncoding region was mediated by the expression of virus-encoded polypeptide 2A. This indicates that 2A is a multifunctional protein involved directly or indirectly in the activation of viral mRNA translation, in addition to its known roles in viral polyprotein processing and in inhibition of cellular protein synthesis. Thus, 2A represents an activator of translation of a viral mRNA that is translated by an internal ribosome binding mechanism. A likely consequence of this role of 2A is the efficient translation of viral mRNAs early in the infectious cycle, when host cell mRNAs can still compete with viral mRNAs for the host cell translation apparatus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agol V. I., Drozdov S. G., Ivannikova T. A., Kolesnikova M. S., Korolev M. B., Tolskaya E. A. Restricted growth of attenuated poliovirus strains in cultured cells of a human neuroblastoma. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4034–4038. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4034-4038.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneville J. M., Sanfaçon H., Fütterer J., Hohn T. Posttranscriptional trans-activation in cauliflower mosaic virus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1135–1143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90769-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley B., Ehrenfeld E. The cap-binding protein complex in uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13599–13606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Feng L., Wek R. C., Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Phosphorylation of initiation factor 2 alpha by protein kinase GCN2 mediates gene-specific translational control of GCN4 in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90193-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elroy-Stein O., Moss B. Cytoplasmic expression system based on constitutive synthesis of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6743–6747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambidge S. J., Sarnow P. Terminal 7-methyl-guanosine cap structure on the normally uncapped 5' noncoding region of poliovirus mRNA inhibits its translation in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6312–6315. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6312-6315.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of polyproteins in the replication of RNA viruses. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 26;28(26):9881–9890. doi: 10.1021/bi00452a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Mechanisms of gene regulation in the general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):248–273. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.248-273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Wimmer E. Initiation of protein synthesis by internal entry of ribosomes into the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1651–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1651-1660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Pestova T. V., Hellen C. U., Witherell G. W., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of picornavirus RNAs: structure and function of the internal ribosomal entry site. Enzyme. 1990;44(1-4):292–309. doi: 10.1159/000468766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. cis-trans models for post-transcriptional gene regulation. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):870–872. doi: 10.1126/science.2683086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macejak D. G., Sarnow P. Internal initiation of translation mediated by the 5' leader of a cellular mRNA. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):90–94. doi: 10.1038/353090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macejak D. G., Sarnow P. Translational regulation of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain binding protein mRNA. Enzyme. 1990;44(1-4):310–319. doi: 10.1159/000468767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy N., Belsham G. J., Brangwyn J. K., Sullivan M., Stone D. M., Almond J. W. Intracellular modifications induced by poliovirus reduce the requirement for structural motifs in the 5' noncoding region of the genome involved in internal initiation of protein synthesis. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1695–1701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1695-1701.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Bernstein H. D., Baltimore D. A poliovirus temperature-sensitive RNA synthesis mutant located in a noncoding region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P. Role of 3'-end sequences in infectivity of poliovirus transcripts made in vitro. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):467–470. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.467-470.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P. Translation of glucose-regulated protein 78/immunoglobulin heavy-chain binding protein mRNA is increased in poliovirus-infected cells at a time when cap-dependent translation of cellular mRNAs is inhibited. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5795–5799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Translation in mammalian cells of a gene linked to the poliovirus 5' noncoding region. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):445–448. doi: 10.1126/science.2839901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E. E., Hershey J. W., Ehrenfeld E. Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 is required for poliovirus 2A protease-induced cleavage of the p220 component of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9529–9533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]