Abstract
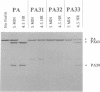
Proteolytic cleavage of the protective antigen (PA) protein of anthrax toxin at residues 164-167 is necessary for toxic activity. Cleavage by a cellular protease at this sequence, Arg-Lys-Lys-Arg, normally follows binding of PA to a cell surface receptor. We attempted to identify this protease by determining its sequence specificity and catalytic properties. Semi-random cassette mutagenesis was used to generate mutants with replacements of residues 164-167 by Arg, Lys, Ser, or Asn. Analysis of 19 mutant proteins suggested that lethal factor-dependent toxicity required the sequence Arg-Xaa-Xaa-Arg. Based on these data, three additional mutants were constructed with the sequences Ala-Lys-Lys-Arg, Arg-Lys-Lys-Ala, and Arg-Ala-Ala-Arg. Of these mutant proteins, Arg-Ala-Ala-Arg was toxic, confirming that the cellular protease can recognize the sequence Arg-Xaa-Xaa-Arg. The mutant containing the sequence Ala-Lys-Lys-Arg was also toxic but required > 13 times more protein to produce equivalent toxicity. This sequence specificity is similar to that of the ubiquitous subtilisin-like protease furin, which is involved in processing of precursors of certain receptors and growth factors. Therefore we tested whether a recombinant soluble furin would cleave PA. This furin derivative efficiently cleaved native PA and the Arg-Ala-Ala-Arg mutant but not the nontoxic PA mutants. In addition, previously identified inhibitors of furin blocked cleavage of receptor-bound PA. These data imply that furin is the cellular protease that activates PA, and that nearly all cell types contain at least a small amount of furin exposed on their cell surface.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr P. J. Mammalian subtilisins: the long-sought dibasic processing endoproteases. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90129-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar R., Singh Y., Leppla S. H., Friedlander A. M. Calcium is required for the expression of anthrax lethal toxin activity in the macrophagelike cell line J774A.1. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2107–2114. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2107-2114.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein R. O., Koehler T. M., Collier R. J., Finkelstein A. Anthrax toxin: channel-forming activity of protective antigen in planar phospholipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2209–2213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan P. A., Leduc R., Thomas L., Thorner J., Gibson H. L., Brake A. J., Barr P. J., Thomas G. Human fur gene encodes a yeast KEX2-like endoprotease that cleaves pro-beta-NGF in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2851–2859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieplak W., Hasemann C., Eidels L. Specific cleavage of diphtheria toxin by human urokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):747–754. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escuyer V., Collier R. J. Anthrax protective antigen interacts with a specific receptor on the surface of CHO-K1 cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3381–3386. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3381-3386.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander A. M. Macrophages are sensitive to anthrax lethal toxin through an acid-dependent process. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7123–7126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAINES B. W., KLEIN F., LINCOLN R. E. QUANTITATIVE ASSAY FOR CRUDE ANTHRAX TOXINS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:74–83. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.74-83.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS-SMITH P. W., SMITH H., KEPPIE J. Production in vitro of the toxin of Bacillus anthracis previously recognized in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):91–103. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka M., Nagahama M., Kim W. S., Watanabe T., Hatsuzawa K., Ikemizu J., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12127–12130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler T. M., Collier R. J. Anthrax toxin protective antigen: low-pH-induced hydrophobicity and channel formation in liposomes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1501–1506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Anthrax toxin edema factor: a bacterial adenylate cyclase that increases cyclic AMP concentrations of eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3162–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Purification and characterization of adenylyl cyclase from Bacillus anthracis. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:153–168. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95162-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Leatherman D. L. Differential sensitivity of reticulocytes to nicked and unnicked diphtheria toxin. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy S. S., Bresnahan P. A., Leppla S. H., Klimpel K. R., Thomas G. Human furin is a calcium-dependent serine endoprotease that recognizes the sequence Arg-X-X-Arg and efficiently cleaves anthrax toxin protective antigen. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16396–16402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Chaudhary V. K., Pastan I., FitzGerald D. J. Processing of Pseudomonas exotoxin by a cellular protease results in the generation of a 37,000-Da toxin fragment that is translocated to the cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20678–20685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn C. P., Singh Y., Klimpel K. R., Leppla S. H. Functional mapping of anthrax toxin lethal factor by in-frame insertion mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20124–20130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H., STANLEY J. L. Purification of the third factor of anthrax toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Nov;29:517–521. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-3-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Rapid entry of nicked diphtheria toxin into cells at low pH. Characterization of the entry process and effects of low pH on the toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9068–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh Y., Chaudhary V. K., Leppla S. H. A deleted variant of Bacillus anthracis protective antigen is non-toxic and blocks anthrax toxin action in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19103–19107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh Y., Leppla S. H., Bhatnagar R., Friedlander A. M. Internalization and processing of Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin by toxin-sensitive and -resistant cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11099–11102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C. Electron microscopic immunocytochemical localization of intracellular antigens in cultured cells: the EGS and ferritin bridge procedures. Histochem J. 1980 Jul;12(4):419–434. doi: 10.1007/BF01011958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Ven W. J., Voorberg J., Fontijn R., Pannekoek H., van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Roebroek A. J., Siezen R. J. Furin is a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme in higher eukaryotes. Mol Biol Rep. 1990 Nov;14(4):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00429896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Keizer G. D., Dorssers L. C., Van de Ven W. J. Structural homology between the human fur gene product and the subtilisin-like protease encoded by yeast KEX2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):664–664. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]