Abstract
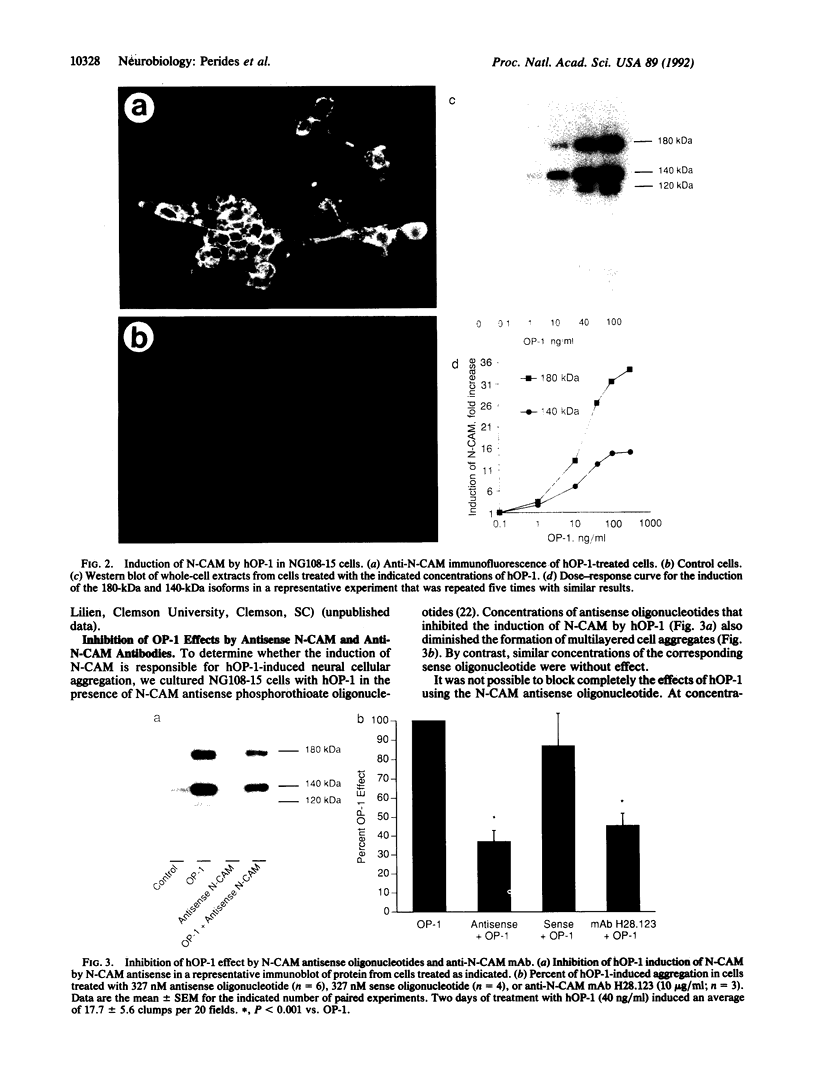
The neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) plays a fundamental role in nervous system development and regeneration, yet the regulation of the expression of N-CAM in different brain regions has remained poorly understood. Osteogenic protein 1 (OP-1) is a member of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily that is expressed in the nervous system. Treatment of the neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cell line NG108-15 for 1-4 days with recombinant human OP-1 (hOP-1) induced alterations in cell shape, formation of epithelioid sheets, and aggregation of cells into multilayered clusters. Immunofluorescence studies and Western blots demonstrated a striking differential induction of the three N-CAM isoforms in hOP-1-treated cells. hOP-1 caused a 6-fold up-regulation of the 140-kDa N-CAM, the isoform showing the highest constitutive expression, and a 29-fold up-regulation of the 180-kDa isoform. The 120-kDa isoform was not detected in control NG108-15 cells but was readily identified in hOP-1-treated cells. Incubation of NG108-15 cells with an antisense N-CAM oligonucleotide reduced the induction of N-CAM by hOP-1 and decreased the formation of multilayered cell aggregates. Anti-N-CAM monoclonal antibodies also diminished the formation of multilayered cell aggregates by hOP-1 and decreased cell-cell adhesion when hOP-1-treated NG108-15 cells were dispersed and replated. Thus, hOP-1 produces morphologic changes in NG108-15 cells, at least in part, by inducing N-CAM. These observations suggest that OP-1 or a homologue may participate in the regulation of N-CAM during nervous system development and regeneration.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson A., Sunshine J. L., Rutishauser U. NCAM polysialic acid can regulate both cell-cell and cell-substrate interactions. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):143–153. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch R. J. Clusters of neural cell adhesion molecule at sites of cell-cell contact. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):449–463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charness M. E., Querimit L. A., Diamond I. Ethanol increases the expression of functional delta-opioid receptors in neuroblastoma x glioma NG108-15 hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3164–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covault J., Sanes J. R. Distribution of N-CAM in synaptic and extrasynaptic portions of developing and adult skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):716–730. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniloff J. K., Levi G., Grumet M., Rieger F., Edelman G. M. Altered expression of neuronal cell adhesion molecules induced by nerve injury and repair. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):929–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson G., Peck D., Moore S. E., Barton C. H., Walsh F. S. Enhanced myogenesis in NCAM-transfected mouse myoblasts. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):348–351. doi: 10.1038/344348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:81–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennarini G., Hirsch M. R., He H. T., Hirn M., Finne J., Goridis C. Differential expression of mouse neural cell-adhesion molecule (N-CAM) mRNA species during brain development and in neural cell lines. J Neurosci. 1986 Jul;6(7):1983–1990. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-07-01983.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet M., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecule is on embryonic muscle cells and mediates adhesion to nerve cells in vitro. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):693–695. doi: 10.1038/295693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamprecht B. Structural, electrophysiological, biochemical, and pharmacological properties of neuroblastoma-glioma cell hybrids in cell culture. Int Rev Cytol. 1977;49:99–170. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61948-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirn M., Pierres M., Deagostini-Bazin H., Hirsch M., Goridis C. Monoclonal antibody against cell surface glycoprotein of neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 15;214(2):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Kinetics of homophilic binding by embryonic and adult forms of the neural cell adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5762–5766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husmann M., Görgen I., Weisgerber C., Bitter-Suermann D. Up-regulation of embryonic NCAM in an EC cell line by retinoic acid. Dev Biol. 1989 Nov;136(1):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. M., Lyons K. M., Hogan B. L. Involvement of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 (BMP-4) and Vgr-1 in morphogenesis and neurogenesis in the mouse. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):531–542. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner J., Zinser G., Werz W., Goridis C., Bizzini B., Schachner M. Experimental modification of postnatal cerebellar granule cell migration in vitro. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 9;377(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90872-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnemann D., Bock E. Cell adhesion molecules in neural development. Dev Neurosci. 1989;11(3):149–173. doi: 10.1159/000111896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons K. M., Jones C. M., Hogan B. L. The DVR gene family in embryonic development. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):408–412. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90265-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mege R. M., Matsuzaki F., Gallin W. J., Goldberg J. I., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Construction of epithelioid sheets by transfection of mouse sarcoma cells with cDNAs for chicken cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7274–7278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. A., Hemperly J. J., Prediger E. A., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Alternatively spliced mRNAs code for different polypeptide chains of the chicken neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM). J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):189–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. C., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Organization of the neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) gene: alternative exon usage as the basis for different membrane-associated domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):294–298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Rueger D. C., Drier E. A., Corbett C., Ridge R. J., Sampath T. K., Oppermann H. OP-1 cDNA encodes an osteogenic protein in the TGF-beta family. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2085–2093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Schnegelsberg P. N., Oppermann H. Murine osteogenic protein (OP-1): high levels of mRNA in kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91342-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice H. M., Moore S. E., Dickson J. G., Doherty P., Walsh F. S. Nerve growth factor-induced changes in neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) in PC12 cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1859–1863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubin R., Deagostini-Bazin H., Hirsch M. R., Goridis C. Modulation of NCAM expression by transforming growth factor-beta, serum, and autocrine factors. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Acheson A., Hall A. K., Mann D. M., Sunshine J. The neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) as a regulator of cell-cell interactions. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):53–57. doi: 10.1126/science.3281256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U. Developmental biology of a neural cell adhesion molecule. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):549–554. doi: 10.1038/310549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Grumet M., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecule mediates initial interactions between spinal cord neurons and muscle cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):145–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampath T. K., Coughlin J. E., Whetstone R. M., Banach D., Corbett C., Ridge R. J., Ozkaynak E., Oppermann H., Rueger D. C. Bovine osteogenic protein is composed of dimers of OP-1 and BMP-2A, two members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13198–13205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Rutishauser U. Guidance of optic axons in vivo by a preformed adhesive pathway on neuroepithelial endfeet. Dev Biol. 1984 Dec;106(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90248-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small S. J., Shull G. E., Santoni M. J., Akeson R. Identification of a cDNA clone that contains the complete coding sequence for a 140-kD rat NCAM polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2335–2345. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin B. C., Hoffman S., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Sulfation and phosphorylation of the neural cell adhesion molecule, N-CAM. Science. 1984 Sep 28;225(4669):1476–1478. doi: 10.1126/science.6474186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Subasinghe C., Shinozuka K., Cohen J. S. Physicochemical properties of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3209–3221. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacke R., Martini R. Changes in expression of mRNA specific for cell adhesion molecules (L1 and NCAM) in the transected peripheral nerve of the adult rat. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Dec 11;120(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90045-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos S., Bonhoeffer F., Rutishauser U. Fiber-fiber interaction and tectal cues influence the development of the chicken retinotectal projection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]