Abstract
We created and tested multi-epitope DNA or protein vaccines with TLR4 ligand emulsion adjuvant (gluco glucopyranosyl lipid adjuvant in a stable emulsion [GLA-SE]) for their ability to protect against Toxoplasma gondii in HLA transgenic mice. Our constructs each included 5 of our best down-selected CD8+ T cell–eliciting epitopes, a universal CD4+ helper T lymphocyte epitope (PADRE), and a secretory signal, all arranged for optimal MHC-I presentation. Their capacity to elicit immune and protective responses was studied using immunization of HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice. These multi-epitope vaccines increased memory CD8+ T cells that produced IFN-γ and protected mice against parasite burden when challenged with T. gondii. Endocytosis of emulsion-trapped protein and cross presentation of the antigens must account for the immunogenicity of our adjuvanted protein. Thus, our work creates an adjuvanted platform assembly of peptides resulting in cross presentation of CD8+ T cell–eliciting epitopes in a vaccine that prevents toxoplasmosis.
Keywords: Vaccines
Keywords: Parasitology
Immunization of HLA Class I transgenic mice with a composite epitope vaccine promotes cross presentation of peptides to CD8+ T cells, eliciting IFNγ and protection against toxoplasmosis.
Introduction
Toxoplasma gondii is an intracellular parasite that can cause severe ocular and neurological diseases in fetuses, newborn infants, and immunocompromised individuals (1). The acute infection is characterized by proliferation of tachyzoites, which replicate rapidly within host cells and lyse their host cells within 24–48 hours to release large numbers of progeny. In response to immune pressure, the parasite differentiates into a slow-growing form called bradyzoites, which resides within intracellular cysts. Formation of tissue cysts normally occurs in long-lived cells such as muscle or neuronal cells.
Although antiparasitic medicines such as sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine are effective against tachyzoites, they are associated with toxicity or hypersensitivity and do not eliminate the latent, cyst form of the parasite (2). Thus, there is a need for development of a safe, protective vaccine. Our recent work has focused on development of an epitope-based vaccine to prevent toxoplamosis to enhance host immunity by stimulating efficacious responses of CD4+ helper T lymphocytes (HTLs) and CD8+ IFN-γ–producing T lymphocytes (3–6) for humans. These CD8+ T cells recognize the octamer/nonamer peptides presented by HLA supermotif major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) molecules on antigen presenting cells (APCs) in humans (3–6). Considerable effort has been made to identify promising vaccine candidate antigens for Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii). Using bioinformatic analyses, multiple predicted CD8+ epitopes of tachyzoite- and bradyzoite-specific antigens have recently entered our vaccine development pipeline (3–6). Candidate amino acid sequences are from surface antigens (SAG1 and SUSA1) and secreted proteins, including dense granule proteins (GRA2, GRA3, GRA6, GRA7) and rhoptry proteins (ROP2, ROP16, ROP18). We reported in our previous studies CD8+ epitopes derived from these antigens that can be presented by HLA-A02, HLA-A03, and HLA-B*07 supermotif human MHC molecules (3–6). These CD8+ T cell–restricted peptides — administered with a universal helper T cell epitope, PADRE, and adjuvants — elicit IFN-γ and reduce parasite burden in HLA-B*07:02, HLA-A*11:01, and HLA-A*02:01 transgenic mice.
In the present study, we selected 5 peptide epitopes — KSFKDILPK (SAG1224-232), STFWPCLLR (SAG2C13-21), AVVSLLRLLK (GRA589-98), SSAYVFSVK (SRS52A250-258), and AMLTAFFLR (GRA6164-172) — that elicited IFN-γ from peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes (PBMCs) from T. gondii seropositive HLA-A03 supertype humans. SAG1 is a surface protein expressed in tachyzoites and mediates adhesion of the parasite to the host cell prior to invasion (7, 8). It is conserved in T. gondii strains and shown to induce cellular immune responses in mice (9). SAG2C appears to be expressed exclusively on the surface of bradyzoites. SRS52A is one of the surface antigen-1–related sequences (SRSs), which comprise a gene family with similar structure to the major tachyzoite immunodominant surface antigen, SAG1. GRA6 is expressed and secreted by both the tachyzoite and the bradyzoite stages of the parasite. GRA5, another dense granule protein, is present in bradyzoites and is strongly concentrated in the cyst wall (10).
As identification of protective epitopes increases, novel ways to present these immunogenic peptide epitopes to a host’s immune system are needed. Development of multi-epitope DNA vaccines has been utilized to protect against other pathogens. However, immunogenicity of epitope-based DNA vaccines is not yet optimal, as immune responses induced by epitope DNA vaccines are often weak (11). In our previous studies, we produced a prototypic Toxoplasma vaccine based on a highly versatile self-assembling protein nanoparticle platform that can repetitively display PADRE-GRA720–28 antigenic epitopes and found a 72% reduction of cysts in type II T. gondii–infected HLA-B*07:02 transgenic mice (12). Thus, our current study is intended to develop new tools to add to a rational design that might be adapted to other platform approaches with CD8+ epitopes that bind to HLA class I molecules or be sufficient by themselves to elicit robust protection in humans.
Herein, we selected 5 potentially protective octamer CD8+ T cells eliciting epitopes that interact with HLA-A*11:01. We generated 2 polypeptides containing the 5 HLA-A*11:01 peptides and PADRE linked with 2 different linkers. We found better protection with the N/NAAA linker. This polypeptide administered with TLR4 ligand containing emulsion gluco glucopyranosyl lipid adjuvant in a stable emulsion (GLA-SE) was more effective than with ALUM adjuvant. Furthermore, we examined the immunogenicity of a synthetic DNA vaccine encoding the 5 octamer CD8+ T cells eliciting epitopes of T. gondii. DNA was delivered by electroporation, as previously described (13, 14), into HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice, and the immunization was followed 2 and 4 weeks later by protein boosts with the multi-epitope recombinant protein containing CD8+ T cell-eliciting epitopes a universal CD4+ HTL epitope, PADRE, and adjuvanted with GLA-SE. Immunization of these mice activated CD8+ T cells to produce IFN-γ, increase memory CD8+ T cells, and it protected against subsequent challenge with a high inoculum of type II parasites. Our results highlight the potential for the use of GLA-SE–adjuvanted CD8+ T cell–restricted epitopes in multi-epitope assemblies as a platform for a vaccine approach to protect against toxoplasmosis.
Results
Identification of candidate T. gondii–specific HLA-A*11:01–restricted epitopes.
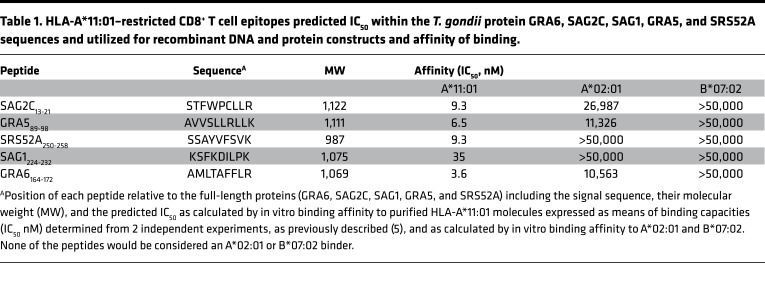
We have searched candidate epitopes from T. gondii that show high-affinity binding to HLA-A*11:01 molecules (Table 1). Five peptide epitopes derived from SAG1, SRS52A, SAG2C, GRA6, and GRA5 have representative affinities for HLA-A*11:01 molecules, a haplotype that covered 16%–30% of the population in China; 7%–16% in Europe and North America; and 1.5%–10% in South America (www.allelefrequencies.net) (Table 1).
Table 1. HLA-A*11:01–restricted CD8+ T cell epitopes predicted IC50 within the T. gondii protein GRA6, SAG2C, SAG1, GRA5, and SRS52A sequences and utilized for recombinant DNA and protein constructs and affinity of binding.
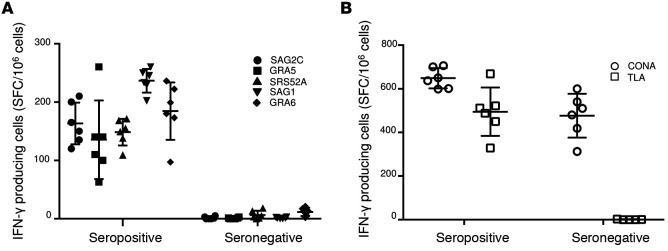
To determine which of these peptides would be recognized in the context of Toxoplasma infection, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from T. gondii–seropositive HLA-A03 supertype individuals were tested for response to these peptides in pools or individually by using an IFN-γ ELISpot assay. Candidate peptides were considered immunogenic if they induced IFN-γ–secreting spot formation that was significant compared with an irrelevant HLA-A*11:01–restricted peptide. As shown in Figure 1, there were 5 peptide pools that stimulated significant (all are P < 0.05) response by PBMC derived from Toxoplasma-seropositive HLA-A03-supertype individuals: SAG1224-232 (KSFKDILPK), SAG2C13-21 (STFWPCLLR), GRA589-98 (AVVSLLRLLK), SRS52A250-258 (SSAYVFSVK), and GRA6164-172 (AMLTAFFLR).
Figure 1. Testing of peptides with PBMCs from HLA-A03 supertype T.
gondiiseropositive and seronegative donors. (A) PBMC from donors who were seropositive and seronegative for T. gondii were tested for response to predicted HLA-A03 –restricted CD8+ T cell epitopes. Individual peptides were tested using IFN-γ ELISpot assay. (B) Concanavalin A (Con A) and tachyzoite antigen lysates (TLA) were used as controls. In A, experiments were performed 3 times. A representative experiment with one seropositive and one seronegative person shows the variability for each individual. For each person for each peptide, there were 6 determinations (wells). Each symbol represents one of these measurements of IFN-γ. The horizontal line is the mean of these 6 determinations with the SD shown. In B, methods, numbers of determinations, and comparisons were the same as for the peptides but were for Con A and TLA stimulation as controls. In 3 replicate experiments, PBMCs also were obtained from 3 T. gondii seropositive and 3 T. gondii seronegative HLA-A03 individuals. In these experiments, in the comparison of 3 seropositive and 3 seronegative persons, differences between the seropositive and seronegative persons were significant for each peptide when tested by Student’s t test (P < 0.05; n = 3 per group, data not shown). Stimulation for seropositive and seronegative persons for TLA were different and achieved statistical significance (P < 0.05). In contrast, stimulation with Con A demonstrated response of PBMC from both seronegative and seropositive donors (data not shown).
Specificity of epitopes for HLA-A*11:01.
The peptides we selected are HLA-A*11:01 specific. This specificity is shown in our binding assay, where our peptides do not significantly bind to HLA-A*02:01 or B*07:02 molecules (Table 1). HLA-A*02:01 and -B*07:02 are among the other most prevalent supermotifs, and our results are consonant with in silico predictions for these haplotypes. In Table 1, none of the peptides would be considered A*02:01 or B*07:02 binders. In Table 2, relative to the background genes in the C57BL/6J mice, there is specificity of presentation of peptides to those that are restricted by HLA-A*11:01 by macrophages from the transgenic HLA-A*11:01 mice but not presented by macrophages from their WT mouse controls. In earlier work by Tan, McLeod et al. and Cong, McLeod et al. (3, 5), for all 5 peptides utilized herein, PBMC from 3 T. gondii–seropositive HLA-A03-supertype persons with serum antibody to T. gondii (seropositive) and 3 persons without serum antibody to T. gondii (seronegative) were tested. PBMC from all the seropositive persons responded to the peptides, and no seronegative persons had PBMC that responded with IFN-γ production demonstrated by ELISpot. Peptides and tachyzoite antigen lysates (TLA) differences were highly significant for seropositive and seronegative persons (P < 0.001), whereas differences for Concanavalin A were not significant. The response to the peptides is specific to the parasite in seropositive persons and not present in those who are seronegative. Herein, the peptides were retested at the same time for the same HLA–A3-supertype seropositive human donor used for our subsequent studies herein. PBMC from HLA–A2, B7 haplotype seropositive persons (and seronegative persons) were without response to individual peptides or the poly-epitope in the ELISpot for IFN-γ in 2 replicate experiments (data not shown).
Table 2. IFN-γ production of CD8+ T cells purified from the spleens of HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice immunized 3 times with T. gondii epitope peptides at 2-week intervals following stimulation with the peptides in vitro.
HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice as a model to assess cellular immunogenicity of 5 identified HLA-A*11:01–restricted CD8+ T cell epitope peptides.
To address the HLA-A11–specific genetic restriction of the 5 HLA-A*11:01 epitopes (plus a GRA7 peptide) identified to prime for IFN-γ responses, HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice were immunized s.c. Immunization was with these peptides mixed with PADRE and adjuvants or the adjuvants alone. As shown in Table 2, robust IFN-γ responses from CD8+ T cells from spleens of mice immunized with peptides plus adjuvants were observed following stimulation by the pool of peptides in the presence of APC from the HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice but not of APC from WT C57BL/6 mice (Table 2). Immunization of HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice with adjuvants alone did not elicit IFN-γ when the CD8+ T cells were stimulated either with or without peptides (i.e., background levels) (Table 2).
Vaccination with peptide pools, PADRE, and GLA-SE adjuvant protects mice and increases memory against type II parasite challenge.
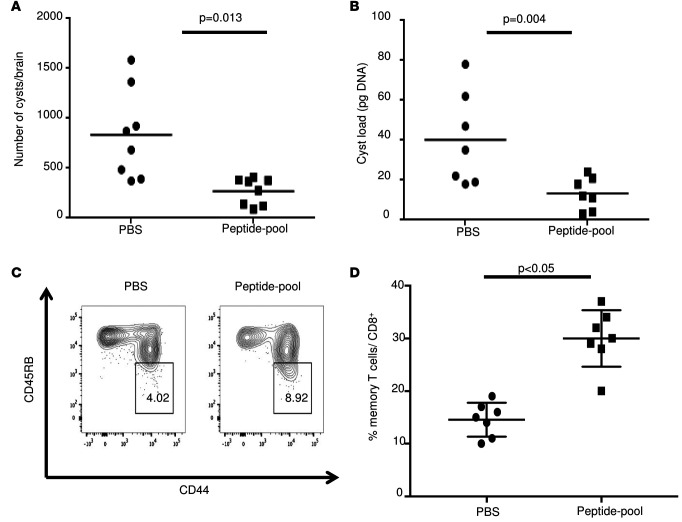
HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice were immunized with peptide pools combined with GLA-SE adjuvant and PADRE 3 times at intervals of 2 weeks. PBS was used as control. Five weeks after the last immunization, mice were challenged with type II parasites. Differences in brain cyst numbers between control and immunized mice were significant (P < 0.013; Figure 2, A and B), with the immunized mice having a reduced cyst burden. Spleens from unchallenged immunized and control mice were tested for the ability of the immunization to induce CD8+ T cell memory response. As shown in Figure 2, C and D, there is an increase of memory CD8+ T cells in the immunized group.
Figure 2. Immunogenicity and efficacy of 5 identified A11-restricted CD8+ T cell epitope pool peptides in combination with PADRE and GLA-SE adjuvant in HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice.
(A) T. gondii brain cysts number was significantly reduced in HLA-A*11:01 mice immunized with pool of peptides plus PADRE and GLA-SE adjuvant at 21 days after challenge with 2,000 T. gondii ME49-Fluc (Type II) parasites (n = 8 mice per group, in 2 replicate experiments with 4 mice per experiment, pooled; *P < 0.013, Student’s t test). (B) Quantitative PCR for the parasite burden in the T. gondii–challenged HLA-A*11:01 mice brains (n = 7 mice per group combining 2 replicate experiments, *P < 0.004, Student’s t test). (C and D) Flow cytometry gating for CD8+ memory T cells 11 weeks after immunization of HLA-A*11:01 mice with pooled adjuvanted peptides. Cells are gated on CD3+CD8+ T cells. Memory T cells were defined as CD44hiCD45RBlo. For each group, a representative FACS plot is shown with the percent of CD8+ memory T cells shown. For each group, n = 3 and differences were significant; P < 0.05, Student’s t test. This experiment is representative of 2 replicates. Horizontal lines are means and SDs are shown in D.
LO and AZ multi-epitope polypeptide immunogenicity in vitro.
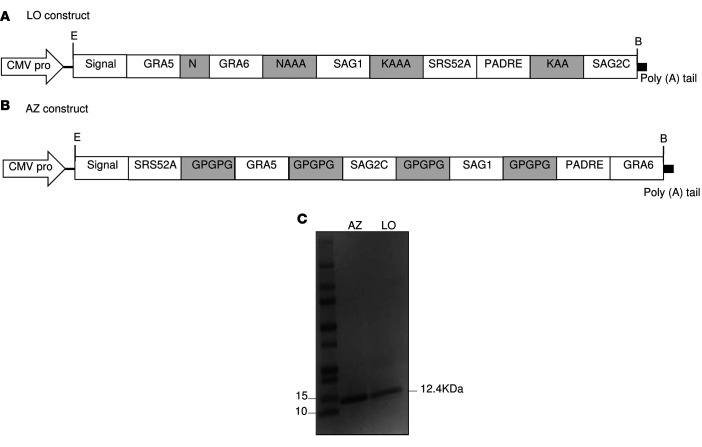
The CD8+ T cell epitopes identified are intended to form the basis of Toxoplasma vaccine for persons with the HLA-A*11:01 supertype. We expressed and purified from E. coli a protein composed of the 5 epitopes linked in a sequence with the universal CD4+ T cell epitope, PADRE (AKFVAAWTLKAAA), and the murine Igκ-chain signal sequence for targeting protein to secretory pathway at the N-terminus. The epitopes were linked with N/K alanines or GPGPG as linkers and named LO and AZ, respectively (Figure 3, A and B). Both proteins were purified via Ni-NTA affinity column, and the molecular weight was verified by SDS-PAGE analysis (Figure 3C). Immunogenicity of the 2 proteins compared with the pool of the 5 individual A11-restricted CD8+ T cell epitope peptides were tested in vitro. Briefly, PBMCs from T. gondii–seropositive HLA-A03 supertype humans were tested for their ability to generate IFN-γ in response to the stimulation with either LO or AZ protein or a pool of the peptides for 2 days to allow time for processing the proteins and presentation thereof to MHC-I. The data in Figure 4, A–C, demonstrate IFN-γ secretion was significantly enhanced by stimulation with either LO or AZ multi-epitope polypeptide compared with a pool of the individual 5 epitope peptides (P < 0.001).
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the DNA vaccine construct.
(A and B) The orientation of the HLA-A*11:01–restricted CD8+ T cell epitopes and PADRE in the synthetic gene is shown with 2 different types of spacers, called LO and AZ, for N/KAAA and GPGPG linker, respectively. (C) SDS-PAGE 4%–20% of the purified LO and AZ proteins.
Figure 4. LO and AZ elicit specific immune responses in HLA-A03 seropositive and seronegative donors.
(A–C) ELISpot showing IFN-γ spot formation. PBMCs were tested using LO, AZ, and pool of peptides. (C) Con A and TLA were used as controls. Variability between determinations for single donors are shown in panels A and B with n = 6 determinations (as described in Figure 1). In A and B, the data shown are a single representative experiment from one T. gondii seropositive and one T. gondii seronegative HLA-A03-supertype donor. Each experiment was carried out with 6 determinations. Replicate experiments also were performed 3 times with PBMCs from 3 T. gondii seropositive and 3 T. gondii seronegative HLA-A03 individuals. Two-tailed Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis comparing differences between the 2 groups (n = 3 per group, P < 0.05). One-way ANOVA was performed before the Student’s t test to determine whether there was an overall difference between the groups. Differences between the stimulation of seropositive and seronegative individuals’ PBMCs by the poly-epitope proteins were significant (P < 0.05, data not shown). Similarly, TLA stimulated the seropositive persons’ PBMCs, but Con A did not (data not shown).
Herein, the peptides and poly-epitope were retested at the same time for the same HLA–A3-supertype seropositive human donor used for our subsequent studies herein and HLA–A2, B7 haplotype seropositive persons (and seronegative persons) whose cells were without response (data not shown).
Immunization with LO and AZ multi-epitope polypeptides with GLA-SE adjuvant confers a potent protection in HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice against T.
gondii. HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice were immunized with a combination of LO and AZ multi-epitope polypeptides with GLA-SE or ALUM adjuvant. As a control, mice were immunized with adjuvant alone or with PBS. Mice were then challenged 2 weeks after the last immunization with type II strains of T. gondii. As shown in Figure 5, 80% of mice immunized with LO and AZ multi-epitope polypeptides emulsified in GLA-SE adjuvant survived parasite challenge. In contrast, only 30% of mice immunized with the ALUM adjuvant plus polypeptides survived parasite challenge (P < 0.05). As a control, neither mice immunized with the adjuvant alone nor those sham-immunized with PBS increase their survival after challenge (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Multivalent polypeptide LO and AZ protective efficacy in vivo with HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice survival curve after challenge with Type II parasites.
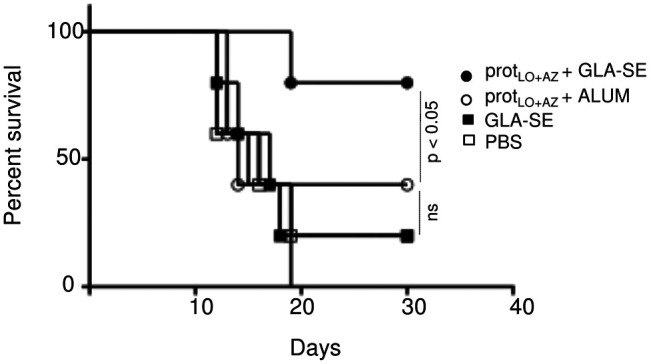
Two weeks after last immunization, the transgenic mice immunized with pooled LO and AZ proteins (prot) in combination with either adjuvant GLA-SE or ALUM adjuvant or injected with PBS were infected with 2,000 Me49 (Fluc) parasites. The survival rates of the 2 groups were recorded. This figure shows data from mice in both of 2 replicate experiments combined (n = 5 control and 5 immunized mice). Kaplan-Meier curves were generated and survival compared across groups using the log-rank test, P < 0.05. Differences between protLO+AZ + GLA-SE and all other groups were significant (P < 0.05) and differences between protLO+AZ + GLA-SE and protLO+AZ + ALUM also were compared for survival using log-rank test and Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Prime/boost strategy: LO and AZ DNA plus multi-epitope polypeptide immunogenicity in vivo.
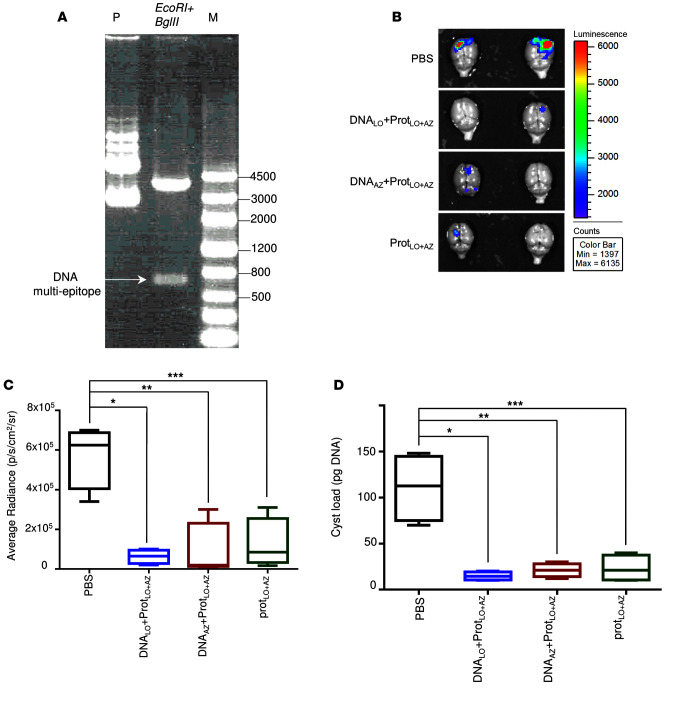
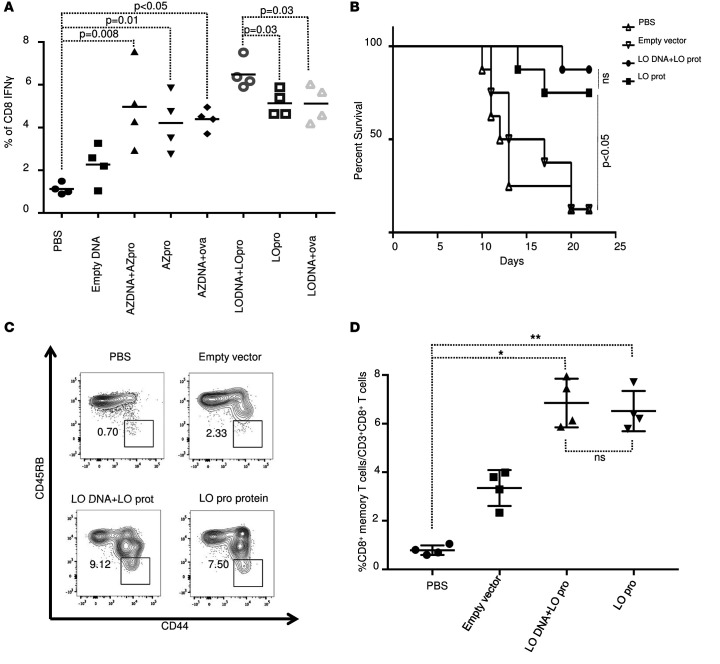
We next addressed whether a prime/boost strategy using DNA encoding the 5 individual epitopes plus PADRE and the polypeptides would confer better protection against parasite challenge in HLA-A*11:01 mice. We constructed synthetic DNAs in which the 5 poly-epitope nucleotides with the N/K alanines or GPGPG linkers plus PADRE were cloned in EcoRI and BglII sites of the vaccine vector pMB75.6 (Figure 6A). During DNA vaccinations, mice were immunized i.m. 2 times at 2-week intervals with 100 μg of LO or AZ DNA vectors followed by another 2 injections of 50 μg of the polypeptides at 2-week intervals. They were challenged with 2,000 ME49 (Fluc) 2 weeks after the last immunization. Brains from these mice were imaged 21 days after the challenge using a Xenogen in vivo imaging system to assess parasite burden in the brain. As shown in Figure 6, B and C, as an additional measure of efficacy for protection against challenge with luciferase-expressing parasites, the numbers of these parasites in HLA-A*11:01 mice immunized with LO or AZ DNA plus multi-epitope polypeptide or polypeptides alone were significantly reduced compared with the mice immunized with control empty vector or PBS. This correlates with the reduction of the number of cysts per brain (Figure 6D). We then analyzed the effect of LO or AZ DNA plus multi-epitope polypeptide on IFN-γ expression in vitro. Briefly, mice were immunized 2 times at 2-week intervals with LO or AZ DNA followed by another 2 injections of either LO polypeptide, AZ polypeptide, or ovalbumin peptide as control. Negative control mice were vaccinated twice with empty vector followed by saline. Two weeks after the last immunization, mice were sacrificed and splenocytes were harvested for immune response analysis. As shown in Figure 7A, considerable amounts of IFN-γ–expressing CD8+ cells were observed following immunization with AZ DNA or LO DNA compared with mice immunized with the empty vector. An even more robust response was achieved when mice immunized with the vectors expressing the polypeptides were stimulated in vitro by the corresponding AZ or LO protein, although the difference was only significant in the LO-treated mice. In contrast, there was no increase in the amount of CD8+ IFN-γ–producing cells observed when the mice were immunized with AZ or LO DNA followed by a challenge with a nonrelevant protein, ovalbumin. There was a very modest increase in protection when DNA administration precedes administration of protein with the LO construct as in survival curves and dot plots (Figure 7B).
Figure 6. DNA prime-protein boost regimen.
(A) pMB75.6 vector used as a DNA vaccine vector for this study. Lane P: pMB75.6 plasmid; lane 2: pMB75.6 plasmid digested with EcoRI and BglII; lane M: KB ladder. (B) T. gondii brain cysts luciferase expression was reduced in HLA-A*11:01 mice immunized with DNA/ protein boost at 21 days after challenge with 2,000 T. gondii ME49-Fluc (Type II) expressing luciferase. (C) Xenogen imaging of brain ex vivo following the injection of luciferin into the retro-orbital plexus and then exposure of the brain to luciferin solution. n = 5 per group, *P = 0.0008, **P = 0.004, ***P = 0.004 (Student’s t test after one-way ANOVA). (D) Enumeration of cysts was performed with brains of mice challenged 21 days after final immunization. These experiments were performed at least 2 times, and one representative experiment of 2 is shown:.n = 5 control and 5 immunized mice. *P = 0.002, **P = 0.003, ***P = 0.004; Student’s t test was used to compere the groups. For C and D, the plots show median, with box extending from the 25th to 75th percentile and the whiskers extending from minimum and maximum values of the data set. One-way ANOVA was performed before the Student’s t test to determine whether there was an overall difference between the groups.
Figure 7. CD8+ T cell responses in HLA-A*11:01 mice following immunization.
(A) Splenocytes from immunized mice with LO DNA, AZ DNA, and multi-epitope polypeptides alone or combined were harvested for 10–14 days after immunization and exposed to LO or AZ polypeptide for ex vivo IFN-γ expression. Quantitation of IFN-γ from mouse splenocytes was evaluated in 2 separate experiments. Each experiment (n = 4 mice) was evaluated for comparison for vaccination with AZ protein compared with control and for LO protein compared with control; significance evaluated with Student’s t test. (B) HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice survival curve after challenge with Type II parasites. Two weeks after last immunization, the transgenic mice immunized with empty vector, LO DNA + LO polypeptide, or LO polypeptide, or were injected with PBS were infected with 2,000 T. gondii ME49-Fluc (Type II) parasites. The survival rates of the 2 groups were recorded. Mice vaccinated with either LO protein alone or LO DNA + LO protein were compared with control mice (PBS or empty vector). Kaplan-Meier curves were generated and survival compared across groups using the log-rank test, P < 0.05. (n = 8 mice per group in 2 replicate experiments with 4 mice, shown pooled). (C and D) CD8+ memory T cells. Flow cytometry gating for CD8+ memory T cells. Spleen cells are gated on CD3+CD8+ T cells. Memory T cells were defined as CD44hiCD45RBlo. For each group, a representative FACS plot is shown with the percent of CD8+ memory T cells shown. All mouse experiments were repeated at least twice (n = 2–4 mice in each group). * P < 0.001, ** P < 0.001. In A and D; one-way ANOVA was performed before the Student’s t test to determine whether there was an overall difference between the groups.
LO DNA plus multi-epitope LO polypeptide are protective against Toxoplasma challenge in HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice.
As shown in Figure 7B, a majority, 7 of 8 (87%), HLA-A*11:01 mice immunized with LO DNA plus LO polypeptide emulsified in GLA-SE adjuvant survived parasite challenge. In contrast, only 1 of 8 (12%) unimmunized mice or immunized with empty vector survived parasite challenge.
LO DNA plus multi-epitope polypeptide increases memory CD8+ T cell response.
We then analyzed the effect of LO DNA plus multi-epitope polypeptide on the T. gondii–specific CD8+ T cell memory response. This was performed by quantifying the levels of memory T cells in the spleen from HLA-A*11:01 mice at 35 days after the last immunization. As shown in Figure 7, C and D, CD8+ memory T cells were significantly increased in mice immunized with either LO protein alone or LO DNA plus LO protein, compared with mice immunized with the empty vector or PBS.
LO protein+GLA-SE emulsion protects against T. gondii challenge.
This protection is shown in Figure 8A.
Figure 8. Multi-epitopes adjuvanted with GLA-SE are captured and presented by MHC molecules on the APCs to T lymphocytes.
(A) HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice immunized with LO protein plus GLA-SE were protected compared with control mice inoculated with PBS when they were challenged with 20,000 T. gondii prugneaud strain (Fluc) luciferase expressing parasites after 4 and 6 days. (n = 4 mice per group, 2 replicate experiments.) (B) Assay demonstrating that GLA-SE is a TLR4 ligand that leads to production of IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α by PBMC. Stimulation of human whole blood with GLA-SE. Heparinized whole blood was collected from 6 healthy donors, and 200 μl was stimulated with 5 μg GLA-SE in 96-well plates at 37oC CO2. After 24 hours, plasma was removed and assayed for IL-6, IL-12(p40), and TNF-α by a custom Luminex-based multiplex immunoassay kit (Affymetrix eBioscience). Data were analyzed using the Masterplex QT software (Miraibio). The cytokine production stimulated by adjuvant was statistically significant for IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α (P < 0.05) compared with the unstimulated groups as assessed by the Mann-Whitney U test (GraphPad Prism software). The plots show median, with box extending from the 25th to 75th percentile and the whiskers extending from minimum and maximum values of the data set. (C) Multi-epitope proteins with GLA-SE are captured by the Antigen-presenting cells (APCs), and the peptides contained are presented by MHC molecules on the APCs to T lymphocytes in both a class I and a class II pathway. This demonstrates that cross presentation into a class I pathway must occur by virtue of effector function. APCs are also activated through recognition of GLA-SE by TLR4 receptors molecules. This activation leads to the production of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-12, IL-6, TNF-α) and the expression of costimulatory molecules on the cell surface.
GLA-SE is a TLR4 ligand that elicits cytokines.
Demonstration that GLA-SE is a TLR4 ligand is shown with data in Figure 8A eliciting IL-6, IL-2, and TNF-α. We determine whether GLA-SE induces cytokine production. As shown in Figure 8B, human whole blood was stimulated with GLA-SE for 24 hours. There was an increase of cytokine production in these cultures. Difference between stimulated and unstimulated cultures are significant (P < 0.05) (Figure 8B). Putative mechanisms are shown schematically in Figure 8C.
Discussion
There is a need for improved vaccination and delivery approaches to induce cellular immune responses against T. gondii. Earlier bioinformatics, immunosense approaches, and empiric studies with human PBMCs facilitated identification of protective peptide epitopes for HLA-A*11:01 supertypes. The most immunogenic of these epitopes (KSFKDILPK [SAG1224-232], STFWPCLLR [SAG2C13-21], AVVSLLRLLK [GRA589-98], SSAYVFSVK [SRS52A250-258], and AMLTAFFLR [GRA6164-172]) were then utilized in comparative studies with differing adjuvants and delivery methods in the HLA-A*11:01 supermotif transgenic mice to characterize immune responses and study protection. Herein, we show a way to present immunogenic peptide epitopes to a host’s immune system based on the assembly of 5 protective CD8+ T cell epitopes for HLA-A*11:01–restricted supertypes. These epitopes were constructed with the universal CD4+ T cell epitope, PADRE linked with N/KAAA or GPGPG spacers, and a secretory signal. These vaccine design features were incorporated to optimize proteasome processing and, subsequently, epitope and vaccine immunogenicity.
Improved delivery approaches are important for successful vaccines. This was showed by previous studies with another transgenic mouse supertype, HLA-B*07: In this work, T gondii–specific HLA-B*07–restricted CD8+ T cell epitope LPQFATAAT derived from GRA720–28 elicited CD8+ T cell–specific IFN-γ with the help of a universal CD4+ epitope, and adjuvant GLA-SE. This immunization conferred protection of HLA-B*07 mice against type II parasite challenge (4). The same epitope used in a nanoparticle platform was found to have better immunogenicity (12), with 72% reduction of cyst burden in the brains of GRA720–28 nanoparticles-immunized mice compared with 54% reduction with immunization with GRA720–28 peptide in combination with PADRE and the adjuvant GLA-SE. This work provided a foundation for the present study, which is intended to improve vaccination and delivery approaches against T. gondii to protect humans.
Herein, we examined the immunogenicity of a multi-epitope protein and a synthetic consensus DNA, the clinically approved mammalian expression vector encoding 5 T. gondii–specific HLA-A*11:01–restricted epitopes. The DNA plasmid vaccine encodes the 5 CD8+ T cell epitopes restricted by HLA-A*11:01 supertype alleles and the universal HTL epitope, PADRE. These DNA constructs were optimized using codon optimization, leader sequence addition, and plasmid production at high concentration, and the DNA was delivered by electroporation as described (13). Immunization of HLA-A*11:01 mice with recombinant multi-epitope formulated with a TLR4–containing adjuvant (GLA-SE) induced antigen-specific IFN-γ–producing CD8+ T cells in their spleens, increased the memory CD8+ T cell population, and conferred a potent protection against T. gondii challenge. The adjuvant ALUM formulated to the recombinant multi-epitope was less effective in conferring protection when compared with the vaccine preparations containing GLA-SE. The present study also demonstrated that DNA prime followed by a multi-epitope protein–GLA-SE boost is more protective than either of the DNA prime followed by ovalbumin (unrelated protein) boost or the recombinant multi-epitope alone.
The major limitation of DNA vaccination in the past has been its relatively weak immunogenicity in vivo for humans. Electroporation has successfully aided in enhancing the delivery of DNA vaccines, leading to the generation of stronger immune responses (10- to 100-fold) compared with naked DNA vaccine delivery alone to muscle or skin (15). Interestingly, a multi-epitope DNA prime-protein boost also appeared to drive a more functionally divergent T cell response (16). Previous studies have shown that protein- and DNA-only vaccination produced similar numbers of IFN-γ+ cells in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, as well as similar numbers of IL-2+ cells in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (16). In contrast, a multi-epitope DNA prime-protein boost resulted in 4 times more IFN-γ+–secreting CD8+ T cells than IFN-γ+–secreting CD4+ T cells and higher IL-2+–secreting CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (16). Notably, our present study showed that protein prime and boost with GLA-SE was also quite effective. The ex vivo stimulation of spleen cells from HLA-A*11:01 mice and PBMC from HLA-A03 seropositive individuals showed that CD8+ T cells were more responsive to the composite polypeptide than to the pooled or single-constituent peptides. Processing and presentation of AZ and LO poly-epitope polypeptide in human cells occur with high efficiency in LO poly-epitope–stimulated cells. These cells demonstrate stronger responses with N/K alanine linkers compared with GPGPG.
The poly-epitope protein induces a more robust response, compared with single peptides with GLA-SE or compared with lipopeptides with single peptides or 3 of the peptides that are linked, but in a different order. In these linked and single-peptide lipopeptides, responses are much less or absent (3, 5). Other arrangements of sequence in DNA vaccines encoding peptides in DNA vaccine or peptides in a nonionic surfactant vesicle (NISV) also elicited less robust response or were or absent (data not shown). In future studies, when constructs for all haplotypes are fully defined and optimized, it will be important to utilize models we have developed for ocular, congenital, peroral encysted bradyzoite, and oocyst infections, as well as immune-compromised models of infections (17–24) and intranasal immunizations (Gigly, Dubey, et al., unpublished observations).
There are a number of aspects of our current approach that make our work herein unique and valuable. This work takes a step toward building immunosense vaccines for humans. These paradigm changes include the following: the GLA-SE emulsion leads to delivery of peptides from an artificial, polypeptide-epitope protein to both class I and class II MHC pathways. This is demonstrated by the epitope content and effector functions they elicit. Another step change is that the poly-epitope with a secretory sequence and with peptides that were arranged so cleavage is optimized in such a way that it includes the intended peptides in the protein. This arrangement allows for optimal processing and presentation. Computer-based modeling was used to design our vaccine component in this manner (25, 26). It was designed to optimize proteasome-mediated epitope processing and to minimize the creation of junctional epitopes. Junctional epitopes occur by the juxtaposition of 2 epitopes. Altering the epitope order and introducing selected amino acid spacers at the C terminus of individual epitopes were strategies used to control these properties (25, 26). This is, to our knowledge, the first and only creation of a artificial protein based on immunosense in conjunction with GLA-SE that successfully immunizes HLA transgenic, or any, mice against T. gondii. Our use of mouse strains with differing HLA supermotif transgenes also makes our work pertinent to begin to protect people globally against Toxoplasma infection with vaccines rather than simply protecting mice against this infection. It presents a paradigm for an immunosense approach for protection against human T. gondii and other infections and diseases. Further, we found earlier that protection and IFN-γ production following immunization with individual peptides pooled or organized with alanine linkers, and linked in lipopeptides, are substantially less robust in eliciting IFN-γ and protection (3, 5) than the approach herein with DNA and protein, or protein and protein immunizations, in HLA-A*011 transgenic mice. Our earlier attempt to include these and many other epitopes that would bind to other supermotifs in a “chain of pearls” DNA vaccine (El Bissati, et al., unpublished work) administered with electroporation or a peptide in NISV (Roberts, et al., unpublished data) were unsuccessful other than a very small response with the DNA vaccine to the N terminal encoded peptide, conferring very modest protection. This was despite finding the peptides by mass spectroscopy when the full-length construct was delivered as a vector transfected into a monocytic cell line (El Bissati, et al., unpublished data).
We tried deconvoluting our peptides in a separate study to characterize whether adding a homologous mouse CD4+ T cell–stimulating peptide would enhance protection. We presented some of these data in another manuscript (El Bissati, et al., unpublished obversations). Surprisingly, in this other study, we found that in female mice, this CD4+ T cell–eliciting nonamer peptide epitope — which added protection in the combination of peptides when tested as a single peptide administered with GLA-SE, as we deconvoluted peptides — was lethal in the booster, second immunization (El Bissati, et al., unpublished observations). This lethality was associated with intestinal, hepatic, spleen, and lymph node pathology due to the CD4+ T cell elicited (El Bissati, et al., unpublished observations). Without the CD8+ T cell–eliciting peptides or PADRE, there was a cytokine storm with IL-6 especially prominent. In contrast to administration of this one peptide with GLA-SE, with inclusion of our CD8+ peptides or addition of only PADRE, there was enhanced protection. What we learned is that it is not only the presence of the particular peptide but the company it keeps that leads to harmful or enhanced protective immune response. Some other recent similar studies make this point a different way. For example, based on the recent work of Blanchard’s group (27), it is also the location in the entire construct that determines immunogenicity and robustness of protection. Similarly, background genes of the host, and also the microbiome (from the work of others), influences robustness and skewing of immune responses (28–30). We had thought, to confirm safety, we should deconvolute the constituents of our vaccines. What we learned was that immunogenicity and protection will depend on the host’s genetics, epigenetics, and company the peptides keep in the final vaccine for humans. Function of the assembled vaccine constituents in the human, not just murine host, will be critical. Our recent work, and very recent work of others (27), indicates that efficacy and toxicity are likely to be more complex and ultimately require safety and efficacy testing in humans.
The in vitro and in vivo murine work in the present study indicates that the GLA-SE nanoemulsion must provide protein for cross presentation by APCs, as shown schematically in Figure 8. As shown in our experiments herein (Figure 8B), GLA-SE is a TLR4 ligand and in multiple other experimental systems and moving toward testing in a clinical setting, triggering MYD88 and downstream signaling pathways (31, 32). The GLA-SE emulsion entraps proteins in nanoparticle structures of approximately 100 nm with multiple associated GLA molecules on their surfaces, although the percentage entrapment and precise location of the GLA-SE was not studied herein. Such particles, as well as proteins that are endocytosed, enter a MHC-II pathway stimulating CD4+ T cells (33). Herein, we demonstrate both MHC-I and -II responses to peptides in our constructed protein. It is likely the small particle size (100 nm) is responsible for this unusual trajectory to MHC-I presenting bound peptides to CD8+ T cells. The effector mechanism restricted by MHC-I for a peptide defines the cross presentation of these antigens. From a poly-epitope, which must enter its host cell by endocytosis, protein or peptides must leave the endocytic vacuole and therefore be cross presented. Further, since completion of the present work, we also placed this poly-epitope protein construct with CD8+ T cell–eliciting epitopes in a self-assembling protein nanoparticle (SAPN) (El Bissati, et al., unpublished observations). Recent electron microscopy studies also demonstrated a malaria SAPN eliciting CD8+ T cells with localization to the proteasome and delayed kinetics of antigen processing and presentation with a time frame consistent with cross presentation (34). Further, we deliver PADRE, which is a universal CD4+ T cell–eliciting epitope, in the same poly-epitope protein as our CD8+ T cell–eliciting epitopes that trigger an MHC-I–eliciting immune response. PADRE from this constructed protein also does enter a class II pathway, so either some poly-epitope is not entrapped or our delivery system must bifurcate to cross presentation to MHC-I and -II pathways. This is an important finding with broad implications for vaccine development when induction of immune responses with protective CD8+ T cells are critical.
Despite the protection afforded by vaccination regimens developed in this study, no preparation provided complete protection against T. gondii, and some brain cysts and parasites in peritoneal fluid were still detected. There is room to improve the vaccine by adding the parasite immunogenic peptides, which generate parasite-specific CD4+ T cells. In addition, the inclusion of B cell epitopes to induce antibodies might also help develop more robust vaccines against T. gondii. Antibodies have not been considered to be the primary protective mechanism for T. gondii, when compared with cell-mediated immunity with the induction of cytolytic T cells and IFN-γ production (35, 36). Nonetheless, antibodies, including IgM, have been implicated in killing extracellular parasites via inducing complement-dependent lysis or by blocking entry of parasites into host cells (37–39).
In summary, our study shows a composite protein, with a secretory signal; 5 CD8+ MHC-I epitopes from T. gondii; and PADRE, a universal CD4+ eliciting peptide, which can be assembled and elicits protective MHC-I, restricted responses. Using HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice, we demonstrate the capacity and specificity of 5 HLA-A*11:01 restricted epitopes to prime and boost an IFN-γ response. In addition, the recombinant multi-epitope polypeptide emulsified in GLA-SE adjuvant confers more protection and increases memory CD8+ T cell response against T. gondii in HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice. Previous studies have found that GLA-SE, formulated with the recombinant fatty acid binding protein Sm14, enhances Th-1 type responses. Production of IFN-γ was the basis of Sm-14–mediated protective immunity both in humans with schistosomiasis and animal models (40). This Sm14 antischistosome vaccine is safe and entering phase 2 trials in Brazil and Africa. In our study, it is likely that the GLA-SE emulsion encloses the protein and presents an optimum configuration decorated with the TLR4 ligand GLA that induces a powerful CD8+ and CD4+ T cell immune response (Figure 8). In addition, DNA encoding the multi-epitope delivered by electroporation and followed by protein boosts is useful for the induction of a strong immune response against T. gondii. Thus, our data provide important support, suggesting that enhanced electroporation-delivered DNA prime-protein boost — and protein prime-protein boost, which would be considerably better tolerated — are useful strategies for delivery of a multi-epitope antiapicomplexan parasite vaccine. As these epitopes for immunization are tailored to HLA and the efficacy of vaccination with these epitopes is evaluated in mice expressing an HLA molecule, they provide a foundation and promise as a vaccine for humans. Potential improvements to this vaccine might be made with the addition of epitopes from various T. gondii proteins encompassing several of the parasite life stages and polymorphogenetic strains in a single platform that could elicit a protective immune response for the HLA class I and II supermotifs present for all the human population.
Methods
Bioinformatic predictions and MHC-peptide binding assays.
Protein sequences derived from SAG1, SRS52A, SAG2C, GRA6, and GRA5 were analyzed for CD8+ T cell epitopes based on predicted binding affinity to HLA-A*11:01 molecules using algorithms available at the Immune Epitope database (IEDB; http://www.iedb.org; refs 41, 42). Quantitative assays to measure binding of peptides to HLA class I molecules are based on inhibition of binding of radiolabeled standard peptide. Assays were performed as described previously (43, 44). Concentration of peptide yielding 50% inhibition of binding of radiolabeled probe peptide (IC50) was calculated. Under the conditions utilized were where [label] < [MHC] and IC50, [MHC], the measured IC50 values are reasonable approximations of the true Kd values.
Human PBMC and ELISpot assay.
PBMC were obtained from individuals seropositive to T. gondii, and their HLA haplotype was determined. These cells were processed and cryopreserved as described previously (3). ELISpot assays with human PBMCs used anti-human IFN-γ mAb (1-D1K) with biotinylated anti-human IFN-γ mAb (7B6-1) with 2 × 105 PBMCs per well (5, 6). All antibodies and reagents used for ELISpot assays were from Mabtech. The PBMC were plated in at least 3 replicate wells for each condition. Results were expressed as the number of spot-forming cells (SFCs) per 11 × 06 PBMCs.
Epitope peptides.
KSFKDILPK (SAG1224-232), STFWPCLLR (SAG2C13-21), AVVSLLRLLK (GRA589-98), SSAYVFSVK (SRS52A250-258), AMLTAFFLR (GRA6164-172), and PADRE-derived universal CD4+ helper epitope (AKFVAAWTLKAAA) were used in the vaccine constructs (45). GLA-SE adjuvant (TLR4 agonist), synthesized by the Infectious Diseases Research Institute (Seattle, Washington, USA) was used as a stable oil-in-water emulsion with specified epitopes during immunization.
Multi-epitope DNA vaccine design.
To maximize epitope immunogenicity in vivo, the peptides encoding minigene included starting codon ATG and the mouse Ig k signal sequence at the 5′ end of the construct, and spacer sequences N/KAAA (LO construct) and GPGPG (AZ construct) residues flanking the C-terminus of all epitopes (Figures 3, A–C). Whereas the former facilitates processing of the CTL epitopes in the ER, the latter favors proper proteasomal processing and prevents the formation of junctional HLA epitopes. The order of the CTL and HTL epitopes in the minigene and type of spacer sequences that favor proper proteasomal cleavage were determined by a customized computer software program (Epimmune) that identifies the most favorable sequence for epitope processing and simultaneously minimizes the creation of new junctional HLA-A11 determinants.
Purification of multi-epitope protein vaccine.
LO and AZ DNA were PCR amplified and cloned in the expression vector pET-22 (Novagen, EMD Millipore). The multi-epitope protein was expressed in the E. coli BL21-CodonPlus strain (Stratagene). Expression clones were grown at 37°C in Luria broth medium containing 50 μg/μl kanamycin and 34 μg/μl chloramphenicol. A culture of E. coli (1 l) was grown to an A600 of 0.6, and protein expression was induced by addition of isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (1 mM final concentration). Recombinant protein was extracted under native conditions by using the BugBuster protein extraction reagent (Novagen, EMD Millipore; 6 ml/g of cell pellet) containing a protease inhibitor mix (Roche Diagnostics) and 10μg/ml lysozyme. All purification steps were performed under 8 M urea denaturing conditions. The His-tagged polypeptides were purified by using nickel-affinity chromatography and followed by Q-Sepharose (GE Healthcare), which used to capture the endotoxin. The eluate, which contains 8 M urea, was dialyzed against a buffer containing 5 mM Hepes-KOH (pH 7.8) and 0.5 mM DTT. The purity of the protein was determined by SDS-PAGE, and the protein concentration was measured by the method of Bradford using BSA as a standard. Using E-TOXATE Kits (Sigma-Aldrich), endotoxin concentration in these proteins is < 25 EU/μg of protein.
Plasmid and gene cloning of multi-epitopes DNA vaccine construct.
The clinically approved mammalian expression vector pMB75.6 (Inovio Pharmaceuticals) was used as a DNA vaccine vector (25). Briefly, the plasmid contains elements essential for expression in mammalian cells: a cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter, intron, and gene of interest followed by the simian virus 40 (SV40) polyadenylation signal.
The oligonucleotides of 5 individual T. gondii peptides shown in Table 1 plus PADRE-derived universal CD4+ helper epitope were linked with different spacers and synthesized using 9 overlapping 50-nucleotide oligonucleotides. LO and AZ were first assembled and amplified as 3 small fragments that were subsequently used as templates to amplify the whole gene. The full-length constructs were cloned into the vaccine vector pMB75.6 using EcoRI/BglII restriction sites. Neither the pMB75.6 vector backbone nor the epitope-encoding region shares significant homology with known human genomic sequences. All recombinant plasmids were propagated in E. coli TOP10 (Invitrogen)and confirmed by restriction analysis and PCR sequencing. Large-scale plasmid DNA was prepared using the endotoxin-free Mega kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen), and the DNA concentrations were determined by A260/A280 absorption measurements. Plasmid DNA was dissolved in sterile endotoxin-free PBS and stored at –20°C until use.
Mice.
HLA-A*11:01/Kb transgenic mice were produced at Pharmexa-Epimmune, were embryo rederived at Taconic and the Jackson Laboratory, and were bred at the University of Chicago. These HLA-A*11:01/Kb transgenic mice express a chimeric gene consisting of the first and second domains of HLA-A*11:01 and the third domain of H-2Kb, and they were created on a C57BL/6 background. Mice were maintained in SPF conditions throughout. Female mice were utilized in these experiments. All studies in Chicago and the USDA were conducted with the approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Chicago and at the USDA, respectively. All animal use at the University of Strathclyde (Figure 8A) conformed to guidelines from the Home Office of the UK Government and was covered by the Home office licence PPL604568, ‘Treatment & prevention of Toxoplasmosis’, with the approval of the University of Strathclyde Animal welfare and Ethical Review Body.
Immunizations of mice and challenge.
To evaluate multi-epitope protein immunogenicity, HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice were inoculated s.c. at the base of the tail using a 30-gauge needle with 50 μg LO or AZ recombinant protein emulsified in 20 μg of GLA-SE (TLR4 agonist) 3 times at 2-week intervals. For immunization by DNA, mice were inoculated by injection of 50 μl of PBS containing 100 μg of DNA into each quadricep muscle using a G26-gauge needle at weeks 0, 2 ,and 4. In a bid to enhance delivery of DNA, we used an electroporation device. Briefly, following injection of DNA, the surface dermal device was applied to the site of injection as described (46). The array was “wiggled” at the injection site to ensure good contact and electro-transfer achieved through pulse generation from the ELGEN 1000 (Inovio Pharmaceuticals) pulse generator. The parameters used were three 15 V pulses of 100 ms duration. Negative control mice were vaccinated with 100 μg empty vector or 50 μl saline. For challenge studies, immunized mice were challenged i.p. 14 days after immunization using 2,000 or 20,000 T. gondii ME49-Fluc (Type II) parasites that express firefly luciferase.
ELISpot assay to determine immune responses with murine splenocytes.
Mice were euthanized 14 days after immunization. Spleens were harvested and pressed through a 70-μm screen to form a single-cell suspension, and erythrocytes were lysed with AKC lysis buffer (160 mM NH4Cl, 10 mM KHCO3, 100 mM EDTA). Splenocytes were washed twice with HBSS and resuspended in complete RPMI medium (RPMI-1640 supplemented with 2 mM L-GlutaMax ; Invitrogen). Murine ELISpot assays were performed using anti–mouse IFN-γ mAb (AN18) and the biotinylated anti–mouse IFN-γ mAb (R4–6A2), and 2.5 × 105 to 5 × 105 splenocytes were plated per well. Cells were plated in at least 3 replicate wells for each condition. Results were expressed as the number of SFCs per 1 × 106 murine splenocytes.
In vivo bioluminescence imaging for determining outcomes of challenge with type II parasites.
Mice infected with 2,000 T. gondii ME49-Fluc (Type II) tachyzoites were imaged 21 days after challenge using the in vivo imaging system (IVIS; Xenogen). Mice were injected retroorbitally with 200 μl (15.4mg/ml) of D-luciferin, anesthetized in an O2-rich induction chamber with 2% isoflurane, and imaged after 12 minutes. Photonic emissions were assessed using Living image 2.20.1 software (Xenogen). Data are presented as pseudocolor representations of light intensity and mean photons/region of interest (ROI). All mouse experiments were repeated at least twice.
Enumeration of cysts in mouse brains following type II parasite challenge.
Mice were euthanized at 21 days after infection with 2,000 of Me49-Fluc, and brains were collected and homogenized with 1 ml of saline (0.85% NaCl). Tissue cysts were counted microscopically in 50 μl of the homogenate, and the count was multiplied by 20 to obtain the number of tissue cysts per brain. This number was confirmed by staining brain cysts with fluorescein-labeled Dolichos biflorus agglutinin (Vector Laboratories) and by quantitation using fluorescence microscopy.
Flow cytometry.
Splenocytes were manually processed using 70-μm filters in DMEM media supplemented with 5% FCS, and rbcs were lysed with ACK lysis buffer. Cells were stained with CD3 APC (145-2C11), CD4 PE (GK1.5), CD8 PerCP (53-6.7), CD44 AF780 (IM7), and CD45RB FITC (C363.16A). All antibodies were purchased from eBioscience. Memory T cells were defined as CD44hiCD45RBlo. All flow cytometry data was collected on LSRII flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and analyzed using FlowJo software 10.0.
Demonstration that GLA-SE is a TLR4 ligand.
Human whole blood was stimulated with GLA-SE as follows: heparinized whole blood was collected from 6 healthy donors, and 200 μl was stimulated with 5 μg GLA-SE in 96-well plates at 37oC CO2. After 24 hours, plasma was removed and assayed for IL-6, IL-12(p40), and TNF-α by a custom Luminex-based multiplex immunoassay kit (Affymetrix eBioscience). Data was analyzed using the Masterplex QT software (Miraibio).
Statistics.
Data for each assay were compared by one-way ANOVA or a Student t test using GraphPad Prism 5 software (GraphPad Software). Differences between the groups were identified by ANOVA and multiple comparison procedures, as we previously described (6). The cytokine production stimulated by adjuvant was statistically significant (P < 0.05) compared with the unstimulated groups as assessed by the Mann-Whitney U test (GraphPad Prism software). Kaplan-Meier curves were generated and survival compared across groups using the log-rank test. Data are expressed as the mean ±SD. Results were considered to be statistically significant at P < 0.05.
Study approval.
Experiments and handling of mice were conducted under federal, state, and local guidelines under an IACUC protocol and with approval from the University of Chicago IACUC. IRB approval was obtained at the University of Chicago for this study. This study also is in compliance with all Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) regulations.
Author contributions
K. El Bissati, AC, PAK, YZ, SW, JPD, CWR, EM, YS, QS, JAG, CF, SB, NC, SKV, and LF performed experiments. LV, JAG, CF, SR, and K.E. Broderick contributed essential reagents or tools. JS, SR, JA, TV, AS, CAB, and JL analyzed and interpreted data. K. El Bissati and RM supervised the work, analyzed and interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge support of this work from the Mann Cornwell, Engel, Morel, Pritzker, Harris, Rooney-Alden, Langel, Samuel, and Mussilami families. This work was supported by DMID-NIAID U01 AI77887, R01 27530 (to RM), Knights Templar Eye Foundation (to K. El Bissati), and The Research to Prevent Blindness Foundation (to RM). We thank I.J. Begeman and K. Wroblewski for their assistance with the preparation of this manuscript. The funding sources had no influence in study design; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Version 1. 09/22/2016
Electronic publication
Version 2. 09/24/2020
The spelling of Laura Fraczek's name was corrected.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Reference information: JCI Insight. 2016;1(15):e85955. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.85955.
Contributor Information
Kamal El Bissati, Email: kelbissati@uchicago.edu.
Ying Zhou, Email: yzhou@bsd.uchicago.edu.
Stuart Woods, Email: stuart.woods@strath.ac.uk.
Jitender P. Dubey, Email: Jitender.Dubey@ARS.USDA.GOV.
Lo Vang, Email: LVang@paxvax.com.
Joseph Lykins, Email: lykinsj@uchicago.edu.
Kate E. Broderick, Email: kbroderick@inovio.com.
Ernest Mui, Email: ernest.mui@gmail.com.
Yasuhiro Suzuki, Email: yasu.suzuki@uky.edu.
Qila Sa, Email: qila.sa@uky.edu.
Stephanie Bi, Email: stephaniebi@uchicago.edu.
Nestor Cardona, Email: nestorivan@yahoo.com.
John Sidney, Email: jsidney@liai.org.
Jeff Alexander, Email: jalexander@paxvax.com.
Alessandro Sette, Email: alex@liai.org.
Tom Vedvick, Email: Tom.Vedvick@idri.org.
Chris Fox, Email: cfox@idri.org.
Rima McLeod, Email: rmcleod@bsd.uchicago.edu.
References
- 1.McLeod R, Kieffer F, Sautter M, Hosten T, Pelloux H. Why prevent, diagnose and treat congenital toxoplasmosis? Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2009;104(2):320–344. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762009000200029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McAuley J, et al. Early and longitudinal evaluations of treated infants and children and untreated historical patients with congenital toxoplasmosis: the Chicago Collaborative Treatment Trial. Clin Infect Dis. 1994;18(1):38–72. doi: 10.1093/clinids/18.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tan TG, et al. Identification of T. gondii epitopes, adjuvants, and host genetic factors that influence protection of mice and humans. Vaccine. 2010;28(23):3977–3989. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.03.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cong H, et al. Toxoplasma gondii HLA-B*0702-restricted GRA7(20-28) peptide with adjuvants and a universal helper T cell epitope elicits CD8(+) T cells producing interferon-γ and reduces parasite burden in HLA-B*07:02 mice. Hum Immunol. 2012;73(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2011.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cong H, et al. Human immunome, bioinformatic analyses using HLA supermotifs and the parasite genome, binding assays, studies of human T cell responses, and immunization of HLA-A*11:01 transgenic mice including novel adjuvants provide a foundation for HLA-A03 restricted CD8+T cell epitope based, adjuvanted vaccine protective against Toxoplasma gondii. Immunome Res. 2010;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1745-7580-6-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cong H, et al. Towards an immunosense vaccine to prevent toxoplasmosis: protective Toxoplasma gondii epitopes restricted by HLA-A*02:01. Vaccine. 2011;29(4):754–762. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.11.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mineo JR, Kasper LH. Attachment of Toxoplasma gondii to host cells involves major surface protein, SAG-1 (P30) Exp Parasitol. 1994;79(1):11–20. doi: 10.1006/expr.1994.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kasper LH, Mineo JR. Attachment and invasion of host cells by Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol Today (Regul Ed) 1994;10(5):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nielsen HV, Lauemøller SL, Christiansen L, Buus S, Fomsgaard A, Petersen E. Complete protection against lethal Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice immunized with a plasmid encoding the SAG1 gene. Infect Immun. 1999;67(12):6358–6363. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.12.6358-6363.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lane A, Soete M, Dubremetz JF, Smith JE. Toxoplasma gondii: appearance of specific markers during the development of tissue cysts in vitro. Parasitol Res. 1996;82(4):340–346. doi: 10.1007/s004360050123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Donnelly JJ, Wahren B, Liu MA. DNA vaccines: progress and challenges. J Immunol. 2005;175(2):633–639. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.2.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.El Bissati K, et al. Effectiveness of a novel immunogenic nanoparticle platform for Toxoplasma peptide vaccine in HLA transgenic mice. Vaccine. 2014;32(26):3243–3248. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.03.092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kutzler MA, et al. Plasmids encoding the mucosal chemokines CCL27 and CCL28 are effective adjuvants in eliciting antigen-specific immunity in vivo. Gene Ther. 2010;17(1):72–82. doi: 10.1038/gt.2009.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lang Kuhs KA, et al. Hepatitis C virus NS3/NS4A DNA vaccine induces multiepitope T cell responses in rhesus macaques mimicking human immune responses [corrected] Mol Ther. 2012;20(3):669–678. doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sardesai NY, Weiner DB. Electroporation delivery of DNA vaccines: prospects for success. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011;23(3):421–429. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Muthumani K, et al. HIV-1 Env DNA vaccine plus protein boost delivered by EP expands B- and T-cell responses and neutralizing phenotype in vivo. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brown CR, et al. Definitive identification of a gene that confers resistance against Toxoplasma cyst burden and encephalitis. Immunology. 1995;85(3):419–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Roberts F, Roberts CW, Ferguson DJ, McLeod R. Inhibition of nitric oxide production exacerbates chronic ocular toxoplasmosis. Parasite Immunol. 2000;22(1):1–5. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3024.2000.00259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kirisits MJ, Mui E, McLeod R. Measurement of the efficacy of vaccines and antimicrobial therapy against infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol. 2000;30(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7519(00)00009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Johnson J, et al. Genetic analysis of influences on survival following Toxoplasma gondii infection. Int J Parasitol. 2002;32(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7519(01)00321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Johnson JJ, et al. In vitro correlates of Ld-restricted resistance to toxoplasmic encephalitis and their critical dependence on parasite strain. J Immunol. 2002;169(2):966–973. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.2.966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dubey JP, Ferreira LR, Martins J, McLeod R. Oral oocyst-induced mouse model of toxoplasmosis: effect of infection with Toxoplasma gondii strains of different genotypes, dose, and mouse strains (transgenic, out-bred, in-bred) on pathogenesis and mortality. Parasitology. 2012;139(1):1–13. doi: 10.1017/S0031182011001673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McLeod R, Frenkel JK, Estes RG, Mack DG, Eisenhauer PB, Gibori G. Subcutaneous and intestinal vaccination with tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii and acquisition of immunity to peroral and congenital toxoplasma challenge. J Immunol. 1988;140(5):1632–1637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lyons RE, et al. Immunological studies of chronic ocular toxoplasmosis: up-regulation of major histocompatibility complex class I and transforming growth factor beta and a protective role for interleukin-6. Infect Immun. 2001;69(4):2589–2595. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2589-2595.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wilson CC, et al. Development of a DNA vaccine designed to induce cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses to multiple conserved epitopes in HIV-1. J Immunol. 2003;171(10):5611–5623. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.10.5611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Livingston BD, Newman M, Crimi C, McKinney D, Chesnut R, Sette A. Optimization of epitope processing enhances immunogenicity of multiepitope DNA vaccines. Vaccine. 2001;19(32):4652–4660. doi: 10.1016/S0264-410X(01)00233-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Feliu V, et al. Location of the CD8 T cell epitope within the antigenic precursor determines immunogenicity and protection against the Toxoplasma gondii parasite. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(6):e1003449. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ochoa-Repáraz J, Kasper LH. Gut microbiome and the risk factors in central nervous system autoimmunity. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(22):4214–4222. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.09.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Telesford K, Ochoa-Repáraz J, Kasper LH. Gut commensalism, cytokines, and central nervous system demyelination. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014;34(8):605–614. doi: 10.1089/jir.2013.0134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang Y, et al. An intestinal commensal symbiosis factor controls neuroinflammation via TLR2-mediated CD39 signalling. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4432. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.van Haren SD, et al. In vitro cytokine induction by TLR-activating vaccine adjuvants in human blood varies by age and adjuvant. Cytokine. 2016;83:99–109. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Coler RN, et al. From mouse to man: safety, immunogenicity and efficacy of a candidate leishmaniasis vaccine LEISH-F3+GLA-SE. Clin Transl Immunology. 2015;4(4):e35. doi: 10.1038/cti.2015.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Roberts CW, Prasad S, Khaliq F, Gazzinelli RT, Khan IA, McLeod R. In: Weiss LM, Kim K, eds. Toxoplasma gondii: the model apicomplexan - perspectives and methods. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier/AP; 2014:819-994. [Google Scholar]
- 34.McCoy ME, et al. Mechanisms of protective immune responses induced by the Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein-based, self-assembling protein nanoparticle vaccine. Malar J. 2013;12:136. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gazzinelli RT, Hakim FT, Hieny S, Shearer GM, Sher A. Synergistic role of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in IFN-gamma production and protective immunity induced by an attenuated Toxoplasma gondii vaccine. J Immunol. 1991;146(1):286–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Suzuki Y, Orellana MA, Schreiber RD, Remington JS. Interferon-gamma: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1988;240(4851):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.3128869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Couper KN, Roberts CW, Brombacher F, Alexander J, Johnson LL. Toxoplasma gondii-specific immunoglobulin M limits parasite dissemination by preventing host cell invasion. Infect Immun. 2005;73(12):8060–8068. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.12.8060-8068.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mack DG, McLeod R. Human Toxoplasma gondii-specific secretory immunoglobulin A reduces T. gondii infection of enterocytes in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1992;90(6):2585–2592. doi: 10.1172/JCI116153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mineo JR, et al. Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii major surface protein (SAG-1, P30) inhibit infection of host cells and are produced in murine intestine after peroral infection. J Immunol. 1993;150(9):3951–3964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tendler M, Almeida M, Simpson A. Development of the Brazilian Anti Schistosomiasis Vaccine Based on the Recombinant Fatty Acid Binding Protein Sm14 Plus GLA-SE Adjuvant. Front Immunol. 2015;6:218. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Moutaftsi M, et al. A consensus epitope prediction approach identifies the breadth of murine T(CD8+)-cell responses to vaccinia virus. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24(7):817–819. doi: 10.1038/nbt1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gulukota K, Sidney J, Sette A, DeLisi C. Two complementary methods for predicting peptides binding major histocompatibility complex molecules. J Mol Biol. 1997;267(5):1258–1267. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.0937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sidney J, et al. Quantitative peptide binding motifs for 19 human and mouse MHC class I molecules derived using positional scanning combinatorial peptide libraries. Immunome Res. 2008;4:2. doi: 10.1186/1745-7580-4-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sidney J, Southwood S, Oseroff C, del Guercio MF, Sette A, Grey HM. Measurement of MHC/peptide interactions by gel filtration. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2001;Chapter 18:Unit 18.3. doi: 10.1002/0471142735.im1803s31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Alexander J, et al. Development of high potency universal DR-restricted helper epitopes by modification of high affinity DR-blocking peptides. Immunity. 1994;1(9):751–761. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(94)80017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Broderick KE, et al. Prototype development and preclinical immunogenicity analysis of a novel minimally invasive electroporation device. Gene Ther. 2011;18(3):258–265. doi: 10.1038/gt.2010.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]