Abstract
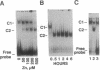
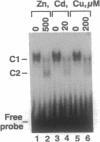
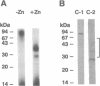
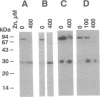
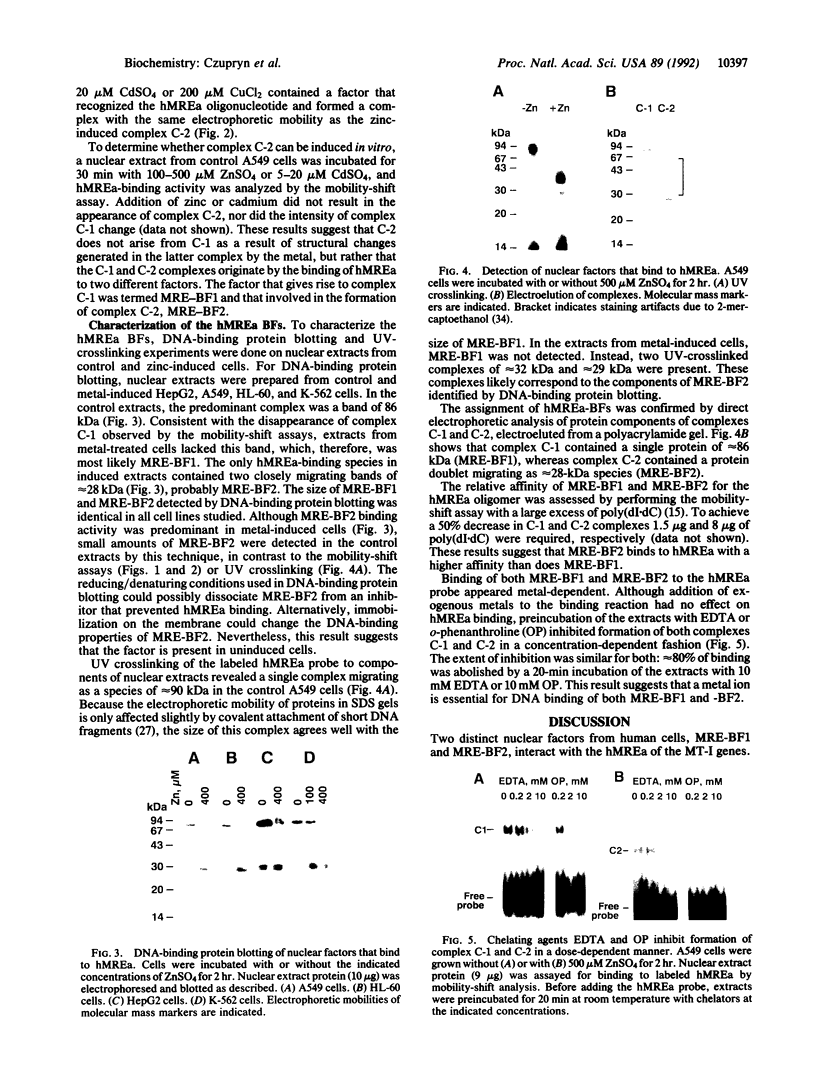
Metal activation of metallothionein gene transcription is mediated by specific promoter sequences, termed metal regulatory elements (MREs). Nuclear extracts prepared from various human cell lines were assayed for their capacity to bind to a synthetic human MREa (hMREa) oligomer. Electrophoretic mobility-shift assays with extracts from control cells detected a single hMREa-containing complex. Addition to the growth medium of zinc, cadmium, or copper--metals known to induce MT biosynthesis in vivo--resulted in the rapid but reversible appearance of a second distinct hMREa-protein complex in all cell lines studied. This result was not seen when the metals were added directly to the extracts from control cells. DNA-binding protein blotting, UV crosslinking, and electroelution experiments were used to characterize the two hMREa-binding factors, termed BF1 and BF2. MRE-BF1 has an apparent molecular mass of approximately 86 kDa and binds to the hMREa in control cells, whereas MRE-BF2 consists of two molecules of approximately 28 kDa and binds to the hMREa in metal-treated cells. EDTA and o-phenanthroline inhibited binding of both factors to hMREa in a dose-dependent manner, indicating that a metal atom or atoms are essential for interaction of the factors with DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen R. D., Taplitz S. J., Oberbauer A. M., Calame K. L., Herschman H. R. Metal-dependent binding of a nuclear factor to the rat metallothionein-I promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6049–6055. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. K. Regulation of metallothionein gene expression. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1990;14(2-3):193–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beis A., Lazou A. Removal of artifactual bands associated with the presence of 2-mercaptoethanol in two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1990 Oct;190(1):57–59. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90132-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler G., Thiele D. J. ACE2, an activator of yeast metallothionein expression which is homologous to SWI5. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):476–485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Hamer D. H. Fine mapping of a mouse metallothionein gene metal response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1376–1380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the mouse metallothionein-I gene by heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5712–5716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Jahroudi N., Varshney U., Gedamu L. Structure and expression of the human metallothionein-IG gene. Differential promoter activity of two linked metallothionein-I genes in response to heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11528–11535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Luisi B. F., Korszun Z. R., Basavappa R., Sigler P. B., Yamamoto K. R. The function and structure of the metal coordination sites within the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):543–546. doi: 10.1038/334543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hu S., Hackett R., Hamer D. Copper activates metallothionein gene transcription by altering the conformation of a specific DNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Hazuda D. J., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Xenopus transcription factor A requires zinc for binding to the 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14120–14125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. A., Cherian M. G., Angel A. Cellular localization of metallothionein in the lung following repeated cadmium inhalation. Toxicology. 1985 Oct;37(1-2):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(85)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmaier H. E., Drasch G. A., Kretschmer E., Summer K. H. Metallothionein, cadmium, copper and zinc levels of human and rat tissues. Toxicol Lett. 1987 Oct;38(3):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(87)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbert J., Zafarullah M., Culotta V. C., Gedamu L., Hamer D. Transcription factor MBF-I interacts with metal regulatory elements of higher eucaryotic metallothionein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5315–5323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., MacDonald J. J., Lees-Miller S., Tjian R. GC box binding induces phosphorylation of Sp1 by a DNA-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90296-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Otsuka F., Yamada H. A nuclear factor that interacts with metal responsive elements of a human metallothionein gene. Chem Biol Interact. 1991;80(2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(91)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H. Overview of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol. 1991;205:613–626. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)05145-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé S., Prévost J., Remondelli P., Leone A., Séguin C. A nuclear factor binds to the metal regulatory elements of the mouse gene encoding metallothionein-I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4225–4231. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins W. K., Roberts M. P., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H. Use of a protein-blotting procedure and a specific DNA probe to identify nuclear proteins that recognize the promoter region of the transferrin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6741–6744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto E., Allen J. M., Young J. E., Palmiter R. D., Maroni G. A DNA segment controlling metal-regulated expression of the Drosophila melanogaster metallothionein gene Mtn. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1710–1715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Coleman J. E. Structure and function of the Zn(II) binding site within the DNA-binding domain of the GAL4 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3145–3149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Heguy A., Karin M. Structural and functional analysis of the human metallothionein-IA gene: differential induction by metal ions and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu C., Gedamu L. Metal-specific posttranscriptional control of human metallothionein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5738–5741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu C., Gedamu L. Regulation of human metallothionein (MT) genes. Differential expression of MTI-F, MTI-G, and MTII-A genes in the hepatoblastoma cell line (HepG2). J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2679–2684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Niedbala D., Wood K., Ptashne M. GAL4 is phosphorylated as a consequence of transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10510–10514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Cohen R. B., Garfinkel S., Thompson J. A. DNA affinity labeling of adenovirus type 2 upstream promoter sequence-binding factors identifies two distinct proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):105–113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F. Zinc dependent binding of a liver nuclear factor to metal response element MRE-a of the mouse metallothionein-I gene and variant sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seguin C., Hamer D. H. Regulation in vitro of metallothionein gene binding factors. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1383–1387. doi: 10.1126/science.3103216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguin C. A nuclear factor requires Zn2+ to bind a regulatory MRE element of the mouse gene encoding metallothionein-1. Gene. 1991 Jan 15;97(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90066-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguin C., Prévost J. Detection of a nuclear protein that interacts with a metal regulatory element of the mouse metallothionein 1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10547–10560. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Auld D. S. Zinc coordination, function, and structure of zinc enzymes and other proteins. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5647–5659. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L. Metallothionein: historical review and perspectives. Experientia Suppl. 1979;34:19–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6493-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L. Zinc biochemistry in normal and neoplastic growth processes. Experientia. 1977 May 15;33(5):600–601. doi: 10.1007/BF01946521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Schaffner W. A zinc-responsive factor interacts with a metal-regulated enhancer element (MRE) of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3763–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafarullah M., Bonham K., Gedamu L. Structure of the rainbow trout metallothionein B gene and characterization of its metal-responsive region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4469–4476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng J., Vallee B. L., Kägi J. H. Zinc transfer from transcription factor IIIA fingers to thionein clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9984–9988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]