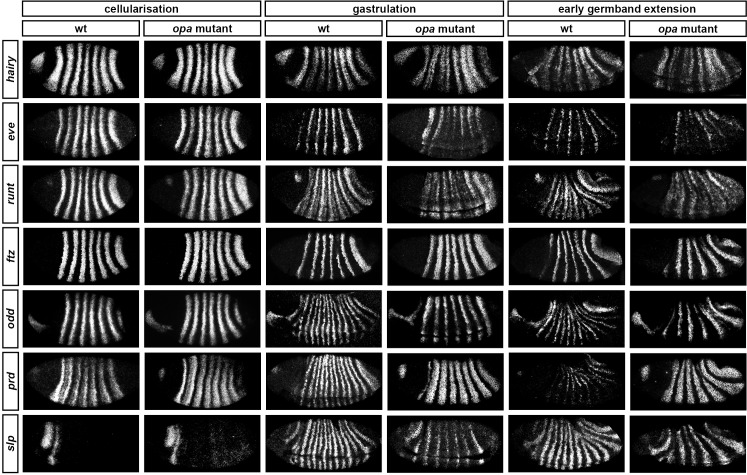
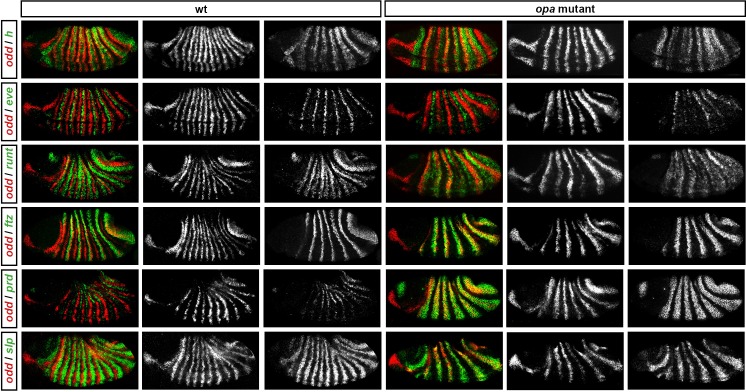
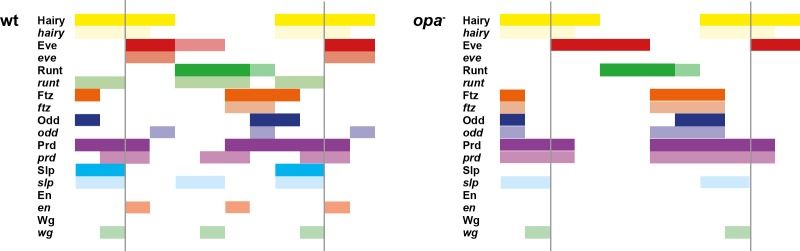
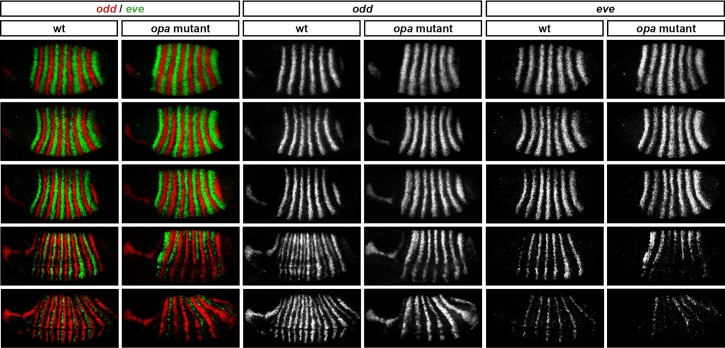
Figure 8. Pair-rule gene expression is perturbed from gastrulation onwards in opa mutant embryos.
Pair-rule gene expression in wild-type and opa mutant embryos at late cellularisation, late gastrulation, and early germband extension. During cellularisation, pair-rule gene expression in opa mutant embryos is very similar to wild-type. Expression from gastrulation onwards is severely abnormal; in particular, note that single-segment patterns do not emerge. All panels show a lateral view, anterior left, dorsal top.
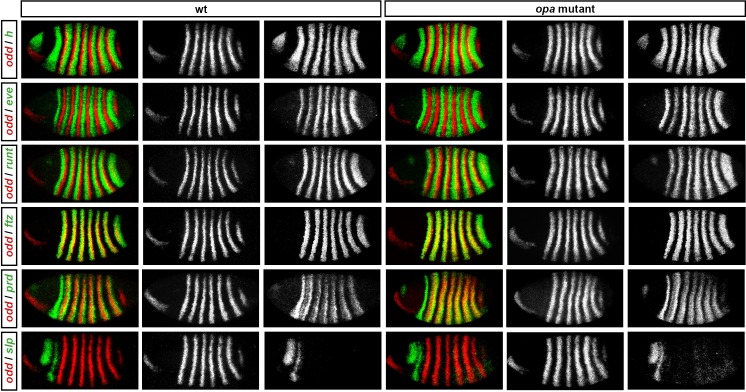
Figure 8—figure supplement 1. Pair-rule gene expression in opa mutant embryos at cellularisation.
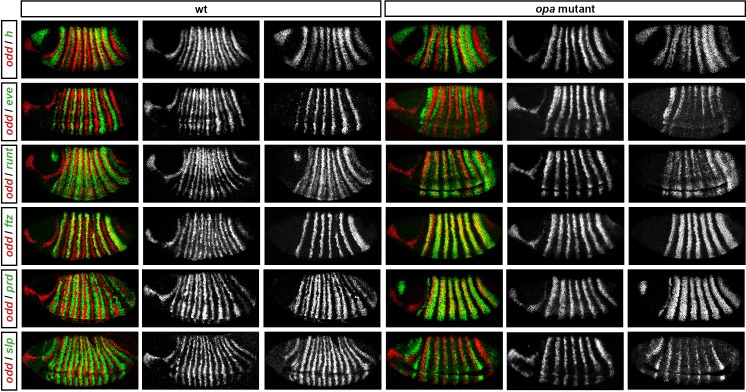
Figure 8—figure supplement 2. Pair-rule gene expression in opa mutant embryos at gastrulation.
Figure 8—figure supplement 3. Pair-rule gene expression in opa mutant embryos at early germband extension.
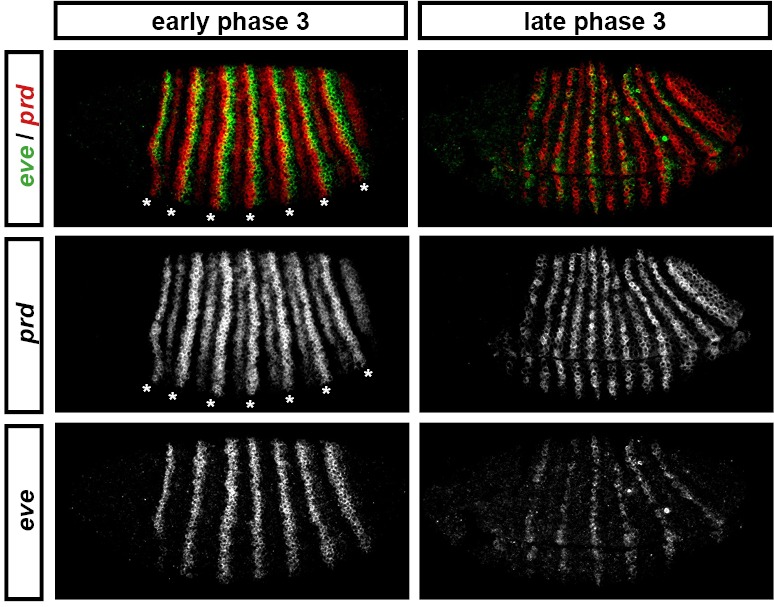
Figure 8—figure supplement 4. The transition to single-segment periodicity does not occur in opa mutant embryos.
Figure 8—figure supplement 5. Opa activates the eve “'late' element.
Figure 8—figure supplement 6. 'Late' eve expression is observed in cells that do not express prd.