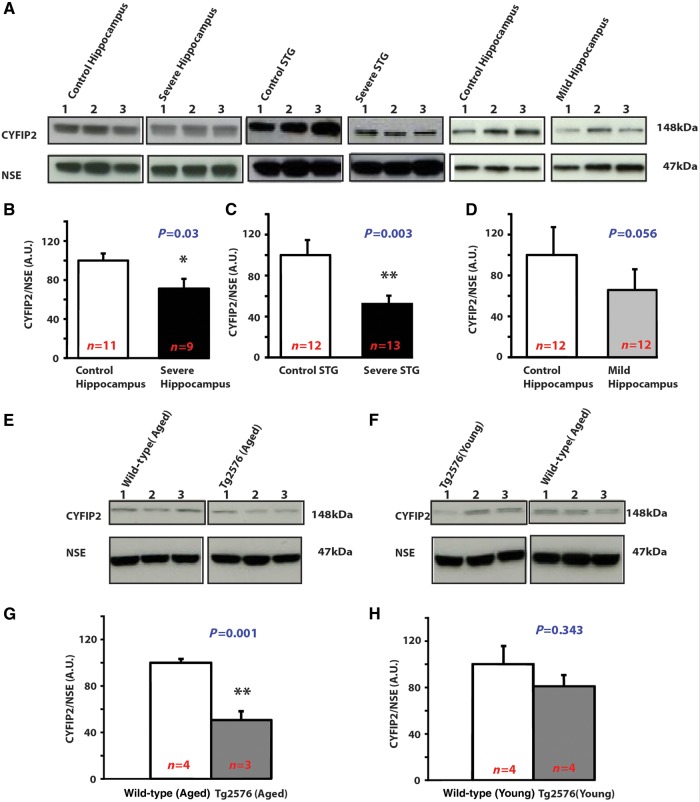
Figure 1.
Reduced CYFIP2 expression in post-mortem Alzheimer’s disease forebrain and in a mouse model of familial Alzheimer’s disease. ( A–D ) CYFIP2 expression is decreased in forebrain of patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease. ( A ) Representative western blots. ( B ) CYFIP2 expression in hippocampal lysates from patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease ( n = 9) and control subjects ( n = 11). ( C ) CYFIP2 expression in lysates of STG from patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease ( n = 13) and control subjects ( n = 12). ( D ) CYFIP2 expression in hippocampal lysates of patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease ( n = 12) and control subjects ( n = 12). ( E–G ) Age-dependent decrease of CYFIP2 expression in forebrain of Tg2576 mice. ( E and F ) Representative western blots. ( G ) CYFIP2 expression in hippocampal–cortical lysates of 12-month-old wild-type mice ( n = 4) and Tg2576 ( n = 3). ( H ) CYFIP2 expression in hippocampal-cortical lysates of 4-month-old wild-type ( n = 4) and Tg2576 mice ( n = 4). In all panels CYFIP2 expression was normalized against NSE. Means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) are shown. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.