Abstract
Objectives
Improvement of skin fibrosis is part of the natural course of diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc). Recognising those patients most likely to improve could help tailoring clinical management and cohort enrichment for clinical trials. In this study, we aimed to identify predictors for improvement of skin fibrosis in patients with dcSSc.
Methods
We performed a longitudinal analysis of the European Scleroderma Trials And Research (EUSTAR) registry including patients with dcSSc, fulfilling American College of Rheumatology criteria, baseline modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) ≥7 and follow-up mRSS at 12±2 months. The primary outcome was skin improvement (decrease in mRSS of >5 points and ≥25%) at 1 year follow-up. A respective increase in mRSS was considered progression. Candidate predictors for skin improvement were selected by expert opinion and logistic regression with bootstrap validation was applied.
Results
From the 919 patients included, 218 (24%) improved and 95 (10%) progressed. Eleven candidate predictors for skin improvement were analysed. The final model identified high baseline mRSS and absence of tendon friction rubs as independent predictors of skin improvement. The baseline mRSS was the strongest predictor of skin improvement, independent of disease duration. An upper threshold between 18 and 25 performed best in enriching for progressors over regressors.
Conclusions
Patients with advanced skin fibrosis at baseline and absence of tendon friction rubs are more likely to regress in the next year than patients with milder skin fibrosis. These evidence-based data can be implemented in clinical trial design to minimise the inclusion of patients who would regress under standard of care.
Keywords: Systemic Sclerosis, Outcomes research, Epidemiology
Introduction
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a highly heterogeneous disease, making clinical management of SSc and patient selection for clinical trials challenging. For skin fibrosis, the modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) is the most widely used measure in clinical practice and it is also the most frequent primary end point in clinical trials.1 2 Identifying predictors of change in mRSS over time is therefore of much interest for risk-tailored clinical management, as well as for clinical trial design to enrich for patients with worsening skin fibrosis.3
In a recent, large-scale, observational study on the European Scleroderma Trials And Research (EUSTAR) database, we identified short disease duration (<15 months), joint synovitis and low baseline mRSS (>7/51 and ≤22/51) as independent predictors of skin progression in patients with diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc).4 This provided an evidence-based tool for the improved identification of patients at risk for progressive skin involvement and is also valuable for cohort enrichment in clinical trials on skin fibrosis.
While the identification of factors predicting progression has been improved, little is known about predictors of regression of skin fibrosis in patients with SSc. Regression of mRSS has long been identified as a characteristic feature of the natural history of skin fibrosis in patients with dcSSc. Regression is thought to occur after the early active phase of the disease has stabilised. However, the time to peak skin score varies widely in patients, leading to a highly heterogeneous pattern of regressing, progressing and stable patients even in early disease stages.5 6
From a therapeutic perspective, there is general agreement that prevention of progression in patients with active skin fibrosis is one of the major treatment goals. However, it is much less established whether a therapeutic benefit can be achieved for patients who are already likely to show improvement of skin fibrosis under standard of care. In such a population the benefit/risk ratio of any treatment would have to be accurately assessed. Therefore, in order to identify those patients who would benefit most from therapeutic interventions, it is important to identify patients with progressive skin fibrosis, and to be aware of patients with skin regression. For trial design, it is important to enrich for progressive patients, and to exclude regressing patients under standard of care to increase the likelihood of identifying treatment effects.
So far, previous attempts to identify predictors of change in mRSS have been largely inconclusive,4 and patients recruited for clinical studies targeting skin fibrosis often show spontaneous regression of mRSS.4 5 Thus, the objective of our study was to provide evidence-based predictors of skin improvement in patients with dcSSc using the EUSTAR database.
Methods
Patients and study design
The longitudinally followed EUSTAR cohort was analysed for this observational study. The whole EUSTAR data set, consisting of 12 274 patients at the time of the first data export (20 February 2015), was considered.
The following inclusion criteria were used for cohort selection: fulfilment of American College of Rheumatology 1980 classification criteria, dcSSc, mRSS ≥7 at the first visit (baseline) and available data for mRSS at 12±2 months follow-up.
Patients with dcSSc were identified according to LeRoy et al7 or, in case of missing values for the LeRoy criteria, by diffuse skin involvement at any visit. The minimum mRSS ≥7 was chosen because it reflects the lowest value classifiable as dcSSc, thus allowing the inclusion of patients with dcSSc with less severe to extensive skin fibrosis. The 1 year follow-up has been shown adequate for capturing significant changes in mRSS and is often used in clinical trials in skin fibrosis in SSc.2
The clinical data in EUSTAR are prospectively collected in a multicentre approach following a standardised protocol.8–10 Regular training courses in skin scoring are organised by EUSTAR and all centres are advised to have the same examiner assessing the skin score in individual patients at follow-up visits.4 Quality indicators for data from the registry include regular external monitoring of large centres and plausibility checks on key items with written requests to centres for clarification. Ethics approval has been obtained from the respective local ethics committees by all participating EUSTAR centres.
Statistical analysis
The primary end point, improvement of skin fibrosis, was defined as a decrease in mRSS of >5 points and ≥25% within 1 year. These thresholds were chosen according to the minimal clinically important difference.11 Similarly, progression of skin fibrosis was defined as an increase in mRSS of >5 points and ≥25% within 1 year as used previously.4 For definitions of the clinical variables see the online supplement.
annrheumdis-2015-208024supp.pdf (264.2KB, pdf)
A subanalysis using receiver operating characteristic analysis was performed with skin improvement, and, respectively, skin progression as the state variable, in order to explore the relationship between different baseline mRSS cut-off points and the proportion of regressors and progressors included in the cohort.
Candidate predictors for skin improvement were selected based on nominal group technique by SSc experts (OD, YA, OK-B, CM, RD), who were asked to suggest clinically meaningful variables with face validity (see the online supplement). All parameters suggested by the experts (see online supplementary table S1) with <50% missing data were considered for the analysis. As a first step, a multivariable logistic regression model including all selected 11 parameters was run after single conditional mean imputation of the data. Baseline mRSS was centred at 7 points as all patients had baseline mRSS ≥7. Because baseline mRSS did not behave linearly, a quadratic term for baseline mRSS was included in the model. The Wald statistics (see online supplementary table S3) showed that the effects were very far from being significant (p value >0.7) for joint contractures and diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide ≥70%. Thus, these parameters were excluded from further models. The interaction between disease duration and baseline mRSS was also tested, but proved to be insignificant, meaning that the effect of baseline mRSS on regression of SSc did not depend on disease duration. The model after single imputation is shown in the online supplementary table S4. Single imputation was done for validation as it is not possible to validate models with multiply imputed data. Thus, bootstrap with 100 repetitions was used to validate the model (see online supplementary table S5). However, as multiple imputation provides more trustworthy estimates and ORs than single imputation, the final logistic regression model from the multiply imputed data set is presented.
The statistical analysis was performed by the biostatistician (NG) using R V.3.1.0 (see the online supplement).
Results
Study population
A total of 919 patients with dcSSc who met the inclusion criteria were analysed. Of these, 218/919 (24%) patients showed skin improvement over 1-year follow-up. The patients' demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in table 1.
Table 1.
Description of the study cohort at baseline (total N=919)
| Age (years) | 51 (40,60) |
| Male | 199/919 (21.7) |
| Female | 720/919 (78.3) |
| Disease duration (months)* | 42.5 (17,104) |
| Short disease duration ≤36 months* | 389/854 (45.6) |
| Raynaud's phenomenon | 898/919 (97.7) |
| Puffy fingers | 235/390 (60.3) |
| Digital ulcers (ever) | 396/914 (43.3) |
| Active digital ulcers | 84/394 (21.3) |
| mRSS | 16 (11,23) |
| Organ involvement | |
| Musculoskeletal | |
| Synovitis† | 196/915 (21.4) |
| Joint contractures | 458/916 (50.0) |
| Tendon friction rubs | 185/914 (20.2) |
| Muscle weakness | 294/915 (32.1) |
| Cardiopulmonary | |
| Dyspnoea (NYHA) | |
| Stage I | 210/369 (56.9) |
| Stage II | 118/369 (32.0) |
| Stage III | 37/369 (10.0) |
| Stage IV | 4/369 (1.1) |
| Conduction blocks | 109/877 (12.4) |
| Diastolic dysfunction | 165/864 (19.1) |
| LVEF <45% | 6/318 (1.9) |
| Pulmonary hypertension by Echo | 167/868 (19.2) |
| Lung fibrosis on chest X-ray | 389/849 (45.8) |
| Lung fibrosis on HRCT | 163/287 (56.8) |
| FVC <80% | 127/362 (35.1) |
| TLC <80% | 80/245 (32.7) |
| DLCO <70% | 357/621 (57.5) |
| Gastrointestinal | |
| Oesophageal symptoms | 625/917 (68.2) |
| Stomach symptoms | 257/916 (28.1) |
| Intestinal symptoms | 222/917 (24.2) |
| Renal crisis | 23/915 (2.5) |
| Laboratory markers | |
| ANA | 859/908 (94.6) |
| ACA | 76/872 (8.7) |
| Anti-Scl70 | 524/886 (59.1) |
| Anti-U1RNP | 16/285 (5.6) |
| Anti-RNA polymerase III | 18/215 (8.4) |
| CK elevation | 112/879 (12.7) |
| Proteinuria | 74/887 (8.3) |
| ESR>25 mm/1 h | 134/368 (36.4) |
| CRP elevation | 107/374 (28.6) |
| Active disease (VAI >3)12 | 146/337 (43.3) |
| Immunosuppressive treatment | 334/436 (76.6) |
For nominal variables, the absolute and relative frequencies are shown: n/total valid cases (%). Continuous variables are described as median and 1st, 3rd quartiles (Q1, Q3).
*Disease duration was calculated as difference between the date of the baseline visit and the date of the first non-Raynaud's symptom of the disease, as reported by the patients.
†Joint synovitis was defined as swelling of the joints as judged by the treating physician.
ACA, anticentromere antibodies; ANA, antinuclear antibodies; Anti-Scl70 antibodies, antitopoisomerase I antibodies; CK, creatine kinase; CRP, C reactive protein; DLCO, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; Echo, echocardiography; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; FVC, forced vital capacity; HRCT, high resolution computer tomography; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; mRSS, modified Rodnan skin score; NYHA, New York Heart Association; RNP, ribonucleoprotein; TLC, total lung capacity; VAI, Valentini Activity Index.
Multivariable analysis
The candidate predictors selected after nominal group technique and exclusion of parameters with higher missing values and finally included in the multivariable analysis are shown in box 1.
Box 1. Candidate predictors of skin improvement selected for the analysis.
Variable
Baseline mRSS
Disease duration
ANA positive
Anti-Scl70 positive
Tendon friction rubs
Proteinuria
Conduction blocks
Abnormal diastolic function
Fibrosis on chest X-ray
DLCO ≥70%
Joint contractures
ANA, antinuclear antibodies; Anti-Scl70 antibodies, antitopoisomerase I antibodies; DLCO, diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; mRSS, modified Rodnan skin score.
The prediction model for skin improvement after single imputation is shown in online supplementary table S4. The most significant predictor was baseline mRSS (p<0.001). Other significant predictors were absence of tendon friction rubs and negative Scl-70 antibodies. The performance parameters of the model before and after validation are shown in online supplementary table S5.
Multiple imputation was used to fit the model and to obtain SEs. The final model with multiply imputed data is shown in table 2.
Table 2.
Final logistic regression model for prediction of skin improvement at 1 year
| Predictors | Estimate | SE | OR | p Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANA positive | −0.378 | 0.339 | 0.685 | 0.266 | 0.352 to 1.334 |
| Anti-Scl70 positive | −0.324 | 0.180 | 0.723 | 0.071 | 0.508 to 1.028 |
| Tendon friction rubs | −0.492 | 0.214 | 0.612 | 0.022 | 0.402 to 0.930 |
| Proteinuria | 0.294 | 0.292 | 1.341 | 0.315 | 0.756 to 2.380 |
| Lung fibrosis | 0.112 | 0.179 | 1.119 | 0.530 | 0.787 to 1.590 |
| Disease duration (months) | −0.001 | 0.001 | 0.999 | 0.287 | 0.997 to 1.001 |
| Baseline mRSS | 0.171 | 0.031 | 1.186 | <0.001 | 1.115 to 1.262 |
| Baseline mRSS2 | −0.003 | 0.001 | 0.997 | 0.004 | 0.996 to 0.999 |
| Intercept | −3.233 | 0.538 | 0.039 | <0.001 | 0.014 to 0.113 |
ANA, antinuclear antibodies; Anti-Scl70 antibodies, antitopoisomerase I antibodies; mRSS, modified Rodnan skin score.
High baseline mRSS remained the strongest predictor of skin improvement (p<0.001). The model for example indicates that the risk for regression within 12 months is more than doubled (OR=2.316) for a patient with a baseline mRSS of 22 points, in comparison to a patient with a baseline mRSS of 14 (all other parameters being equal). Furthermore, absence of tendon friction rubs significantly predicted skin improvement. Absence of anti-Scl-70 antibodies, which was also a significant predictor in the model after single imputation (see online supplementary table S3), only retained a trend in the model from the multiply imputed data set.
Baseline mRSS as predictor of the pattern of skin change in dcSSc over 1 year
The observation that high baseline mRSS was the strongest predictor of skin improvement complements our previous findings indicating low baseline mRSS as an important predictor of skin worsening.4 This was also confirmed in the current cohort: the 95/919 (10%) patients with dcSSc who showed skin progression within 1 year had lower baseline mRSS (p<0.001). Baseline mRSS is thus a predictor of change in skin score after 1 year, patients with lower skin scores being prone to progress and those with higher skin scores prone to improve within the next 12 months (see online supplementary figure S1).
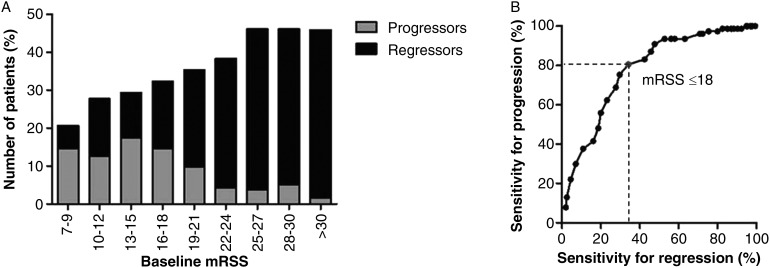
Having in mind the optimisation of cohort enrichment with maximal number of progressive patients and minimal numbers of regressive patients, we checked for the optimal mRSS cut-off (figure 1). In this cohort, an upper baseline mRSS cut-off value of 18 points performed best, including the highest proportion of progressors (78.9%) and the lowest proportion of regressors (35.3%, figure 1).
Figure 1.
(A) Percentage of progressors and regressors per baseline modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) range. Patients with lower skin score are more likely to progress, whereas those with higher skin scores are much more likely to regress. (B) Sensitivity for progression and regression depending on different cut-off values for baseline mRSS.
If translated into clinical study design, this suggests a baseline mRSS between 7 and 18 as an inclusion criterion, raising questions for feasibility of recruiting patients. Thus, we next analysed the impact of higher cut-offs for upper baseline mRSS on the proportion of progressive and regressive patients. This analysis showed that a baseline mRSS between 18 and 25 would still allow identifying a reasonably high rate of progressors over regressors, whereas for skin scores higher than 25 a considerable drop of the included progressors and a dramatic increase in the percentage of regressors was observed (table 3).
Table 3.
Proportion of progressors and regressors depending on different cut-offs for baseline mRSS
| mRSS cut-off | Progressors (%) | 95% CI* | Regressors (%) | 95% CI* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <18 | 13.70 | 10.99 to 16.95 | 12.92 | 10.28 to 16.10 |
| <19 | 13.64 | 11.02 to 16.76 | 14.00 | 11.35 to 17.15 |
| <20 | 13.15 | 10.67 to 16.11 | 15.51 | 12.82 to 18.65 |
| <21 | 13.20 | 10.77 to 16.07 | 16.06 | 13.40 to 13.13 |
| <22 | 13.11 | 10.74 to 15.91 | 16.62 | 13.96 to 19.66 |
| <23 | 12.77 | 10.48 to 15.47 | 17.42 | 14.77 to 20.43 |
| <24 | 12.68 | 10.43 to 15.33 | 17.89 | 15.24 to 20.88 |
| <25 | 12.38 | 10.18 to 14.97 | 18.57 | 15.91 to 21.56 |
| ≤25 | 11.94 | 9.81 to 14.45 | 19.23 | 16.58 to 22.20 |
| >25 | 3.03 | 1.30 to 6.90 | 44.24 | 36.88 to 51.87 |
Data are shown as percentage (%) from the total number of patients (N=919).
*Newcombe–Wilson method without continuity correction.
mRSS, modified Rodnan skin score.
Discussion
Patients with improvement of skin fibrosis under standard of care are less likely to benefit from therapeutic interventions than patients with progressive skin fibrosis. In this large EUSTAR analysis of 919 patients with dcSSc with clinically derived real life data, we have identified parameters which can predict improvement of skin fibrosis over a 12 month observation period, the strongest being high baseline mRSS.
To our knowledge, this is the first report of an evidence-based model for the prediction of skin improvement in a non-selected cohort of patients with dcSSc. In a previous study, Steen et al specifically focused on improvement of skin thickening in a cohort of 278 patients with early dcSSc. In this study, independent predictors for skin improvement could not be identified (except for D-Penicillamine use, which is however contradictory to the negative results of the dedicated randomised controlled trial).13–15 Potential explanations for this lack of predictors include the lower sample size, and the higher baseline mRSS in this study. The higher baseline mRSS might also explain the higher rate of improvers in this study (63% vs 22% in our EUSTAR analysis).
A key message resulting from our study is the important role of baseline mRSS to predict either progression or regression of skin fibrosis. This also supports our previous EUSTAR analysis on worsening of skin fibrosis.4 In a pooled analysis of patients with dcSSc from seven multicentre clinical trials, mRSS at baseline had a weak negative correlation with any change in mRSS.6 Furthermore, in a recent analysis from the Canadian cohort, baseline mRSS was the only baseline parameter significantly associated with a significant change in mRSS at follow-up (defined as difference in 8 points).16 These data underline the value of mRSS for cohort enrichment in clinical trials. Our study also provides evidence-derived data on different thresholds of baseline mRSS and their performance to enrich for progressors over regressors in clinical trials (table 3). Thus, the optimal baseline mRSS cut-off for a specific study can be chosen from these data taking into account feasibility versus optimised cohort enrichment.
Another important aspect to consider is the natural regression to the mean phenomenon: the more extreme the skin score values in the study population at baseline, the more likely they are to decrease towards the mean at follow-up, thus not necessarily reflecting treatment response. The regression to the mean is most likely the statistical effect that explains the selection of baseline mRSS as a strong predictor of worsening and regression, respectively.
While our study addresses a very large SSc cohort with multiple data quality controls and external data monitoring, it also has several limitations. It has the natural drawbacks of registry data, such as missing data. However, we have addressed this issue by applying acknowledged imputation methods to compensate for missing data. Nonetheless, some of the candidate predictors had too much missing data which did not allow a trustable imputation, hence we could not include them in the analysis. The inclusion threshold of mRSS>7 aimed at identifying patients with true dcSSc with minimum involvement of distal upper extremities, but is, nonetheless, somewhat arbitrary. Our data also have to be confirmed in other cohorts with different baseline characteristics, for example, with higher prevalence of anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies. Additional information from in-between visits (eg, at 3 months, 6 months) as well as health assessment questionnaire data17 could bring additional valuable information on the course of skin fibrosis. Moreover, it has to be mentioned that the final prediction model only explains about 16% of the variation in skin fibrosis regression (see online supplementary table S4), indicating that other yet unknown factors such as, for example, biomarkers have an important role in determining the improvement of skin fibrosis in dcSSc. Further, modifications on how to measure the mRSS (eg, averaging vs maximising skin thickness over a certain skin area) will have great impact on the specific baseline mRSS values and have to be considered when these data are applied to clinical trials.
In conclusion, our study provides novel evidence-based data for cohort enrichment in clinical trials on skin fibrosis in patients with dcSSc. These data further support a lower baseline mRSS as inclusion criteria to optimise the ratio of progressors over regressors for recruitment into clinical trials. Other significant predictors of improvement with potential application to clinical trials resulting from these data are absence of tendon friction rubs, and, potentially, negativity for anti-Scl70 antibodies.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Nicole Schneider for excellent administration and data entry to the EUSTAR cohort and Terkia Medkour for data management of the EUSTAR database.
Footnotes
Collaborators: EUSTAR Collaborators (numerical order of centres): Marco Matucci Cerinic, Serena Guiducci, Department of Medicine, Section of Rheumatology, University of Florence, Italy; Ulrich Walker, Department of Rheumatology, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland; Giovanni Lapadula, Florenzo Iannone, Rheumatology Unit-DiMIMP, School of Medicine University of Bari, Italy; Radim Becvar, Institute of Rheumatology, 1st Medical School, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic; Stanislaw Sierakowsky, Department of Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Medical University of Bialystok, Bialystok, Poland; Maurizio Cutolo, Alberto Sulli, Research Laboratory and Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Genova, Italy; Gabriele Valentini, Giovanna Cuomo, Serena Vettori, Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine ‘F-Magrassi’ II Policlinico, Unit of Rheumatology, Naples, Italy; Gabriela Riemekasten, Department of Rheumatology, University of Lübeck, Germany; Elise Siegert, Department of Rheumatology, Charitè University Hospital, Berlin, German Rheumatism Research Centre Berlin (DRFZ), a Leibniz Institute, Germany; Simona Rednic, Ileana Nicoara, Department of Rheumatology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy ‘Iuliu Hatieganu’ Cluj, Cluj-Napoca, Romania; André Kahan, Department of Rheumatology, University Paris Descartes and Cochin Hospital, Paris, France; P. Vlachoyiannopoulos, Department of Pathopysiology, Medical School, National University of Athens, Greece; C. Montecucco, Roberto Caporali, Unita’ Operativa e Cattedra di Reumatologia, IRCCS Policlinico S Matteo, Pavia, Italy; Patricia E. Carreira, Division of Rheumatology, Hospital 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain; Srdan Novak, Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Internal Medicine, KBC Rijeka, Croatia; László Czirják, Cecilia Varju, Department of Immunology and Rheumatology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Pécs, Hungary; Carlo Chizzolini, Department of Immunology and Allergy, University Hospital, Geneva, Switzerland; Eugene J. Kucharz, Anna Kotulska, Magdalena Kopec-Medrek, Malgorzata Widuchowska, Department of Internal Medicine and Rheumatology, Medical University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland; Franco Cozzi, Rheumatology Unit, Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, University of Padova, Italy; Blaz Rozman, University Medical Center Ljublijana, Division of Internal Medicine, Department of Rheumatology, Ljubliana, Slovenia; Carmel Mallia, Bernard Coleiro, ‘Stella Maris’, Balzan, Malta; Armando Gabrielli, Dipartimento di Scienze Cliniche e Molecolari, Clinica Medica, Università Politecnica delle Marche, Ancona, Italy; Dominique Farge, Chen Wu, Zora Marjanovic, Helene Faivre, Darin Hij, Roza Dhamadi, Department of Internal Medicine, Hospital Saint-Louis, Paris, France; Paolo Airò, Spedali Civili di Brescia, Servizio di Reumatologia Allergologia e Immunologia Clinica, Brescia, Italy; Roger Hesselstrand, Frank Wollheim, Dirk M Wuttge, Kristofer Andréasson, Department of Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden; Duska Martinovic, Department of Internal Medicine, Clinical Hospital of Split, Croatia; Alexandra Balbir-Gurman, Yolanda Braun-Moscovici, B. Shine Rheumatology Unit, Rambam Health Care Campus, Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Haifa, Israel; F. Trotta, Andrea Lo Monaco, Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Rheumatology Unit, University of Ferrara, Italy; Nicolas Hunzelmann, Department of Dermatology, University Hospital Cologne, Germany; Raffaele Pellerito, Ospedale Mauriziano, Centro di Reumatologia, Torino, Italy; Lisa Maria Bambara, Paola Caramaschi, Unità di Reumatologia, AOUI, Verona Italy; Carol Black, Christopher Denton, Centre for Rheumatology, Royal Free and University College London Medical School, Royal Free Campus, United Kingdom; Nemanja Damjanov, Institute of Rheumatology, Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro; Jörg Henes, Medizinische Universitätsklinik, Abt. II (Onkologie, Hämatologie, Rheumatologie, Immunologie, Pulmonologie), Tübingen, Germany; Vera Ortiz Santamaria, Rheumatology Granollers General Hospital, Barcelona, Spain; Stefan Heitmann, Department of Rheumatology, Marienhospital Stuttgart, Germany; Dorota Krasowska, Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Lublin, Poland; Matthias Seidel, Medizinische Universitäts-Poliklinik, Department of Rheumatology, Bonn, Germany; Harald Burkhardt, Andrea Himsel, Klinikum der Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universität, Medizinische Klinik III, Rheumatologische Ambulanz, Frankfurt am Main, Germany; Maria J. Salvador, José Antonio Pereira Da Silva, Rheumatology Department, Hospitais da Universidade, Coimbra, Portugal; Bojana Stamenkovic, Aleksandra Stankovic, Institute for Prevention, Treatment and Rehabilitation of Rheumatic and Cardiovascular Diseases, Niska Banja, Serbia and Montenegro; Mohammed Tikly, Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine Chris Hani Haragwanath, Hospital and University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa; Lidia P. Ananieva, Lev N. Denisov, Institute of Rheumatology, Russian Academy of Medical Science, Moscow, Russia; Ulf Müller-Ladner, Marc Frerix, Ingo Tarner, Justus-Liebig University Giessen, Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Kerckhoff-Klinik Bad Nauheim, Germany; Raffaella Scorza, U.O. Immunologia Clinica, Centro di Riferimento per le Malattie Autoimmuni Sistemiche, Milano, Italy; Merete Engelhart, Gitte Strauss, Henrik Nielsen, Kirsten Damgaard, Department of Rheumatology, University Hospital of Gentofte, Hellerup, Denmark; Antonio Zea Mendoza, Carlos de la Puente, Sifuentes Giraldo WA, Servicio de Reumatología, Hospital Ramon Y Cajal, Madrid, Spain; Øyvind Midtvedt, Silje Reiseter, Department of Rheumatology, Rikshospitalet University Hospital, Oslo, Norway; Eric Hachulla, David Launay, Department of Internal Medicine, Hôpital Claude Huriez, Lille cedex, France; Guido Valesini, Valeria Riccieri, Department of Internal Medicine and Medical Specialities, ‘Sapienza’ University of Rome, Italy; Ruxandra Maria Ionescu, Daniela Opris, Laura Groseanu, Department of Rheumatology, St. Mary Hospital, Carol Davila, University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania; Roxana Sfrent Cornateanu, Razvan Ionitescu, Ana Maria Gherghe, Alina Soare, Marilena Gorga, Mihai Bojinca, Department of Internal Medicine and Rheumatology, Cantacuzino Hospital, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania; Georg Schett, Jörg HW Distler, Christian Beyer, Department of Internal Medicine 3, University Hospital Erlangen, Germany; Pierluigi Meroni, Francesca Ingegnoli, Division of Rheumatology, Istituto Gaetano Pini, Department of Clinical Sciences and Community Health, University of Milano, Milano, Italy; Luc Mouthon, Department of Internal Medicine, Hôpital Cochin, Paris, France; Filip De Keyser, Vanessa Smith, University of Ghent, Department of Rheumatology, Gent, Belgium; Francesco P. Cantatore, Ada Corrado, U.O. Reumatologia-Università degli Studi di Foggia, Ospedale ‘Col. D'Avanzo’, Foggia, Italy; Maria R. Pozzi, Dipartimento di Medicina, Ospedale San Gerardo, Monza, Italy; Kilian Eyerich, Rüdiger Hein, Elisabeth Knott, Department of Dermatology and Allergy of the TU Munich, Germany; Piotr Wiland, Magdalena Szmyrka-Kaczmarek, Renata Sokolik, Ewa Morgiel, Marta Madej, Department of Rheumatology and Internal Diseases, Wroclaw University of Medicine, Wroclaw, Poland; Brigitte Krummel-Lorenz, Petra Saar, Endokrinologikum Frankfurt, Germany; Martin Aringer, Claudia Günther, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine III/Department of Dermatology, University Medical Center Carl Gustav Carus, Technical University of Dresden, Germany; Rene Westhovens, Ellen de Langhe, Jan Lenaerts, Catholic University of Leuven, Department of Rheumatology, Leuven, Belgium; Branimir Anic, Marko Baresic, Miroslav Mayer, University Hospital Centre Zagreb, Division of Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, Zagreb, Croatia; Sebastião C. Radominski, Carolina de Souza Müller, Valderílio F. Azevedo, Hospital de Clínicas da Universidade Federal do Paraná, Curitiba - Paraná, Brasil; Svetlana Agachi, Liliana Groppa, Lealea Chiaburu, Eugen Russu, Sergei Popa, Municipal Centres of Research in Scleroderma, Hospital ‘Sacred Trinity’, Department of Rheumatology/Department of Rheumatology, Republican Clinical Hospital, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova; Thierry Zenone, Department of Medicine, Unit of Internal Medicine, Valence cedex 9, France; Simon Stebbings, John Highton, Dunedin School of Medicine, Dunedin, New Zealand; Lisa Stamp, Peter Chapman, John O’Donnell, Department of Medicine, University of Otago, Christchurch, New Zealand; Kamal Solanki, Alan Doube, Waikato University Hospital, Rheumatology Unit, Hamilton City, New Zealand; Douglas Veale, Marie O'Rourke, Department of Rheumatology, Bone and Joint Unit, St. Vincent's University Hospital, Dublin, Ireland; Esthela Loyo, Reumatologia e Inmunologia Clinica, Hospital Regional Universitario Jose Ma Cabral y Baez, Clinica Corominas, Santiago, Dominican Republic; Mengtao Li, Department of Rheumatology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital (West Campus), Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China; Edoardo Rosato, Antonio Amoroso, Antonietta Gigante, Centro per la Sclerosi Sistemica - Dipartimento di Medicina Clinica, Università La Sapienza, Policlinico Umberto I, Roma, Italy; Cristina-Mihaela Tanaseanu, Monica Popescu, Alina Dumitrascu, Isabela Tiglea, Clinical Emergency Hospital St. Pantelimon, Bucharest, Romania; Rosario Foti, U.O. di Reumatologia, A.O.U. Policlinico Vittorio Emanuele, Catania, Italy; Rodica Chirieac, Codrina Ancuta, Division of Rheumatology and Rehabilitation GR.T.Popa, Center for Biomedical Research, European Center for Translational Research, "GR.T.Popa" University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Rehabilitation Hospital, Iasi, Romania; Peter Villiger, Sabine Adler, Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology/Allergology, Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland; Paloma García de la Peña Lefebvre, Silvia Rodriguez Rubio, Marta Valero Exposito, Hospital Universitario Madrid Norte Sanchinarro, Madrid, Spain; Jean Sibilia, Emmanuel Chatelus, Jacques Eric Gottenberg, Hélène Chifflot, University Hospital of Strasbourg, Department of Rheumatology, Hôpital de Hautepierre, Service de Rhumatologie, Strasbourg Cedex, France; Ira Litinsky, Department of Rheumatology, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel; Algirdas Venalis, Irena Butrimiene, Paulius Venalis, Rita Rugiene, Diana Karpec, State Research Institute for Innovative Medicine, Vilnius University, Vilnius, Lithuania; Lesley Ann Saketkoo, Joseph A. Lasky, Tulane University Lung Center, Tulane/University Medical Center Scleroderma and Sarcoidosis Patient Care and Research Center, New Orleans, USA; Eduardo Kerzberg, Fabiana Montoya, Vanesa Cosentino, Osteoarticular Diseases and Osteoporosis Centre, Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacological Research Centre, School of medicine, University of Buenos Aires, Rheumatology and Collagenopathies Department, Ramos Mejía Hospital, Buenos Aires, Argentina; Massimiliano Limonta, Antonio Luca Brucato, Elide Lupi, USSD Reumatologia, Ospetali Riuniti di Bergamo, Italy; François Spertini, Camillo Ribi, Guillaume Buss, Department of Rheumatology, Clinical Immunology and Allergy, Lausanne, Switzerland; Jean Louis Pasquali, Thierry Martin, Audrey Gorse, Clinical Immunology and Internal Medicine, National Referral Center for Systemic Autoimmune Diseases, Strasbourg, France.
Contributors: RD: design of the study, acquisition of data, analysis, interpretation of data, drafting the article. BM: design of the study, acquisition of data, analysis, interpretation of data, revising the article. NG: analysis and interpretation of data, revising the article. SJ: introduction and interpretation of data, revising the article. CM, OK-B, YA: design of the study, analysis, interpretation of data, revising the manuscript. OD: acquisition of data, design of the study, analysis, interpretation of data, drafting the article. All authors have finally approved the submitted version to be published and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Funding: OD's research was supported by an European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR)-ODP grant. RD's research activity was supported by an Articulum Fellowship (2013–2014), a EULAR training bursary and the DeSScipher FP-7 Project.
Competing interests: OD has/had consultancy relationship and/or has received research funding in the area of systemic sclerosis and related conditions from Actelion, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Ergonex, BMS, Sanofi-Aventis, United BioSource Corporation, Roche/Genentech, Medac, Biovitrium, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, Novartis, 4D Science, Active Biotec, Bayer, Sinoxa, Serodapharm, EpiPharm, Biogen, Inventiva and GSK. YA has/had consultancy relationships and/or has received research funding in the area of systemic sclerosis and related conditions from Actelion, Bayer, Biogen, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, Inventiva, Medac, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Sanofi-Aventis and Servier. CM has/had consultancy relationships in the area of systemic sclerosis and related conditions from Actelion/Geneva Romfarm and Abbvie.
Ethics approval: Ethics approval has been obtained from all respective local ethics committees.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed
Contributor Information
Collaborators: Marco Matucci Cerinic, Serena Guiducci, Ulrich Walker, Giovanni Lapadula, Florenzo Iannone, Radim Becvar, Stanislaw Sierakowsky, Maurizio Cutolo, Alberto Sulli, Gabriele Valentini, Giovanna Cuomo, Serena Vettori, Gabriela Riemekasten, Elise Siegert, Simona Rednic, Ileana Nicoara, André Kahan, P. Vlachoyiannopoulos, C. Montecucco, Roberto Caporali, Patricia E. Carreira, Srdan Novak, László Czirják, Cecilia Varju, Carlo Chizzolini, Eugene J. Kucharz, Anna Kotulska, Magdalena Kopec-Medrek, Malgorzata Widuchowska, Franco Cozzi, Blaz Rozman, Carmel Mallia, Bernard Coleiro, Armando Gabrielli, Dominique Farge, Chen Wu, Zora Marjanovic, Helene Faivre, Darin Hij, Roza Dhamadi, Paolo Airò, Roger Hesselstrand, Frank Wollheim, Dirk M Wuttge, Kristofer Andréasson, Duska Martinovic, Alexandra Balbir-Gurman, Yolanda Braun-Moscovici, F. Trotta, Andrea Lo Monaco, Nicolas Hunzelmann, Raffaele Pellerito, Ospedale Mauriziano, Lisa Maria Bambara, Paola Caramaschi, Carol Black, Christopher Denton, Nemanja Damjanov, Jörg Henes, Vera Ortiz Santamaria, Stefan Heitmann, Dorota Krasowska, Matthias Seidel, Harald Burkhardt, Andrea Himsel, Maria J. Salvador, José Antonio Pereira Da Silva, Bojana Stamenkovic, Aleksandra Stankovic, Niska Banja, Mohammed Tikly, Lidia P. Ananieva, Lev N. Denisov, Ulf Müller-Ladner, Marc Frerix, Ingo Tarner, Raffaella Scorza, Merete Engelhart, Gitte Strauss, Henrik Nielsen, Kirsten Damgaard, Antonio Zea Mendoza, Carlos de la Puente, Walter A. Sifuentes Giraldo, Øyvind Midtvedt, Silje Reiseter, Eric Hachulla, David Launay, Guido Valesini, Valeria Riccieri, Ruxandra Maria Ionescu, Daniela Opris, Laura Groseanu, Roxana Sfrent Cornateanu, Razvan Ionitescu, Ana Maria Gherghe, Alina Soare, Marilena Gorga, Mihai Bojinca, Georg Schett, Jörg HW Distler, Christian Beyer, Pierluigi Meroni, Francesca Ingegnoli, Luc Mouthon, Filip De Keyser, Vanessa Smith, Francesco P. Cantatore, Ada Corrado, Maria R. Pozzi, Kilian Eyerich, Rüdiger Hein, Elisabeth Knott, Piotr Wiland, Magdalena Szmyrka-Kaczmarek, Renata Sokolik, Ewa Morgiel, Marta Madej, Brigitte Krummel-Lorenz, Martin Aringer, Claudia Günther, Rene Westhovens, Ellen de Langhe, Jan Lenaerts, Branimir Anic, Marko Baresic, Miroslav Mayer, Sebastião C. Radominski, Carolina de Souza Müller, Valderílio F. Azevedo, Svetlana Agachi, Liliana Groppa, Lealea Chiaburu, Eugen Russu, Sergei Popa, Thierry Zenone, Simon Stebbings, John Highton, Lisa Stamp, Peter Chapman, John O’Donnell, Kamal Solanki, Alan Doube, Douglas Veale, Marie O'Rourke, Esthela Loyo, Mengtao Li, Edoardo Rosato, Antonio Amoroso, Antonietta Gigante, Cristina-Mihaela Tanaseanu, Monica Popescu, Alina Dumitrascu, Isabela Tiglea, Rosario Foti, Rodica Chirieac, Codrina Ancuta, Peter Villiger, Sabine Adler, Paloma García de la Peña Lefebvre, Silvia Rodriguez Rubio, Marta Valero Exposito, Jean Sibilia, Emmanuel Chatelus, Jacques Eric Gottenberg, Hélène Chifflot, Ira Litinsky, Algirdas Venalis, Irena Butrimiene, Paulius Venalis, Rita Rugiene, Diana Karpec, Lesley Ann Saketkoo, Joseph A. Lasky, Eduardo Kerzberg, Fabiana Montoya, Vanesa Cosentino, Massimiliano Limonta, Antonio Luca Brucato, Elide Lupi, François Spertini, Camillo Ribi, Guillaume Buss, Jean Louis Pasquali, Thierry Martin, and Audrey Gorse
References
- 1.Khanna D, Merkel PA. Outcome measures in systemic sclerosis: an update on instruments and current research. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2007;9:151–7. 10.1007/s11926-007-0010-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wiese AB, Berrocal VJ, Furst DE, et al. Correlates and responsiveness to change of measures of skin and musculoskeletal disease in early diffuse systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2014;66:1731–9. 10.1002/acr.22339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lafyatis R. Application of biomarkers to clinical trials in systemic sclerosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2012;14:47–55. 10.1007/s11926-011-0216-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Maurer B, Graf N, Michel BA, et al. Prediction of worsening of skin fibrosis in patients with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis using the EUSTAR database. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:1124–31. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205226 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Amjadi S, Maranian P, Furst DE, et al. Course of the modified Rodnan skin thickness score in systemic sclerosis clinical trials: analysis of three large multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum 2009;60:2490–8. 10.1002/art.24681 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Merkel PA, Silliman NP, Clements PJ, et al. Patterns and predictors of change in outcome measures in clinical trials in scleroderma: an individual patient meta-analysis of 629 subjects with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 2012;64:3420–9. 10.1002/art.34427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.LeRoy EC, Black C, Fleischmajer R, et al. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol 1988;15:202–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Müller-Ladner U, Tyndall A, Czirjak L, et al. Ten years EULAR Scleroderma Research and Trials (EUSTAR): what has been achieved? Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:324–7. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Walker UA, Tyndall A, Czirják L, et al. Clinical risk assessment of organ manifestations in systemic sclerosis: a report from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials And Research group database. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66:754–63. 10.1136/ard.2006.062901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Meier FM, Frommer KW, Dinser R, et al. Update on the profile of the EUSTAR cohort: an analysis of the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research group database. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:1355–60. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200742 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Khanna D, Furst DE, Hays RD, et al. Minimally important difference in diffuse systemic sclerosis: results from the D-penicillamine study. Ann Rheum Dis 2006;65:1325–9. 10.1136/ard.2005.050187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Valentini G, D'Angelo S, Della Rossa A, et al. European Scleroderma Study Group to define disease activity criteria for systemic sclerosis. IV. Assessment of skin thickening by modified Rodnan skin score. Ann Rheum Dis 2003;62:904–5. 10.1136/ard.62.9.904 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Steen VD, Medsger TA Jr. Improvement in skin thickening in systemic sclerosis associated with improved survival. Arthritis Rheum 2001;44:2828–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Clements PJ, Furst DE, Wong WK, et al. High-dose versus low-dose D-penicillamine in early diffuse systemic sclerosis: analysis of a two-year, double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:1194–203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Furst DE, Clements PJ. D-penicillamine is not an effective treatment in systemic sclerosis. Scand J Rheumatol 2001;30:189–91. 10.1080/030097401316909495 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Choy T, Baron M, Pope J. Estimating benefits from immunosuppressive treatment in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: data from the Canadian scleroderma research group. Open J Rheumatol Autoimmune Dis 2014;4:248–53. 10.4236/ojra.2014.44034 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sultan N, Pope JE, Clements PJ. The health assessment questionnaire (HAQ) is strongly predictive of good outcome in early diffuse scleroderma: results from an analysis of two randomized controlled trials in early diffuse scleroderma. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004;43:472–8. 10.1093/rheumatology/keh070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
annrheumdis-2015-208024supp.pdf (264.2KB, pdf)