Abstract
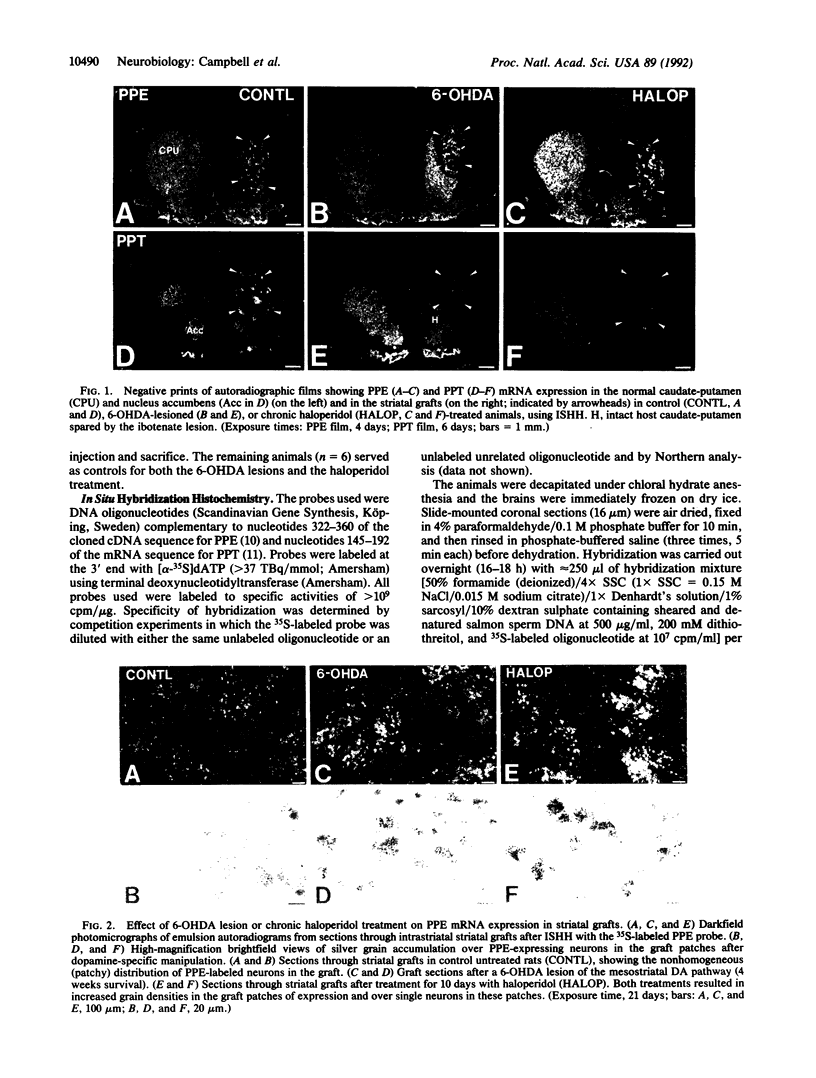
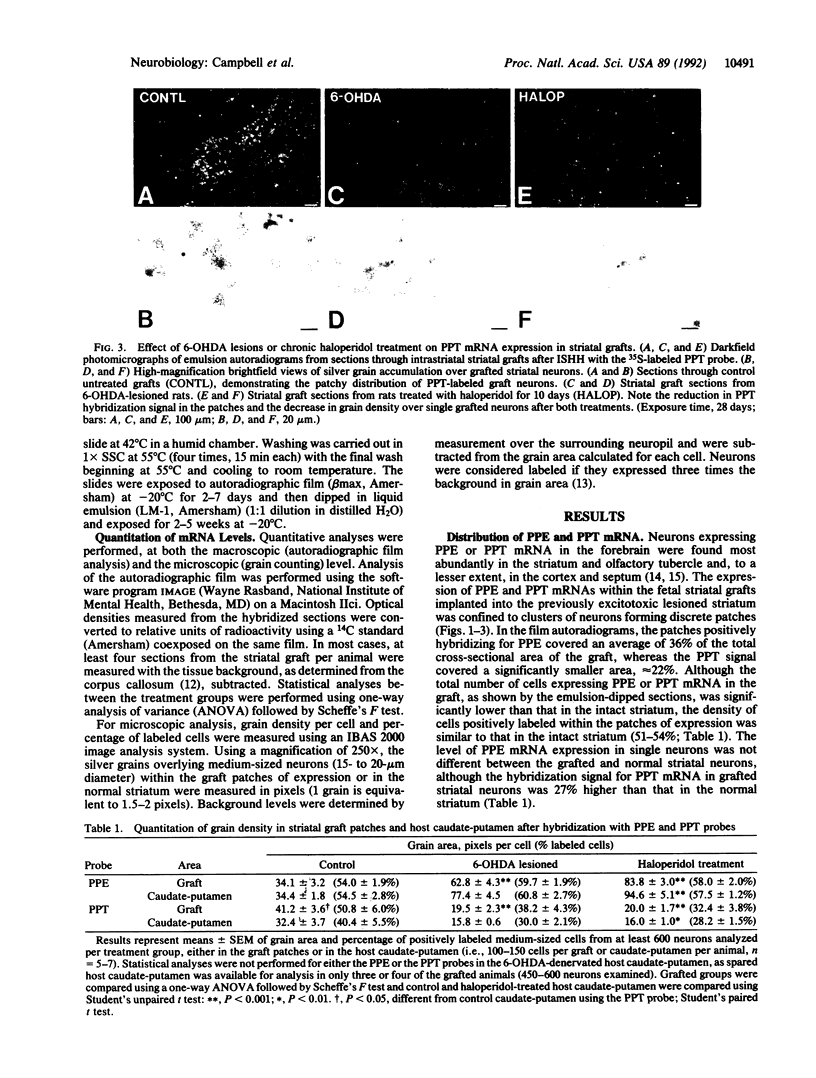
The effects of dopamine-specific manipulations on neuropeptide gene expression in intrastriatal grafts of fetal striatal tissue were studied by quantitative in situ hybridization histochemistry, using 35S-labeled oligonucleotide probes. Messenger RNA transcripts for the striatal neuropeptides preproenkephalin (PPE) and preprotachykinin (PPT) were detected in neurons forming discrete patches in the striatal grafts. The relative abundance of PPE and PPT mRNA-expressing neurons within the graft patches (51-54%) was similar to that found in normal caudate-putamen. In specimens with intact dopamine afferents the expression of PPE mRNA in grafted neurons was similar to that found in normal caudate putamen, whereas the hybridization signal for PPT mRNA was 27% higher in the graft neurons than in the normal caudate-putamen. Removal of host dopaminergic afferents by 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the ipsilateral mesostriatal dopamine pathway increased the hybridization signal for PPE mRNA both in the grafts (+84%) and in the spared ipsilateral host caudate-putamen (+125%), whereas the PPT signal was reduced by 53% in the grafts and by 51% in the remaining host caudate-putamen. Similarly, chronic treatment of grafted animals with the dopamine receptor antagonist haloperidol (2 mg/kg per day for 10 days) produced a 146% increase in the PPE signal in the grafts and a 175% increase in the intact contralateral caudate-putamen, whereas the signal for PPT mRNA was again decreased by 52% and 51% in the grafts and host caudate-putamen, respectively. These results show that the host nigrostriatal dopamine pathway differentially regulates enkephalin and substance P gene expression within striatal grafts and thereby exerts a tonic functional influence over grafted striatal neurons.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlson J. H., Bergstrom D. A., Demo S. D., Walters J. R. Nigrostriatal lesion alters neurophysiological responses to selective and nonselective D-1 and D-2 dopamine agonists in rat globus pallidus. Synapse. 1990;5(2):83–93. doi: 10.1002/syn.890050202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. J., Dunnett S. B., Isacson O., Sirinathsinghji D. J., Björklund A. Striatal grafts in rats with unilateral neostriatal lesions--I. Ultrastructural evidence of afferent synaptic inputs from the host nigrostriatal pathway. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):791–801. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragunow M., Williams M., Faull R. L. Haloperidol induces Fos and related molecules in intrastriatal grafts derived from fetal striatal primordia. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 22;530(2):309–311. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnett S. B., Isacson O., Sirinathsinghji D. J., Clarke D. J., Björklund A. Striatal grafts in rats with unilateral neostriatal lesions--III. Recovery from dopamine-dependent motor asymmetry and deficits in skilled paw reaching. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):813–820. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Powell J. F., Smith A. D. Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive boutons in synaptic contact with identified striatonigral neurons, with particular reference to dendritic spines. Neuroscience. 1984 Dec;13(4):1189–1215. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., McGinty J. F., Young W. S., 3rd Dopamine differentially regulates dynorphin, substance P, and enkephalin expression in striatal neurons: in situ hybridization histochemical analysis. J Neurosci. 1991 Apr;11(4):1016–1031. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-04-01016.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R. The neostriatal mosaic: multiple levels of compartmental organization. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Apr;15(4):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90355-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Liu F. C., Dunnett S. B. Intrastriatal grafts derived from fetal striatal primordia. I. Phenotypy and modular organization. J Neurosci. 1989 Sep;9(9):3250–3271. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-09-03250.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M. Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):244–254. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90104-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howells R. D., Kilpatrick D. L., Bhatt R., Monahan J. J., Poonian M., Udenfriend S. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of rat preproenkephalin cDNA: sensitive probe for studying transcriptional changes in rat tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7651–7655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacson O., Brundin P., Gage F. H., Björklund A. Neural grafting in a rat model of Huntington's disease: progressive neurochemical changes after neostriatal ibotenate lesions and striatal tissue grafting. Neuroscience. 1985 Dec;16(4):799–817. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacson O., Dawbarn D., Brundin P., Gage F. H., Emson P. C., Björklund A. Neural grafting in a rat model of Huntington's disease: striosomal-like organization of striatal grafts as revealed by acetylcholinesterase histochemistry, immunocytochemistry and receptor autoradiography. Neuroscience. 1987 Aug;22(2):481–497. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause J. E., Chirgwin J. M., Carter M. S., Xu Z. S., Hershey A. D. Three rat preprotachykinin mRNAs encode the neuropeptides substance P and neurokinin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):881–885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Inagaki S., Kito S. Innervation of substance P neurons by catecholaminergic terminals in the neostriatum. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 4;375(1):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90969-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Inagaki S., Kito S., Takagi H., Smith A. D. Ultrastructural evidence of dopaminergic input to enkephalinergic neurons in rat neostriatum. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 5;367(1-2):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91622-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindefors N. Amphetamine and haloperidol modulate preprotachykinin A mRNA expression in rat nucleus accumbens and caudate-putamen. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Mar;13(1-2):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90055-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. C., Dunnett S. B., Robertson H. A., Graybiel A. M. Intrastriatal grafts derived from fetal striatal primordia. III. Induction of modular patterns of fos-like immunoreactivity by cocaine. Exp Brain Res. 1991;85(3):501–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00231733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel R. J., Wictorin K., Cenci M. A., Björklund A. Fos expression in intrastriatal striatal grafts: regulation by host dopaminergic afferents. Brain Res. 1992 Jun 26;583(1-2):207–215. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(10)80026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer E., Heavens R. P., Sirinathsinghji D. J. Autoradiographic localisation of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in primordial striatal tissue grafts in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Feb 16;109(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90006-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell I. J., Clarke C. E., Boyce S., Robertson R. G., Peggs D., Sambrook M. A., Crossman A. R. Neural mechanisms underlying parkinsonian symptoms based upon regional uptake of 2-deoxyglucose in monkeys exposed to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Neuroscience. 1989;32(1):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Höllt V., Herz A. Dopaminergic regulation of striatal proenkephalin mRNA and prodynorphin mRNA: contrasting effects of D1 and D2 antagonists. Neuroscience. 1988 May;25(2):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. B., Calderon S. F., Giordano M., Sanberg P. R. Striatal tissue transplants attenuate apomorphine-induced rotational behavior in rats with unilateral kainic acid lesions. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Mar;27(3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand E., Popovici T., Onteniente B., Fellmann D., Piatier-Tonneau D., Auffray C., Bloch B. Dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra modulate preproenkephalin A gene expression in rat striatal neurons. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 26;439(1-2):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91459-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan H. S., Walters J. R. Unilateral lesion of the nigrostriatal pathway decreases the firing rate and alters the firing pattern of globus pallidus neurons in the rat. Synapse. 1988;2(6):650–656. doi: 10.1002/syn.890020612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. C., Difiglia M. Localization of immunoreactive GABA and enkephalin and NADPH-diaphorase-positive neurons in fetal striatal grafts in the quinolinic-acid-lesioned rat neostriatum. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Aug 15;274(3):406–421. doi: 10.1002/cne.902740309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano G. J., Shivers B. D., Harlan R. E., Howells R. D., Pfaff D. W. Haloperidol increases proenkephalin mRNA levels in the caudate-putamen of the rat: a quantitative study at the cellular level using in situ hybridization. Brain Res. 1987 Apr;388(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirinathsinghji D. J., Morris B. J., Wisden W., Northrop A., Hunt S. P., Dunnett S. B. Gene expression in striatal grafts--I. Cellular localization of neurotransmitter mRNAs. Neuroscience. 1990;34(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trugman J. M., Wooten G. F. Selective D1 and D2 dopamine agonists differentially alter basal ganglia glucose utilization in rats with unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine substantia nigra lesions. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2927–2935. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02927.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Navia B., Douglas J. Differential expression of preproenkephalin and preprodynorphin mRNAs in striatal neurons: high levels of preproenkephalin expression depend on cerebral cortical afferents. J Neurosci. 1988 Dec;8(12):4755–4764. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-12-04755.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weick B. G., Walters J. R. Effects of D1 and D2 dopamine receptor stimulation on the activity of substantia nigra pars reticulata neurons in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats: D1/D2 coactivation induces potentiated responses. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 10;405(2):234–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wictorin K. Anatomy and connectivity of intrastriatal striatal transplants. Prog Neurobiol. 1992 Jun;38(6):611–639. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(92)90044-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wictorin K., Ouimet C.C., Björklund A. Intrinsic Organization and Connectivity of Intrastriatal Striatal Transplants in Rats as Revealed by DARPP-32 Immunohistochemistry: Specificity of Connections with the Lesioned Host Brain. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 Jan;1(6):690–701. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z. C., Wilson C. J., Emson P. C. Restoration of the corticostriatal projection in rat neostriatal grafts: electron microscopic analysis. Neuroscience. 1989;29(3):539–550. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Bonner T. I., Brann M. R. Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9827–9831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]