Abstract
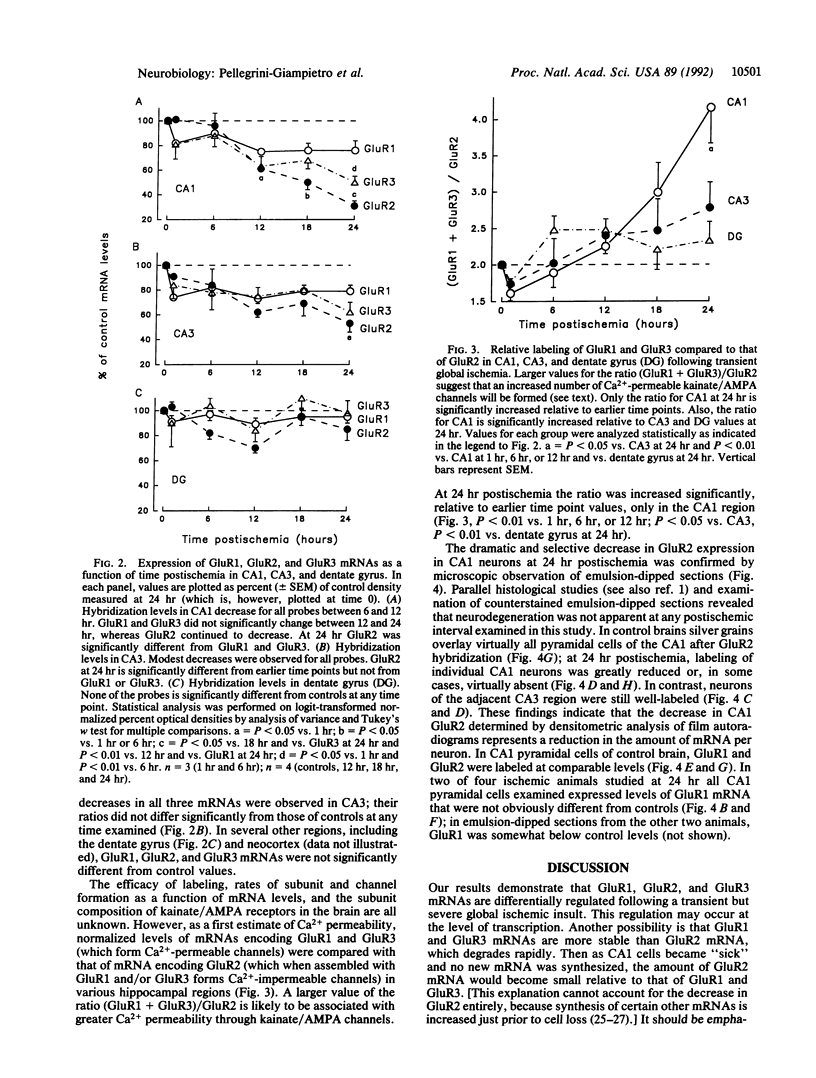
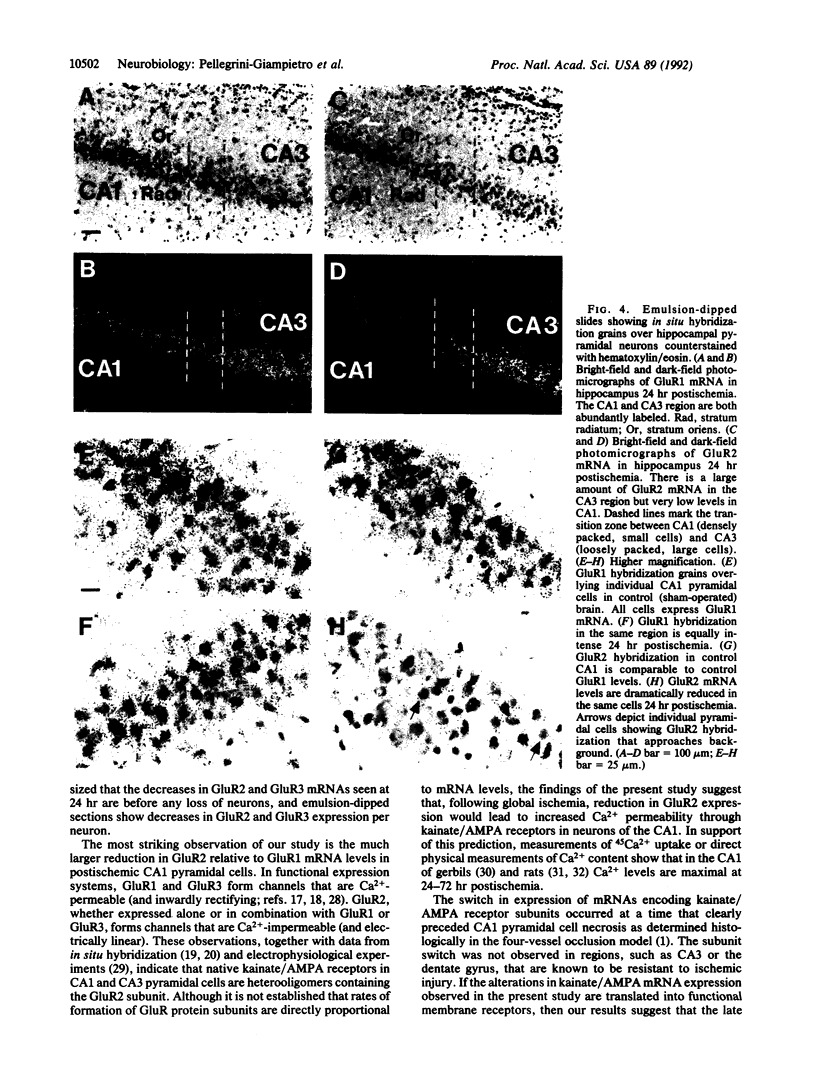
Severe, transient global ischemia of the brain induces delayed damage to specific neuronal populations. Sustained Ca2+ influx through glutamate receptor channels is thought to play a critical role in postischemic cell death. Although most kainate-type glutamate receptors are Ca(2+)-impermeable, Ca(2+)-permeable kainate receptors have been reported in specific kinds of neurons and glia. Recombinant receptors assembled from GluR1 and/or GluR3 subunits in exogenous expression systems are permeable to Ca2+; heteromeric channels containing GluR2 subunits are Ca(2+)-impermeable. Thus, altered expression of GluR2 in development or following a neurological insult or injury to the brain can act as a switch to modify Ca2+ permeability. To investigate the molecular mechanism underlying delayed postischemic cell death, GluR1, GluR2, and GluR3 gene expression was examined by in situ hybridization in postischemic rats. Following severe, transient forebrain ischemia GluR2 gene expression was preferentially reduced in CA1 hippocampal neurons at a time point that preceded their degeneration. The switch in expression of kainate/AMPA receptor subunits coincided with the previously reported increase in Ca2+ influx into CA1 cells. Timing of the switch indicates that it may play a causal role in postischemic cell death.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste H., Drejer J., Schousboe A., Diemer N. H. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1369–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Egebjerg J., Sharma G., Pecht G., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Moll C., Stevens C. F., Heinemann S. Cloning of a putative glutamate receptor: a low affinity kainate-binding subunit. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90292-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A. M., Li H., Cho S., Pulsinelli W. A. Blockade of the AMPA receptor prevents CA1 hippocampal injury following severe but transient forebrain ischemia in adult rats. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Nov 11;132(2):255–258. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90314-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A., Li H., Pulsinelli W. A. The N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, MK-801, fails to protect against neuronal damage caused by transient, severe forebrain ischemia in adult rats. J Neurosci. 1991 Apr;11(4):1049–1056. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-04-01049.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Khodorova A., Jonas P., Helm P. J., Wisden W., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Calcium-permeable AMPA-kainate receptors in fusiform cerebellar glial cells. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.1317970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande J. K., Siesjö B. K., Wieloch T. Calcium accumulation and neuronal damage in the rat hippocampus following cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987 Feb;7(1):89–95. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienel G. A. Regional accumulation of calcium in postischemic rat brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Oct;43(4):913–925. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux E., Mies G., Hossmann K. A., Siklós L. Calcium in the mitochondria following brief ischemia of gerbil brain. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Aug 5;78(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Hartley M., Heinemann S. Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA--gated glutamate receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1709304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Ozawa S., Tsuzuki K. Permeation of calcium through excitatory amino acid receptor channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:151–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen M. B., Johansen F. F., Diemer N. H. Post-ischemic and kainic acid-induced c-fos protein expression in the rat hippocampus. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991 Oct;84(4):352–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1991.tb04968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keinänen K., Wisden W., Sommer B., Werner P., Herb A., Verdoorn T. A., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):556–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2166337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirino T. Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res. 1982 May 6;239(1):57–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90833-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Miller R. J. Excitatory amino acid receptors, second messengers and regulation of intracellular Ca2+ in mammalian neurons. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jun;11(6):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. N., Miller R. J. Regulation of Ca++ influx into striatal neurons by kainic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Apr;249(1):184–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Cleef M., Röhn G., Bonnekoh P., Pajunen A. E., Bernstein H. G., Paschen W. Ornithine decarboxylase in reversible cerebral ischemia: an immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;83(1):39–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00294428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller T., Möller T., Berger T., Schnitzer J., Kettenmann H. Calcium entry through kainate receptors and resulting potassium-channel blockade in Bergmann glial cells. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.1317969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak T. S., Jr Localization of 70 kDa stress protein mRNA induction in gerbil brain after ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 May;11(3):432–439. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini-Giampietro D. E., Bennett M. V., Zukin R. S. Differential expression of three glutamate receptor genes in developing rat brain: an in situ hybridization study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4157–4161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulsinelli W. A., Brierley J. B., Plum F. Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann Neurol. 1982 May;11(5):491–498. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheardown M. J., Nielsen E. O., Hansen A. J., Jacobsen P., Honoré T. 2,3-Dihydroxy-6-nitro-7-sulfamoyl-benzo(F)quinoxaline: a neuroprotectant for cerebral ischemia. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):571–574. doi: 10.1126/science.2154034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siesjö B. K., Bengtsson F. Calcium fluxes, calcium antagonists, and calcium-related pathology in brain ischemia, hypoglycemia, and spreading depression: a unifying hypothesis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989 Apr;9(2):127–140. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Keinänen K., Verdoorn T. A., Wisden W., Burnashev N., Herb A., Köhler M., Takagi T., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Flip and flop: a cell-specific functional switch in glutamate-operated channels of the CNS. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1580–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.1699275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan J. H., Evans M. C., Meldrum B. S. Long-term development of selective neuronal loss and the mechanism of protection by 2-amino-7-phosphonoheptanoate in a rat model of incomplete forebrain ischaemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Feb;8(1):64–78. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Structural determinants of ion flow through recombinant glutamate receptor channels. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1715–1718. doi: 10.1126/science.1710829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





