Abstract
The success of molecular modeling and computational chemistry efforts are, by definition, dependent on quality software applications. Open source software development provides many advantages to users of modeling applications, not the least of which is that the software is free and completely extendable. In this review we categorize, enumerate, and describe available open source software packages for molecular modeling and computational chemistry.
1. Introduction
What is Open Source?
Free and open source software (FOSS) is software that is both considered “free software,” as defined by the Free Software Foundation (http://fsf.org) and “open source,” as defined by the Open Source Initiative (http://opensource.org). The distinctions between free and open source software are largely philosophical - the free software movement is primary motivated by user freedoms (“free as in speech, not free as in beer”) while the open source movement is more concerned with promoting an open development model to enhance software quality. However, as a practical matter, especially with regards to scientific software, such distinctions remain philosophical rather than practical as the most popular software licenses are both free and open source.
The unifying theme of open source software licenses is that they allow users to use, modify, and distribute software without significant restrictions. This is achieved by making the full source code of the software available to users. Broadly speaking, open source licenses fall into two categories: permissive and copyleft. Permissive licenses, such as the Apache, BSD, MIT, and Python licenses, place minimal restrictions on how modified code may be distributed, such as requiring attribution and limiting liability. They specifically do not require that redistributions of modified source code be licensed under the same license as the original source code. This enables source code licensed under a permissive license to be incorporated into commercial, proprietary programs that are not open source. In contrast, copyleft licenses, such as the different versions of the GNU Public License (GPL), require that public redistributions of licensed software remain licensed under a GPL license. That is, the source code must remain publicly and freely available. The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is slightly less restrictive version of the GPL used primarily for libraries as it does not require software that uses LGPL licensed software as a library to be licensed under the LGPL. Although copyleft licenses do not prohibit selling software, since the full source code must remain freely available, in practice vendors of copylefted software must commercialize the support of the product, rather than the product itself. Finally, we note there are other software licenses that make source code available, but are not open source licenses. These licenses typically prohibit the redistribution of the source code. Such licenses, which we will refer to as “source-available” licenses, have some popularity in academia as they allow source code to be distributed to other researchers in non-profit institutions, but allow the code to be sold to commercial entities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Open Source
The value of open source software in cheminformatics and molecular modeling is somewhat controversial. Unsurprisingly, those affiliated with commercial scientific software argue that traditional commercial development, with its associated support and continuous development, provides a superior value [1], while open source advocates feel the benefits outweigh the burdens [2, 3]. Our goal is not to revisit these arguments. Instead, we assert that open source scientific software is a de facto part of the scientific community, and so in this review we catalog those open source packages that fall within the domain of cheminformatics and molecular modeling.
There are a few aspects of the open source software debate that we find particularly relevant. First, opponents are right to point out that free software is not free - users of open source software generally take on a much greater burden in supporting the software than with commercial software. This is one reason why it is important, when possible, to seek open source software that is under active development and supported by a broad community. Therefore, in this review we attempt to quantify the current level of development and usage of each package as an indirect measure of quality and usability. Second, the primary advantage of open source software is the ability to redistribute code without restriction. This inherently enables reproducibility and lets scientists “stand on the shoulders of giants” instead of reinventing the wheel. Consequently, in this review we limit ourselves to a survey of true open source software and exclude source-available software that may place restrictions on the publication of reproducible research results.
2. Methods
We organize software packages into seven categories: cheminformatics, visualization, QSAR (quantitative structure–activity relationship) and ADMET modeling, quantum chemistry, ligand dynamics and free energy calculations, and virtual screening (including ligand design). We identified open source software packages by browsing the relevant categories (Molecular Science, Chemistry, Bio-Informatics, Medical Science) on the popular Source-Forge (http://sourceforge.net) repository, searching for categories on GitHub (http://github.com), searching for categories on OpenHub (https://www.openhub.net), searching for categories together with “open source software” on Google, and browsing the Click2Drug (http://click2drug.org) and VLS3D [4] directories. Finally, a draft document was tweeted (@david_koes) to solicit suggestions for additional packages from the community.
For every identified software package, we report its primary URL and software license and assign it an activity code. For simplicity, BSD-like licenses (e.g. NCSA) are reported as BSD. Activity codes consist of a development activity level (alphabetical) and usage activity level (numerical). Activity codes were assigned as follows:
Development Activity
Substantial development (e.g. a new major release, the addition of new features, or substantial refinements of existing features) within the last 18 months. Note this includes all projects that were created in the last 18 months.
Evidence of some development within the last 18 months such as a minor release or bug fixes to a development branch.
No evidence of development (changes to the source code or documentation) within the last 18 months. Note that in cases where a package does not follow an open development model (i.e., source is only released with official releases) the estimate of development activity will be overly conservative.
Usage Activity
Substantial user usage within the last 18 months (more than 20 downloads a month on average from SourceForge, more than 20 stars or forks on GitHub, more than 10 citations a year, and/or a clearly active user community as indicated by traffic on mailing lists or discussion boards).
Moderate user usage within the last 18 months.
Minimal or no identifiable user usage within the last 18 months (fewer than 50 downloads total on SourceForge, three or fewer stars and/or forks on GitHub, or fewer than one citation a year).
We omit some packages with extended periods of inactivity (e.g. more than 10 years) where there is little evidence of any usage or packages that are referenced in the literature but for which we could not find a extant source code repository. We also omit packages that provide common and/or trivial functionality (e.g. molecular weight calculators) and those that require non-open source packages in order to function.
3. Cheminformatics
Cheminformatics involves the representation, manipulation and analysis of molecular data [5, 6]. Cheminformatic toolkits, although they may contain standalone utility programs, are primarily designed to function as libraries for other programs so that common functions, such as parsing molecular data, need not be reimplemented. As libraries, the native programming language of a toolkit is particularly relevant as it influences the language programs that integrate with the toolkit can be written in. In some cases, alternative language bindings, which essentially translate between programming languages, may be available, but due to the use of different idioms by different languages (e.g. object-oriented vs. functional, manual vs. automatic memory management) use of these non-native bindings may be cumbersome. In addition to toolkits, we catalog standalone programs, including conformer generators for converted 2D information into 3D molecular structures (some of which have been critically evaluated [7]), and graphical environments for creating and managing workflows.
Toolkits (Table 1)
Table 1.
Open source cheminformatics toolkits.
The Biochemical Algorithms Library (BALL) [8] provides an object-oriented C++ library for structural bioinformatics, and its capabilities include molecular mechanics, support for reading and writing a variety of file formats, protein-ligand scoring, docking, and QSAR modeling.
The Chemistry Development Kit (CDK) [9] is a cheminformatics toolkit written in Java. Its capabilities include support for reading and writing a variety of chemical formats, descriptor and fingerprint calculation, force field calculations, substructure search, and structure generation.
Chemf [10] is a minimal cheminformatics toolkit written in the functional language Scala.
chemfp [11] is a high-performance library with a Python interface for generating and searching for molecular fingerprints.
chemkit is a C++ cheminformatics toolkit that includes support for visualization with the Qt framework and molecular modeling.
ChemmineR [12] is a cheminformatics package for the R statistical programming language that is built using Open Babel. Its capabilities include property calculations, similarity search, and classification and clustering of compounds.
Cinfony [13] provides a single, simple standardized interface to other cheminformatics toolkits, including Open Babel, RDKit, the CDK, Indigo, JChem, OPSIN, and several web services.
CurlySMILES [14] provides parsing functionality for an extension of the SMILES format that supports the description of complex molecular systems.
DisCuS (Database System for Compound Selection) [15] provides support for analyzing the results of a high-throughput screen.
Fafoom (flexible algorithm for optimization of molecules) [16] is a Python library for identifying low energy conformers using a genetic algorithm.
fmcsR [41] is an R package that efficiently performs flexible maximum common substructure matching that allows minor mismatches between atoms and bonds in the common substructure.
Frowns is a cheminformatics toolkit mostly written in Python that provides basic support for SMILES and SD files, SMARTS search, fingerprint generation, and property perception.
Helium is a cheminformatics toolkit written using modern C++ idioms that provides support for SMILES files, fingerprints generation, and SMARTS and SMIRKS.
Indigo [18] is a cheminformatics toolkit written in C++ with C, Python, Java (including a KNIME node), and C# bindings. Its capabilities include general support for manipulating molecules, property calculation, combinatorial chemistry, scaffold detection and R-group decomposition, reaction processing, substructure matching and similarity search.
JOELib is a cheminformatics toolkit written in Java. Its capabilities include SMARTS substructure search, descriptor calculation, and processing/filtering pipes.
LICSS [19] integrates with the CDK to provide representations and analysis of chemical data embedded within Microsoft Excel.
MayChemTools is a collection of Perl scripts for manipulating chemical data, interfacing with databases, generating fingerprints, performing similarity search, and computing molecular properties.
Mychem is built using OpenBabel and provides an extension to the MySQL database package that adds the ability to search, analyze, and convert chemical data within a MySQL database.
The Open Drug Discovery Toolkit (ODDT) [21] is entirely written in Python, is built on top of RDKit and Open Babel, and is focused on providing enhanced functionality for managing and implementing drug discovery workflows, such as making it easy to implement a docking pipeline.
Open Babel [22] is substantial cheminformatics toolkit written in C++ with Python, Perl, Java, Ruby, R, PHP, and Scala bindings. Its capabilities include support for more than 100 chemical file formats, fingerprint generation, property determination, similarity and substructure search, structure generation, and molecular force fields. It has absorbed the Confab [47] conformer generator which produces 3D structures through the systematic enumeration of torsions and energy minimization.
OPSIN [23], the Open Parser for Systematic IUPAC nomenclature, converts plain-text chemical nomenclature to machine readable CML or InChi formats.
OrChem is built using the CDK and provides an extension to Oracle databases that adds the ability to incorporate and search chemical data.
OSRA [25] provides optical structure recognition. It takes as input an image and generates a SMILES string.
Ouch (Ouch Uses Chemical Haskell) is a minimal cheminformatics toolkit written in the functional language Haskell.
Pybel [26] provides the full functionality of Open Babel, but common routines are provided in a simplified, more ‘pythonic’ interface.
rcdk [27] provides an R interface to the CDK and working with fingerprints.
RDKit is a substantial cheminformatics toolkit written in C++ with Python, Java and C# bindings. Its capabilities include file handling, manipulation of molecular data, chemical reactions, substantial support for fingerprinting, substructure and similarity search, 3D conformer generation, property determination, force field support, shape-based alignment and screening, and integration with PyMOL, KNIME, and PostgreSQL.
RInChI provides tools for creating and manipulating reaction InChIs, a unique string for describing a reaction.
rpubchem is an R package for interfacing with the PubChem database.
rubabel [28] is similar to Pybel in that it provides a native Ruby interface to Open Babel.
The Small Molecule Subgraph Detector (SMSD) [29] is a Java library for calculating the maximum common subgraph between small molecules.
Som-it™ is an R package for creating and visualizing self-organizing maps from large datasets.
webchem is an R package for interfacing with a dozen different on-line resources for chemical data.
Standalone Programs (Table 2)
Table 2.
Standalone open source cheminformatics software.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cApp | http://www.structuralchemistry.org/pcsb | GPL | A3 | [30] |
| checkmol/matchmol | http://merian.pch.univie.ac.at/~nhaider/cheminf/cmmm.html | GPL | C3 | [31] |
| ConvertMAS | http://sourceforge.net/projects/convertmas | GPL | A3 | |
| Filter-it™ | http://silicos-it.be | LGPL | C3 | |
| Frog2 | https://github.com/tuffery/Frog2 | GPL | B2 | [32] |
| LMR | https://github.com/IanAWatson/Lilly-Medchem-Rules | GPL | B2 | [33] |
| Molpher | https://www.assembla.com/spaces/molpher/wiki | GPL | C2 | [34] |
| MoSS | http://www.borgelt.net/moss.html | MIT | A2 | [35] |
| OMG | http://sourceforge.net/projects/openmg | GPL | C1 | [36] |
| sdf2xyz2sdf | http://sdf2xyz2sdf.sourceforge.net | GPL | C2 | [37] |
| sdsorter | https://sourceforge.net/projects/sdsorter | GPL | B3 | |
| Shape | http://sourceforge.net/projects/shapega | GPL | C3 | [38] |
| Strip-it™ | http://silicos-it.be | LGPL | C3 |
cApp [30] is a Java application that provides tools for evaluating physico-chemical properties, performing similarity searches, and querying the PubChem database.
The utilities checkmol and matchmol [31] decompose and compare functional groups of input molecules.
ConvertMAS is a utility for converting between formats and merging and splitting multi- molecule files.
Filter-it™ filters a set of molecules based on their properties such as physicochemical parameters and graph-based properties.
Frog2 [32] uses a two stage Monte Carlo approach coupled with energy minimization to rapidly generate 3D conformers.
The Lilly MedChem Rules (LMR) [33] apply filters to avoid reactive and promiscuous compounds.
Molpher [34] generates a virtual chemical library that represents the chemical space between two input molecules as it consists of the path found by morphing one molecule to another.
MoSS (Molecular Subsstructure miner) [35] finds common molecular substructures and discriminative fragments within a compound library.
The Open Molecule Generator (OMG) [36] enumerates all possible chemical structures given constraints on their composition.
sdf2xyz2sdf [37] converts between SDF and TINKER XYZ files.
sdsorter provides convenient routines for manipulating, sorting, and filtering the contents of sdf molecular data files based on the embedded sd data tags.
Shape [38] employs a genetic algorithm to generate conformations of carbohydrates.
Strip-it™ is built using Open Babel and extracts molecular scaffolds.
Graphical Development Environments (Table 3)
Table 3.
Open source graphical development environments for cheminformatics.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMBIT | http://ambit.sourceforge.net | GPL | A1 | [39] |
| Bioclipse | http://www.bioclipse.net | Eclipse | B1 | [40] |
| Galaxy Tool | https://github.com/bgruening/galaxytools | Academic | A1 | [41] |
| KNIME | https://www.knime.org | GPL | A1 | [42] |
| Orange | orange.biolab.si | BSD | A1 | [43] |
| SA2 | http://sa2.sourceforge.net | GPL | A1 | [44] |
| Taverna | http://www.taverna.org.uk | LGPL | A1 | [45] |
| Weka | https://sourceforge.net/projects/weka | GPL | A1 | [46] |
Ambit [39] integrates with the CDK to provide web-based applications for chemical search and analysis and includes a tautomer generation algorithm [48].
Bioclipse [40] is a workbench, based on the Eclipse framework, for manipulating and analyzing biochemical data and databases. It integrates with the CDK and Jmol to provide cheminformatic functionality and also has modules for bioinformatics (primarly sequence analysis) and QSAR modeling.
Galaxy [41] is a web platform for exploring biomedical data and includes as a component a Chemical Toolbox that integrates a number of other cheminformatics tools to offer an array of molecular search, property calculation, clustering, and manipulation capabilities.
The Konstanz Information Miner (KNIME) is a general workflow environment that includes a number of plugins for cheminformatics, such as CDK [49] and RDKit modules, as well as bioinformatics and machine learning modules.
Orange [43] is a graphical interface for construction interactive workflows and performing data analysis and visualization.
Screening Assistant 2 (SA2) [44] is a GUI written in Java that integrates with other toolkits to help manage, analyze, and visualize libraries of compounds.
Taverna [45] is a graphical workflow editor that includes support for integrating with web services and the CDK [50].
Weka [46] is a platform for data mining and machine learning that can be adapted for cheminformatics.
4. Visualization
An essential component of any molecular modeling exercise is the ability to visualize and, sometimes, edit molecular data. Visualization software usually either deals with exclusively 2D or 3D molecular data and may be primarily intended for desktop usage (native ‘fat’ clients) or as a component embedded in a web browser. Packages designed for visualizing entire datasets are cataloged in the QSAR section (Table 10) and those with a particular emphasize on visualizing the output of quantum chemistry packages are in the Quantum Chemistry section (Table 13).
Table 10.
Open source software for visualizing QSAR models and compound datasets.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CheS-Mapper | http://ches-mapper.org | GPL | A2 | [84] |
| DataWarrior | http://www.openmolecules.org/datawarrior | GPL | A1 | [85] |
| DecoyFinder | http://urvnutrigenomica-ctns.github.io/DecoyFinder | GPL | A1 | [86] |
| Scaffold Hunter | http://scaffoldhunter.sf.net | GPL | A1 | [87] |
| Synergy Maps | https://github.com/richlewis42/synergy-maps | MIT | A2 | [88] |
| VIDEAN | https://github.com/jimenamartinez/VIDEAN | BSD | A3 | [89] |
| WCSE | http://www.cheminfo.org/wikipedia | BSD | A2 | [90] |
| WebChemViewer | http://sourceforge.net/projects/webchemviewer | BSD | C3 | [91] |
Table 13.
Open source software for quantum chemistry visualization.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCP1GUI | http://www.scd.stfc.ac.uk/research/app/40501.aspx | GPL | C3 | |
| ccwatcher | http://sourceforge.net/projects/ccwatcher | GPL | B2 | |
| Gabedit | http://gabedit.sourceforge.net | BSD | C1 | [116] |
| J-ICE | http://j-ice.sourceforge.net | GPL | A1 | [117] |
| QMForge | http://qmforge.sourceforge.net | GPL | A1 | |
| wxMacMolPlt | http://brettbode.github.io/wxmacmolplt | GPL | A1 | [118] |
2D Desktop Applications (Table 4)
Table 4.
Open source tools for 2D molecular visualization and editing on the desktop.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKchem | http://bkchem.zirael.org | GPL | C3 | |
| chemfig | https://www.ctan.org/pkg/chemfig | LaTeX | A2 | |
| Chemtool | http://ruby.chemie.uni-freiburg.de/~martin/chemtool | GPL | B3 | |
| JChemPaint | http://jchempaint.github.io | LGPL | B1 | [51] |
| LeView | http://www.pegase-biosciences.com/leview-ligand-environment-viewer | GPL | B3 | [52] |
| mol2chemfig | http://chimpsky.uwaterloo.ca/mol2chemfig | LaTeX | C3 | [53] |
| Molsketch | http://sourceforge.net/projects/molsketch | GPL | A1 | |
| SketchEl | http://sketchel.sourceforge.net | GPL | A1 |
BKChem is a 2D molecular editor written in python that uses the Tk GUI toolkit.
chemfig is a tool for embedding chemical drawings in LaTeX documents.
Chemtool is a 2D molecular editor for Linux systems that uses the GTK toolkit.
JChemPaint [51] is a Java-based 2D molecular editor built using the CDK toolkit.
LeView [52] generates 2D representations of ligand-protein interactions that highlight features such as hydrogen bonds.
mol2chemfig [53] converts SMILES files into LaTeX source code.
Molsketch is a 2D molecular editor written in C++ with the Qt toolkit that includes support for the Windows and Android operating systems.
SketchEl is a Java-based 2D molecular editor that includes support for a datasheet view for handling multi-molecule files.
3D Desktop Applications (Table 5)
Table 5.
Open source tools for 3D molecular visualization and editing on the desktop.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avogadro | http://avogadro.cc | GPL | A1 | [54] |
| BALLView | http://www.ball-project.org/ballview | LPGL | A2 | [55] |
| gMol | https://github.com/tjod/gMol/wiki | GPL | A3 | |
| Jamberoo | https://sourceforge.net/projects/jbonzer | LGPL | A3 | |
| LPMV | https://sourceforge.net/projects/lpmolecularviewer | LGPL | B3 | |
| Luscus | https://sourceforge.net/projects/luscus | Academic | A1 | [56] |
| Molecular Rift | https://github.com/Magnusnorrby/MolecularRift | GPL | A3 | [57] |
| OpenStructure | http://www.openstructure.org | LGPL | A2 | [58] |
| PLIP | https://github.com/ssalentin/plip | Apache | A2 | [59] |
| PyMOL | https://sourceforge.net/projects/pymol | Python | A1 | |
| RasTop | https://sourceforge.net/projects/rastop | GPL | C1 | |
| OpenRasMol | https://sourceforge.net/projects/openrasmol | GPL | C1 | |
| SPADE | http://www.spadeweb.org | BSD | C3 | [60] |
| QuteMol | http://qutemol.sourceforge.net | GPL | C1 | [61] |
Avogadro [54] is a 3D molecular viewer and editor with a modular plugin architecture with both Python and C++ bindings that includes interactive structure optimization for real-time editing.
BALLView [55] provides interactive 3D visualizations as part of the BALL [8] cheminformatics toolkit.
gMol provides basic interactive 3D visualizations of molecular data readable by Open Babel.
Jamberoo provides a basic Java-based 3D molecular viewer and editor.
LP Molecular Viewer is an ActiveX/ATL control for embedding interactive 3D representations of molecular data in Microsoft products.
Luscus [56] is a 3D viewer and editor that is designed with a focus on electronic structure information.
Molecular Rift [57] integrates with the Oculus Rift virtual reality headset to provide immersive visualization of 3D molecular data.
OpenStructure [58] is a computational structural biology framework that provides a 3D viewer for manipulating structural information and includes an interactive Python shell.
PLIP (Protein-Ligand Interaction Profiler) [59] runs as a web application and analyzes and visualizes protein-ligand interactions in 3D.
PyMOL is a substantial 3D molecular viewer that includes a full Python interface to support scripting and plugin development.
RasTop and OpenRasMol are based off the venerable RasMol software and provide basic 3D visualization.
SPADE (Structural Proteomics Application Development Environment) [60] is a graphical Python interface for structural informatics.
QuteMol [61] provides high-quality, visually engaging renderings of 3D molecular data.
Web-Based Visualization (Table 6)
Table 6.
Open source tools for web-based molecular visualization.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Dmol.js | 3dmol.csb.pitt.edu | BSD | A1 | [62] |
| CH5M3D | https://sourceforge.net/projects/ch5m3d | GPL | C1 | [63] |
| Chemozart | https://chemozart.com | Apache | A1 | [64] |
| CWC | https://web.chemdoodle.com | GPL | A1 | [65] |
| JSME | http://peter-ertl.com/jsme | BSD | A1 | [66] |
| Jmol | http://jmol.sourceforge.net | LGPL | A1 | [67] |
| JSmol | https://sourceforge.net/projects/jsmol | LGPL | A1 | [68] |
| NGL | http://proteinformatics.charite.de/ngl | MIT | A1 | [69] |
| PV | https://biasmv.github.io/pv | MIT | A1 | [70] |
3Dmol.js [62] is a JavaScript library that provides WebGL-accelerated interactive 3D visualizations of molecular structures and surfaces.
CH5M3D [63] uses JavaScript and HTML5 to provide visualization and editing of 3D structures of small molecules.
Chemozart [64] is a WebGL-based web application for 3D editing of small molecules.
CWC (ChemDoodle Web Components) [65] provides a suite of web-based visualizers and editors for 2D and 3D molecular data.
JSME [66] is a pure JavaScript 2D molecular editor that can export and import SMILES data.
Jmol [67] is a Java applet for interactive 3D visualization that provides significant cheminformatics support and a custom scripting language.
JSmol [68] is the JavaScript port of Jmol and does not require the Java plugin to run.
NGL [69] is a WebGL-accelerated viewer and JavaScript library for interactive 3D visualization of macromolecules.
PV (Protein Viewer) [70] is a WebGL-accelerated viewer for interactive 3D visualization of macromolecules with a functional-style API.
5. QSAR/ADMET Modeling
Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) approaches find relationships between the chemical structures of a series of compounds (or structural-related properties) and a biological activity [71], including ADMET properties (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity). QSAR methods calculate relevant molecular descriptors, build informative models using these descriptors and then apply the models. Models and datasets may also be visualized to aid in model development and understanding of compound libraries. Note that most of the cheminformatics toolkits shown in Table 1 also are capable of generating descriptors (and are often used as libraries by QSAR modeling software).
Descriptor Calculators (Table 7)
Table 7.
Open source software for computing molecular descriptors.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4D-FAP | http://www.ra.cs.uni-tuebingen.de/software/4DFAP | LGPL | C2 | [72] |
| BlueDesc | http://www.ra.cs.uni-tuebingen.de/software/bluedesc | GPL | C3 | |
| MolSig | http://molsig.sourceforge.net | GPL | C2 | [73] |
| PaDEL-descriptor | http://www.yapcwsoft.com/dd/padeldescriptor | Public Domain | C1 | [74] |
| TMACC | http://comp.chem.nottingham.ac.uk/download/tmacc | GPL | C2 | [75] |
4D Flexible Atom-Pair Kernel (4D FAP) computes a ‘4D’ similarity measure from the molecular graphs of an ensemble of conformations which can be incorporated into QSAR models.
The BlueDesc descriptor calculator is a command-line tool that converts an MDL SD file into ARFF and LIBSVM format using CDK and JOELib2 for machine learning and data mining purposes. It computes 174 descriptors taken from both libraries.
MolSig [73] computes molecular graph descriptors that include stereochemistry information.
PaDEL-Descriptor [74] calculates molecular descriptors and fingerprints. It computes 1875 descriptors (1444 1D, 2D descriptors and 431 3D descriptors) and 12 types of finger-prints.
Topological maximum cross correlation descriptors (TMACC) [75] generates 2D autocorrelation descriptors that are low dimensional and interpretable and appropriate for QSAR modeling.
Model Building (Table 8)
Table 8.
Open source software for building QSAR models.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZOrange | https://github.com/AZCompTox/AZOrange | LGPL | C2 | [76] |
| Bioalerts | https://github.com/isidroc/bioalerts | GPL | A3 | [77] |
| camb | https://github.com/cambDI | GPL | B2 | [78] |
| eTOXlab | https://github.com/manuelpastor/eTOXlab | GPL | B3 | [79] |
| Open3DGRID | http://open3dgrid.sourceforge.net | GPL | B1 | |
| Open3DQSAR | http://open3dqsar.sourceforge.net | GPL | B1 | [80] |
| QSAR-tools | https://github.com/dkoes/qsar-tools | BSD | A3 |
AZOrange [76] is a machine learning package that supports QSAR model building in a full work flow from descriptor computation to automated model building, validation and selection. It promotes model accuracy by using several high performance machine learning algorithms for efficient data set specific selection of the statistical approach.
Bioalerts [77] uses RDKit fingerprints to create models from discrete (e.g., toxic/non-toxic) and continuous data. It includes the capability to visualize problematic functional groups.
Chemistry aware model builder (camb) [78] is an R package for the generation of quantitative models. Its capabilities include descriptor calculation (including 905 two-dimensional and 14 fingerprint type descriptors for small molecules, 13 whole protein sequence descriptors, and 8 types of amino acid descriptors), model generation, ensemble modeling, and visualization.
eTOXLab [79] provides a portable modeling framework embedded in a self-contained virtual machine for easy deployment.
Open3DGrid and Open3DQSAR [80] are a suite of related tools that build 3D QSAR models. Open3DGrid generates molecular interaction fields (MIFs) in a variety of formats, and Open3DQSAR builds predictive models from the MIFs of aligned molecules. Calculations can be visualized in real time in PyMOL.
QSAR-tools is a set of Python scripts that use RDKit to build linear QSAR models from 2D chemical data.
Model Application (Table 9)
Table 9.
Open source software that applies a QSAR model.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMARTCyp | http://www.farma.ku.dk/smartcyp | LGPL | C1 | [81] |
| Toxtree | http://toxtree.sourceforge.net | GPL | A1 | [82] |
| UG-RNN | http://cdb.ics.uci.edu/cgibin/tools/AquaSolWeb.py | Apache | C1 | [83] |
SMARTCyp [92] is a QSAR model that predicts the sites of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of drug-like molecules directly from the 2D structure of a molecule using fragment-based energy rules.
Toxtree [82] is a Java GUI application for estimating the “toxic hazard” of molecules using a variety of toxicity prediction modules, such as oral toxicity, skin and eye irritation prediction, covalent protein binding and DNA binding, Cytochrome P450-mediated drug metabolism (using SMARTCyp) and more.
UG-RNN/AquaSol [83] is an undirected graph recursive neural network that has been trained to predict aqueous solubility from molecular graphs.
Visualization (Table 10)
CheS-Mapper (chemical space mapper) [93, 84]. is a 3D-viewer for small compounds in chemical datasets. It embeds a dataset into 3D space by performing dimensionality reduction on the properties of the compounds.
DataWarrior [85] is a data visualization and analysis tool for chemical data with a rich set of available property calculations, similarity metrics, modeling capabilities, and data set representations.
DecoyFinder [86] provides a GUI for selecting a set of decoy compounds from a large library that are appropriate matches to a given set of actives.
Scaffold Hunter [87] provides a Java-based GUI for visualizing the relationship between compounds in a dataset.
Synergy Maps [88] visualizes synergistic activity extracted from screens of drug combinations.
VIDEAN (visual and interactive descriptor analysis) [89] is a visual tool for iteratively choosing a subset of descriptors appropriate for predicting a target property with the aid of statistical methods.
WCSE (Wikipedia chemical structure explorer) [90] runs as a web application and provides a 2D interface for visualizing and searching for 2D molecules.
WebChemViewer [91] is an online viewer for viewing and interacting with lists of compounds and their associated data.
6. Quantum Chemistry
Quantum mechanics (QM) is increasingly accessible and relevant to molecular modeling and in silico drug design [94]. Quantum chemistry models molecules at the level of their wave function and offers enhanced accuracy and detail compared to classical models at a substantial increase in computation time. Corresponding to the large diversity of solution methods for Schrödinger’s equation, there are many software packages for ab initio quantum chemistry, as well as programs for interpreting and visualizing the results of these calculations.
Ab initio Calcuation (Table 11)
Table 11.
Open source quantum chemistry software for performing ab initio calculations.
ABINIT [95] can calculate the total energy, charge density and electronic structure of molecules and periodic solids with density functional theory (DFT) and Many-Body Perturbation Theory (MBPT), using pseudopotentials and a planewave or wavelet basis. ABINIT also can optimize the geometry, perform molecular dynamics simulations, or generate dynamical matrices, Born effective charges, and dielectric tensors and many more properties.
ACES [96] performs calculations such as single point energy calculations, analytical gradients, and analytical Hessians, and is highly parallelized, including support for GPU computing. A focus of ACES is the use of MBPT and the coupled-cluster approximation to reliable treat electron correlation.
BigDFT [119, 120, 97] performs ab initio calculations using Daubechies wavelets and has the capability to use a linear scaling method. Periodic systems, surfaces and isolated systems can be simulated with the proper boundary conditions. It is included as part of ABINIT.
CP2K [98] performs simulations of solid state, liquid, molecular and biological systems. Its particular focus is massively parallel and linear scaling electronic structure methods and state-of-the-art ab-initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) simulations. It is optimized for the mixed Gaussian and Plane-Waves method using pseudopotentials and can run on parallel and on GPUs.
Dacapo is a total energy program that uses density functional theory. It can do molecular dynamics/structural relaxation while solving the Schrödinger equations. It has support for parallel execution and is used through the Atomic Simulation Environment (ASE) [99]
ErgoSCM [100] is a quantum chemistry program for large-scale self-consistent field calculations. It performs electronic structure calculations using Hartree-Fock and Kohn-Sham density functional theory and achieves linear scaling for both CPU usage and memory utilization.
ERKALE [101] is designed to compute X-ray properties, such as ground-state electron momentum densities and Compton profiles, and core (x-ray absorption and x-ray Raman scattering) and valence electron excitation spectra of atoms and molecules.
GPAW [102] is a DFT code that uses the projector-augmented wave (PAW) technique [121, 122] and integrates with the atomic simulation environment (ASE) [99].
HORTON (Helpful Open-source Research TOol for N-fermion systems) has as a primary design goal ease of extensibility for researching new methods in ab initio electronic structure theory.
JANPA [103] computes natural atomic orbitals from a reduced one-particle density matrix.
MPQC (massively parallel quantum chemistry program) [104] offers many features including closed shell, unrestricted and general restricted open shell Hartree-Fock energies and gradients, closed shell, unrestricted and general restricted open shell density functional theory energies and gradients, second order open shell perturbation theory and Z-averaged perturbation theory energies.
NWChem [105] provides a full suite of methods for modeling both classical and QM systems. Its capabilities include molecular electronic structure, QM/MM, pseudopotential plane-wave electronic structure, and molecular dynamics and is designed to scale across hundreds of processors.
Octopus pervorms ab initio calculations using time-dependent DFT (TDDFT) and pseudopotentials. Included in the project is libxc [123] which is a standalone library of exchange-correlation functionals for DFT (released under the LGPL).
OpenMX (Open source package for material eXplorer) [107] is designed for nano-scale material simulations based on DFT, norm-conserving pseudopotentials, and pseudo-atomic localized basis functions. OpenMX is capable of performing calculations of physical properties such as magnetic, dielectric, and electric transport properties and is optimized for large-scale parallelism.
Psi4 [108] is a suite of ab initio quantum chemistry programs that supports a wide range of computations (e.g., Hartree–Fock, MP2, coupled-cluster) and general procedures such as geometry optimization and vibrational frequency analysis with more than 2500 basis functions.
PyQuante is a collection of modules, mostly written in Python, for performing Hartree-Fock and DFT calculations with a focus on providing a well-engineered set of tools. A new version is under development (https://github.com/rpmuller/pyquante2).
PySCF is also written primarily in Python and supports several popular methods such as Hartree-Fock, DFT, and MP2. It also has easy of use and extension as primary design goals.
QMCPACK [109] is a many-body ab initio quantum Monte Carlo implementation for computing electronic structure properties of molecular, quasi-2D and solid-state systems. The standard file formats utilized for input and output are in XML and HDF5.
QUANTUM ESPRESSO [110] is designed for modeling at the nanoscale using DFT, plane waves, and pseudopotentials and its capabilities include ground-state calculations, structural optimization, transition states and minimum energy paths, ab initio molecular dynamics, DFT perturbation theory, spectroscopic properties, and quantum transport.
RMG [111] is a DFT code that uses real space grids to provide high scalability across thousands of processors and GPU acceleration for both structural relaxation and molecular dynamics.
Siam Quantum (SQ) is optimized for parallel computation and its capabilities include the calculation of Hartree-Fock and MP2 energies, minimum energy crossing point calculations, geometry optimization, population analysis, and quantum molecular dynamics.
Helper Applications (Table 12)
Table 12.
Open source software for analyzing the results of quantum chemistry calculations.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FragIt | https://github.com/FragIt | GPL | A2 | [112] |
| cclib | https://github.com/cclib/cclib | LGPL | A1 | [113] |
| GaussSum | http://sourceforge.net/projects/gausssum | GPL | A1 | [113] |
| Geac | https://github.com/LaTruelle/Geac | GPL | A3 | |
| Nancy_EX | http://sourceforge.net/projects/nancyex | GPL | A2 | [114] |
| orbkit | http://orbkit.sourceforge.net | GPL | A2 | [115] |
FragIt [112] generates fragments of large molecules to use as input files in quantum chemistry programs that support fragment based methods.
cclib [113] provides a consistent interface for parsing and interpreting the results of a number of quantum chemistry packages.
GaussSum [113] uses cclib to extract useful information from the results of quantum chemistry programs (ADF, GAMESS, Gaussian, Jaguar) including monitoring the progress of geometry optimization, the UV/IR/Raman spectra, molecular orbital (MO) levels and MO contributions.
Geac (Gaussian ESI Automated Creator) extracts data from Gaussian log files.
Nancy_EX [114] post-processes Gaussian output and analyzes excited states including natural transition orbitals, detachment and attachment density matrices, and charge-transfer descriptors.
orbkit [115] is a post-processing tool for the results of quantum chemistry programs. It has native support for a number of programs (MOLPRO, TURBOMOLE, GAMESS-US, PROAIMS/AIMPAC, Gaussian) and additionally interfaces with cclib for additional file format support. It can extract grid-based quantities such as molecular orbitals and electron density, as well as Muliken population charges and other properties.
Visualization (Table 13)
CCP1GUI provides a graphical user interface to various computational chemistry codes with an emphasis on integration with the GAMESS-UK quantum chemistry program.
ccwatcher provides a graphical interface for the monitoring of computational chemistry programs.
Gabedit [116] is a graphical user interface to a large number of quantum chemistry packages. It can create input files and graphically visualize calculation results.
J-ICE [117] is a Jmol-based viewer for crystallographic and electronic properties that can be deployed as a Java applet embedded in a web browser.
QMForge provides a graphical user interface for analyzing and visualizing results of quantum chemistry DFT calculations (Gaussian, ADF, GAMESS, Jaguar, NWChem, ORCA, QChem). Analyses include a number of population analyses, Mayer’s bond order, charge decomposition, and fragment analysis.
wxMacMolPlt [118] is a multi-platform GUI for setting up and visualizing input and output files for the GAMESS quantum chemistry software.
7. Ligand Dynamics and Free Energy Calculations
Simulation based approaches for analyzing ligand-protein interactions have the potential to fully account for the dynamics of the ligand, protein, and water system. Molecular dynamics simulation is a powerful tool for computing free energies as long as the system can be properly parameterized and the simulation code adapted and analyzed to implement the desired free energy method.
Simulation Software (Table 14)
Table 14.
Open source software for performing molecular simulations.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campari | http://campari.sourceforge.net | GPL | B1 | [124] |
| DL POLY Classic | http://www.ccp5.ac.uk/DL_POLY_CLASSIC/ | BSD | C3 | [125] |
| GALAMOST | http://galamost.ciac.jl.cn | GPL | A2 | [126] |
| Gromacs | http://www.gromacs.org | LGPL | A1 | [127] |
| Iphigenie | https://sourceforge.net/projects/iphigenie | GPL | A2 | [128] |
| LAMMPS | http://lammps.sandia.gov | GPL | A1 | [129] |
| MDynaMix | http://www.fos.su.se/~sasha/mdynamix | GPL | A1 | [130] |
| MMTK | http://dirac.cnrs-orleans.fr/MMTK | CeCILL | C1 | [131] |
| OpenMM | https://simtk.org/home/openmm | GPL/MIT | A1 | [132] |
| ProtoMol | http://protomol.sourceforge.net | GPL | C1 | [133] |
| ProtoMS | http://www.essexgroup.soton.ac.uk/ProtoMS | GPL | A2 | [134] |
| Sire | http://siremol.org | GPL | C2 | |
| WESTPA | https://westpa.github.io/westpa | GPL | A2 | [135] |
| yank | http://getyank.org | LGPL | A2 |
Campari [124] conducts flexible Monte Carlo sampling of biopolymers in internal coordinate space, with built-in analysis routines to estimate structural properties and support for replica exchange and Wang-Landau sampling.
DL_POLY Classic [125] is a general purpose molecular dynamics simulation package that can run in parallel and includes a Java graphical user interface.
GALAMOST (GPU accelerated large-scale molecular simulation toolkit) [126] uses GPU computing to perform traditional molecular dynamics with a special focus on polymeric systems at mesoscopic scales.
Gromacs [127] is a complete and well-established package for molecular dynamics simulations that provides high performance on both CPUs and GPUs. It can be used for free energy and QM/MM calculations and includes a comprehensive set of analysis tools.
Iphigenie [128] is a molecular mechanics program that features polarizable force fields, the HADES reaction field, and QM/(P)MM hybrid simulations.
LAMMPS (Large-scale Atomic/Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator) [129] is a highly modular classical molecular dynamics simulator that includes a diverse array of energy potentials and integrators.
MDynaMix [130] is a basic general purpose molecular dynamics package.
MMTK (Molecular Modelling Toolkit) [131] is a library written in Python (with some time critical parts written in C) for constructing and simulating molecular systems. Its capabilities include molecular dynamics, energy minimization, and normal mode analysis and it is well-suited for methods development.
OpenMM [132] is a substantial toolkit for high performance molecular dynamics simulations that includes support for GPU acceleration.
ProtoMol [133], and the associated MDLab Python bindings [151], provides an object-oriented framework for prototyping algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations and includes an interface to OpenMM.
ProtoMS [134] is a Monte Carlo biomolecular simulation program which can be used to calculate relative and absolute free energies and water placement with the GCMC and JAWS methodologies.
Sire is a collection of modular libraries intended to facilitate fast prototyping and the development of new algorithms for molecular simulation and molecular design. It has apps for system setup, simulation, and analysis.
WESTPA (The Weighted Ensemble Simulation Toolkit with Parallelization and Analysis) [135] is a library for performing weighted ensemble simulations to sample rare events and compute rigorous kinetics.
yank is built off of OpenMM and provides a Python interface for performing alchemical free energy calculations.
Simulation Setup and Analysis (Table 15)
Table 15.
Open source software for setting up and analyzing molecular simulations.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AmberTools | http://ambermd.org | GPL | A1 | [136] |
| LOOS | http://loos.sourceforge.net | GPL | A1 | [137] |
| lsfitpar | http://mackerell.umaryland.edu/~kenno/lsfitpar | GPL | A2 | [138] |
| MDAnalysis | http://mdanalysis.org | GPL | A1 | [139] |
| MDTraj | mdtraj.org | LGPL | A1 | [140] |
| MEMBPLUGIN | https://sourceforge.net/projects/membplugin | GPL | C1 | [141] |
| MEPSA | http://bioweb.cbm.uam.es/software/MEPSA | GPL | A3 | [142] |
| MSMBuilder | http://msmbuilder.org | LGPL | A1 | [143] |
| packmol | http://www.ime.unicamp.br/~martinez/packmol | GPL | A1 | [144] |
| PDB2PQR | http://www.poissonboltzmann.org | BSD | A1 | [145] |
| PLUMED | http://www.plumed.org | LGPL | A1 | [146] |
| ProDy | http://prody.csb.pitt.edu | MIT | A1 | [147] |
| Pteros | http://pteros.sourceforge.net | Artistic | B2 | [148] |
| PyEMMA | http://www.emma-project.org | LGPL | A1 | [149] |
| PyRED | http://upjv.q4md-forcefieldtools.org | GPL | C1 | [150] |
| PYTRAJ | https://github.com/Amber-MD/pytraj | GPL | A1 | |
| simpletraj | https://github.com/arose/simpletraj | GPL | A2 | |
| WHAM | http://membrane.urmc.rochester.edu/content/wham | BSD | C1 |
AmberTools [136] is an open source component of the non-open source Amber package and provides a large suite of analysis programs. As of Amber15, AmberTools includes the lower performance, but readily extendable, sander molecular dynamics code.
LOOS (Lightweight Object-Oriented Structure library) [137] is a C++ library (with Python bindings) for reading and analyzing molecular dynamics trajectories that also includes a number of standalone programs.
lsfitpar [138] derives bonded parameters for Class I force fields by performing a robust fit to potential energy scans provided by the user.
MDAnalysis [139] is a Python library for reading and analyzing molecular dynamics simulations with some time critical sections written in C.
MDTraj [140] provides high-performance reading, writing, and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectories in a diversity of formats from a Python interface.
MEMBPLUGIN [141] analyzes molecular dynamics simulations of lipid bilayers and is most commonly used as a VMD plugin.
MEPSA (Minimum Energy Pathway Analysis) [142] provides tools for analyzing energy landscapes and pathways.
MSMBuilder [143] is an application and Python library for building Markov models of high-dimensional trajectory data.
packmol [144] is a utility for setting molecular systems by realistically packing molecules to obey a variety of constraints and can create solvent mixtures and lipid bilayers.
PDB2PQR [145] prepares structures for electrostatics calculations by adding hydrogens, calculating sidechain pKa, adding missing heavy atoms, and assigning force field-dependent parameters; users can specify an ambient pH.
PLUMED [146] interfaces with an assortment of molecular dynamics software packages to provide a unified interface for performing free energy calculations using methods such as metadynamics, umbrella sampling and steered MD (Jarzynski).
ProDy [147] is a Python toolkit for analyzing proteins and includes facilities for trajectory analysis and druggability predictions using simulations of molecular probes [152].
Pteros [148] is a C++ library (with Python bindings) for reading and analyzing molecular dynamics trajectories.
PyEMMA [149] is a Python library for performing kinetic and thermodynamic analyses of molecular dynamics simulations using Markov models.
PyRED [150] generates RESP and ESP charges for the AMBER, CHARMM, OPLS, and Glycam and force fields.
PYTRAJ is a Python interface to the cpptraj tool of AmberTools.
simpletraj is a lightweight Python library for parsing molecular dynamics trajectories.
WHAM (Weighted Histogram Analysis Method) calculates the potential of mean force (PMF) from umbrella sampling simulations.
8. Virtual Screening and Ligand Design
The goal of virtual, or in silico, screening is to computationally identify small molecules in a compound library that are active against a given target. Virtual screening methods usually adopt either a ligand-based approach, where properties of known active compounds are used to identify additional compounds, or a structure-based approach, where the interactions between putative ligands and the receptor structure are used. Tools for chemical similarity, which can be used for ligand-based screening, are cataloged in the Cheminformatics section.
In contrast to virtual screening, which evaluates predetermined compounds, de novo ligand design attempts to create a molecule ‘from scratch’ that binds to a protein. Methods differ in how they specify the objective to optimize (e.g., docking score to a protein) and how candidate molecules are created, where a key challenge is maintaining synthetic accessibility.
Ligand-Based (Table 16)
Table 16.
Open source software for ligand-based virtual screening.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACPC | https://github.com/UnixJunkie/ACPC | BSD | B2 | [153] |
| Align-it | http://silicos-it.be | LGPL | C3 | |
| Open3DALIGN | http://open3dalign.sourceforge.net | GPL | B2 | [37] |
| PAPER | https://simtk.org/home/paper | GPL | C2 | [154] |
| Pharmer | http://pharmer.sf.net | GPL | B1 | [155] |
| Pharmit | http://pharmit.sf.net | GPL | A3 | [156] |
| Shape-it | http://silicos-it.be | LGPL | C3 | |
| USRCAT | https://bitbucket.org/aschreyer/usrcat | MIT | C2 | [157] |
ACPC (AutoCorrelation of Partial Charges) [153] computes ligand similarity based on a rotation and translation invariant electrostatic descriptor.
Align-it™ is a successor of Pharao [158] and aligns and scores 3D representations of molecules based on their pharmacophore features. It includes a plugin for integration with PyMOL.
Open3DALIGN [37] performs unsupervised rigid-body molecular alignment.
PAPER [154] performs GPU accelerated alignment of molecular shapes using Gaussian overlays.
Pharmer [155] uses efficient data structures to rapidly screen large libraries for ligand conformations that match a pharmacophore.
Pharmit [156] is a successor of Pharmer that also incorporates shape matching and energy minimization (if a receptor structure is available) as part of the screen. It is primarily intended to be used as a backend to a web service.
Shape-it™ uses Gaussian volumes to align and score molecular shapes.
USRCAT [157] performs “ultra-fast shape recognition” with the addition of pharmacophoric information to rapidly screen compound libraries for similar molecules.
Docking and Scoring (Table 17)
Table 17.
Open source software for molecular docking and scoring.
ADplugin is a plugin for PyMOL for interfacing with AutoDock and AutoDock Vina.
APBS [159] performs solvation free energy calculations using the Poisson-Boltzmann implicit solvent method.
AutoDock [160] is an automated docking program that uses a physics-based semiempirical scoring function [182] mapped to atom type grids to evaluate poses and a genetic algorithm to explore the conformational space. It includes the ability to incorporate sidechain flexibility and covalent docking.
AutoDock Vina [161] is an entirely separate code base and approach from Autodock that was developed with a focus on runtime performance and ease of system setup. It uses a fully empirical scoring function and an iterated local search global optimizer to produce docked poses. It includes support for multi-threading and flexible sidechains.
Clusterizer-DockAccessor [162] are tools for accessing the quality of docking protocols. It interfaces with a number of open source and free tools.
DockoMatic [163] provides a graphical user interface for setting up and analyzing AutoDock and AutoDock Vina docking jobs, including when run on a cluster. It also includes the ability to run inverse virtual screens (find proteins that bind a given ligand) and support for homology model construction.
DOVIS [164] is an extension of AutoDock 4.0 that provides more efficient parallelization of large virtual screening jobs.
idock [165] is a multi-threaded docking program that includes support for the AutoDock Vina scoring function and a random forest scoring function. I can output per-atom free energy information for hotspot detection.
MOLA [166] is a pre-packaged distribution of AutoDock and AutoDock Vina for deployment on multi-platform computing clusters.
NNScore [167] uses a neural network model to score protein-ligand poses.
Paradocks [168] is a parallelized docking program that includes a number of population-based metaheuristics, such as particle swarm optimization, for exploring the space of potential poses.
PyRx [169] is a visual interface for AutoDock and AutoDock Vina that simplifies setting up and analyzing docking workflows. Its future as an open-source solution is in doubt due to a recent shift to commercialization.
rDock [170] is designed for docking against proteins or nucleic acids and can incorporate user-specified constraints. It uses an empirical scoring function that includes solvent accessible surface area terms. A combination of genetic algorithms, Monte Carlo, and simplex minimization is used to explore the conformational space. Distinct scoring functions are provided for docking to proteins and nucleic acids.
RF-Score [171, 183] uses a random forest classifier to score protein-ligand poses.
smina [172] is a fork of AutoDock Vina designed to better support energy minimization and custom scoring function development (scoring function terms and atom type properties can be specified using a run-time configuration file). It also simplifies the process of setting up a docking run with flexible sidechains.
VHELIBS (Validation HElper for LIgands and Binding Sites) [173] assists the non-crystallographer in validating ligand geometries with respect to electron density maps.
VinaLC [174] is a fork of AutoDock Vina designed to run on a cluster of multiprocessor machines.
VinaMPI [175] is a wrapper for AutoDock Vina that uses OpenMPI to run large-scale virtual screens on a computing cluster.
Zodiac [176] is a visual interface for structure-based drug design that includes support for haptic feedback.
Pocket Detection (Table 18)
Table 18.
Open source software for pocket detection.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eFindSite | http://brylinski.cct.lsu.edu/efindsite | GPL | C2 | [177] |
| fpocket | http://fpocket.sourceforge.net | GPL | C1 | [178] |
| KVFinder | http://lnbio.cnpem.br/facilities/bioinformatics/software-2 | GPL | B1 | [179] |
| mcvol | http://www.bisb.uni-bayreuth.de/data/mcvol/mcvol.html | GPL | C2 | [180] |
| PAPCA | https://sourceforge.net/projects/papca | BSD | C2 | |
| PCS | https://sourceforge.net/projects/cavity-search | GPL | C2 | |
| PocketPicker | http://gecco.org.chemie.uni-frankfurt.de/pocketpicker | BSD | C1 | [181] |
| POVME | https://sourceforge.net/projects/povme | GPL | C1 | [91] |
eFindSite [177] using homology modeling and machine learning predicts ligand binding sites in a protein structure.
fpocket [178] detects and delineates protein cavities using Voronoi tessellation and is able to process molecular dynamics simulations.
KVFinder [179] is a PyMOL plugin for identifying and characterizing pockets.
mcvol [180] calculates protein volumes and identifying cavities using a Monte Carlo algorithm.
PAPCA (PocketAnalyzerPCA) is a pocket detection utility designed to analyze ensembles of protein conformations.
PCS (Pocket Cavity Search) measures the volume of internal cavities and evaluates the environment of ionizable residues.
PocketPicker [181] is a PyMOL plugin that automatically identifies potential ligand binding sites using a grid-based shape descriptor.
POVME (POcket Volume MEasurer) [91] is a tool for measuring and characterizing pocket volumes that includes a graphical user interface.
Ligand Design
AutoClickChem [184] performs in silico click chemistry to generate large libraries of synthetically accessible compounds.
AutoGrow [185] uses a genetic algorithm to explore the space of reactants and reactions accessible via AutoClickChem and identifies compounds that dock well using AutoDock Vina.
igrow, like AutoGrow, uses a genetic algorithm but transforms ligands using branch exchange and uses idock as the underlying docking evaluation protocol.
OpenGrowth [186] assembles candidate ligands by connecting small organic fragments in the active site of proteins. It includes a graphical user interface.
9. Discussion
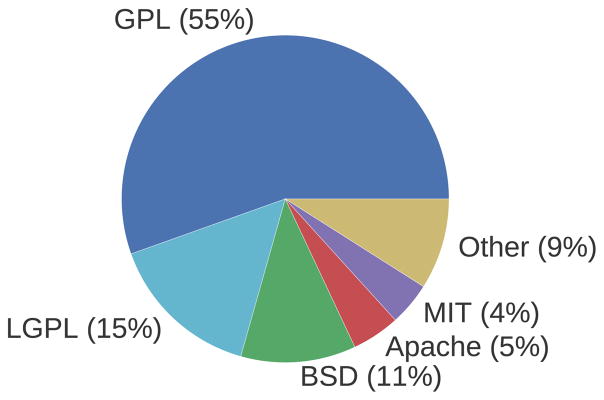
We have cataloged 208 open-source packages for molecular modeling that provide a wide range of capabilities. As shown in Figure 1, the most popular license (55%) is some variant of the copyleft GNU Public License, which ensures that derivative works remain open source. Interestingly 78% of the packages cataloged have a corresponding citeable publication which suggests that much of the software originates from academia. The distribution of average citations generated a year (as reported by Google Scholar) for the citeable publications is shown in Figure 3. A significant majority (84%) of publications generate at least one citation a year, a quarter generate at least 10 citations, and 8% generate more than 100 citations a year on average.
Figure 1.
Distribution of open source licenses used in cataloged software packages.
Figure 3.
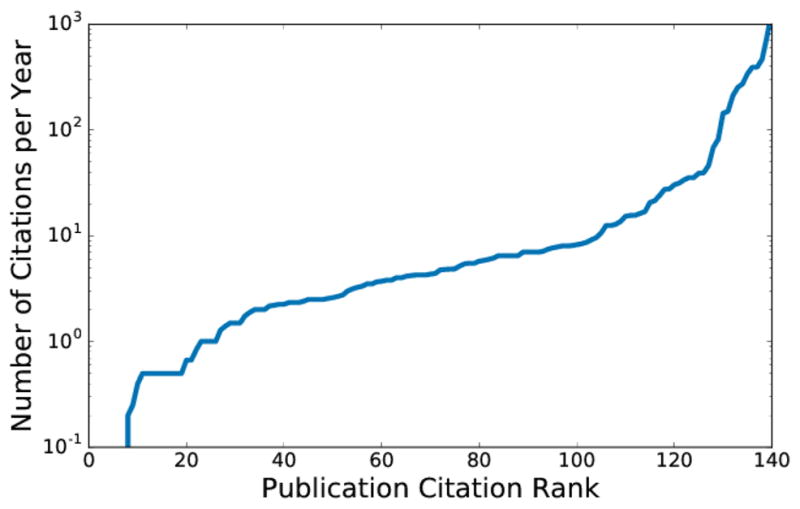
Distribution of citations as reported by Google Scholar generated on average every year by those software packages with citeable publications.
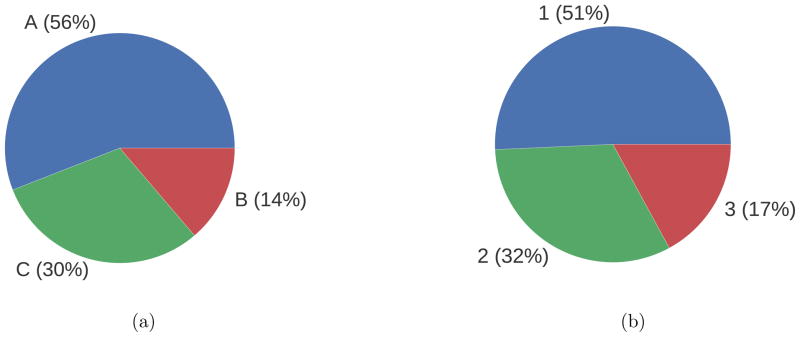
A substantial portion of the packages cataloged are under active development and see significant usage, as shown in Figure 2. We rated 56% of the packages as ‘A’ level development, meaning major features or releases were made within the last 18 months, and 51% see substantial usage (rank 1). There are a number of projects (30%) where development has apparently ceased (no changes within the last 18 months). Note that our methodology for identifying packages ignores cases where software is no longer available, this is an underestimate. However, although we did find instances where an open source package was referenced in a paper but was no longer available, we did not find this to be a common occurrence. Most packages, even those that have remained unchanged for a decade, see some usage. In fact, a number of packages (23), still see significant usage despite having received no development for the past 18 months. This underlies the importance of releasing source code through a third-party site such as SourceForge or GitHub as it ensures the continued existence of a project.
Figure 2.
Activity distributions of cataloged software packages. (a) Distribution of development activity. (b) Distribution of user activity.
A major advantage of open source is that in cases where a popular project is not being actively developed (e.g. AutoDock Vina [161]) new projects can fork the source code and continue development (e.g. smina [172]). However, a potential problem area with open source development is the lack of central coordination and efficient pooling of resources. For example, there are several forks of AutoDock Vina that improve it’s performance on computing clusters and there are an array of tools in several categories that effiectively perform the same task. This underscores the importance of efforts like Blue Obelisk [187, 188] and Open Chemistry (http://www.openchemistry.org) which foster collaboration among open source cheminformatics projects.
It is clear that open source software plays an important role in the scientific community and is a vibrant sub-community of its own with a wide assortment of projects under development and in widespread use. The open source software packages cataloged here provide launching points for the development of new tools for enabling further scientific discovery.
Table 19.
Open source software for ligand design.
| Name | URL | License | Activity | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AutoClickChem | https://sourceforge.net/projects/autoclickchem | GPL | C2 | [184] |
| AutoGrow | http://autogrow.ucsd.edu | GPL | A1 | [185] |
| igrow | https://github.com/HongjianLi/igrow | Apache | A3 | |
| OpenGrowth | http://opengrowth.sf.net | GPL | A1 | [186] |
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Twitter users @DrBostrom, @KirkD CO, @wojcikowskim, @egonwillighagen, @macinchem, @rguha, @ghutchis, @janhjensen, @rmcgibbo, @synapticarbors, and @khinsen for their helpful feedback on a draft of this manuscript. This work was supported by the National Institute of Health [R01GM108340].
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Krylov AI, Herbert JM, Furche F, Head-Gordon M, Knowles PJ, Lindh R, Manby FR, Pulay P, Skylaris CK, Werner HJ. What Is the Price of Open-Source Software? J Phys Chem Lett. 2015;6(14):2751–2754. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01258. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gezelter JD. Open Source and Open Data Should Be Standard Practices. J Phys Chem Lett. 2015;6(7):1168–1169. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b00285. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b00285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jacob CR. How Open Is Commercial Scientific Software? J Phys Chem Lett. 2016;7(2):351–353. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b02609. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b02609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Villoutreix BO, Lagorce D, Labbé CM, Sperandio O, Miteva MA. One hundred thousand mouse clicks down the road: selected online resources supporting drug discovery collected over a decade. Drug Discovery Today. 2013;18(21–22):1081–1089. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.06.013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2013.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Leach AR, Gillet VJ. An Introduction To Chemoinformatics. Springer Science + Business Media; 2007. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6291-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gasteiger J. Chemoinformatics. Wiley-Blackwell; 2003. Introduction; pp. 1–13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/3527601643.ch1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ebejer J-P, Morris GM, Deane CM. Freely Available Conformer Generation Methods: How Good Are They? Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2012;52(5):1146–1158. doi: 10.1021/ci2004658. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci2004658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hildebrandt A, Dehof A, Rurainski A, Bertsch A, Schumann M, Toussaint NC, Moll A, Stöckel D, Nickels S, Mueller SC, Lenhof H-P, Kohlbacher O. BALL - biochemical algorithms library 1.3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11(1):531. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-531. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Steinbeck C, Hoppe C, Kuhn S, Floris M, Guha R, Willighagen E. Recent Developments of the Chemistry Development Kit (CDK) - An Open-Source Java Library for Chemo- and Bioinformatics. CPD. 2006;12(17):2111–2120. doi: 10.2174/138161206777585274. http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/138161206777585274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Höck S, Riedl R. chemf: A purely functional chemistry toolkit. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2012;4(1):38. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-4-38. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-4-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dalke A. chemfp-fast and portable fingerprint formats and tools. J Cheminformatics. 2011;3(S-1):12. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cao Y, Charisi A, Cheng L-C, Jiang T, Girke T. ChemmineR: a compound mining framework for R. Bioinformatics. 2008;24(15):1733–1734. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn307. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btn307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.O’Boyle NM, Hutchison GR. Cinfony – combining Open Source cheminformatics toolkits behind a common interface. Chemistry Central Journal. 2008;2(1):24. doi: 10.1186/1752-153x-2-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-2-24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Drefahl A. CurlySMILES: a chemical language to customize and annotate encodings of molecular and nanodevice structures. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2011;3(1):1. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-3-1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wójcikowski M, Zielenkiewicz P, Siedlecki P. DiSCuS: An Open Platform for (Not Only) Virtual Screening Results Management. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2014;54(1):347–354. doi: 10.1021/ci400587f. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci400587f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Supady A, Blum V, Baldauf C. First-Principles Molecular Structure Search with a Genetic Algorithm. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2015;55(11):2338–2348. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00243. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang Y, Backman TWH, Horan K, Girke T. fmcsR: mismatch tolerant maximum common substructure searching in R. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(21):2792–2794. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt475. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pavlov D, Rybalkin M, Karulin B, Kozhevnikov M, Savelyev A, Churinov A. Indigo: universal cheminformatics API. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2011;3(Suppl 1):P4. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-3-s1-p4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-S1-P4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lawson KR, Lawson J. LICSS - a chemical spreadsheet in microsoft excel. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2012;4(1):3. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-4-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-4-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sud M. MayaChemTools: An open source package for computational discovery. 243rd ACS National Meeting & Exposition; San Diego, CA. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wójcikowski M, Zielenkiewicz P, Siedlecki P. Open Drug Discovery Toolkit (ODDT): a new open-source player in the drug discovery field. J Cheminform. 7(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0078-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0078-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.O’Boyle NM, Banck M, James CA, Morley C, Vandermeersch T, Hutchison GR. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2011;3(1):33. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-3-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lowe DM, Corbett PT, Murray-Rust P, Glen RC. Chemical Name to Structure: OPSIN an Open Source Solution. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2011;51(3):739–753. doi: 10.1021/ci100384d. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci100384d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rijnbeek M, Steinbeck C. OrChem - An open source chemistry search engine for Oracle®. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2009;1(1):17. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-1-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-1-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Filippov IV, Nicklaus MC. Optical Structure Recognition Software To Recover Chemical Information: OSRA An Open Source Solution. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2009;49(3):740–743. doi: 10.1021/ci800067r. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci800067r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.O’Boyle NM, Morley C, Hutchison GR. Pybel: a Python wrapper for the Open-Babel cheminformatics toolkit. Chemistry Central Journal. 2008;2(1):5. doi: 10.1186/1752-153x-2-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-2-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Guha R, et al. Chemical informatics functionality in R. Journal of Statistical Software. 2007;18(5):1–16. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Smith R, Williamson R, Ventura D, Prince JT. Rubabel: wrapping open Babel with Ruby. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2013;5(1):35. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-5-35. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-5-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rahman S, Bashton M, Holliday GL, Schrader R, Thornton JM. Small Molecule Subgraph Detector (SMSD) toolkit. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2009;1(1):12. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-1-12. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-1-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Amani P, Sneyd T, Preston S, Young ND, Mason L, Bailey U-M, Baell J, Camp D, Gasser RB, Gorse A-D, Taylor P, Hofmann A. A practical Java tool for small-molecule compound appraisal. J Cheminform. 7(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0079-1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0079-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Haider N. Functionality Pattern Matching as an Efficient Complementary Structure/Reaction Search Tool: an Open-Source Approach. Molecules. 2010;15(8):5079–5092. doi: 10.3390/molecules15085079. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Miteva MA, Guyon F, Tuffery P. Frog2: Efficient 3D conformation ensemble generator for small compounds. Nucleic Acids Research. 2010;38(Web Server):W622–W627. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq325. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bruns RF, Watson IA. Rules for Identifying Potentially Reactive or Promiscuous Compounds. J Med Chem. 2012;55(22):9763–9772. doi: 10.1021/jm301008n. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm301008n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hoksza D, Škoda P, Voršsilák M, Svozil D. Molpher: a software framework for systematic chemical space exploration. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2014;6(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-6-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-6-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Borgelt C, Meinl T, Berthold M. MoSS. Proceedings of the 1st international workshop on open source data mining frequent pattern mining implementations - OSDM ’05; Association for Computing Machinery (ACM); 2005. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/1133905.1133908. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Peironcely JE, Rojas-Chertó M, Fichera D, Reijmers T, Coulier L, Faulon J-L, Hankemeier T. OMG: Open Molecule Generator. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2012;4(1):21. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-4-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-4-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tosco P, Balle T, Shiri F. SDF2XYZ2SDF: how to exploit TINKER power in cheminformatics projects. Journal of Molecular Modeling. 2011;17(11):3021–3023. doi: 10.1007/s00894-011-1111-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rosen J, Miguet L, Pérez S. Shape: automatic conformation prediction of carbohydrates using a genetic algorithm. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2009;1(1):16. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-1-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-1-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jeliazkova N, Jeliazkov V. AMBIT RESTful web services: an implementation of the OpenTox application programming interface. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2011;3(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-3-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Spjuth O, Alvarsson J, Berg A, Eklund M, Kuhn S, Mäsak C, Torrance G, Wagener J, Willighagen EL, Steinbeck C, Wikberg JE. Bioclipse 2: A scriptable integration platform for the life sciences. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10(1):397. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-397. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Goecks J, Nekrutenko A, Taylor J, Team TG. Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol. 2010;11(8):R86. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-r86. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-r86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Berthold MR, Cebron N, Dill F, Gabriel TR, Kötter T, Meinl T, Ohl P, Thiel K, Wiswedel B. KNIME - the Konstanz information miner. SIGKDD Explor Newsl. 2009;11(1):26. doi: 10.1145/1656274.1656280. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/1656274.1656280. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Demšar J, Curk T, Erjavec A, Črt Gorup, Hočevar T, Milutinovič M, Možina M, Polajnar M, Toplak M, Starič A, Štajdohar M, Umek L, Žagar L, Žbontar J, Žitnik M, Zupan B. Orange: Data Mining Toolbox in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research. 2013;14:2349–2353. http://jmlr.org/papers/v14/demsar13a.html. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Guilloux V, Arrault A, Colliandre L, Bourg S, Vayer P, Morin-Allory L. Mining collections of compounds with Screening Assistant 2. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2012;4(1):20. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-4-20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-4-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wolstencroft K, Haines R, Fellows D, Williams A, Withers D, Owen S, Soiland-Reyes S, Dunlop I, Nenadic A, Fisher P, Bhagat J, Belhajjame K, Bacall F, Hardisty A, de la Hidalga AN, Vargas MPB, Sufi S, Goble C. The Taverna workflow suite: designing and executing workflows of Web Services on the desktop web or in the cloud. Nucleic Acids Research. 2013;41(W1):W557–W561. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt328. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hall M, Frank E, Holmes G, Pfahringer B, Reutemann P, Witten IH. The WEKA data mining software. SIGKDD Explor Newsl. 2009;11(1):10. doi: 10.1145/1656274.1656278. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/1656274.1656278. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.O’Boyle NM, Vandermeersch T, Flynn CJ, Maguire AR, Hutchison GR. Confab - Systematic generation of diverse low-energy conformers. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2011;3(1):8. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-3-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kochev NT, Paskaleva VH, Jeliazkova N. Ambit-Tautomer: An Open Source Tool for Tautomer Generation. Mol Inf. 2013;32(5–6):481–504. doi: 10.1002/minf.201200133. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/minf.201200133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Beisken S, Meinl T, Wiswedel B, de Figueiredo LF, Berthold M, Steinbeck C. KNIME-CDK: Workflow-driven cheminformatics. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14(1):257. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-257. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kuhn T, Willighagen EL, Zielesny A, Steinbeck C. CDK-Taverna: an open workflow environment for cheminformatics. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11(1):159. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-159. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Krause S, Willighagen E, Steinbeck C. JChemPaint - Using the Collaborative Forces of the Internet to Develop a Free Editor for 2D Chemical Structures. Molecules. 2000;5(1):93–98. doi: 10.3390/50100093. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/50100093. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Caboche S. LeView: automatic and interactive generation of 2D diagrams for biomacromolecule/ligand interactions. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2013;5(1):40. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-5-40. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-5-40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Brefo-Mensah EK, Palmer M. mol2chemfig a tool for rendering chemical structures from molfile or SMILES format to LATE X code. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2012;4(1):24. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-4-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-4-24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hanwell MD, Curtis DE, Lonie DC, Vandermeersch T, Zurek E, Hutchison GR. Avogadro: an advanced semantic chemical editor visualization, and analysis platform. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2012;4(1):17. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-4-17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-4-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Moll A, Hildebrandt A, Lenhof H-P, Kohlbacher O. BALLView: a tool for research and education in molecular modeling. Bioinformatics. 2005;22(3):365–366. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti818. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kovačević G, Veryazov V. Luscus: molecular viewer and editor for MOLCAS. J Cheminform. 7(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0060-z. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0060-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Norrby M, Grebner C, Eriksson J, Boström J. Molecular Rift: Virtual Reality for Drug Designers. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2015;55(11):2475–2484. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00544. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Biasini M, Schmidt T, Bienert S, Mariani V, Studer G, Haas J, Johner N, Schenk AD, Philippsen A, Schwede T. OpenStructure: an integrated software framework for computational structural biology. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Cryst. 2013;69(5):701–709. doi: 10.1107/s0907444913007051. http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0907444913007051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Salentin S, Schreiber S, Haupt VJ, Adasme MF, Schroeder M. PLIP: fully automated protein–ligand interaction profiler. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(W1):W443–W447. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv315. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sweeney DJ. PhD thesis. Wright State University; 2011. A Computational Tool for Biomolecular Structure Analysis Based On Chemical and Enzymatic Modification of Native Proteins. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tarini M, Cignoni P, Montani C. Ambient Occlusion and Edge Cueing for Enhancing Real Time Molecular Visualization. IEEE Trans Visual Comput Graphics. 2006;12(5):1237–1244. doi: 10.1109/tvcg.2006.115. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2006.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rego N, Koes D. 3Dmol.js: molecular visualization with WebGL. Bioinformatics. 2014;31(8):1322–1324. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu829. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Earley CW. CH5M3D: an HTML5 program for creating 3D molecular structures. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2013;5(1):46. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-5-46. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-5-46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mohebifar M, Sajadi F. Chemozart: a web-based 3D molecular structure editor and visualizer platform. J Cheminform. 7(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0101-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0101-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Burger MC. ChemDoodle Web Components: HTML5 toolkit for chemical graphics interfaces, and informatics. J Cheminform. 7(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0085-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0085-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bienfait B, Ertl P. JSME: a free molecule editor in JavaScript. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2013;5(1):24. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-5-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-5-24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hanson RM. Jmol – a paradigm shift in crystallographic visualization. J Appl Cryst. 2010;43(5):1250–1260. doi: 10.1107/s0021889810030256. http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0021889810030256. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hanson RM, Prilusky J, Renjian Z, Nakane T, Sussman JL. JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Israel Journal of Chemistry. 2013;53(3–4):207–216. doi: 10.1002/ijch.201300024. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Rose AS, Hildebrand PW. NGL Viewer: a web application for molecular visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(W1):W576–W579. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv402. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Biasini M. pv: v1.8.1. 2015 doi: 10.5281/zenodo.20980. http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.20980. [DOI]
- 71.Exploring QSAR. Analytical Chemistry. 1995;67(17):563A–563A. doi: 10.1021/ac00113a734. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ac00113a734. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Jahn A, Hinselmann G, Fechner N, Henneges C, Zell A. Probabilistic Modeling of Conformational Space for 3D Machine Learning Approaches. Mol Inf. 2010;29(5):441–455. doi: 10.1002/minf.201000036. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/minf.201000036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Carbonell P, Carlsson L, Faulon J-L. Stereo Signature Molecular Descriptor. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2013;53(4):887–897. doi: 10.1021/ci300584r. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci300584r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Yap CW. PaDEL-descriptor: An open source software to calculate molecular descriptors and fingerprints. J Comput Chem. 2010;32(7):1466–1474. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21707. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Melville JL, Hirst JD. TMACC: Interpretable Correlation Descriptors for Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2007;47(2):626–634. doi: 10.1021/ci6004178. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci6004178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Stålring JC, Carlsson LA, Almeida P, Boyer S. AZOrange - High performance open source machine learning for QSAR modeling in a graphical programming environment. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2011;3(1):28. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-3-28. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Cortes-Ciriano I. Bioalerts: a python library for the derivation of structural alerts from bioactivity and toxicity data sets. J Cheminform. 8(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-016-0125-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-016-0125-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Murrell DS, Cortes-Ciriano I, van Westen GJP, Stott IP, Bender A, Malliavin TE, Glen RC. Chemically Aware Model Builder (camb): an R package for property and bioactivity modelling of small molecules. J Cheminform. 7(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0086-2. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0086-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Carrió P, López O, Sanz F, Pastor M. eTOXlab an open source modeling framework for implementing predictive models in production environments. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2015;7(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0058-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0058-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Tosco P, Balle T. Open3DQSAR: a new open-source software aimed at high-throughput chemometric analysis of molecular interaction fields. Journal of Molecular Modeling. 2010;17(1):201–208. doi: 10.1007/s00894-010-0684-x. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-010-0684-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Rydberg P, Rostkowski M, Gloriam DE, Olsen L. The Contribution of Atom Accessibility to Site of Metabolism Models for Cytochromes P450. Mol Pharmaceutics. 2013;10(4):1216–1223. doi: 10.1021/mp3005116. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/mp3005116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Patlewicz G, Jeliazkova N, Safford R, Worth A, Aleksiev B. An evaluation of the implementation of the Cramer classification scheme in the Toxtree software. SAR and QSAR in Environmental Research. 2008;19(5–6):495–524. doi: 10.1080/10629360802083871. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10629360802083871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Lusci A, Pollastri G, Baldi P. Deep Architectures and Deep Learning in Chemoinformatics: The Prediction of Aqueous Solubility for Drug-Like Molecules. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2013;53(7):1563–1575. doi: 10.1021/ci400187y. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci400187y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Gütlein M, Karwath A, Kramer S. CheS-Mapper 2.0 for visual validation of (Q)SAR models. J Cheminform. 6(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-014-0041-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-014-0041-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Sander T, Freyss J, von Korff M, Rufener C. DataWarrior: An Open-Source Program For Chemistry Aware Data Visualization And Analysis. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2015;55(2):460–473. doi: 10.1021/ci500588j. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci500588j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Cereto-Massague A, Guasch L, Valls C, Mulero M, Pujadas G, Garcia-Vallve S. DecoyFinder: an easy-to-use python GUI application for building target-specific decoy sets. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(12):1661–1662. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts249. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wetzel S, Klein K, Renner S, Rauh D, Oprea TI, Mutzel P, Waldmann H. Interactive exploration of chemical space with Scaffold Hunter. Nature Chemical Biology. 2009;5(8):581–583. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.187. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Lewis R, Guha R, Korcsmaros T, Bender A. Synergy Maps: exploring compound combinations using network-based visualization. J Cheminform. 7(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0090-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0090-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Martínez MJ, Ponzoni I, Díaz MF, Vazquez GE, Soto AJ. Visual analytics in cheminformatics: user-supervised descriptor selection for QSAR methods. J Cheminform. 7(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0092-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0092-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Ertl P, Patiny L, Sander T, Rufener C, Zasso M. Wikipedia Chemical Structure Explorer: substructure and similarity searching of molecules from Wikipedia. J Cheminform. 7(1) doi: 10.1186/s13321-015-0061-y. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13321-015-0061-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Durrant JD, Votapka L, Sørensen J, Amaro RE. POVME 2.0: An Enhanced Tool for Determining Pocket Shape and Volume Characteristics. J Chem Theory Comput. 2014;10(11):5047–5056. doi: 10.1021/ct500381c. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ct500381c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Rydberg P, Gloriam DE, Zaretzki J, Breneman C, Olsen L. SMARTCyp: A 2D Method for Prediction of Cytochrome P450-Mediated Drug Metabolism. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2010;1(3):96–100. doi: 10.1021/ml100016x. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ml100016x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Gütlein M, Karwath A, Kramer S. CheS-Mapper - Chemical Space Mapping and Visualization in 3D. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2012;4(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-4-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-4-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Vivo MD. Bridging quantum mechanics and structure-based drug design. Frontiers in Bioscience. 2011;16(1):1619. doi: 10.2741/3809. http://dx.doi.org/10.2741/3809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Gonze X, Amadon B, Anglade P-M, Beuken J-M, Bottin F, Boulanger P, Bruneval F, Caliste D, Caracas R, Côté M, Deutsch T, Genovese L, Ghosez P, Giantomassi M, Goedecker S, Hamann D, Hermet P, Jollet F, Jomard G, Leroux S, Mancini M, Mazevet S, Oliveira M, Onida G, Pouillon Y, Rangel T, Rignanese G-M, Sangalli D, Shaltaf R, Torrent M, Verstraete M, Zerah G, Zwanziger J. ABINIT: First-principles approach to material and nanosystem properties. Computer Physics Communications. 2009;180(12):2582–2615. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2009.07.007. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2009.07.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lotrich V, Flocke N, Ponton M, Yau AD, Perera A, Deumens E, Bartlett RJ. Parallel implementation of electronic structure energy gradient, and Hessian calculations. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 2008;128(19):194104. doi: 10.1063/1.2920482. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2920482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Mohr S, Ratcliff LE, Genovese L, Caliste D, Boulanger P, Goedecker S, Deutsch T. Accurate and efficient linear scaling DFT calculations with universal applicability. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015;17(47):31360–31370. doi: 10.1039/c5cp00437c. http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00437C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Hutter J, Iannuzzi M, Schiffmann F, VandeVondele J. cp2k: atomistic simulations of condensed matter systems. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science. 2013;4(1):15–25. doi: 10.1002/wcms.1159. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/wcms.1159. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Bahn S, Jacobsen K. An object-oriented scripting interface to a legacy electronic structure code. Comput Sci Eng. 2002;4(3):56–66. doi: 10.1109/5992.998641. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/5992.998641. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Rudberg E, Rubensson EH, Sałek P. Kohn-Sham Density Functional Theory Electronic Structure Calculations with Linearly Scaling Computational Time and Memory Usage. J Chem Theory Comput. 2011;7(2):340–350. doi: 10.1021/ct100611z. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ct100611z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Lehtola J, Hakala M, Sakko A, Hämäläinen K. ERKALE-A flexible program package for X-ray properties of atoms and molecules. J Comput Chem. 2012;33(18):1572–1585. doi: 10.1002/jcc.22987. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.22987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Enkovaara J, Rostgaard C, Mortensen JJ, Chen J, Dułak M, Ferrighi L, Gavnholt J, Glinsvad C, Haikola V, Hansen HA, Kristoffersen HH, Kuisma M, Larsen AH, Lehtovaara L, Ljungberg M, Lopez-Acevedo O, Moses PG, Ojanen J, Olsen T, Petzold V, Romero NA, Stausholm-Møller J, Strange M, Tritsaris GA, Vanin M, Walter M, Hammer B, Häkkinen H, Madsen GKH, Nieminen RM, Nørskov JK, Puska M, Rantala TT, Schiøtz J, Thygesen KS, Jacobsen KW. Electronic structure calculations with GPAW: a real-space implementation of the projector augmented-wave method. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 2010;22(25):253202. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/22/25/253202. http://stacks.iop.org/0953-8984/22/i=25/a=253202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Nikolaienko TY, Bulavin LA, Hovorun DM. JANPA: An open source cross-platform implementation of the Natural Population Analysis on the Java platform. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry. 2014;1050:15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.comptc.2014.10.002. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.comptc.2014.10.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Janssen C, Seidl E, Colvin M. Object-Oriented Implementation of Parallel Ab Initio Programs. ACS Symposium Series, Parallel Computing in Computational Chemistry; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 105.Valiev M, Bylaska E, Govind N, Kowalski K, Straatsma T, Dam HV, Wang D, Nieplocha J, Apra E, Windus T, de Jong W. NWChem: A comprehensive and scalable open-source solution for large scale molecular simulations. Computer Physics Communications. 2010;181(9):1477–1489. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2010.04.018. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2010.04.018. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Andrade X, Strubbe D, Giovannini UD, Larsen AH, Oliveira MJT, Alberdi-Rodriguez J, Varas A, Theophilou I, Helbig N, Verstraete MJ, Stella L, Nogueira F, Aspuru-Guzik A, Castro A, Marques MAL, Rubio A. Real-space grids and the Octopus code as tools for the development of new simulation approaches for electronic systems. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015;17(47):31371–31396. doi: 10.1039/c5cp00351b. http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00351B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ozaki T, Kino H. Efficient projector expansion for the ab initio LCAO method. Phys Rev B. 72(4) doi: 10.1103/physrevb.72.045121. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.045121. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Turney JM, Simmonett AC, Parrish RM, Hohenstein EG, Evangelista FA, Fermann JT, Mintz BJ, Burns LA, Wilke JJ, Abrams ML, Russ NJ, Leininger ML, Janssen CL, Seidl ET, Allen WD, Schaefer HF, King RA, Valeev EF, Sherrill CD, Crawford TD. Psi4: an open-source ab initio electronic structure program. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science. 2011;2(4):556–565. doi: 10.1002/wcms.93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/wcms.93. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kim J, Esler K, McMinis J, Ceperley DM. Quantum monte carlo algorithms: making most of large-scale multi/many-core clusters. J of Physics; Conference Series,(Chattanooga, TN), Scientific Discovery through Advanced Computing (SciDac); 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 110.Giannozzi P, Baroni S, Bonini N, Calandra M, Car R, Cavazzoni C, Ceresoli D, Chiarotti GL, Cococcioni M, Dabo I, Corso AD, de Gironcoli S, Fabris S, Fratesi G, Gebauer R, Gerstmann U, Gougoussis C, Kokalj A, Lazzeri M, Martin-Samos L, Marzari N, Mauri F, Mazzarello R, Paolini S, Pasquarello A, Paulatto L, Sbraccia C, Scandolo S, Sclauzero G, Seitsonen AP, Smogunov A, Umari P, Wentzcovitch RM. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 2009;21(39):395502. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/21/39/395502. http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/21/39/395502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Moore S, Briggs E, Hodak M, Lu W, Bernholc J, Lee C-W. Scaling the RMG quantum mechanics code. Proceedings of the Extreme Scaling Workshop; Urbana-Champaign: University of Illinois; 2012. p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Steinmann C, Ibsen MW, Hansen AS, Jensen JH. FragIt: A Tool to Prepare Input Files for Fragment Based Quantum Chemical Calculations. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(9):e44480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044480. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0044480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.O’boyle NM, Tenderholt AL, Langner KM. cclib: A library for package-independent computational chemistry algorithms. J Comput Chem. 2008;29(5):839–845. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20823. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Etienne T, Assfeld X, Monari A. New Insight into the Topology of Excited States through Detachment/Attachment Density Matrices-Based Centroids of Charge. J Chem Theory Comput. 2014;10(9):3906–3914. doi: 10.1021/ct500400s. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ct500400s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Hermann G, Pohl V, Tremblay JC, Paulus B, Hege H-C, Schild A. ORBKIT-A Modular Python Toolbox for Cross-Platform Post-Processing of Quantum Chemical Wavefunction Data. doi: 10.1002/jcc.24358. arXiv preprint arXiv:1601.03069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Allouche A-R. Gabedit-A graphical user interface for computational chemistry softwares. J Comput Chem. 2010;32(1):174–182. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21600. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Canepa P, Hanson RM, Ugliengo P, Alfredsson M. J-ICE: a new Jmol interface for handling and visualizing crystallographic and electronic properties. J Appl Cryst. 2010;44(1):225–229. doi: 10.1107/s0021889810049411. http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0021889810049411. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Bode BM, Gordon MS. Macmolplt: a graphical user interface for GAMESS. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling. 1998;16(3):133–138. doi: 10.1016/s1093-3263(99)00002-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1093-3263(99)00002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Genovese L, Neelov A, Goedecker S, Deutsch T, Ghasemi SA, Willand A, Caliste D, Zilberberg O, Rayson M, Bergman A, Schneider R. Daubechies wavelets as a basis set for density functional pseudopotential calculations. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 2008;129(1):014109. doi: 10.1063/1.2949547. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2949547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Mohr S, Ratcliff LE, Boulanger P, Genovese L, Caliste D, Deutsch T, Goedecker S. Daubechies wavelets for linear scaling density functional theory. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 2014;140(20):204110. doi: 10.1063/1.4871876. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4871876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Blöchl PE. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B. 1994;50(24):17953–17979. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.50.17953. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.50.17953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Kresse G, Joubert D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B. 1999;59(3):1758–1775. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.59.1758. http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.59.1758. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Marques MA, Oliveira MJ, Burnus T. Libxc: A library of exchange and correlation functionals for density functional theory. Computer Physics Communications. 2012;183(10):2272–2281. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2012.05.007. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2012.05.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Vitalis A, Pappu RV. Methods for Monte Carlo simulations of biomacro-molecules. Annual Reports in Computational Chemistry. 2009;5:49–76. doi: 10.1016/S1574-1400(09)00503-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1574-1400(09)00503-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Smith W, Yong C, Rodger P. DL POLY: Application to molecular simulation. Molecular Simulation. 2002;28(5):385–471. doi: 10.1080/08927020290018769. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/08927020290018769. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Zhu Y-L, Liu H, Li Z-W, Qian H-J, Milano G, Lu Z-Y. GALAMOST: GPU-accelerated large-scale molecular simulation toolkit. J Comput Chem. 2013;34(25):2197–2211. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23365. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Pronk S, Pall S, Schulz R, Larsson P, Bjelkmar P, Apostolov R, Shirts MR, Smith JC, Kasson PM, van der Spoel D, Hess B, Lindahl E. GROMACS 4.5: a high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(7):845–854. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt055. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Lorenzen K, Schwörer M, Tröster P, Mates S, Tavan P. Optimizing the Accuracy and Efficiency of Fast Hierarchical Multipole Expansions for MD Simulations. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation. 2012;8(10):3628–3636. doi: 10.1021/ct300080n. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ct300080n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Plimpton S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular Dynamics. Journal of Computational Physics. 1995;117(1):1–19. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1995.1039. http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jcph.1995.1039. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Lyubartsev AP, Laaksonen A. M.DynaMix – a scalable portable parallel MD simulation package for arbitrary molecular mixtures. Computer Physics Communications. 2000;128(3):565–589. doi: 10.1016/s0010-4655(99)00529-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0010-4655(99)00529-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Hinsen K. The molecular modeling toolkit: A new approach to molecular simulations. J Comput Chem. 2000;21(2):79–85. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-987x(20000130)21:2<79::aid-jcc1>3.0.co;2-b. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(20000130)21:2<79::AID-JCC1>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Eastman P, Friedrichs MS, Chodera JD, Radmer RJ, Bruns CM, Ku JP, Beauchamp KA, Lane TJ, Wang L-P, Shukla D, Tye T, Houston M, Stich T, Klein C, Shirts MR, Pande VS. OpenMM 4: A Reusable Extensible, Hardware Independent Library for High Performance Molecular Simulation. J Chem Theory Comput. 2013;9(1):461–469. doi: 10.1021/ct300857j. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ct300857j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Matthey T, Cickovski T, Hampton S, Ko A, Ma Q, Nyerges M, Raeder T, Slabach T, Izaguirre JA. ProtoMol an object-oriented framework for prototyping novel algorithms for molecular dynamics. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software. 2004;30(3):237–265. doi: 10.1145/1024074.1024075. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/1024074.1024075. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Michel J, Taylor RD, Essex JW. Efficient Generalized Born Models for Monte Carlo Simulations. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation. 2006;2(3):732–739. doi: 10.1021/ct600069r. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ct600069r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Zwier MC, Adelman JL, Kaus JW, Pratt AJ, Wong KF, Rego NB, Suárez E, Lettieri S, Wang DW, Grabe M, Zuckerman DM, Chong LT. WESTPA: An Interoperable Highly Scalable Software Package for Weighted Ensemble Simulation and Analysis. J Chem Theory Comput. 2015;11(2):800–809. doi: 10.1021/ct5010615. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ct5010615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Salomon-Ferrer R, Case DA, Walker RC. An overview of the Amber biomolecular simulation package. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science. 2012;3(2):198–210. doi: 10.1002/wcms.1121. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/wcms.1121. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Romo TD, Leioatts N, Grossfield A. Lightweight object oriented structure analysis: Tools for building tools to analyze molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem. 2014;35(32):2305–2318. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23753. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Vanommeslaeghe K, Yang M, ADM Robustness in the fitting of molecular mechanics parameters. Journal of Computational Chemistry. 2015;36(14):1083–1101. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23897. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Michaud-Agrawal N, Denning EJ, Woolf TB, Beckstein O. MDAnalysis: A toolkit for the analysis of molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem. 2011;32(10):2319–2327. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21787. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.McGibbon RT, Beauchamp KA, Harrigan MP, Klein C, Swails JM, Hernández CX, Schwantes CR, Wang L-P, Lane TJ, Pande VS. MDTraj: A Modern Open Library for the Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectories. Biophysical Journal. 2015;109(8):1528–1532. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.08.015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2015.08.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Guixà-González R, Rodriguez-Espigares I, Ramírez-Anguita JM, Carrió-Gaspar P, Martinez-Seara H, Giorgino3 T, Selent J. MEMBPLUGIN: studying membrane complexity in VMD. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(10):1478–1480. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu037. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Marcos-Alcalde I, Setoain J, Mendieta-Moreno JI, Mendieta J, Gómez-Puertas P. MEPSA: minimum energy pathway analysis for energy landscapes: Fig. 1. Bioinformatics. 2015:btv453. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv453. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv453. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 143.Beauchamp KA, Bowman GR, Lane TJ, Maibaum L, Haque IS, Pande VS. MSMBuilder2: Modeling Conformational Dynamics on the Picosecond to Millisecond Scale. J Chem Theory Comput. 2011;7(10):3412–3419. doi: 10.1021/ct200463m. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ct200463m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Martínez L, Andrade R, Birgin EG, Martínez JM. PACKMOL: A package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem. 2009;30(13):2157–2164. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21224. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Dolinsky TJ, Czodrowski P, Li H, Nielsen JE, Jensen JH, Klebe G, Baker NA. PDB2PQR: expanding and upgrading automated preparation of biomolecular structures for molecular simulations. Nucleic Acids Research. 2007;35(Web Server Issue):W522–W525. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm276. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Tribello GA, Bonomi M, Branduardi D, Camilloni C, Bussi G. PLUMED 2: New feathers for an old bird. Computer Physics Communications. 2014;185(2):604–613. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2013.09.018. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2013.09.018. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Bakan A, Meireles LM, Bahar I. ProDy: Protein Dynamics Inferred from Theory and Experiments. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(11):1575–1577. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr168. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Yesylevskyy SO. Pteros 2.0: Evolution of the fast parallel molecular analysis library for C++ and python. J Comput Chem. 2015;36(19):1480–1488. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23943. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Scherer MK, Trendelkamp-Schroer B, Paul F, Pérez-Hernández G, Hoffmann M, Plattner N, Wehmeyer C, Prinz J-H, Noé F. PyEMMA 2: A Software Package for Estimation Validation, and Analysis of Markov Models. J Chem Theory Comput. 2015;11(11):5525–5542. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00743. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Dupradeau F-Y, Pigache A, Zaffran T, Savineau C, Lelong R, Grivel N, Lelong D, Rosanskia W, Cieplak P. The R.E.D. tools: advances in RESP and ESP charge derivation and force field library building. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 12(28) doi: 10.1039/c0cp00111b. http://dx.doi/org/10.1039/c0cp00111b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Cickovski T, Chatterjee S, Wenger J, Sweet CR, Izaguirre JA. MDLab: A molecular dynamics simulation prototyping environment. J Comput Chem. 2009 doi: 10.1002/jcc.21418. NA–NA. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21418. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 152.Bakan A, Nevins N, Lakdawala AS, Bahar I. Druggability Assessment of Allosteric Proteins by Dynamics Simulations in the Presence of Probe Molecules. J Chem Theory Comput. 2012;8(7):2435–2447. doi: 10.1021/ct300117j. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ct300117j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Berenger F, Voet A, Lee X, Zhang KY. A rotation-translation invariant molecular descriptor of partial charges and its use in ligand-based virtual screening. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2014;6(1):23. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-6-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-6-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Haque IS, Pande VS. PAPER: Accelerating parallel evaluations of ROCS. J Comput Chem. 2010;31(1):117–132. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21307. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Koes DR, Camacho CJ. Pharmer: Efficient and Exact Pharmacophore Search. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2011;51(6):1307–1314. doi: 10.1021/ci200097m. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci200097m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Sunseri J, Koes DR. Pharmit: interactive exploration of chemical space. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016:gkw287. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw287. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 157.Schreyer AM, Blundell T. USRCAT: real-time ultrafast shape recognition with pharmacophoric constraints. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2012;4(1):27. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-4-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-4-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Taminau J, Thijs G, Winter HD. Pharao: Pharmacophore alignment and optimization. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling. 2008;27(2):161–169. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2008.04.003. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2008.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Baker NA, Sept D, Joseph S, Holst MJ, McCammon JA. Electrostatics of nanosystems: Application to microtubules and the ribosome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001;98(18):10037–10041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.181342398. http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.181342398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem. 2009;30(16):2785–2791. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21256. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Trott O, Olson AJ. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem. 2009:NA–NA. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 162.Ballante F, Marshall GR. An Automated Strategy for Binding-Pose Selection and Docking Assessment in Structure-Based Drug Design. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2016;56(1):54–72. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00603. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Bullock C, Cornia N, Jacob R, Remm A, Peavey T, Weekes K, Mallory C, Oxford JT, McDougal OM, Andersen TL. DockoMatic 2.0: High Throughput Inverse Virtual Screening and Homology Modeling. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2013;53(8):2161–2170. doi: 10.1021/ci400047w. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci400047w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Jiang X, Kumar K, Hu X, Wallqvist A, Reifman J. DOVIS 2.0: an efficient and easy to use parallel virtual screening tool based on AutoDock 4.0. Chemistry Central Journal. 2008;2(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1752-153x-2-18. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-2-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Li H, Leung K-S, Wong M-H. idock: A multithreaded virtual screening tool for flexible ligand docking. 2012 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB); Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers (IEEE); 2012. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/CIBCB.2012.6217214. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Abreu RM, Froufe HJ, Queiroz M, Ferreira IC. MOLA: a bootable self-configuring system for virtual screening using AutoDock4/Vina on computer clusters. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2010;2(1):10. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-2-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-2-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Durrant JD, McCammon JA. NNScore 2.0: A Neural-Network Receptor–Ligand Scoring Function. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2011;51(11):2897–2903. doi: 10.1021/ci2003889. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci2003889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Meier R, Pippel M, Brandt F, Sippl W, Baldauf C. ParaDockS: A Framework for Molecular Docking with Population-Based Metaheuristics. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2010;50(5):879–889. doi: 10.1021/ci900467x. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci900467x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Dallakyan S, Olson AJ. Methods in Molecular Biology. Springer Science + Business Media; 2014. Small-Molecule Library Screening by Docking with PyRx; pp. 243–250. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2269-7_19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Ruiz-Carmona S, Alvarez-Garcia D, Foloppe N, Garmendia-Doval AB, Juhos S, Schmidtke P, Barril X, Hubbard RE, Morley SD. rDock: A Fast Versatile and Open Source Program for Docking Ligands to Proteins and Nucleic Acids. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014;10(4):e1003571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003571. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Li H, Leung K-S, Wong M-H, Ballester PJ. Improving AutoDock Vina Using Random Forest: The Growing Accuracy of Binding Affinity Prediction by the Effective Exploitation of Larger Data Sets. Mol Inf. 2015;34(2–3):115–126. doi: 10.1002/minf.201400132. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/minf.201400132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Koes DR, Baumgartner MP, Camacho CJ. Lessons Learned in Empirical Scoring with smina from the CSAR 2011 Benchmarking Exercise. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2013;53(8):1893–1904. doi: 10.1021/ci300604z. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci300604z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Cereto-Massagué A, Ojeda M, Joosten RP, Valls C, Mulero M, Salvado M, Arola-Arnal A, Arola L, Garcia-Vallvé S, Pujadas G. The good the bad and the dubious: VHELIBS a validation helper for ligands and binding sites. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2013;5(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-5-36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-5-36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Zhang X, Wong SE, Lightstone FC. Message passing interface and multithreading hybrid for parallel molecular docking of large databases on petascale high performance computing machines. J Comput Chem. 2013;34(11):915–927. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23214. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Ellingson SR, Smith JC, Baudry J. VinaMPI: Facilitating multiple receptor high-throughput virtual docking on high-performance computers. J Comput Chem. 2013;34(25):2212–2221. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23367. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.23367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Zonta N, Grimstead IJ, Avis NJ, Brancale A. Accessible haptic technology for drug design applications. Journal of Molecular Modeling. 2008;15(2):193–196. doi: 10.1007/s00894-008-0387-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-008-0387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Brylinski M, Feinstein WP. eFindSite: Improved prediction of ligand binding sites in protein models using meta-threading machine learning and auxiliary ligands. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design. 2013;27(6):551–567. doi: 10.1007/s10822-013-9663-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10822-013-9663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Schmidtke P, Bidon-Chanal A, Luque FJ, Barril X. MDpocket: open-source cavity detection and characterization on molecular dynamics trajectories. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(23):3276–3285. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr550. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Oliveira SH, Ferraz FA, Honorato RV, Xavier-Neto J, Sobreira TJ, de Oliveira PS. KVFinder: steered identification of protein cavities as a PyMOL plugin. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014;15(1):197. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-197. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-15-197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Till MS, Ullmann GM. McVol - A program for calculating protein volumes and identifying cavities by a Monte Carlo algorithm. Journal of Molecular Modeling. 2009;16(3):419–429. doi: 10.1007/s00894-009-0541-y. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-009-0541-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Weisel M, Proschak E, Schneider G. PocketPicker: analysis of ligand binding-sites with shape descriptors. Chemistry Central Journal. 2007;1(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1752-153x-1-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-1-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Huey R, Morris GM, Olson AJ, Goodsell DS. A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J Comput Chem. 2007;28(6):1145–1152. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20634. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Ballester PJ, Mitchell JBO. A machine learning approach to predicting protein-ligand binding affinity with applications to molecular docking. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(9):1169–1175. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq112. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Durrant JD, McCammon JA. AutoClickChem: Click Chemistry in Silico. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(3):e1002397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002397. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Durrant JD, Lindert S, McCammon JA. AutoGrow 3.0: An improved algorithm for chemically tractable semi-automated protein inhibitor design. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling. 2013;44:104–112. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2013.05.006. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2013.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Chéron N, Jasty N, Shakhnovich EI. OpenGrowth: An Automated and Rational Algorithm for Finding New Protein Ligands. J Med Chem. 2015 doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00886. 150923135558008. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00886. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 187.Guha R, Howard MT, Hutchison GR, Murray-Rust P, Rzepa H, Steinbeck C, Wegner J, Willighagen EL. The Blue Obelisk—Interoperability in Chemical Informatics. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2006;46(3):991–998. doi: 10.1021/ci050400b. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ci050400b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.O’Boyle NM, Guha R, Willighagen EL, Adams SE, Alvarsson J, Bradley JC, Filippov IV, Hanson RM, Hanwell MD, Hutchison GR, James CA, Jeliazkova N, Lang AS, Langner KM, Lonie DC, Lowe DM, Pansanel J, Pavlov D, Spjuth O, Steinbeck C, Tenderholt AL, Theisen KJ, Murray-Rust P. Open Data Open Source and Open Standards in chemistry: The Blue Obelisk five years on. Journal of Cheminformatics. 2011;3(1):37. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-3-37. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]