Abstract
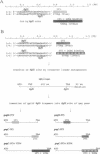
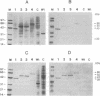
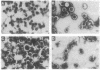
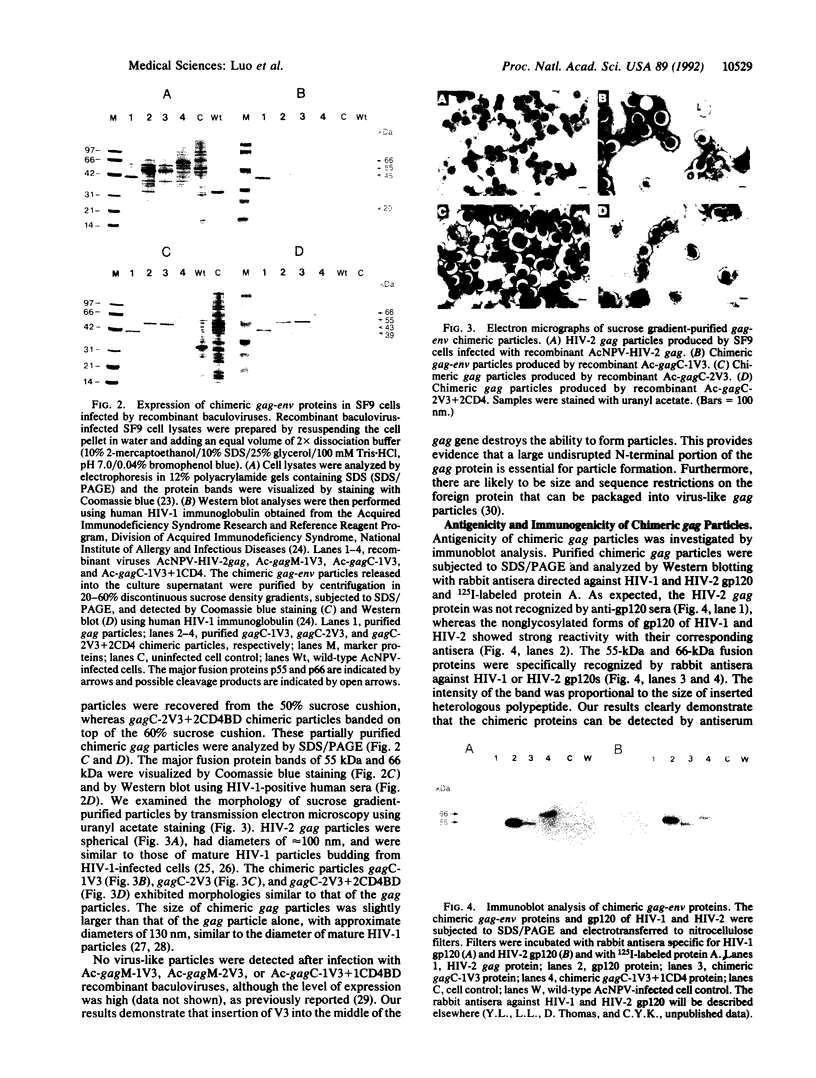
A 41-kDa unprocessed human immunodeficiency virus 2 (HIV-2) gag precursor protein that has a deletion of a portion of the viral protease assembles as virus-like particles by budding through the cytoplasmic membrane of recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. We have constructed six different combinations of chimeric genes by coupling the truncated HIV-2 gag gene to the neutralizing domain (V3) or the neutralizing and the CD4 binding domains (V3+CD4BD) of gp120 env gene sequences from HIV-1 or HIV-2. The env gene sequences were inserted either into the middle of the gag gene or at the 3' terminus of the gag gene. Virus-like particles were formed by chimeric gene products only when the env gene sequences were linked to the 3' terminus of the gag gene. Insertion of env gene sequence in the middle of the gag gene resulted in high-level chimeric gene expression but without the formation of virus-like particles. Three different chimeric genes [gag gene with HIV-1 V3 (1V3), gag gene with HIV-2 V3 (2V3), and gag gene with HIV-2 V3+CD4BD (2V3+CD4BD)] formed virus-like particles that were secreted into the cell culture medium. In contrast, the HIV-1 V3+CD4BD/HIV-2 gag construct did not form virus-like particles. The chimeric gag-env particles had spherical morphology and the size was slightly larger than that of the gag particles, but the chimeric particles were similar to the mature HIV particles. Western blot analysis showed that the gag-env chimeric proteins were recognized by antibodies in HIV-positive human serum and rabbit anti-gp120 serum. Rabbit anti-gag 1V3 and anti-gag 2V3 sera reacted with authentic gp120 of HIV-1 and HIV-2, respectively, and neutralized homologous HIV infectivity. Our results show that precursor gag protein has potential as a carrier for the presentation of foreign epitopes in good immunological context. The gag protein is highly immunogenic and has the ability to carry large foreign inserts; as such, it offers an attractive approach for HIV vaccine development.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman P. W., Gregory T. J., Riddle L., Nakamura G. R., Champe M. A., Porter J. P., Wurm F. M., Hershberg R. D., Cobb E. K., Eichberg J. W. Protection of chimpanzees from infection by HIV-1 after vaccination with recombinant glycoprotein gp120 but not gp160. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):622–625. doi: 10.1038/345622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björling E., Broliden K., Bernardi D., Utter G., Thorstensson R., Chiodi F., Norrby E. Hyperimmune antisera against synthetic peptides representing the glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 can mediate neutralization and antibody-dependent cytotoxic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6082–6086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broliden P. A., Ljunggren K., Hinkula J., Norrby E., Akerblom L., Wahren B. A monoclonal antibody to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 which mediates cellular cytotoxicity and neutralization. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):936–940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.936-940.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrystie I. L., Almeida J. D. The morphology of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) by negative staining. J Med Virol. 1988 Jul;25(3):281–288. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890250305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson K., Percival H., Kang C. Y. The N-terminal env-derived amino acids of v-rel are required for full transforming activity. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R., Hausmann E. H., Ozel M., Pauli G., Koch M. A. Fine structure of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and immunolocalization of structural proteins. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M., Kieny M. P., Pinter A., Barre-Sinoussi F., Nara P., Kolbe H., Kusumi K., Chaput A., Reinhart T., Muchmore E. Immunization of chimpanzees confers protection against challenge with human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):542–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Debouck C., Meloen R. H., Smit L., Bakker M., Asher D. M., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization epitope with conserved architecture elicits early type-specific antibodies in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4478–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho R. J., Burke R. L., Merigan T. C. Antigen-presenting liposomes are effective in treatment of recurrent herpes simplex virus genitalis in guinea pigs. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2951–2958. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2951-2958.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsy J., Meyer M., Tateno M., Clarkson S., Levy J. A. The Fc and not CD4 receptor mediates antibody enhancement of HIV infection in human cells. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1357–1360. doi: 10.1126/science.2786647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. L., Essex M., Lee T. H. Localization of immunogenic domains in the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 envelope. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):5073–5079. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.5073-5079.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imberti L., Sottini A., Bettinardi A., Puoti M., Primi D. Selective depletion in HIV infection of T cells that bear specific T cell receptor V beta sequences. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.1948066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y. Baculovirus vectors for expression of foreign genes. Adv Virus Res. 1988;35:177–192. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60711-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kion T. A., Hoffmann G. W. Anti-HIV and anti-anti-MHC antibodies in alloimmune and autoimmune mice. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1138–1140. doi: 10.1126/science.1909456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Davide J. P., Weinhold K., Waterbury J. A., Profy A. T., Lewis J. A., Langlois A. J., Dreesman G. R., Boswell R. N., Shadduck P. Conserved sequence and structural elements in the HIV-1 principal neutralizing determinant. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.2392685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo L., Li Y., Kang C. Y. Expression of gag precursor protein and secretion of virus-like gag particles of HIV-2 from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):874–880. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90159-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Cort S. P., Kennedy M. S., Mawle A. C. Binding of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV/ARV/HIV to the CD4 (T4) molecule: conformation dependence, epitope mapping, antibody inhibition, and potential for idiotypic mimicry. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2937–2944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa S., Booth T. F., Bishop D. H. Analyses of the requirements for the synthesis of virus-like particles by feline immunodeficiency virus gag using baculovirus vectors. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):288–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90141-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Hatch W. C., Dunlop N. M., Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Gonda M. A., Fischinger P. J. Simple, rapid, quantitative, syncytium-forming microassay for the detection of human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibody. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Fall;3(3):283–302. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orentas R. J., Hildreth J. E., Obah E., Polydefkis M., Smith G. E., Clements M. L., Siliciano R. F. Induction of CD4+ human cytolytic T cells specific for HIV-infected cells by a gp160 subunit vaccine. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1234–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.2190315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Clark M. E., Langlois A. J., Matthews T. J., Weinhold K. J., Randall R. R., Bolognesi D. P., Haynes B. F. Type-specific neutralization of the human immunodeficiency virus with antibodies to env-encoded synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papsidero L. D., Sheu M., Ruscetti F. W. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies which react with p17 core protein: characterization and epitope mapping. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):267–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.267-272.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Horowitz B., Baker L., Shulman R. W., Ralph H., Valinsky J., Cundell A., Brotman B., Boehle W., Rey F. Failure of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) immune globulin to protect chimpanzees against experimental challenge with HIV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6944–6948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Matthews T. J., Robey W. G., Lynn D. L., Robert-Guroff M., Mueller W. T., Langlois A. J., Ghrayeb J., Petteway S. R., Jr, Weinhold K. J. HTLV-III/LAV-neutralizing antibodies to an E. coli-produced fragment of the virus envelope. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1392–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.2431482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Matthews T. J., Langlois A., Copeland T. D., Lerche N. W., Oroszlan S., Bolognesi D. P., Gilden R. V., Fischinger P. J. Prospect for prevention of human immunodeficiency virus infection: purified 120-kDa envelope glycoprotein induces neutralizing antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7023–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Kawamura T., Gorny M. K., Lake D., Xu J. Y., Matsumoto Y., Sugano T., Masuho Y., Mitchell W. M., Hersh E. Human monoclonal antibodies to the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) transmembrane glycoprotein gp41 enhance HIV-1 infection in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3185–3189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Javaherian K., McDanal C., Petro J., Lynn D. L., Grimaila R., Langlois A., Gallo R. C., Arthur L. O., Fischinger P. J. Antibodies that inhibit fusion of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells bind a 24-amino acid sequence of the viral envelope, gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach J., Popovic M., Gilden R. V., Gonda M. A., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C. Serological analysis of a subgroup of human T-lymphotropic retroviruses (HTLV-III) associated with AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):503–505. doi: 10.1126/science.6200937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung W. L., Zahab D. M., MacDonald C. A., Tam C. S. Synthesis of mutant parathyroid hormone genes via site-specific recombination directed by crossover linkers. Gene. 1986;47(2-3):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Cohen J., Hosmalin A., Cease K. B., Houghten R., Cornette J. L., DeLisi C., Moss B., Germain R. N., Berzofsky J. A. An immunodominant epitope of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein gp160 recognized by class I major histocompatibility complex molecule-restricted murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3105–3109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Nakagawa Y., Pendleton C. D., Houghten R. A., Yokomuro K., Germain R. N., Berzofsky J. A. Induction of broadly cross-reactive cytotoxic T cells recognizing an HIV-1 envelope determinant. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):333–336. doi: 10.1126/science.1372448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weldon R. A., Jr, Erdie C. R., Oliver M. G., Wills J. W. Incorporation of chimeric gag protein into retroviral particles. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4169–4179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4169-4179.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]