Abstract
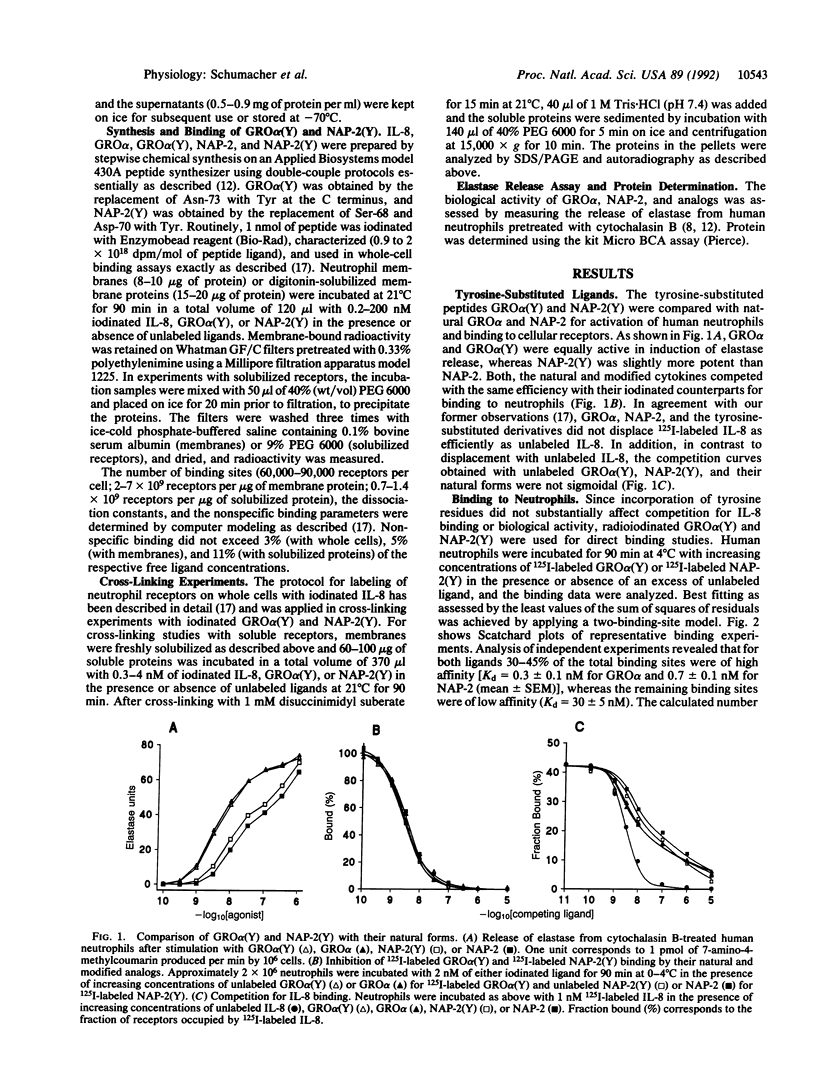
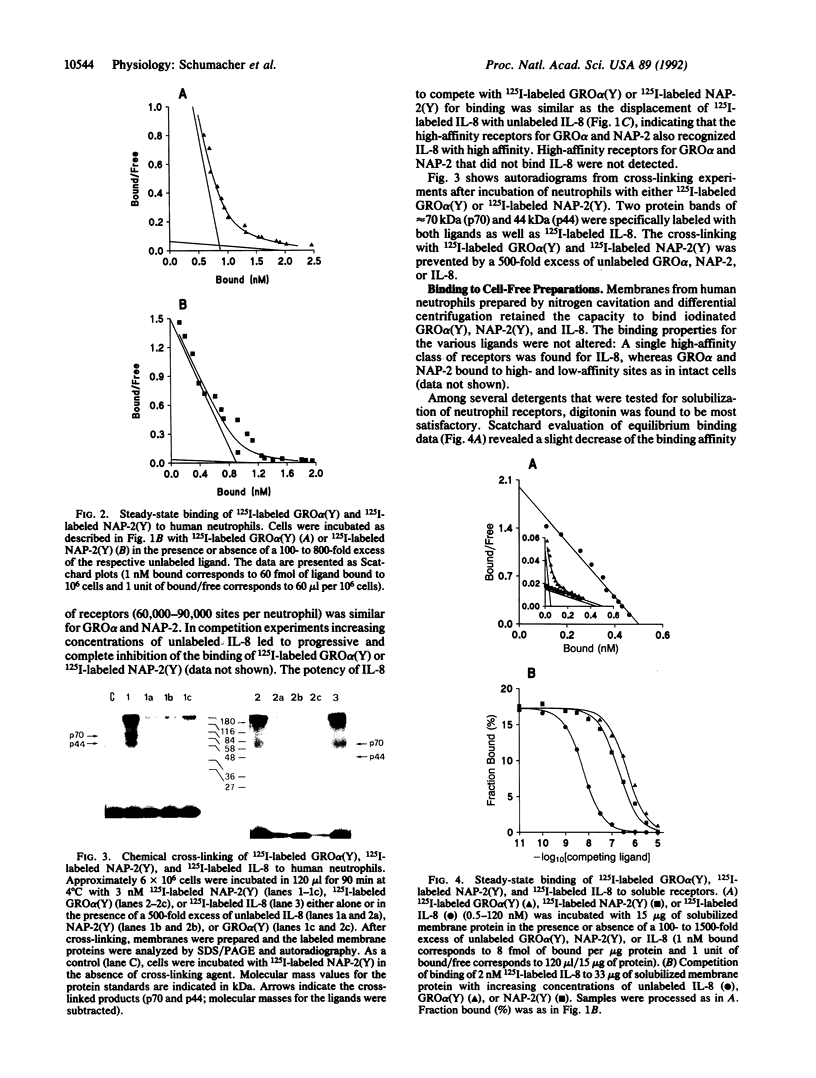
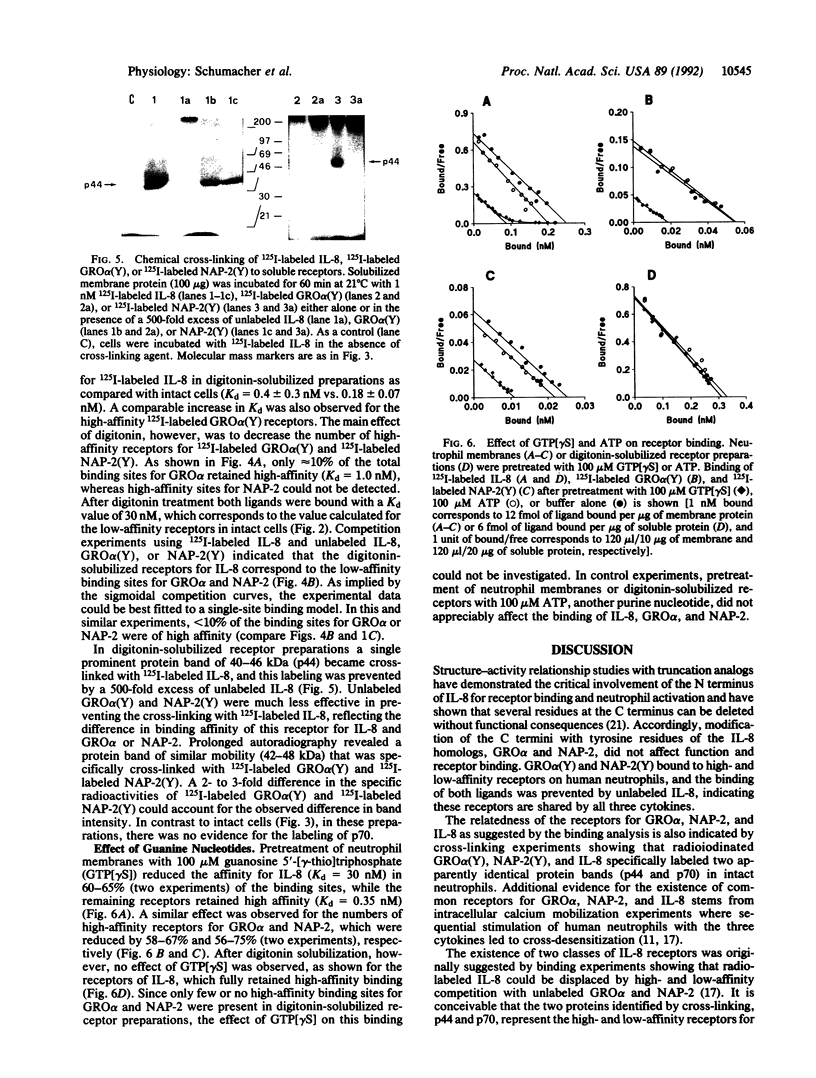
GRO alpha and neutrophil-activating peptide 2 (NAP-2), like their analog interleukin 8 (IL-8), are considered to be inflammatory mediators since they recruit and activate neutrophil leukocytes. After introduction of tyrosines by substitution for other residues at the C terminus, GRO alpha and NAP-2 were labeled with 125I and used for binding studies. A total of 60,000-90,000 receptors per neutrophil were found for either ligand. Of these 30-45% were of high affinity with a mean Kd value of 0.3 and 0.7 nM for GRO alpha and NAP-2, respectively, and 55-70% of low affinity (Kd = 30 nM). Two proteins of approximately 70 kDa and 44 kDa (p70 and p44) were specifically cross-linked with labeled GRO alpha, NAP-2, and IL-8. Unlabeled IL-8 fully inhibited this cross-linking and the binding of labeled GRO alpha or NAP-2 to the high-affinity sites on neutrophils or neutrophil membranes. Treatment of membranes with digitonin resulted in the preferential solubilization of a single receptor species, corresponding to p44, that bound GRO alpha and NAP-2 with low affinity (Kd = 30 nM) and IL-8 with high affinity (Kd = 0.4 nM). Exposure of neutrophil membranes to 100 microM guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate led to a 75-fold increase of the Kd in approximately 60% of the IL-8 receptors. High-affinity receptors for GRO alpha and NAP-2 were similarly affected. In contrast, guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate had no effect on the binding of IL-8 to p44 solubilized by digitonin. These results demonstrate that human neutrophils bear two classes of receptors for GRO alpha, NAP-2, and IL-8 (p70 and p44) that may differ in their mode of interaction with GTP regulatory proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anisowicz A., Zajchowski D., Stenman G., Sager R. Functional diversity of gro gene expression in human fibroblasts and mammary epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9645–9649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Imboden P., Detmers P. Neutrophil activation and the effects of interleukin-8/neutrophil-activating peptide 1 (IL-8/NAP-1). Cytokines. 1992;4:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besemer J., Hujber A., Kuhn B. Specific binding, internalization, and degradation of human neutrophil activating factor by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17409–17415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Moser B., Walz A., Baggiolini M., Scott G. J., Aebersold R. Chemical synthesis, purification, and characterization of two inflammatory proteins, neutrophil activating peptide 1 (interleukin-8) and neutrophil activating peptide. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 26;30(12):3128–3135. doi: 10.1021/bi00226a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Schumacher C., Baggiolini M., Moser B. Structure-activity relationships of interleukin-8 determined using chemically synthesized analogs. Critical role of NH2-terminal residues and evidence for uncoupling of neutrophil chemotaxis, exocytosis, and receptor binding activities. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23128–23134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Sidiropoulos D., Jakobs K. H. Two distinct Gi-proteins mediate formyl peptide receptor signal transduction in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21470–21473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. M., David E., Warren T. C., DeLeon R. P., Farina P. R., Homon C. A. Characterization of a receptor for human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor/interleukin-8. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8311–8316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. E., Lee J., Kuang W. J., Rice G. C., Wood W. I. Structure and functional expression of a human interleukin-8 receptor. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1278–1280. doi: 10.1126/science.1840701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser B., Clark-Lewis I., Zwahlen R., Baggiolini M. Neutrophil-activating properties of the melanoma growth-stimulatory activity. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1797–1802. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser B., Schumacher C., von Tscharner V., Clark-Lewis I., Baggiolini M. Neutrophil-activating peptide 2 and gro/melanoma growth-stimulatory activity interact with neutrophil-activating peptide 1/interleukin 8 receptors on human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10666–10671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. M., Tiffany H. L. Cloning of complementary DNA encoding a functional human interleukin-8 receptor. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1280–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.1891716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Zachariae C. O., Mukaida N., Matsushima K. Properties of the novel proinflammatory supergene "intercrine" cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:617–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond A., Balentien E., Thomas H. G., Flaggs G., Barton D. E., Spiess J., Bordoni R., Francke U., Derynck R. Molecular characterization and chromosomal mapping of melanoma growth stimulatory activity, a growth factor structurally related to beta-thromboglobulin. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2025–2033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins T. E., Siciliano S., Springer M. S. Solubilization of the functional C5a receptor from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta A. K., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. Identification and characterization of specific receptors for monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDNCF) on human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1185–1189. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta A. K., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. Interleukin 8 (monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor) dynamically regulates its own receptor expression on human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):183–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano S. J., Rollins T. E., Springer M. S. Interaction between the C5a receptor and Gi in both the membrane-bound and detergent-solubilized states. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19568–19574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Edge S., Lane B. A chemoattractant receptor on macrophages exists in two affinity states regulated by guanine nucleotides. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):444–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckle M. Y., Barker K. A. Two burgeoning families of platelet factor 4-related proteins: mediators of the inflammatory response. New Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):313–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Peveri P., Kernen P., von Tscharner V., Walz A., Baggiolini M. Mechanism of neutrophil activation by NAF, a novel monocyte-derived peptide agonist. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2702–2706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Dewald B., von Tscharner V., Baggiolini M. Effects of the neutrophil-activating peptide NAP-2, platelet basic protein, connective tissue-activating peptide III and platelet factor 4 on human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1745–1750. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Meloni F., Clark-Lewis I., von Tscharner V., Baggiolini M. [Ca2+]i changes and respiratory burst in human neutrophils and monocytes induced by NAP-1/interleukin-8, NAP-2, and gro/MGSA. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Sep;50(3):279–286. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.3.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten R., Bokoch G. M. GTP binding proteins and signal transduction in the human neutrophil. Immunol Lett. 1990 Oct;26(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90167-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





