Abstract
A rapid decline in the development of new antimicrobial therapeutics has coincided with the emergence of new and more aggressive multidrug-resistant pathogens. Pathogens are protected from antibiotic activity by their ability to enter an aggregative biofilm state. Therefore, disrupting this process in pathogens is a key strategy for the development of next-generation antimicrobials. Here, we present a suite of compounds, based on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa 2-heptyl-4(1H)-quinolone (HHQ) core quinolone interkingdom signal structure, that exhibit noncytotoxic antibiofilm activity toward the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. In addition to providing new insights into what is a clinically important bacterium-fungus interaction, the capacity to modularize the functionality of the quinolone signals is an important advance in harnessing the therapeutic potential of signaling molecules in general. This provides a platform for the development of potent next-generation small-molecule therapeutics targeting clinically relevant fungal pathogens.
INTRODUCTION
With the ever-increasing emergence of antibiotic-resistant pathogens and the lack of new antibiotics coming to market, we are entering a “postantibiotic era” (1–3). This realization has underpinned a global initiative to identify new and innovative approaches to infection management. As such, targeting virulence as a potential strategy for developing new antimicrobial drugs has been the focus of several research initiatives (4–11). In principle, suppressing virulence behavior and locking pathogens in a vegetative non-biofilm-forming lifestyle renders them less infective and more susceptible to conventional antibiotics (4, 12). While some success has been achieved against bacterial pathogens (6, 10, 13–19), less focus has been placed on fungal infections, which nevertheless continue to cause serious complications and mortality in patients (8, 20–22). Indeed, despite the medical and economic damage caused by fungal biofilms, there remains an urgent and largely unmet need for the identification of compounds able to specifically and selectively target and inhibit this mode of growth in clinically relevant fungal pathogens (23).
The predominant nosocomial fungal pathogens, which include Candida spp., Aspergillus spp., and Fusarium spp., are difficult to diagnose and cause high morbidity and mortality, even following antifungal therapy (21). Candida albicans causes a variety of complications ranging from mucosal disease to deep-seated mycoses, particularly in immunocompromised individuals (21, 24). Along with other fungal and yeast pathogens, C. albicans is known to form structured communities called biofilms on medical devices either pre- or postimplantation, leading to recurring infections and in some cases death (25, 26). Once established in the biofilm phase, C. albicans presents a significant clinical problem, with current treatment options severely limited by the intrinsic tolerance of fungal biofilms for antimycotics (20, 27, 28). Recent combination therapies incorporating antibacterial and antifungal agents have shown some success (29). However, as with all antibiotic-based strategies, reports of resistance continue to emerge (27), and biofilms themselves are considered a breeding ground for the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, effectively hastening the onset of the perfect storm where the rapid decline in new antibiotic production has been met by an equally rapid increase in multidrug-resistant organisms (1). Thus, there is a need to consider new anti-infective strategies that do not target essential processes in the target organism. While blocking biofilms in these organisms remains a major clinical challenge (26, 30), exploiting our increased understanding of microbial signaling networks to control virulence and biofilm behavior is one innovative approach with significant potential.
Many sites of infection are colonized by communities of mixed fungal and bacterial organisms, and several layers of communication significantly impact the dynamics and flux of these populations (31, 32). For example, C. albicans is known to coexist with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the cystic fibrosis (CF) lung, and interkingdom communication between the two organisms has previously been reported (16, 33). The Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS), 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone, and its biological precursor, 2-heptyl-4-quinolone (HHQ), are important virulence factors produced by P. aeruginosa. Structurally, PQS and HHQ differ by the presence of a hydrogen at C-3 in HHQ and a hydroxyl group in PQS, giving rise to the increased interest in modulating this position to assign biological function to the structures of the molecules (34–37). Previously, we have shown that HHQ, but not PQS, suppresses biofilm formation by C. albicans (10). In response, C. albicans produces farnesol, which has been shown to modulate PQS production in P. aeruginosa (33). As both PQS and HHQ promote virulence and pathogenicity of P. aeruginosa (38, 39), their utility as an anti-Candida treatment falls short of being a viable antifungal treatment. However, the amenability of these small molecules to chemical modification provides an opportunity to develop compounds with specificity of function.
The transcriptional data and microscopic imaging described in this study have implicated components of the cell wall as key factors in the response of C. albicans to P. aeruginosa alkylhydroxyquinolone (AHQ) signaling. Furthermore, the biological activity of each class of analogue in bacterial, fungal, and host systems provides new insight into the possible interkingdom role of AHQs, particularly in a clinical setting such as the CF lung, where all three systems coexist. From a translational perspective, lead HHQ analogues with four key features were identified: (i) they have potent antibiofilm activity toward C. albicans, (ii) they have selective noncytotoxicity toward mammalian cell lines, (iii) they are nonagonistic and (iv) they are potentially antagonistic to the virulent pathogen P. aeruginosa. Several analogues retained the significant potency of the parent HHQ molecule against C. albicans biofilm formation while simultaneously becoming inactive in P. aeruginosa quorum sensing. This suggests that these molecules have the potential to be further optimized for use as anti-infectives for Candida without the concomitant limitation of P. aeruginosa virulence augmentation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
C. albicans stock maintenance and culturing conditions.
C. albicans strain SC5314 was subcultured from 15% (vol/vol) glycerol stocks at −80°C onto yeast-peptone-dextrose (YPD) medium (1% [wt/vol] yeast extract, 2% [wt/vol] peptone, and 2% [wt/vol] dextrose) and incubated at 30°C overnight.
P. aeruginosa stock maintenance and culturing conditions.
P. aeruginosa strains, PAO1 and a pqsA mutant, containing the chromosomally inserted pqsA-lacZ promoter fusion on plasmid pUC18-mini-Tn7, were maintained on Luria-Bertani (LB) agar plates supplemented with carbenicillin (200 μg/ml) and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (X-Gal) (40 μg/ml) and incubated at 37°C overnight. Single colonies were inoculated into LB broth (20 ml) supplemented with carbenicillin (200 μg/ml) and incubated at 37°C with shaking at 180 rpm overnight. For subsequent experiments, the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was recorded, and a starting OD600 of 0.02 was inoculated into fresh LB broth supplemented with carbenicillin (200 μg/ml) and incubated at 37°C with shaking at 180 rpm.
Structural modification of HHQ.
The synthesis of HHQ, PQS (40, 41), and other HHQ-based analogues (36, 37) was carried out via previously described methods. Novel compounds and compounds that required modified synthesis are described below and in the supplemental material.
TLC analysis.
Silica thin-layer chromatographic (TLC) plates, activated by soaking in 5% (wt/vol) K2HPO4 for 30 min, were placed in an oven at 100°C for 1 h (42). Analogues (5 μl; 10 mM) were spotted approximately 1 cm from the bottom. The spots were dried, and the plates were placed in a mobile phase comprising dichloromethane-methanol (95:5). The plate was viewed under UV light when the mobile phase had run 5 cm below the top of the plate.
Biofilm formation, quantification, and visualization.
C. albicans biofilm formation was carried out in 96-well plates, as previously described (43). Seeding densities for all subsequent experiments (n = 3) were an OD600 of 0.05. Biofilm formation was measured as previously described, using a semiquantitative tetrazolium salt, 2,3-bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide inner salt (XTT) reduction assay (44). Experiments were repeated at least three times, with at least eight technical replicates. Visualization of biofilm formation was performed on glass coverslips in 6-well plates using confocal scanning laser microscopy (CSLM). All images were captured using the Zeiss HBO-100 microscope illuminating system, processed using the Zen AIM application imaging program, and converted to JPGs using Axiovision 40 version 4.6.3.0. A minimum of three independent biological repetitions were carried out.
Viable-colony biofilm assay.
C. albicans biofilms, supplemented with analogues and parent compounds, were grown in 6-well plates and incubated overnight at 37°C. Briefly, the OD600s of C. albicans yeast nitrogen base (YNB) cultures were measured, and the cultures were diluted to an OD600 of 0.05 in YNB-NP (see below), supplemented with analogues, plated onto 6-well plates, and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. The medium was removed, and the wells were washed twice with sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and supplemented with fresh YNB-NP with analogues. The plates were incubated overnight at 37°C, after which the medium was removed and the wells were washed with sterile PBS. For serial dilutions, biofilms were harvested by scraping adherent cells into 1 ml PBS, vortexed, and serially diluted in sterile PBS. The serial dilutions (100 μl) were plated onto YPD agar and incubated overnight at 37°C. Colonies were counted and recorded the next day.
C. albicans growth curves.
Overnight C. albicans cultures grown in YNB were diluted to an OD600 of 0.05 in YNB supplemented with analogues. Cultures (200 μl) were added to each well of a 100-well plate and grown for 24-h period on a Bioscreen C spectrophotometer (Growth Curves USA).
RNA isolation and qRT-PCR transcriptional analysis.
Overnight C. albicans cultures were diluted to an OD600 of 0.05 in either YNB or YNB-NP (Difco). The YNB cultures were supplemented with methanol, whereas YNB-NP cultures were supplemented with either 100 μM HHQ or the methanol volume equivalent. The cultures were grown at 37°C with agitation (180 rpm) for 6 h, after which they were centrifuged at 4,000 rpm, the supernatants were discarded, and the pellets were frozen at −20°C until they were processed. RNA was isolated using the MasterPure Yeast RNA purification kit (Cambio Ltd., Cambridge, United Kingdom) according to the manufacturer's specifications and quantified using an ND-1000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, USA). Genomic DNA was enzymatically removed using Turbo DNA-free DNase (Ambion), and samples were confirmed DNA free by PCR. RNA was converted to cDNA using random primers and avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV) reverse transcriptase (Promega) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Quantitative real-time (qRT)-PCR was carried out using the Universal Probe Library (UPL) system (Roche) according to the manufacturer's specifications, and samples were normalized to C. albicans actin transcript expression (ACT1). A full list of primers and UPL probes used in this study is provided in Table S1 in the supplemental material.
Phenazine extraction.
P. aeruginosa strains were cultured as described above for 24 h, with the addition of analogues (100 μM), and pyocyanin was extracted as described previously (45). The cultures were centrifuged at 4,000 rpm for 10 min, and the cell-free supernatant (5 ml) was removed. Chloroform (3 ml) was added and mixed by vortexing. After centrifugation at 4,000 rpm for 5 min, the lower aqueous phase was transferred to 0.2 M HCl (2 ml). Samples were mixed by vortexing and centrifuged at 4,000 rpm for 5 min to separate the phases. An aliquot of the top phase (1 ml) was removed and spectrophotometrically analyzed at OD570. Phenazine production was calculated using the following formula: OD570 × 2 × 17.072, with the units expressed in micrograms per milliliter.
Promoter fusion-based expression analysis.
Promoter fusion analyses were performed in a 96-well format, with β-galactosidase activity measured as described previously (46). Briefly, overnight cultures of wild-type PAO1 pqsA-lacZ (pLP0996) and mutant strain PAO1 pqsA mutant pqsA-lacZ were diluted to an OD600 of 0.02 in LB broth. Analogues at 100 μM final concentration were added, mixed, aliquoted into 96-well plates, and incubated overnight at 37°C with shaking. The next day, OD600 values were recorded in a plate reader. Aliquots of cells (0.02 ml) were permeabilized (100 mM dibasic sodium phosphate [Na2HPO4], 20 mM KCl, 2 mM MgSO4, 0.8 mg/ml CTAB [hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide], 0.4 mg/ml sodium deoxycholate, 5.4 μl/ml β-mercaptoethanol) and added to substrate solution (60 mM Na2HPO4, 40 mM NaH2PO4, 1 mg/ml o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactoside [ONPG], 2.7 μl/ml β-mercaptoethanol). The kinetics of color development was monitored, and the reactions were stopped using 1 M NaCO3. OD420 values were recorded as described above. Miller units were calculated using the following equation; 1,000 × [(OD420/OD600) × 0.02 ml × reaction time (min)].
Cytotoxicity assay.
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release from a panel of mammalian cells was assayed as a measure of cytotoxicity using an LDH colorimetric kit (Roche) according to the manufacturer's instructions (36). Briefly, IB3-1 lung epithelial cells, A549 human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cells, DU-145 human prostate cancer cells, and HeLa cervical cancer cells were seeded onto 96-well plates and treated with methanol (control) and analogues. Following 16 h of incubation at 37°C and 5% CO2, the supernatants were removed and added to a catalyst reaction mixture in a fresh plate and further incubated at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 30 min to allow color development. After this period, the plate was analyzed on an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plate reader at OD490. Cytotoxicity was expressed as a percentage of that of cells treated with 0.1% (vol/vol) Triton (100% cytotoxicity).
Statistical analysis.
All graphs were compiled using GraphPad Prism (version 5.01) unless otherwise stated. All data were analyzed using built-in GraphPad Prism (version 5.01) functions as specified. The level of significance was set at a P value of 0.05, and post hoc comparisons between groups were performed using the Bonferroni multiple-comparison test.
RESULTS
Key modifications of the quinolone framework retain antibiofilm activity toward C. albicans.
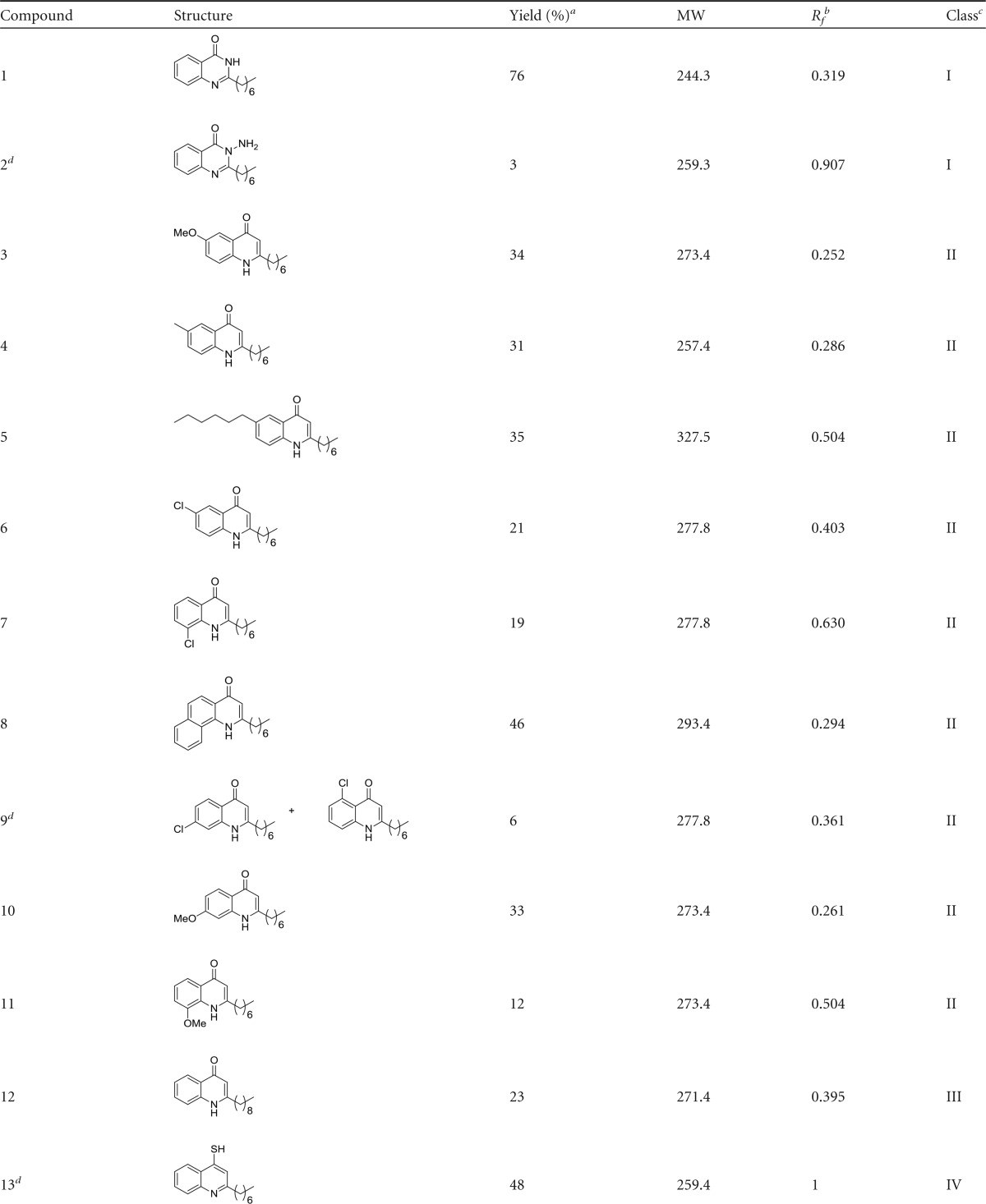
The HHQ molecule has previously been shown to suppress biofilm formation in C. albicans at concentrations from 10 to 100 μM (2.47 to 24.7 μg/ml) independent of any effects on the growth of planktonic cells (10). Previous structure-function analysis of the activity of the quinolone framework had implicated the C-3 position as a key component of interspecies antibiofilm activity (36). We undertook further modification of the HHQ parent molecule with the aim of developing viable antibiofilm compounds to target C. albicans. These compounds were incorporated into a larger collection of alkylquinolone analogues, systematically modified at different positions on the molecule, and classified on the basis of their substitutions relative to the parent framework HHQ (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Compound data
Yields were isolated over all steps.
TLC on silica plates with dichloromethane-MeOH (95:5) mobile phase.
Class I, modified C-3; class II, modified anthranilate ring; class III, modified alkyl chain; class IV, modified C-4; class V, modified anthranilate ring and alkyl chain.
New compounds synthesized in this study.
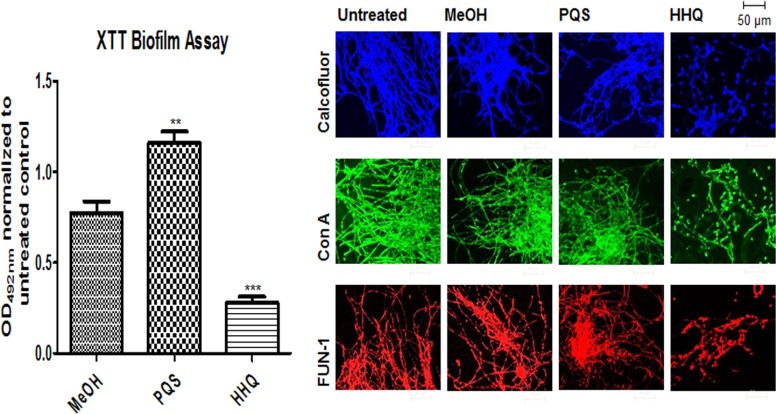
The suite of analogues was first tested to establish their potency as antibiofilm compounds against C. albicans using an optimized XTT assay, a commonly used quantitative method to assess Candida biofilm mass and growth (47). As previously described (10), HHQ significantly suppressed biofilm formation compared to untreated and methanol-treated cells, whereas PQS appeared to induce biofilm formation (Fig. 1). When all the analogues were similarly screened by XTT assay, several had antibiofilm activities similar to that of HHQ (compounds 1 and 2 [class I; modified at C-3]; 3, 4, 6, 7, and 9 [class II; modified anthranilate ring]; and 12 [class III; modified alkyl chain]) (Fig. 2a). These analogues were diverse members of classes I, II, and III, suggesting that several components of the HHQ framework contribute to the antibiofilm activity of the parent compound. A number of substitutions led to intermediate antibiofilm activity, including 5, 8, 10, and 11 (class II; modified anthranilate ring) and 15 (class V; modified anthranilate ring and alkyl chain length), while some analogues had completely lost the ability to suppress C. albicans biofilm formation, e.g., 13 (class IV; modified C-4) and the class V compounds 14, 16, and 17 (Fig. 2a). While modification of the C-3 position to produce PQS led to loss of antibiofilm activity (Fig. 1), incorporation of an -N-NH2 moiety (compound 2) at the 3 position or substitution of C-3 with NH (1) did not affect the ability to suppress C. albicans biofilm formation (Fig. 2a). Addition of chlorine (Cl) at the C-6 and C-8 positions of the anthranilate ring (compounds 6 and 7) also did not lead to loss of antibiofilm activity. In contrast, the introduction of considerable steric bulk with the addition of an n-hexyl alkyl chain at C-6 of the anthranilate ring (compound 5) or elaboration of the aromatic group, as with the naphthyl compound (compound 8), resulted in compounds with significantly less potent antibiofilm activity than HHQ. These data suggest an exquisite level of specificity for the interaction between HHQ and the C. albicans biofilm intracellular machinery. Modification of the C-2 alkyl chain from n-heptyl (HHQ) to n-nonyl C9 (compound 12) did not affect antibiofilm activity, while parallel modification of the anthranilate ring resulted in a complete loss, as with the class V compound 16 or 17. After modifying the C-4 position (C = O to C = S) (compound 13), the quinolone thiol exhibited an increase in XTT activity (P < 0.05) relative to controls (Fig. 2a), comparable to the increase observed in the presence of PQS (Fig. 1). Previously, we have shown that HHQ elicits a dose-dependent reduction in C. albicans biofilm formation (10). In order to determine if this also applied to the analogues that retain antibiofilm activity, dose-response analysis of selected compounds, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 12 representing classes I, II, and IV, was undertaken. This revealed compound-specific responses, with 10 μM compounds 2, 4, and 12 being sufficient to elicit a statistically significant reduction in biofilm formation (Fig. 2b). All five compounds reduced biofilm formation when applied at 50 μM and 100 μM. To further confirm the antibiofilm activity of the lead compounds, viable-colony counts were performed on selected analogues using the maximum 100 μM compound dose. This confirmed the outputs from the XTT assays; all the analogues, along with HHQ, significantly reduced viable biofilm cells in comparison to the control (see Fig. S1a in the supplemental material). Importantly, the antibiofilm activity was found to be independent of planktonic growth, which was unaffected in the presence of selected compounds (see Fig. S1b in the supplemental material).
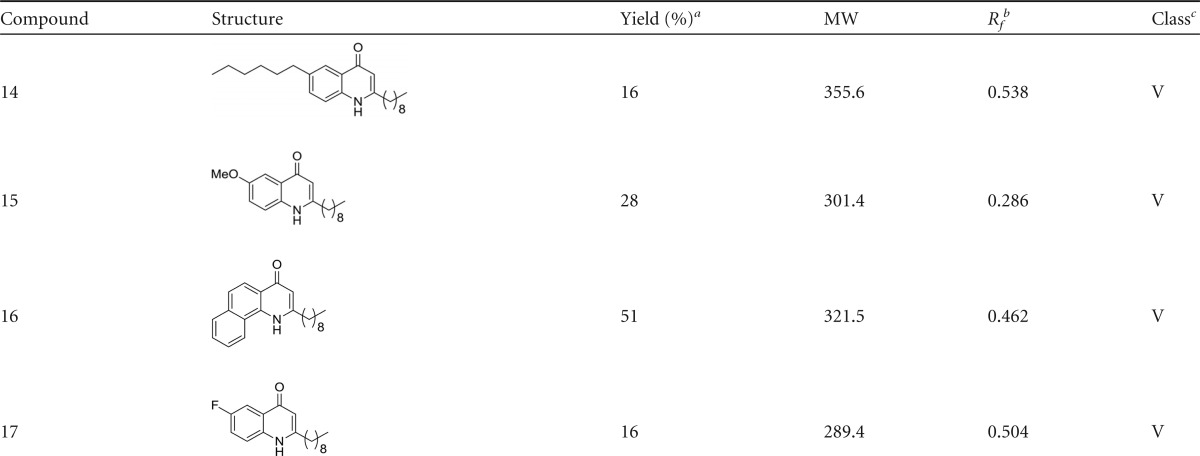
FIG 1.
C. albicans biofilms are altered in the presence of HHQ. Filamentous C. albicans biofilms grown in the presence of PQS and HHQ (100 μM) were assessed structurally by confocal microscopy and metabolically using the XTT biofilm assay. The data (means and standard errors of the mean [SEM]) are representative of three independent biological experiments and are presented relative to the untreated control. A two-tailed paired Student t test was performed by comparison of C. albicans in the presence of HHQ and PQS with C. albicans treated with methanol or ethanol (**, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001). ConA, concanavalin A.
FIG 2.
Decoration of HHQ exhibits variable biofilm activity against C. albicans. (a) A panel of HHQ-derivatized analogues were incubated with filamentous C. albicans and screened for biofilm formation using the metabolic XTT biofilm assay. The data are presented as OD492 spectrophotometric output normalized to the untreated control and are representative of at least three independent biological replicates, with error bars representing SEM. (b) Dose-dependent XTT analysis of selected antibiofilm compounds applied at 10, 50, and 100 μM. The data are the averages from at least two independent biological replicates, each constituting eight technical replicates. Statistical analysis of both data sets was performed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni corrective testing, and the results are presented relative to the MeOH control values; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.
Microscopic staining reveals structural changes in C. albicans biofilms.
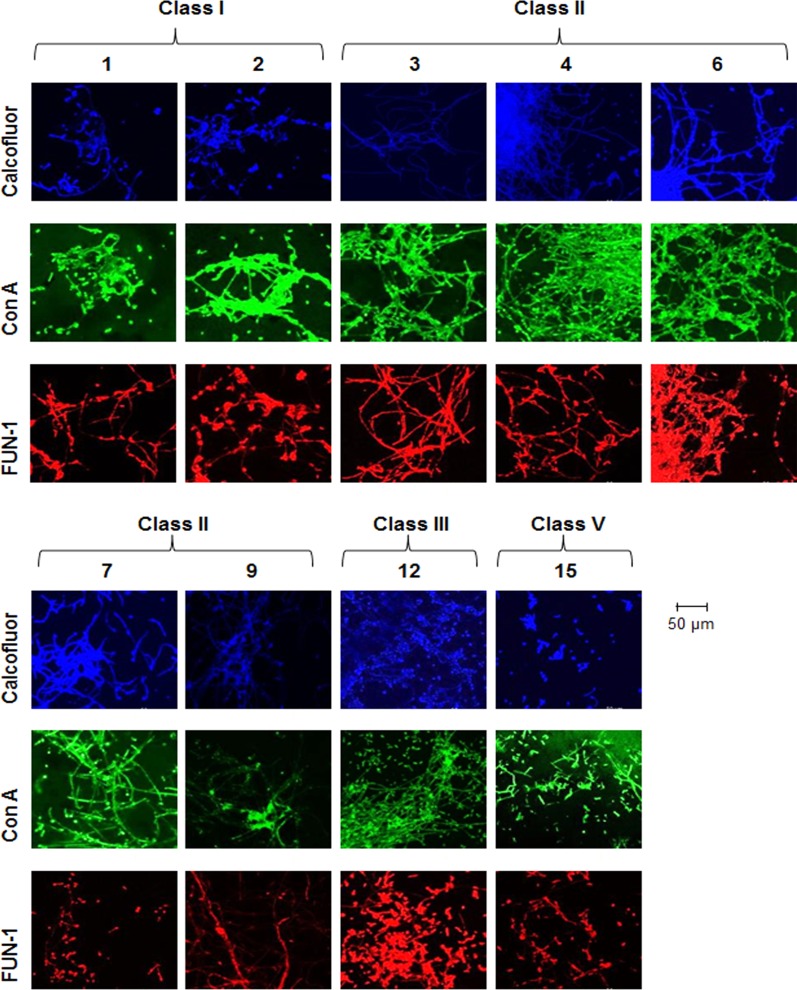
The formation of biofilms in bacteria, yeasts, and fungi is a highly ordered process involving multicellular behavior and has been defined in several stages (22). Confocal microscopy combined with intracellular staining was used to assess the structural integrity and cellular morphology of C. albicans incubated on coverslips. Biofilms were individually stained with each of the dyes, and multiple fields of view were visualized to accurately represent the effects of the analogues. The biofilms observed for methanol-treated and untreated controls displayed all the characteristics of a typical C. albicans biofilm and were classified as wild type (Fig. 1). Calcofluor, concanavalin A, and FUN-1 staining revealed uniform distribution of chitin/cellulose and cell wall mannosyl/glucosyl residues indicative of viable wild-type morphology (Fig. 1). The analogues identified by XTT assay as causing impaired biofilm formation (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 12, and 15) exhibited markedly disrupted structures when grown on coverslips and were classified as atypical morphologies (Fig. 3). Cells treated with class I analogues were found to be largely compromised in their biofilm-forming capabilities and were classified as morphologically atypical. Biofilms produced with both 1 and 2 were significantly distorted, displaying a spindle-like phenotype. Hyphae were short and predominantly displayed yeast cell types rather than hyphal structures. Other structure-disrupting analogues were from classes II, III, and V, suggesting that specific modifications on the anthranilate ring and alkyl chain variation do not significantly affect the antibiofilm activity compared to the parent compound (Fig. 3).
FIG 3.
Microscopic analysis reveals altered biofilm structures. Analogues that lead to reduced C. albicans biofilm formation in the XTT assay (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 12, and 15) exhibit compromised biofilm structures. Filamentous C. albicans biofilm in the presence of analogues (100 μM) was stained for chitin and cellulose (calcofluor; blue); lectins that bind to sugars, glycolipids, and glycoproteins (concanavalin A; green); and live/dead cells (FUN-1; red).
Some analogues, including those that exhibited intermediate activity in the XTT assay, did not alter the biofilm structure, with 5, 11, 13, 14, and 16 all placed into the wild-type morphology group. Biofilms formed in the presence of compound 13 showed hyperproduction of short hyphae, creating a dense mycelial network (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). The remaining analogues from class II, 8 and 10 (see Fig. S1a in the supplemental material), caused significant biofilm disruption, with fragmented hyphae, stunted vegetative growth, and quite large cell debris fields. Cells incubated with the class V molecule 17 induced a severely compromised phenotype (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material) where debris fields comprising yeast cells and blastospores characterized the structural phenotype.
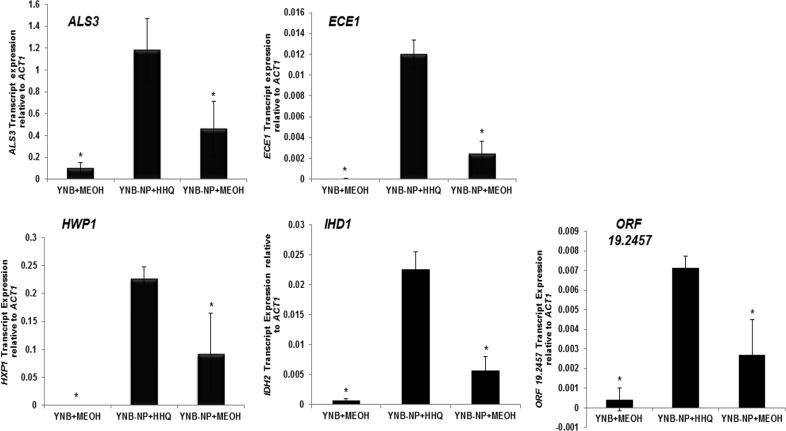
Enhanced gene transcript expression of HWP1, ECE1, ALS3, IHD1, and the uncharacterized open reading frame (ORF) orf19.2457 provides a molecular mechanism for alkyl quinolone activity toward C. albicans.
In addition to providing new insights into the interkingdom relationship between these important pathogens, strong emphasis has recently been placed on ligand-receptor interactions and the need to provide molecular mechanisms for the action of any potential therapeutic compound (48). We previously implicated TUP1 in the HHQ-mediated suppression of biofilm formation in C. albicans, suggesting a role for the cell wall in this interaction (10, 16). More recently, several reports have shown changes in expression of cell wall-associated genes linked to biofilm formation in the organism (16, 20, 28, 49–51). They included a cohort of eight genes that are proposed to constitute the core filamentous response network, namely, ALS3, ECE1, HGT2, HWP1, IHD1, RBT1, DCK1, and the orf19.2457 gene with unknown function (51). Therefore, transcript expression of a cohort of genes implicated in cell wall biogenesis, hyphal development, biofilm formation, and other related functions that were previously shown to be upregulated during the morphological transition from yeast to filamentous growth was investigated (see Table S1 in the supplemental material) (16, 51). The housekeeping gene ACT1 was chosen for normalization based on previous biofilm studies (52). We observed that several transcripts were hyperexpressed in an HHQ-dependent manner, specifically, HWP1, ECE1, ALS3, IDH1, and the as yet uncharacterized orf19.2457 (Fig. 4). The remaining transcripts (CPH1, EFB1, ESS1, RBT1, TUP1, BCR1, DCK1, and HGT2) yielded expression patterns similar to those of control cells (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). It was perhaps somewhat surprising that, while treatment of C. albicans with P. aeruginosa supernatants has previously been shown to downregulate expression of the RBT1, RBT5, and RBT8 genes (16), expression of RBT1 was unaltered in the presence of HHQ (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). Taken together, these data suggest that HHQ induces a specific subset of cell wall proteins in C. albicans. Further work is needed to identify the upstream components of this response, although in silico screening of C. albicans genome sequences has ruled out the presence of an obvious PQS receptor (unpublished data).
FIG 4.
Hyphal pathway genes are hyperexpressed in response to HHQ. Transcript expression analysis (real-time RT-PCR) of a panel of biofilm genes was assessed in C. albicans grown in YNB-NP (filament-inducing medium) in 100 μM HHQ for 6 h at 37°C. All the data were normalized to a housekeeping gene (ACT1). The error bars represent standard deviations (SD) of three independent biological replicates. A two-tailed paired Student t test was performed by comparison of HHQ-treated cells with methanol control in YNB-NP inducing medium (*, P ≤ 0.05).
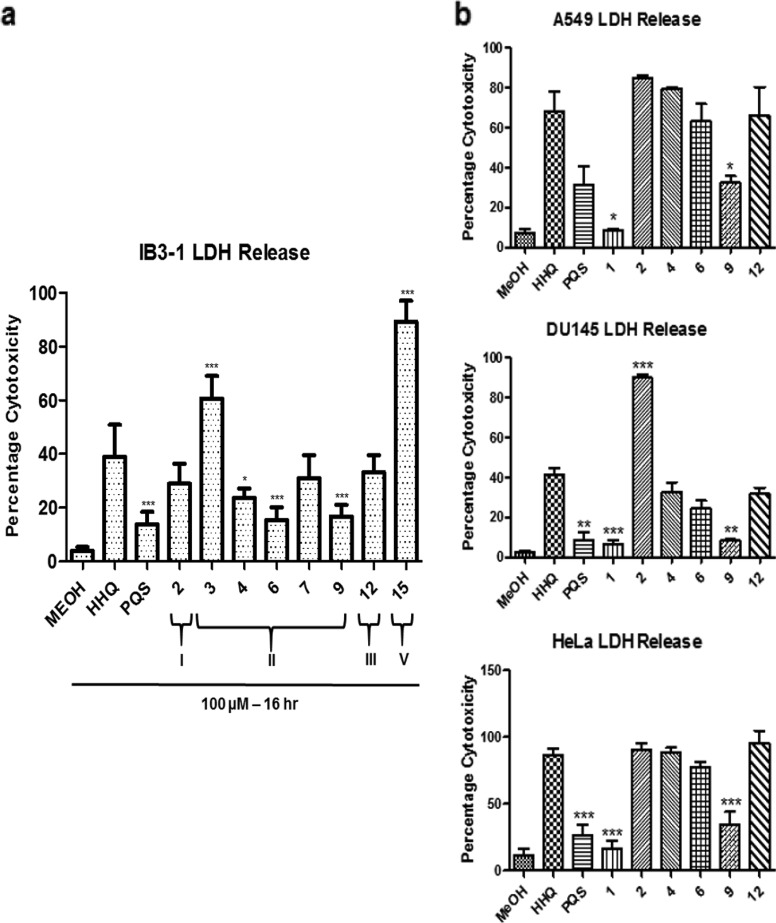
Lead compounds display reduced cytotoxic activity toward specific mammalian cell lines.
Evaluating the cytotoxicity of synthetic compounds is crucial in the context of developing targeted and highly optimized molecular therapeutics that are benign to human cellular physiology and ideal for use in a clinical environment. In previous work, we showed that analogue 1 was significantly less cytotoxic than HHQ, with an 80% reduction in LDH release relative to the parent compound (36). Therefore, the suite of analogues was tested for in vitro cytotoxicity toward IB3-1 airway epithelial cells. Class I analogues exhibited reduced cytotoxicity to IB3-1 cells, with compound 2 displaying approximately 34% toxicity (Fig. 5a). Several class II analogues (4, 6, and 9) exhibited reduced cytotoxicity relative to IB3-1 cells treated with HHQ, with 7 not reaching statistical significance. The class III analogue 12 was comparable to HHQ. Of the analogues that did not retain antibiofilm activity, 5, 8, 10, and 11 exhibited variable cytotoxicity to IB3-1 cells, whereas 13 exhibited considerably reduced cytotoxicity to IB3-1 cells (see Fig. S4 in the supplemental material). Finally, compound 16 exhibited very low levels of cytotoxicity, while 17 was reduced relative to HHQ-treated cells. Compound 15 was the most toxic, killing approximately 91% of all cells (Fig. 5a).
FIG 5.
Cytotoxicity toward specific mammalian cell lines is reduced in lead compounds. (a) Cytotoxicity, measured as a percentage of total LDH released from IB3-1 cells treated with 0.1% Triton X-100 (100% cytotoxicity), was significantly reduced in the presence of several lead compounds. The data (means and SEM) are representative of three independent biological experiments. (b) Selected lead compounds were tested against A549, DU145, and HeLa cell lines. The data represent four independent biological replicates, and all the data points are normalized to Triton X-100 as described for panel a. One-way ANOVA was performed, with Bonferroni corrective testing on all data sets, and comparison to an MeOH control is presented; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.
In order to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the selective toxicity of the lead compounds, several additional cell lines were tested (Fig. 5b). LDH release assays were performed in A549, DU145, and HeLa cell lines in the presence of 100 μM of the lead compounds and revealed distinct cytotoxicity profiles, with 1 and 9 consistently proving the least cytotoxic of the compounds tested. Compounds 4 and 6 exhibited reduced cytotoxicity in DU145 cells (although not statistically significant) but were comparable to HHQ in both the A549 and HeLa cell lines, while compound 2 exhibited increased cytotoxicity relative to HHQ in DU145 cells (Table 2). These data suggest that cell-specific cytotoxicity analysis will need to be performed prior to the introduction of these compounds in an applied setting.
TABLE 2.
Selective toxicity indices of lead compounds
| Compound | Selective toxicity index (% toxicity) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IB3-1 | A549 | DU145 | HeLa | |
| HHQ | 26–50 | 51–75 | 26–50 | 76–100 |
| PQS | 0–25 | 26–50 | 0–25 | 0–25 |
| 1 | 0–25 | 0–25 | 0–25 | 0–25 |
| 2 | 26–50 | 76–100 | 76–100 | 76–100 |
| 4 | 0–25 | 76–100 | 26–50 | 76–100 |
| 6 | 26–50 | 51–75 | 0–25 | 76–100 |
| 9 | 0–25 | 26–50 | 0–25 | 26–50 |
| 12 | 26–50 | 51–75 | 26–50 | 76–100 |
HHQ analogues display a spectrum of agonist activity toward P. aeruginosa virulence.
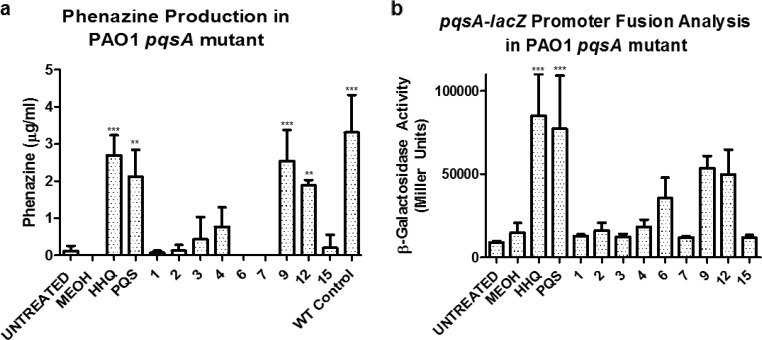
Taken together, compounds 1, 4, 6, and 9 pass both the first and second criteria described above, i.e., they retain antibiofilm activity toward C. albicans while exhibiting reduced selective cytotoxicity toward specific host cell lines. However, both HHQ and PQS are coinducers of the virulence-associated LysR-type transcriptional regulator PqsR (41). The structural moieties that underpin the interaction between HHQ/PQS and PqsR remain to be fully characterized, although recent studies have reported diverse classes of PqsR antagonists (53–55) and implicated the hydrophobic pocket situated within the PqsR protein (56). Therefore, in order to assess whether the lead compounds could elicit a virulence response from P. aeruginosa, phenazine production and pqsA promoter activity (57) were monitored in a pqsA mutant where the capacity to produce native HHQ and PQS had been lost.
Both HHQ and PQS restored phenazine production in the pqsA mutant strain (Fig. 6a). In contrast, the majority of analogues did not restore phenazine production in the strain, with the notable exception of compound 9. Several analogues from different classes did partially restore phenazine production in the mutant background, including compounds 10, 12, and 17 (Fig. 6; see Fig. S5 in the supplemental material). None of the analogues interfered with phenazine production in the wild-type PAO1 strain, suggesting that they are ineffective as PQS antagonists (see Fig. S5 in the supplemental material).
FIG 6.
Influence of HHQ analogues on PQS-dependent virulence phenotypes in P. aeruginosa. Phenazine production (a) and pqsA-lacZ promoter activity (b) were quantified in a PAO1 pqsA mutant in the presence of HHQ, PQS, and lead compounds. The data are presented as means and SEM and are representative of at least three independent biological replicates. One-way ANOVA was performed, with Bonferroni corrective testing, and statistical significance relative to the MeOH control is presented; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.
Similarly, while some degree of PqsR agonist activity was observed in the presence of compounds 6, 9, 10, 12, 13, and 17, only HHQ and PQS significantly induced promoter activity. All the other analogues did not influence promoter activity in this system (Fig. 6B; see Fig. S5 in the supplemental material). Somewhat surprisingly, antagonistic activity toward pqsA promoter activity was not observed, with almost all the analogues failing to significantly suppress pqsA promoter activity in the wild-type strain (see Fig. S5 in the supplemental material). The relative ineffectiveness of these analogues as PQS antagonists may in part be due to hydroxylation of HHQ analogues (H at C-3) to PQS analogues (OH at C-3), thus establishing the nonantagonistic behavior explained by a recent report by Lu and colleagues, where the action of PqsH rendered anti-PQS compounds ineffective through bioconversion (55).
DISCUSSION
Current antimicrobial therapies tend to be non-pathogen specific, and there is evidence to suggest that the availability of relatively nontoxic broad-spectrum therapies has contributed to the emergence of resistance among both targeted and nontargeted microbes (58, 59). Consequently, there is an urgent need to create innovative new options for the targeted prevention of microbial infection while avoiding the inevitable emergence of resistance that is the hallmark of broad-spectrum antibiotic therapies (59, 60). Increasingly, industry, academia, and regulatory bodies have become interested in single-pathogen therapies to treat highly resistant or totally resistant bacterial pathogens, rightly viewed as an area of high unmet need (61–63). Exploiting interkingdom communication networks, and the mode of action of the chemical messages or signals employed therein, offers us a powerful platform from which to meet this need.
Previously, we showed that the HHQ interkingdom signal molecule from P. aeruginosa could suppress biofilm formation in C. albicans at concentrations ranging from 10 to 100 μM (2.47 to 24.7 μg/ml) (10). This suppression occurred independently of any growth limitation in planktonic cells, and morphogenesis on spider medium was also found to be unaffected (10). The design and subsequent analysis of a suite of analogues based on the core HHQ quinolone framework has led to the identification of several lead compounds that retain antibiofilm activity toward C. albicans but exhibit significantly reduced cytotoxicity toward IB3-1 epithelial cells compared with the parent HHQ molecule. The selective cytotoxicities of the lead compounds, together with the dose-dependent antibiofilm effects, will be key considerations in determining the cell line-specific therapeutic index of lead analogues as part of the ongoing development of these compounds. Furthermore, unlike HHQ, these lead compounds are now inactive toward the P. aeruginosa PqsR quorum-sensing system, a critical requirement for their potential future development as antibiofilm therapeutics. In addition, the ability to generate hydrochloride salts of the compounds (reference 36 and data not shown) suggests that the solubility of future therapeutics based on these scaffolds will not be a bottleneck. Several strategies have been proposed for the implementation of antibiofilm compounds as clinical therapeutics to target C. albicans biofilm infections (64). As the HHQ analogues possess antibiofilm, but not anti-Candida, activity, they would disrupt the formation of biofilms but not likely remove the planktonic cells that remain at the site of infection. Therefore, combination with conventional antifungal compounds would be required for effective clearance. Alternatively, where the potency of the antibiofilm activity can be synthetically enhanced through further derivatization, clearance by the immune system might also be realistic.
The molecular mechanisms through which AHQs and the lead compounds identified in this study disrupt the formation of biofilms by C. albicans remain to be fully elucidated. Previously, we have shown that HHQ does not affect adhesion, but rather directly impacts the subsequent developmental stages in a TUP1-dependent manner (10). In this study, we have shown that the expression of several cell wall-associated genes is increased in response to HHQ during the switch to hyphal growth. These genes have previously been implicated in the formation of C. albicans biofilms and have been shown to exhibit increased levels of expression during the hyphal transition (50, 51, 65). Therefore, antibiofilm compounds might be expected to suppress this induction rather than enhance it. However, five of the target genes tested exhibited an increase in expression relative to control cells under inducing conditions. This may be a reflection of the previous observation that HHQ interferes with the later stages of biofilm development (10). Alternatively, this hyperexpression phenotype may affect the capacity of the cell to engineer a community-based biofilm. Future studies will focus on elucidating the pathways through which C. albicans perceives and responds to challenge with HHQ with the aim of identifying potential therapeutic targets.
Further work using defined in vivo models of biofilms and infection will be required to further the development and evaluation of these small molecules as antibiofilm compounds. Models are now available for the investigation of infections involving medical devices, such as vascular catheters, dentures, urinary catheters, and subcutaneous implants, as well as mucosal biofilm infections (66). The ongoing development of cell-based or animal models to study in vivo infections (66–69), whether as single-pathogen or coculture systems (70), has provided a well-equipped tool kit for the preclinical assessment of these AHQ-based compounds.
Conclusions.
In this study, we have functionalized the important microbial signaling molecules HHQ and PQS in order to exploit their interkingdom roles in controlling biofilm formation in C. albicans. In addition to deciphering further insights into the molecular mechanism through which these chemical messages elicit a biofilm-suppressive response from C. albicans, the bioactivity of several lead compounds has provided a viable platform for the development of next-generation therapeutics. Crucially, some of these compounds are nontoxic to mammalian cells and have been rendered incapable of activating P. aeruginosa virulence systems, thus highlighting their potential utility as an effective therapy combatting human infection.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
F.J.R., G.P.M., and F.O. conceived and designed the investigation. F.J.R., J.P.P., L.G., and D.F.W. performed the biological experimentation, while R.C., R.M.S., and E.O.M. conducted the chemical synthesis. F.J.R., J.P.P., and F.O. wrote the manuscript, and we all read and edited the final draft.
Funding Statement
G.P.M. thanks the Irish Research Council (R.M.S. and R.C.) and the UCC Strategic Research Fund (E.O.M.). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00190-16.
REFERENCES
- 1.Cooper MA, Shlaes D. 2011. Fix the antibiotics pipeline. Nature 472:32. doi: 10.1038/472032a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and Europrean Medicines Agency. 2009. The bacterial challenge: time to react. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and Europrean Medicines Agency, Stockholm, Sweden. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Spellberg B, Powers JH, Brass EP, Miller LG, Edwards JE Jr. 2004. Trends in antimicrobial drug development: implications for the future. Clin Infect Dis 38:1279–1286. doi: 10.1086/420937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bjarnsholt T, Ciofu O, Molin S, Givskov M, Hoiby N. 2013. Applying insights from biofilm biology to drug development; can a new approach be developed? Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:791–808. doi: 10.1038/nrd4000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Davies D. 2003. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:114–122. doi: 10.1038/nrd1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dong YH, Wang LH, Xu JL, Zhang HB, Zhang XF, Zhang LH. 2001. Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserine lactonase. Nature 411:813–817. doi: 10.1038/35081101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fux CA, Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Stoodley P. 2005. Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol 13:34–40. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hoiby N, Ciofu O, Johansen HK, Song ZJ, Moser C, Jensen PO, Molin S, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T, Bjarnsholt T. 2011. The clinical impact of bacterial biofilms. Int J Oral Sci 3:55–65. doi: 10.4248/IJOS11026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rasmussen TB, Givskov M. 2006. Quorum sensing inhibitors: a bargain of effects. Microbiology 152:895–904. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28601-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Reen FJ, Mooij MJ, Holcombe LJ, McSweeney CM, McGlacken GP, Morrissey JP, O'Gara F. 2011. The Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS), and its precursor HHQ, modulate interspecies and interkingdom behaviour. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 77:413–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rutherford ST, Bassler BL. 2012. Bacterial quorum sensing: its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a012427. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ternent L, Dyson RJ, Krachler AM, Jabbari S. 2015. Bacterial fitness shapes the population dynamics of antibiotic-resistant and -susceptible bacteria in a model of combined antibiotic and anti-virulence treatment. J Theor Biol 372:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cox CE, McClelland M, Teplitski M. 2013. Consequences of disrupting Salmonella AI-2 signaling on interactions within soft rots. Phytopathology 103:352–361. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-09-12-0237-FI. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dong YH, Gusti AR, Zhang Q, Xu JL, Zhang LH. 2002. Identification of quorum-quenching N-acyl homoserine lactonases from Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1754–1759. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.4.1754-1759.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hentzer M, Riedel K, Rasmussen TB, Heydorn A, Andersen JB, Parsek MR, Rice SA, Eberl L, Molin S, Hoiby N, Kjelleberg S, Givskov M. 2002. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 148:87–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Holcombe LJ, McAlester G, Munro CA, Enjalbert B, Brown AJ, Gow NA, Ding C, Butler G, O'Gara F, Morrissey JP. 2010. Pseudomonas aeruginosa secreted factors impair biofilm development in Candida albicans. Microbiology 156:1476–1486. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.037549-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Janssens JC, Steenackers H, Robijns S, Gellens E, Levin J, Zhao H, Hermans K, De Coster D, Verhoeven TL, Marchal K, Vanderleyden J, De Vos DE, De Keersmaecker SC. 2008. Brominated furanones inhibit biofilm formation by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6639–6648. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01262-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.O'Loughlin CT, Miller LC, Siryaporn A, Drescher K, Semmelhack MF, Bassler BL. 2013. A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:17981–17986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1316981110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zambelloni R, Marquez R, Roe AJ. 2015. Development of antivirulence compounds: a biochemical review. Chem Biol Drug Des 85:43–55. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Desai JV, Mitchell AP, Andes DR. 2014. Fungal biofilms, drug resistance, and recurrent infection. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 4:a019729. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a019729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Perlroth J, Choi B, Spellberg B. 2007. Nosocomial fungal infections: epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Med Mycol 45:321–346. doi: 10.1080/13693780701218689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ramage G, Rajendran R, Sherry L, Williams C. 2012. Fungal biofilm resistance. Int J Microbiol 2012:528521. doi: 10.1155/2012/528521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Feldman M, Shenderovich J, Al-Quntar AA, Friedman M, Steinberg D. 2015. Sustained release of a novel anti-quorum-sensing agent against oral fungal biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:2265–2272. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04212-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Moudgal V, Sobel J. 2010. Antifungals to treat Candida albicans. Expert Opin Pharmacother 11:2037–2048. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2010.493875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chandra J, Mukherjee P, Ghannoum A. 2012. Candida biofilms associated with CVC and medical devices. Mycoses 55:46–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2011.02149.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lynch AS, Robertson GT. 2008. Bacterial and fungal biofilm infections. Annu Rev Med 59:415–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.59.110106.132000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bink A, Pellens K, Cammue BPA, Thevissen K. 2011. Anti-biofilm strategies: how to eradicate candida biofilms. Open Mycol J 5:29–38. doi: 10.2174/1874437001105010029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Finkel JS, Xu W, Huang D, Hill EM, Desai JV, Woolford CA, Nett JE, Taff H, Norice CT, Andes DR, Lanni F, Mitchell AP. 2012. Portrait of Candida albicans adherence regulators. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002525. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Miceli MH, Bernardo SM, Lee SA. 2009. In vitro analyses of the combination of high-dose doxycycline and antifungal agents against Candida albicans biofilms. Int J Antimicrob Agents 34:326–332. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bose S, Ghosh AK. 2011. Biofilms: a challenge to medical science. J Clin Diagn Res 5:127–130. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Peleg AY, Hogan DA, Mylonakis E. 2010. Medically important bacterial-fungal interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:340–349. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wargo MJ, Hogan DA. 2006. Fungal-bacterial interactions: a mixed bag of mingling microbes. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:359–364. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cugini C, Morales DK, Hogan DA. 2010. Candida albicans-produced farnesol stimulates Pseudomonas quinolone signal production in LasR-defective Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Microbiology 156:3096–3107. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.037911-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hodgkinson JT, Galloway WR, Saraf S, Baxendale IR, Ley SV, Ladlow M, Welch M, Spring DR. 2011. Microwave and flow syntheses of Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) and analogues. Org Biomol Chem 9:57–61. doi: 10.1039/C0OB00652A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mashburn-Warren L, Howe J, Brandenburg K, Whiteley M. 2009. Structural requirements of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal for membrane vesicle stimulation. J Bacteriol 191:3411–3414. doi: 10.1128/JB.00052-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Reen FJ, Clarke SL, Legendre C, McSweeney CM, Eccles KS, Lawrence SE, O'Gara F, McGlacken GP. 2012. Structure-function analysis of the C-3 position in analogues of microbial behavioural modulators HHQ and PQS. Org Biomol Chem 10:8903–8910. doi: 10.1039/c2ob26823j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Reen FJ, Shanahan R, Cano R, O'Gara F, McGlacken GP. 2015. A structure activity-relationship study of the bacterial signal molecule HHQ reveals swarming motility inhibition in Bacillus atrophaeus. Org Biomol Chem 13:5537–5541. doi: 10.1039/C5OB00315F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Deziel E, Lepine F, Milot S, He J, Mindrinos MN, Tompkins RG, Rahme LG. 2004. Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) reveals a role for 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline in cell-to-cell communication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:1339–1344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307694100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Diggle SP, Matthijs S, Wright VJ, Fletcher MP, Chhabra SR, Lamont IL, Kong X, Hider RC, Cornelis P, Camara M, Williams P. 2007. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-quinolone signal molecules HHQ and PQS play multifunctional roles in quorum sensing and iron entrapment. Chem Biol 14:87–96. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.11.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McGlacken GP, McSweeney CM, O'Brien T, Lawrence SE, Elcoate CJ, Reen FJ, O'Gara F. 2010. Synthesis of 3-halo-analogues of HHQ, subsequent cross-coupling and first crystal structure of Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS). Tetrahedron Lett 51:5919–5921. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2010.09.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pesci EC, Milbank JB, Pearson JP, McKnight S, Kende AS, Greenberg EP, Iglewski BH. 1999. Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:11229–11234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.20.11229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fletcher MP, Diggle SP, Camara M, Williams P. 2007. Biosensor-based assays for PQS, HHQ and related 2-alkyl-4-quinolone quorum sensing signal molecules. Nat Protoc 2:1254–1262. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ramage G, Vande Walle K, Wickes BL, Lopez-Ribot JL. 2001. Standardized method for in vitro antifungal susceptibility testing of Candida albicans biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:2475–2479. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.9.2475-2479.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hawser S. 1996. Comparisons of the susceptibilities of planktonic and adherent Candida albicans to antifungal agents: a modified XTT tetrazolium assay using synchronised C-albicans cells. J Med Vet Mycol 34:149–152. doi: 10.1080/02681219680000231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Essar DW, Eberly L, Hadero A, Crawford IP. 1990. Identification and characterization of genes for a second anthranilate synthase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: interchangeability of the two anthranilate synthases and evolutionary implications. J Bacteriol 172:884–900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Miller JH. 1972. Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Nett JE, Cain MT, Crawford K, Andes DR. 2011. Optimizing a Candida biofilm microtiter plate model for measurement of antifungal susceptibility by tetrazolium salt assay. J Clin Microbiol 49:1426–1433. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02273-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Baell J, Walters MA. 2014. Chemistry: chemical con artists foil drug discovery. Nature 513:481–483. doi: 10.1038/513481a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bandara HM, Cheung BP, Watt RM, Jin LJ, Samaranayake LP. 2013. Secretory products of Escherichia coli biofilm modulate Candida biofilm formation and hyphal development. J Investig Clin Dent 4:186–199. doi: 10.1111/jicd.12048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Finkel JS, Mitchell AP. 2011. Genetic control of Candida albicans biofilm development. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:109–118. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Martin R, Albrecht-Eckardt D, Brunke S, Hube B, Hunniger K, Kurzai O. 2013. A core filamentation response network in Candida albicans is restricted to eight genes. PLoS One 8:e58613. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nailis H, Coenye T, Van Nieuwerburgh F, Deforce D, Nelis HJ. 2006. Development and evaluation of different normalization strategies for gene expression studies in Candida albicans biofilms by real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 7:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-7-25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Klein T, Henn C, de Jong JC, Zimmer C, Kirsch B, Maurer CK, Pistorius D, Muller R, Steinbach A, Hartmann RW. 2012. Identification of small-molecule antagonists of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa transcriptional regulator PqsR: biophysically guided hit discovery and optimization. ACS Chem Biol 7:1496–1501. doi: 10.1021/cb300208g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lu C, Kirsch B, Zimmer C, de Jong JC, Henn C, Maurer CK, Musken M, Haussler S, Steinbach A, Hartmann RW. 2012. Discovery of antagonists of PqsR, a key player in 2-alkyl-4-quinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem Biol 19:381–390. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lu C, Maurer CK, Kirsch B, Steinbach A, Hartmann RW. 2014. Overcoming the unexpected functional inversion of a PqsR antagonist in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: an in vivo potent antivirulence agent targeting pqs quorum sensing. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53:1109–1112. doi: 10.1002/anie.201307547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ilangovan A, Fletcher M, Rampioni G, Pustelny C, Rumbaugh K, Heeb S, Camara M, Truman A, Chhabra SR, Emsley J, Williams P. 2013. Structural basis for native agonist and synthetic inhibitor recognition by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing regulator PqsR (MvfR). PLoS Pathog 9:e1003508. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.McGrath S, Wade DS, Pesci EC. 2004. Dueling quorum sensing systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa control the production of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS). FEMS Microbiol Lett 230:27–34. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00849-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Casadevall A. 1996. Crisis in infectious diseases: time for a new paradigm? Clin Infect Dis 23:790–794. doi: 10.1093/clinids/23.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Casadevall A. 2009. The case for pathogen-specific therapy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 10:1699–1703. doi: 10.1517/14656560903066837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Spellberg B, Rex JH. 2013. The value of single-pathogen antibacterial agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:963. doi: 10.1038/nrd3957-c1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.European Medicines Agency. 2012. Addendum to the note for guidance on evaluation of medicinal products indicated for treatment of bacterial infections (CPMP/EWP/558/95 REV 2) to address indication-specific clinical data. European Medicines Agency, London, United Kingdom. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Alemayehu D, Quinn J, Cook J, Kunkel M, Knirsch CA. 2012. A paradigm shift in drug development for treatment of rare multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens. Clin Infect Dis 55:562–567. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2012. White paper: recommendations on the conduct of superiority and organism-specific clinical trials of antibacterial agents for the treatment of infections caused by drug-resistant bacterial pathogens. Clin Infect Dis 55:1031–1046. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Nett JE. 2014. Future directions for anti-biofilm therapeutics targeting Candida. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 12:375–382. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2014.885838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Desai JV, Mitchell AP. 2015. Candida albicans biofilm development and its genetic control. Microbiol Spectr 3. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0005-2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Nett JE, Andes DR. 2015. Fungal biofilms: in vivo models for discovery of anti-biofilm drugs. Microbiol Spectr 3. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0008-2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Chauhan A, Bernardin A, Mussard W, Kriegel I, Esteve M, Ghigo JM, Beloin C, Semetey V. 2014. Preventing biofilm formation and associated occlusion by biomimetic glycocalyxlike polymer in central venous catheters. J Infect Dis 210:1347–1356. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Chauhan A, Ghigo JM, Beloin C. 2016. Study of in vivo catheter biofilm infections using pediatric central venous catheter implanted in rat. Nat Protoc 11:525–541. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kucharikova S, Neirinck B, Sharma N, Vleugels J, Lagrou K, Van Dijck P. 2015. In vivo Candida glabrata biofilm development on foreign bodies in a rat subcutaneous model. J Antimicrob Chemother 70:846–856. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sobue T, Diaz P, Xu H, Bertolini M, Dongari-Bagtzoglou A. 2016. Experimental models of C. albicans-streptococcal coinfection. Methods Mol Biol 1356:137–152. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3052-4_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.