Abstract
Central nervous system-based cancers have a much higher mortality rate with the 2016 estimates at 6.4 for incidence and 4.3 for deaths per 100,000 individuals. Grade IV astrocytomas, known as glioblastomas are highly aggressive and show a high proliferation index, diffused infiltration, angiogenesis, microvascular proliferation and pleomorphic vessels, resistance to apoptosis, and pseudopalisading necrosis. Extensive hypoxic regions in glioblastomas contribute to the highly malignant phenotype of these tumors. Hypoxic regions of glioblastoma exacerbate the prognosis and clinical outcomes of the patients as hypoxic tumor cells are resistant to chemo- and radiation therapy and are also protected by the malfunctional vasculature that developed due to hypoxia. Predominantly, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor, transforming growth factor-β, epidermal growth factor receptor and PI3 kinase/Akt signaling systems are involved in tumor progression and growth. Glioblastomas are predominantly glycolytic and hypoxia-induced factors are useful in the metabolic reprogramming of these tumors. Abnormal vessel formation is crucial in generating pseudopalisading necrosis regions that protect cancer stem cells residing in that region from therapeutic agents and this facilitates the cancer stem cell niche to expand and contribute to cell proliferation and tumor growth. Therapeutic approaches that target hypoxia-induced factors, such as use of the monoclonal antibody against VEGF, bevacizumab, have been useful only in stabilizing the disease but failed to increase overall survival. Hypoxia-activated TH-302, a nitroimidazole prodrug of cytotoxin bromo-isophosphoramide mustard, appears to be more attractive due to its better beneficial effects in glioblastoma patients. A better understanding of the hypoxia-mediated protection of glioblastoma cells is required for developing more effective therapeutics.
Keywords: glioblastoma, astrocytoma, hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, vascular endothelial growth factor, pseudopalisading necrosis, cancer stem cells
1. Introduction
Central nervous system (CNS)-based cancers account for approximately 1.4% of all cancers worldwide and account for proportionally more deaths, i.e., 2.7% among cancer-related mortalities (1). Estimates for incidence of CNS cancer in 2016 were 6.4/100,000 individuals and for deaths this was 4.3/100,000 (2). Notably, of the many types of cells in CNS, most of the malignant tumors in brain originate from astrocytes. There are four distinct types of astrocytomas, classified on the basis of microscopic characteristics, grades (I–IV). Only the relatively rare grade I astrocytomas are curable while the other gliomas are incurable. Although grade III and IV gliomas are considered high-grade gliomas, only grade IV glioma is commonly known as glioblastoma multiforme. Glioblastomas show a high mitotic/proliferation index, diffused infiltration, angiogenesis, microvascular proliferation and pleomorphic vessel resistance to apoptosis, nuclear atypia, and pseudopalisading necrosis (3,4). Gliomas progress with time from the time of diagnosis to aggressiveness and approximately 90% of astrocytoma present de novo as a glioblastoma. From the stage of glioblastoma occurrence, there is a poor survival rate, with a median of 16 months and survival rate of approximately 3% (5). It is extremely difficult to eliminate the glioblastoma even with total resection, as tumor cells persist microscopically, with tumor recurrence occurring in 90% of the patients at the original tumor location (6). The frequently seen extensive hypoxic regions in glioblastomas contribute to the highly malignant phenotype of these tumors, exacerbating the prognosis and clinical outcomes of the patients. Hypoxic tumor cells are more resistant to chemo- and radiation therapy (7,8) and are protected by the vasculature that develops due to hypoxia-mediated molecular processes (3). Hypoxia also supports the survival of neural and glioma stem cells, which are drug resistant and possess tumorigenicity potential (9,10). Considering the significance of hypoxia in the growth and aggressiveness of glioblastomas, targeting hypoxia potentially improves the outcomes in patients with this lethal cancer type.
2. Significance of hypoxia in development of glioblastoma
The pathognomonic feature of pseudopalisading necrosis, which is the area of hypercellularity surrounding necrotic regions, and vascular proliferation observed in glioblastoma tumors is a manifestation of hypoxia. These hypercellularity regions are highly hypoxic and represent tumor cells migrating away from vasoocclusive, distorted and degenerating blood vessels from the tumor center. Additionally, the cells have a high expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which promote angiogenesis (11). A subset of growth factors including angiopoietins, fibroblast growth factors, chemokines and matrix metalloproteinases, play an important role in tumor angiogenesis (12). These new vessels are deformed, leaky and have gaps between endothelial cells, resulting in vascular stasis. Repeated cycle of events of angiogenesis, vascular collapse due to deformation and cancer cell migration, contribute to rapid tumor expansion in adjacent normal tissue and invasion (13). Inasmuch as hypoxia drives the progression and aggressiveness of glioblastoma tumors, a strategy for the treatment of this type of cancer has been developed by measuring tumor volume and the extent of intratumoral hypoxia, using fluoromisonidazole probe-based positron emission tomography, followed by appropriate targeting of hypoxic cells to improve the treatment outcome (14). As mentioned above, tumor stem cells residing in hypoxic pseudopalisading zones are protected from chemoradiation because of vascular stasis and depletion of molecular oxygen. In a prospective clinical trial testing bevacizumab and irinotecan in glioblastoma patients, it was observed that hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase (CA9) and HIF-2α were major and significant predictors of treatment effectiveness and overall survival (15).
3. Hypoxia, growth factors and tumor angiogenesis
Hypoxic response is essentially mediated by HIF-1α, which is induced under conditions of low oxygen, in a nuclear factor-κB-dependent manner. HIF-1α is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of approximately 60 genes involved in several cell pathways such as glycolysis, angiogenesis, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, which are critical for tumor growth and proliferation (Fig. 1). HIF-1α likely mediates the hypoxic response, partly through the upregulation of glucose transporter 1 (Glut1) and glycolytic genes, thereby promoting anerobic glycolysis and metabolism to survive the unfavorable conditions encountered during hypoxia. Tumor initiating cancer stem cells undergo HIF-1α-mediated adaptation to hypoxia and thus have an elevated expression of various HIF-regulated genes (15). It has been shown that hypoxic area volume in the tumor is inversely proportional to the survival of the patients and thus hypoxic volume ratios greater than the median, survived only ~4 months as compared to >12 months in the patients with less than median hypoxic burden (14).
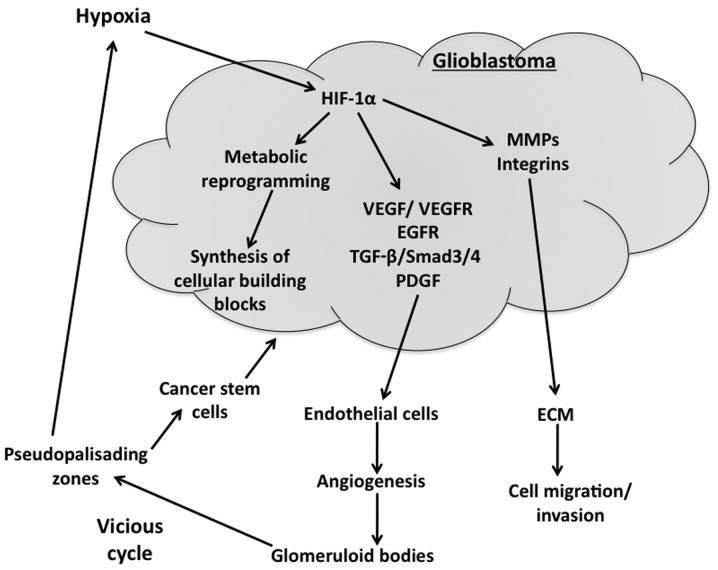
Figure 1.
Hypoxia-driven events contribute to glioblastoma progression. Hypoxia stabilizes hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in glioblastoma cells, thereby elevating the transcription of HIF-1α targets. The major tumor-promoting targets of HIF-1α are: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGF receptor (VEGFR), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), plate-derived growth factor (PDGF), matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) and integrins. MMPs and integrins facilitate the migration of cancer cells through the extracellular matrix (ECM). VEGF, VEGFR and EGFR promote angiogenesis which leads to malfunctional glomeruloid vessel bodies. These malfunctional vessels lead to areas of pseudopalisading necrotic regions that are hypoxic and protect cancer stem cells, which further proliferate and lead to tumor expansion.
Multiple pro-angiogenic factors, which are under the regulation of HIF-1α and other transcription factors, are present in glioblastoma and contribute to the formation of new vessels (Fig. 1). VEGF, a prominent pro-angiogenic factor and its receptor VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2), are highly expressed in glioblastomas and tumor vasculature (17,18). In addition to angiogenesis, VEGF regulates vascular permeability and contributes to vasogenic edema. Most of the approaches developed for glioblastoma therapy that specifically address targeting angiogenesis, mainly focused on blocking VEGF signaling pathways (19). Primary glioblastomas also exhibit a high proportion of mutations and/or the overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene. The EGFR gene codes for a 170-kDa receptor, which is a tyrosine kinase receptor, and a glycosylated plasma membrane. Altered EGFR function often leads to oncogenesis in various cell types and contributes to glioblastoma initiation, cancer cell proliferation and growth, invasion, resistance to apoptosis, chemo- and radiotherapy and angiogenesis (20,21). It has been observed that almost 40% of glioblastomas have amplified EGFR gene expression with 50% of them showing overexpression of the receptor protein (22). Even in less malignant astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas, there are elevated EGFR mRNA levels, suggesting that other oncogenic events play a role in the amplification of the EGFR gene (23).
Another important growth factor is transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), whose signaling controls different cell functions such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis and thus plays an important role in cancer progression, remodeling of the extracellular matrix and angiogenesis (24). The isoforms of TGF-β, TGF-β1/−β2 and their complete cognate signaling machinery are known to be highly expressed in glioblastomas, and contribute to enhanced proliferation and invasion of tumor cells and tumor angiogenesis (25). TGF-β2 has been shown to contribute to aberrant vascular gene expression via Smad 2/4 and Smad 3/4 signaling pathways in glioblastoma (26). Experimental studies indicated that plate-derived growth factor (PDGF)-B overexpression in murine neural and glial progenitor cells leads to the formation of malignant gliomas (27), and it is known that human glioblastomas show elevated expression of PDGF and PDGF-receptor. PDGF-B, derived from tumor cells is shown to enhance angiogenesis in endothelial cells via increased production of VEGF (28). The net effect on overall angiogenesis in glioblastoma tumors is dependent on the source and availability of PDGF-B and the counteracting effects of Wnt/β-catenin signaling on angiogenesis (29).
4. Significance of abnormal vessel formation in glioblastoma
Glioblastomas are characterized by the presence of morphologically abnormal and dysfunctional vasculature, also known as glomeruloid bodies or vascular tufts (30). These glomeruloid bodies have multiple layers of endothelial cells, pericytes and smooth muscle cells and exhibit a thick basement membrane. Such morphology constitutes a typical diagnosis for glioblastoma, albeit not for low-grade gliomas (19). The origin of these vessels is not clear and controversial. Previous in vitro studies indicated that glioma stem-like cells can be induced to differentiate to an endothelial cell type and that glioblastoma stem-like cells contribute to vessel formation (Fig. 1) in experimental models (31,32). Although the blood-brain barrier, which consists of endothelial cells and pericytes astrocytes in normal brain vessels, is disrupted in glioblastoma, with a resultant increase in vascular permeability (33), this barrier appears to remain intact at the invasive front of the tumor and the normal cortex, which is invaded by migratory glioblastoma cells. Thus, therapeutic agents that target glioblastoma to cross the blood-brain barrier to attack the invasive glioblastoma cells. Of note, the malformed blood vessels in the glioblastoma tumors in turn contribute to increasing hypoxic conditions in the tumor, as these vessels are poorly perfused (34). As mentioned earlier, hypoxia is a potent inducer of tumor progression through metabolic reprogramming, resistance to cell death, immunosuppression, inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells (13). The stabilized and thus elevated HIF-1α in glioma cells causes an increase in the expression of VEGF and CXC chemokine ligand 12, both of which promote angiogenesis through different mechanisms, eventually leading to the formation of the malformed vessels, thus leading to a vicious cycle that promotes glioblastoma tumor growth and aggressiveness (Fig. 1) (35).
5. Hypoxia and glioblastoma stem cells
Cancer stem cells are more potent in inducing tumors when injected into the brains of immunocompromised mice, as compared to non-stem cells from tumors. Cancer stem cells have a high level of resistance to radiation through activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and to chemoresistance (36,37). An important function of the tumor vasculature is to provide a supply of glioblastoma stem-like cells (38), which are critical for the progression of tumor growth and resistance to chemo- and radiotherapy. Notably, hypoxia is shown to increase the expression of CD133, a stem cell marker, in brain tumors and this increase is probably mediated by the HIF family of transcription factors (36,39). Of the HIF transcription factors, HIF-1α promotes proliferation and survival of all cancer cells and is activated in normal neural progenitors, thus limiting its value, in terms of therapeutic targeting. HIF-2α, which is practically absent in non-glioma stem cells, is specifically elevated in glioblastoma stem cells, even under modest hypoxic conditions, thereby making HIF-2α an interesting therapeutic target in glioblastomas (40). HIF-2α regulates chromatin structure by activating proteins/processes that modify chromatin epigenetically, such as the histone methyltransferase and mixed lineage leukemia 1 (41). Other hypoxia-induced genes, that are expressed at elevated levels in glioblastoma stem cells, include Oct4, Glut1, SerpinB9, and VEGF. In addition to promoting angiogenesis by the glioma stem cells, hypoxia also increases other microenvironmental interactions by these cancer stem cells including the suppression of immune response. Hypoxia activates pSTAT signaling, thereby increasing the secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines such as CSF1 and CCL2, which are useful in inhibiting T-cell proliferation and macrophage phagocytosis, which in turn accelerate tumor progression (42).
Glioma stem cells show enhanced Notch signaling pathways (43,44), which contribute to their radioresistance (45). Thus, blocking Notch signaling in human glioblastoma stem cells with high doses of γ-secretase inhibitors reduces proliferation of these cancer stem cells and tumor formation, and increases differentiation (46). Other enhanced signaling pathways include PI3 kinase/Akt, Hedgehog and Stat3 (47–49).
6. Therapeutic implications
Inasmuch as hypoxia and hypoxia-induced factors promote the growth of glioblastomas, therapeutic measures addressing hypoxia have been developed. Thus, a monoclonal antibody against VEGF, bevacizumab, has been developed and approved as a second-line monotherapy of glioblastoma patients. However, bevacizumab therapy achieved improvement in progression-free survival but was not beneficial for overall survival (50). On the other hand, a subset of patients who positively responded to cediranib, a pan-VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which increased blood perfusion, showed improved survival (51). A better understanding of the significance and pathophysiology of tumor vasculature and associated factors is needed to develop effective therapeutics that target these elements of glioblastomas.
An interesting direct approach using a prodrug is via a hypoxia-activated TH-302, which is a nitroimidazole prodrug of bromo-isophosphoramide mustard (Br-IPM), a cytotoxin. Under hypoxic conditions, TH-302 is converted by intracellular reductases to the alkylating agent Br-IPM, which functions as a DNA cross-linking agent damaging the hypoxic tumor cells, in which it is formed. Br-IPM may also diffuse into the extracellular matrix and the nearby normoxic cells, showing its cytotoxic effects in these cells as well. However, TH-302 per se is not effective under normoxic conditions and requires hypoxic conditions to show its cytotoxic effects (52). A recent study showed that TH-302 is well tolerated when administered after a 4-week period of postsurgical recovery, to glioblastoma patients, in combination with bevacizumab (10 mg/kg), with a promising clinical benefit rate of 62% (53).
A major advance in the treatment of glioblastoma during the last decade is the concomitant chemoradiotherapy with temozolomide. It has been shown that the median survival of patients receiving radiation therapy alone is 12.1 months, whereas a combination of radiation with temozolomide increased the median survival to ≤14.6 months (54). One of 5 glioblastoma patients survived in the temozolomide-treated population, whereas essentially none of the patients without temozolomide survived to 3 years, during the follow-up. The survival promoting action of temozolomide is essentially due to the epigenetic modification of the methyl guanine methyl transferase (MGMT) promoter, in the glioblastoma cells, which leads to reduced or no expression of this enzyme and thus the inability to repair the guanine methylation induced by temozolomide. However, MGMT silencing by promoter modification is seen only in 40% of the glioblastoma cases. Therefore, the treatment benefit of temozolomide is not evident in the remaining 60% of the glioblastoma patients who harbor normal expression of the MGMT, which is capable of repairing the temozolomide-mediated guanine methylation (55).
Other agents that have been examined as therapeutic agents targeting HIFs are amphotericin B, an anti-fungal drug, which inhibits HIF-1α transcription (56); and 2-methoxyestradiol, an inhibitor of HIF-1α, which has been tested in phase-I clinical trials with some success showing stable disease in 38% of the enrolled patients (57). Despite the significant leaps in our understanding of the molecular events that underlie the aggressiveness and progression of glioblastomas, much progress is needed for effective therapeutic development that goes much further than extending life by a short period of time.
7. Conclusions
Among the CNS cancer grade IV astrocytomas, glioblasomas are highly aggressive. The extensive hypoxic regions in glioblastomas contribute to the highly malignant phenotype of these tumors, exacerbating the prognosis of the patients. Hypoxic tumor cells are resistant to chemo- and radiation therapy and are also protected by the malfunctional vasculature that developed due to hypoxia. The abnormal and malfunctional vessels play a critical role in generating pseudopalisading necrotic regions that are hypoxic and protect cancer stem cells residing in that region from therapeutic agents, which facilitates cancer stem cell proliferation and tumor growth, thus causing a vicious cycle of tumor growth. Therapeutic approaches that target hypoxia-induced factors such as use of monoclonal antibody against VEGF, bevacizumab, have been useful only in stabilizing the disease but failed to increase the overall survival. Hypoxia-activated TH-302 appears to be more attractive due to its better beneficial effects in glioblastoma patients. A better understanding of the hypoxia mediated protection of the glioblastoma cells is needed in future studies in order to develop more effective therapeutics.
References
- 1.Filippini G. Epidemiology of primary central nervous system tumors. Handb Clin Neurol. 2012;104:3–22. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-52138-5.00001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Howlader N, Noone A, Krapcho M, Miller D, Bishop K, Altekruse S, Kosary C, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, et al., editors. Seer cancer statistics review, 1975-2013. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: Apr 15, 2016. Accessed. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114:97–109. doi: 10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2683–2710. doi: 10.1101/gad.1596707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Liao P, Rouse C, Chen Y, Dowling J, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan J. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2007-2011. Neuro-oncol. 2014;16(Suppl 4):iv1–iv63. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hou LC, Veeravagu A, Hsu AR, Tse VC. Recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: A review of natural history and management options. Neurosurg Focus. 2006;20:E5. doi: 10.3171/foc.2006.20.4.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rong Y, Durden DL, Van Meir EG, Brat DJ. ‘Pseudopalisading’ necrosis in glioblastoma: A familiar morphologic feature that links vascular pathology, hypoxia, and angiogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006;65:529–539. doi: 10.1097/00005072-200606000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hsieh CH, Shyu WC, Chiang CY, Kuo JW, Shen WC, Liu RS. NADPH oxidase subunit 4-mediated reactive oxygen species contribute to cycling hypoxia-promoted tumor progression in glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS One. 2011;6:e23945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA, Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD, Dirks PB. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature. 2004;432:396–401. doi: 10.1038/nature03128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD, Rich JN. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. 2006;444:756–760. doi: 10.1038/nature05236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Brat DJ, CastellanoSanchez AA, Hunter SB, Pecot M, Cohen C, Hammond EH, Devi SN, Kaur B, Van Meir EG. Pseudopalisades in glioblastoma are hypoxic, express extracellular matrix proteases, and are formed by an actively migrating cell population. Cancer Res. 2004;64:920–927. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT. Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:610–622. doi: 10.1038/nrn2175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jain RK. Normalizing tumor microenvironment to treat cancer: Bench to bedside to biomarkers. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2205–2218. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.3653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Spence AM, Muzi M, Swanson KR, O'Sullivan F, Rockhill JK, Rajendran JG, Adamsen TC, Link JM, Swanson PE, Yagle KJ, et al. Regional hypoxia in glioblastoma multiforme quantified with [18F]fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography before radiotherapy: Correlation with time to progression and survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2623–2630. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sathornsumetee S, Cao Y, Marcello JE, Herndon JE, II, McLendon RE, Desjardins A, Friedman HS, Dewhirst MW, Vredenburgh JJ, Rich JN. Tumor angiogenic and hypoxic profiles predict radiographic response and survival in malignant astrocytoma patients treated with bevacizumab and irinotecan. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:271–278. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mannino M, Chalmers AJ. Radioresistance of glioma stem cells: Intrinsic characteristic or property of the ‘microenvironment-stem cell unit’? Mol Oncol. 2011;5:374–386. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2011.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature. 1992;359:845–848. doi: 10.1038/359845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L. VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:359–371. doi: 10.1038/nrm1911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dimberg A. The glioblastoma vasculature as a target for cancer therapy. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014;42:1647–1652. doi: 10.1042/BST20140278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.KarpelMassler G, Schmidt U, Unterberg A, Halatsch ME. Therapeutic inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade gliomas: Where do we stand? Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:1000–1012. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Squatrito M, Holland EC. DNA damage response and growth factor signaling pathways in gliomagenesis and therapeutic resistance. Cancer Res. 2011;71:5945–5949. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Riddick G, Fine HA. Integration and analysis of genome-scale data from gliomas. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011;7:439–450. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2011.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Reifenberger J, Reifenberger G, Ichimura K, Schmidt EE, Wechsler W, Collins VP. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in oligodendroglial tumors. Am J Pathol. 1996;149:29–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Massagué J. TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell. 2008;134:215–230. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bruna A, Darken RS, Rojo F, Ocaña A, Peñuelas S, Arias A, Paris R, Tortosa A, Mora J, Baselga J, et al. High TGFbeta-Smad activity confers poor prognosis in glioma patients and promotes cell proliferation depending on the methylation of the PDGF-B gene. Cancer Cell. 2007;11:147–160. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dieterich LC, Mellberg S, Langenkamp E, Zhang L, Zieba A, Salomäki H, Teichert M, Huang H, Edqvist PH, Kraus T, et al. Transcriptional profiling of human glioblastoma vessels indicates a key role of VEGF-A and TGFβ2 in vascular abnormalization. J Pathol. 2012;228:378–390. doi: 10.1002/path.4072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shih AH, Holland EC. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and glial tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2006;232:139–147. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guo P, Hu B, Gu W, Xu L, Wang D, Huang HJ, Cavenee WK, Cheng SY. Platelet-derived growth factor-B enhances glioma angiogenesis by stimulating vascular endothelial growth factor expression in tumor endothelia and by promoting pericyte recruitment. Am J Pathol. 2003;162:1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63905-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lindblom P, Gerhardt H, Liebner S, Abramsson A, Enge M, Hellstrom M, Backstrom G, Fredriksson S, Landegren U, Nystrom HC, et al. Endothelial PDGF-B retention is required for proper investment of pericytes in the microvessel wall. Genes Dev. 2003;17:1835–1840. doi: 10.1101/gad.266803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kanu OO, Mehta A, Di C, Lin N, Bortoff K, Bigner DD, Yan H, Adamson DC. Glioblastoma multiforme: A review of therapeutic targets. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009;13:701–718. doi: 10.1517/14728220902942348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.RicciVitiani L, Pallini R, Biffoni M, Todaro M, Invernici G, Cenci T, Maira G, Parati EA, Stassi G, Larocca LM, et al. Tumour vascularization via endothelial differentiation of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Nature. 2010;468:824–828. doi: 10.1038/nature09557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Soda Y, Marumoto T, FriedmannMorvinski D, Soda M, Liu F, Michiue H, Pastorino S, Yang M, Hoffman RM, Kesari S, et al. Transdifferentiation of glioblastoma cells into vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:4274–4280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016030108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wolburg H, Noell S, FallierBecker P, Mack AF, Wolburg-Buchholz K. The disturbed blood-brain barrier in human glioblastoma. Mol Aspects Med. 2012;33:579–589. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gmeiner M, Sonnberger M, Wurm G, Weis S. Glioblastoma with the appearance of arteriovenous malformation: Pitfalls in diagnosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013;115:501–506. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Würth R, Bajetto A, Harrison JK, Barbieri F, Florio T. CXCL12 modulation of CXCR4 and CXCR7 activity in human glioblastoma stem-like cells and regulation of the tumor microenvironment. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:144. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Blazek ER, Foutch JL, Maki G. Daoy medulloblastoma cells that express CD133 are radioresistant relative to CD133- cells, and the CD133+ sector is enlarged by hypoxia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.09.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Todaro M, Alea MP, Di Stefano AB, Cammareri P, Vermeulen L, Iovino F, Tripodo C, Russo A, Gulotta G, Medema JP, et al. Colon cancer stem cells dictate tumor growth and resist cell death by production of interleukin-4. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:389–402. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Calabrese C, Poppleton H, Kocak M, Hogg TL, Fuller C, Hamner B, Oh EY, Gaber MW, Finklestein D, Allen M, et al. A perivascular niche for brain tumor stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2007;11:69–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Platet N, Liu SY, Atifi ME, Oliver L, Vallette FM, Berger F, Wion D. Influence of oxygen tension on CD133 phenotype in human glioma cell cultures. Cancer Lett. 2007;258:286–290. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Li Z, Bao S, Wu Q, Wang H, Eyler C, Sathornsumetee S, Shi Q, Cao Y, Lathia J, McLendon RE, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors regulate tumorigenic capacity of glioma stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:501–513. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Heddleston JM, Wu Q, Rivera M, Minhas S, Lathia JD, Sloan AE, Iliopoulos O, Hjelmeland AB, Rich JN. Hypoxia-induced mixed-lineage leukemia 1 regulates glioma stem cell tumorigenic potential. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:428–439. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wei J, Wu A, Kong LY, Wang Y, Fuller G, Fokt I, Melillo G, Priebe W, Heimberger AB. Hypoxia potentiates glioma- mediated immunosuppression. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kanamori M, Kawaguchi T, Nigro JM, Feuerstein BG, Berger MS, Miele L, Pieper RO. Contribution of Notch signaling activation to human glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurosurg. 2007;106:417–427. doi: 10.3171/jns.2007.106.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lino MM, Merlo A, Boulay JL. Notch signaling in glioblastoma: A developmental drug target? BMC Med. 2010;8:72. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang J, Wakeman TP, Lathia JD, Hjelmeland AB, Wang XF, White RR, Rich JN, Sullenger BA. Notch promotes radioresistance of glioma stem cells. Stem Cells. 2010;28:17–28. doi: 10.1002/stem.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fan X, Khaki L, Zhu TS, Soules ME, Talsma CE, Gul N, Koh C, Zhang J, Li YM, Maciaczyk J, et al. NOTCH pathway blockade depletes CD133-positive glioblastoma cells and inhibits growth of tumor neurospheres and xenografts. Stem Cells. 2010;28:5–16. doi: 10.1002/stem.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wei Y, Jiang Y, Zou F, Liu Y, Wang S, Xu N, Xu W, Cui C, Xing Y, Liu Y, Cao B, Liu C, Wu G, Ao H, Zhang X, Jiang Activation of PI3K/Akt pathway by CD133-p85 interaction promotes tumorigenic capacity of glioma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:6829–6834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217002110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Morgenroth A, Vogg AT, Ermert K, Zlatopolskiy B, Mottaghy FM. Hedgehog signaling sensitizes glioma stem cells to endogenous nano-irradiation. Oncotarget. 2014;5:5483–5493. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Liu M, Inoue K, Leng T, Guo S, Xiong ZG. TRPM7 channels regulate glioma stem cell through STAT3 and Notch signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2014;26:2773–2781. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.08.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Keunen O, Johansson M, Oudin A, Sanzey M, Rahim SA, Fack F, Thorsen F, Taxt T, Bartos M, Jirik R, et al. Anti-VEGF treatment reduces blood supply and increases tumor cell invasion in glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:3749–3754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014480108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sorensen AG, Emblem KE, Polaskova P, Jennings D, Kim H, Ancukiewicz M, Wang M, Wen PY, Ivy P, Batchelor TT, et al. Increased survival of glioblastoma patients who respond to antiangiogenic therapy with elevated blood perfusion. Cancer Res. 2012;72:402–407. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Meng F, Evans JW, Bhupathi D, Banica M, Lan L, Lorente G, Duan JX, Cai X, Mowday AM, Guise CP, et al. Molecular and cellular pharmacology of the hypoxia-activated prodrug TH-302. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11:740–751. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cavazos DA, Brenner AJ. Hypoxia in astrocytic tumors and implications for therapy. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;85:227–233. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.06.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, et al. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N, Weller M, Kros JM, Hainfellner JA, Mason W, Mariani L, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:997–1003. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yeo EJ, Ryu JH, Cho YS, Chun YS, Huang LE, Kim MS, Park JW. Amphotericin B blunts erythropoietin response to hypoxia by reinforcing FIH-mediated repression of HIF-1. Blood. 2006;107:916–923. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kirkpatrick J, Desjardins A, Quinn J, Rich J, Vredenburgh J, Sathornsumetee S, Gururangan S, Sidor C, Friedman H, Reardon D. Phase ii open-label, safety, pharmacokinetic and efficacy study of 2-methoxyestradiol nanocrystal colloidal dispersion administered orally to patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol (ASCO Annual Meeting abs.) 2007;25:2065. [Google Scholar]