Abstract
Background: To characterize the potential function and clinical significance of Transketolase (TKT) in esophageal cancer.
Methods: High invasive esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell line CE48T/VGH was used. Cellular functions in response to TKT modulation were examined, including cell growth, migration and invasion. The underlying molecules involved in the TKT regulatory mechanism were determined by western blot and confocal microscopic analysis. Clinically, TKT expressions in 76 ESCC patients were assessed by immunohistochemical (IHC) method, and the association with treatment outcome was determined.
Results: TKT silencing inhibited cell migration and invasion but had a minimal effect on cell growth. This TKT silencing also induced the reversion of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), as evidenced by the spindle to cuboidal morphological change, increased the expression of epithelial markers (γ-catenin), and decreased the levels of mesenchymal markers (fibronectin and N-cadherin). Mechanically, TKT was shown to modulate the EMT through the pERK-Slug/Snail-associated signaling pathway. Clinically, a high level of TKT in the cancer tissues of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma was associated with poor survival (P = 0.042). In the multivariate analysis, a high TKT level was also shown to be an independent unfavorable prognostic factor (Odds ratio: 1.827, 95% confidence interval: 1.045-3.196, P = 0.035).
Conclusions: TKT contributes to esophageal cancer by promoting cell invasion via meditating EMT process. Clinically, the over-expression of TKT in ESCC patients predicts poorer survival. TKT inhibition may be a useful strategy to intervene in cancer cell invasion and metastasis, which may lead to better prognosis for ESCC patients.
Keywords: transketolase, esophageal cancer, prognosis, cell invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Introduction
Cancer cells display high rates of aerobic glycolysis, even in the presence of oxygen, which is a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect 1,2. Because ATP generation via aerobic glycolysis is far less efficient than that by oxidative phosphorylation (2 versus 38 ATP generated per glucose molecule), cancer cells need to consume far more glucose than normal cells to maintain a sufficient ATP supply for their active metabolism and proliferation. In cancer diagnostics, the Warburg effect is currently being exploited for the detection of tumors and metastases using fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) and positron emission tomography (PET), but to date, this knowledge has not led to the development of targeted therapies 2.
Aerobic glycolysis is controlled by the non-oxidative portion of the pentose phosphate pathway, which converts six-carbon glucose to five-carbon ribose to provide ATP and other metabolic products for nucleic acid synthesis and other cellular needs 1,2. This aerobic glycolytic pathway is crucially regulated by the transketolase reaction, which involves three human genes: transketolase (TKT) and two TKT-like genes (TKTL1 and TKTL2) 3. Although these three TKT isoenzymes have been recognized, to date, their relative contributions to specific pathological conditions have not been investigated. Several studies had been performed to determine the associations between the TKT gene family and cancer carcinogenesis. TKTL1 has been shown to participate in tumorigenesis in various human cancers. For example, the overexpression of TKTL1 has been found in lung, colorectal, endometrial, and head and neck cancer 4-8. Expression of this enzyme is also correlated with cancer progression and poor patient outcome in lung and colorectal cancer 7,8. Furthermore, gene silencing of TKTL1 by siRNA was found to significantly reduce cell proliferation in gastric, colon, and uterine cancer cell lines 9,10. Recently, TKT isoenzyme has also been found participating in cancer formation. TKT is up-regulated in ovarian cancer and promotes cell proliferation 11. Knockdown TKT sensitizes cancer cells to chemo-drug treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma 12. However, the association of TKT enzyme family in esophageal cancer has not yet been addressed.
Esophageal cancer is a highly lethal disease with poor survival 13. Identification of pathological or molecular markers that can facilitate better prognostic stratification and may serve as novel targets for cancer intervention are urgently needed. In the present study, we investigated the potential function of TKT in esophageal carcinoma. We found that TKT contributes to cancer cell invasion by promoting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). The clinical study also shows TKT is an independent prognosticator in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Our study provides knowledge foundation for the future development of a therapeutic modality to intervene TKT expression, which may lead to better prognosis for ESCC patients.
Methods
Cell culture and cell growth assay
Esophageal SCC cell line CE48T/VGH was used 14, which was cultured in DMEM medium (Gibco BRL, CA, USA) with 10% FCS and 1% antibiotics at 37°C in a humidified incubator containing 5% CO2. Cell growth was monitored by counting cell numbers on a daily basis. Cell viability was determined by staining with 0.25% trypan blue.
Cloning and transfection of small hairpin interference RNA (shRNA) plasmid
The PGSH-GFP vector was used to construct two clones of TKT-shRNA plasmids, similar as we previously described 15. The hairpin oligonucleotide complementary to TKT mRNA was designed. The sequence of the TKT-sh1 oligonucleotide was: 5'-GAT- AAG- GAG- TCT- TGG- CATG- caagcttc- CATC- CCA- AGA- CTC- CTT- ATC-3'. The sequence of the TKT-sh2 oligonucleotide was: 5'-GCC- CCT- GGA- CAG- AAA- ACTC- caagcttc- GAGT- TTT- CTG- TCC- AGG- GGC-3'. TKT-shRNA oligonucleotides were cloned to vector through the BamH1- and Not-1 digestion sites. The plasmids were transfectioned using Lipofectamine 2000TM reagent in Opti-MEM medium (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). After which, the medium was replaced with fresh complete medium.
Protein extraction and western blot analysis
Proteins were extracted from cells using CHAPS lysis buffer containing protease inhibitor. A total of 20 μg protein was separated by 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were blocked in 5% low-fat milk solution in PBST (phosphate-buffered saline with 0.05% Triton X-100). The membranes were hybridized with specific primary antibodies (rabbit anti-TKT polyclonal antibody, clone 236B4, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA) followed by incubation with secondary antibodies conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (Santa Cruz Biotech., CA, USA). Chemifluorescence reagents (ECL Western blotting detection reagents, Millipore Corp., Bedford, MA) were used for visualization, per the manufacturer's instructions. Using the Gel Image System (Scion Corporation, MD), the density of each band was determined after normalization to an actin control band.
Cell migration assay
Cell migration assays were performed by using Transwell culture system (BD Biosciences, Bedford, MA). Cells in DMEM medium containing 1% FCS were seeded in the upper chamber of the Transwell polycarbonate chamber. After 12 hours, the cells migrated to the lower chamber were fixed with 1% glutaraldehyde, stained with 0.5% crystal violet, and photography. For quantitation of the migrated cells, cells were incubated for 30 minutes at 37°C, and eluted with 0.5 ml of Sorensen's solution. The absorbance was determined with a microtiter plate reader at 570 nm.
Cell invasion assay
The cell invasion assay was performed by using Matrigel-coated Millicell system. Cell suspended in the DMEM medium containing 1% FBS was seeded in the upper chamber of Matrigel-coated Millicell inserts (BD Biosciences, Bedford, MA). The lower chamber was filled with DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS. The total number of cells that invaded to the lower chamber was counted daily for 4 days. All experiments were carried out in triplicate.
Immunofluorescent staining and confocal microscopy
Immunofluorescent staining was performed similarly as previously described 16. Briefly, cells were grown on coverslips coated with 1% poly-L-lysine, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, and permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS. After washing, cells were blocked with FBS and incubated with anti-fibronectin or anti-TKT primary antibodies overnight. After washing, cells were incubated with FITC- or PE-conjugated secondary antibodies, and mounted with Vectashield H-1200 Mounting Medium (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). The immunofluorescence was visualized under a Zeiss fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss, Thornword, NY).
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis was performed similarly as previous described 17, Briefly, tissue samples were fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin. The tissue sections were deparaffinized by xylene, blocked with hydrogen peroxide, and stained with anti-TKT antibody (clone 236B4, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA). IHC analysis and color development were performed using the Vectastain Elite ABC detection system (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The sections were then counterstained with hematoxylin and mounted. The staining reactions were evaluated by two pathologists under a dual-head microscopic examination. The immunostaining of normal esophageal epithelium was used as positive internal control. For negative control, the slides were processed in the same way, except that the primary antibody was omitted (buffer substitution). When both pathologists agreed that the staining intensity of carcinoma cells was apparently no or less than that of normal esophageal epithelium, those tumors were categorized as negative intensity score; when cells were stained at a similar or slightly higher level as normal epithelium, those tumors were categorized as weak positive expression intensity. While a staining intensity was apparently stronger than normal epithelium, those tumors were categorized as either intermediate or high intensity. The Histo-score (H-score; range = 0-300) was calculated by multiplying the intensity score (0 = negative; 1 = weak; 2 = intermediate; 3 = strong) and the fraction score (percentage of positive tumor cells; range = 0-100) in the tissue staining. Finally, the mean H-score of the study cohort was used as the cut-off point of high and low TKT expression.
Patients, treatment, and statistical analysis
A retrospective study was performed for 76 ESCC patients treated with chemoradiotherapy and esophagectomy. To examine the association of TKT protein expression and clinicopathological features, the Person's chi-square test was used. To determine the potential significance of TKT in the prediction of prognosis, the survival analyses were performed. We defined disease specific survival (DSS) as the interval between the date of surgery to the date of known cancer-related death. Survival curve was calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method. Multi-variant Cox regression analysis was applied with stepwise selection to determine the proportional hazards. SPSS 16.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical analyses.
Results
TKT silencing inhibits cell migration and invasion
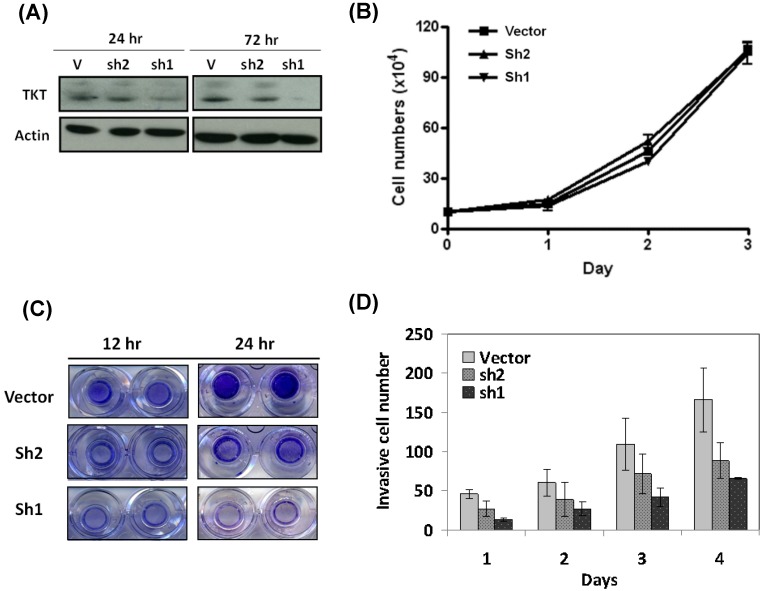
Two clones of TKT-shRNA plasmid were constructs (sh1 and sh2), and the silencing effect was determined by western blot analysis after 3 days of transfection. As shown in the Figure 1A, the two lines of TKT-shRNA transfected cells showed different levels of TKT inhibition, with much stronger effect in the TKT-sh1 transfectants. Compared to the control, TKT was reduced over 90% by sh1 and 42% by sh2 demonstrating the strong and partial inhibitions of TKT by sh1 and sh2 clones.
Figure 1.
TKT silencing inhibited cell migration and invasion but minimal effect on cell growth. (A) Silencing TKT expression by shRNA. Tow plasmid clones of TKT-shRNA sh1 and sh2 were constructed, and transfected into CE48T/VGH cells for 1 to 3 days. The cellular proteins were extracted for determination of TKT expression by western blot method. Actin protein level was determined as internal control. (B) TKT silencing has minimal effect on cell growth. Total of 5 × 105 cells were seeded in a 10-mm dish plate. After transfection with TKT-shRNA or the vector plasmids, cells were continuously cultured for up to 4 days. Cell numbers were counted every 24 hours. (C) TKT silencing inhibited cell migration. After transfection with TKT-shRNA or the vector plasmids, cells were seeded in the upper chamber of the Transwell polycarbonate chamber. After 12 or 24 hours, the cells migrated to the lower chamber were fixed and stained with 0.5% crystal violet and photography. (D) TKT silencing suppressed cell invasion. After transfection with TKT-shRNA or the vector plasmids, cells were seeded in the 24-well plate coated with Matrigel in a Millicell invasion chamber. The numbers of cells invading through the Matrigel to the lower chamber were determined daily for 4 days. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
The potential effect of TKT silencing by the shRNA (TKTi) on cell growth was first examined. As shown in the Figure 1B, TKTi by either clone of shRNA had no significant effect on cell growth after 3 days of study, suggesting that TKT has minimum effect on cell growth.
The cellular effect of TKTi on the malignant phenotypes of cell migration was next examined. Cells were seeded in the upper chamber of the Transwell culture plate. After 12 hours, the cells migrating to the lower chamber were examined. As showed in the Figure 1C, TKTi showed partial inhibition of cell migration in the sh2 clones, while significant suppression in the sh1 clones. At 24 hours, the migrated cells were approximately reduced to 48% in sh2 clone and 17% in sh1 clone cells. Apparently, TKT silencing inhibits the migration ability of esophageal cancer cells.
The cellular effect of cell invasion was determined by matrigel invasion assay. The TKTi cells were seeded in the upper chamber of Matrigel-coated Millicells. The number of cells invading to the lower chamber was determined daily. As showed in the Figure 1D, TKTi cell showed a gradual but substantial decrease in the numbers of invade cells. By day 4, the invading cells were reduced to 53% in sh2 clone and 38% in sh1 clone cells. These dose dependent manner of phenotypic regulation suggested that TKT plays a significant role in the invasion of esophageal cancer cells.
TKT silencing reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Recent reports have suggested EMT in a subset of cancer cells is acquisition for cell mobility alteration and metastatic potential 18, 19, we therefore investigated whether TKT regulates cell mobility via promoting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions (EMT). As shown in the Figure 2A, TKT silencing decreased the levels of mesenchymal markers (fibronectin, N-cadherin, and IQGAP1 scaffold protein) and increased the expression of epithelial marker (γ-catenin). This transition of cellular marker expressions was further supported by immunofluorescent staining and confocal microscopy examination. As shown in Figure 2B, TKTi displayed a mesenchymal-like nature of the contractile morphology, indicating the cell-extracellular matrix contacts were broke down up TKT silencing. Consistently, the TKTi increased the expressions of fibronectin and N-cadherin, while reduction of γ-catenin expression Taking together, TKT facilitates cell invasion may through the regulation of EMT process.
Figure 2.
TKT silencing reversed epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). (A) TKT regulated EMT molecules as determined by western blot assay. After transfection with TKT-shRNA or the vector plasmids, the cellular protein was extracted and subjected to western blot analysis. The expressions of EMT-associated molecules, including fibronectin, N-cadherin, IQGAP1, and r-catenin were evaluated. Actin protein levels were determined as an internal control for protein expression. (B) TKT regulated EMT molecules as examined by confocal microscopy. After transfection with TKT-shRNA or the vector plasmids, the cells were fixed and subjected to immunostaining analysis. These staining included antibodies against fibronectin with Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody (red imaging), N-cadherin with Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody (red imaging), or r-catenin with FITC-conjugated secondary antibody (green imaging). Cells were further stained with DAPI (blue imaging) to show the localization of nucleus. Cells were then observed by confocal microscopy.
TKT silencing suppresses the Slug/Snail expression and Erk signaling pathway
We next examined the potential alterations of EMT regulatory molecules by using TKTi cells. The Slug and Snail which are well-known transcriptional factors to regulate cell polarity and drive EMT process 20-22 were investigated by confocal microscopy. As shown in Figure 3A, TKT silencing inhibited Slug and Snail expressions, with a lighter effect on sh2- and strong effect on sh1-transfectants. This dose-dependent effect indicates that TKT has specific suppression on Slug and Snail expressions.
Figure 3.
TKT silencing suppressed EMT associated signaling molecules. (A) TKT regulated Slug and Snail protein expressions as examined by immunostaining and confocal microscopy. After transfection with TKT-shRNA or the vector plasmids, the cells were stained with antibodies against Slug or Sanil with Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody (red imaging). Cells were further stained with DAPI (blue imaging) to show the localization of nucleus and observed by confocal microscopy. (B) TKT regulated phosphor-ERK and phosphor-p38 protein levels as determined by western blot assay. After transfection with TKT-shRNA or the vector plasmids, the cellular protein was extracted and subjected to western blot analysis to examine the expressions of phosphor-ERK and phosphor-p38 proteins. Actin protein levels were determined as internal controls.
It has been reported that activation of the extracellular signal regulatory kinase Erk1/2 and p38/Jun can induce Slug expression and play important signaling pathway for EMT induction 23-26. We therefore examined the possible involvement of ERK signaling cascade in TKT-mediated Slug expression. Western analysis was used to analyze the association of this molecular pathway. As shown in Figure 3B, the phosphoryated forms of Erk1/2 and p38/Jun proteins were partially reduced by sh2- and substantially by sh1-transfectants, demonstrating TKT silencing rendered a specific suppression on the phsophoryation levels of Erk1/2 and p38 molecules. Taken together, our results reveal that TKT modulates cell mobility through EMT process and a mechanism involving pERK/p38Slug/Snail signaling axis.
TKT is over-expressed in esophageal cancer tissues and predicts a poor prognosis
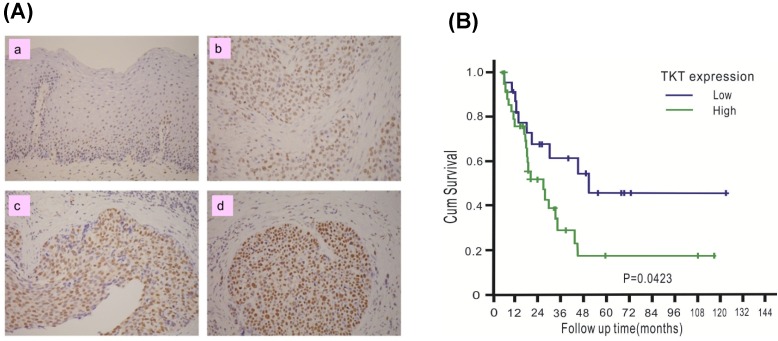
The clinical significance of TKT in esophageal cancer was assessed. A total of 76 patients with ESCC were recruited, including 74 males and 2 females. The mean age of the patients was 56.1 years, with a range of 38-79 years. The patient characteristics are listed in Table 1. TKT expression in each tumor tissue was analyzed by IHC methods and scored by the H-scoring system. Example results are shown in Figure 4A. TKT expression was significantly higher in the cancer tissues (b, c, d) than in the normal esophageal epithelium (a, used as internal positive control). Of all tissue sections, 54% demonstrated moderate or strong intensity, and 76% had a staining fraction of greater than 70%. The mean H-score was 121, and scores higher than the mean accounted for 44.7% of the cohort. A clinical association study was performed using this value as cutoff point. As shown in Table 1, no association was observed between TKT expression and the clinicopathological variables. These results indicated that esophageal cancer formation is associated with multiple factor and that the TKT enzyme may not represent a significant contributing factor.
Table 1.
Correlation between tumor TKT expression and Patient characteristics.
| TKT expression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Total | Low (n=35) | High (n=41) | P |
| Age (Mean±SD) | 56±11.77 | 54.1±9.7 | 57±10.2 | 0.73 |
| Sex | 0.21 | |||
| Male | 74 | 33 | 41 | |
| Female | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
| Grade | 0.11 | |||
| Well | 3 | 3 | 0 | |
| Moderate | 54 | 22 | 32 | |
| Poor | 19 | 10 | 9 | |
| ypT stage | 0.44 | |||
| T1 | 27 | 10 | 17 | |
| T2 | 44 | 23 | 21 | |
| T3 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| ypN stage | 0.23 | |||
| N(-) | 59 | 25 | 34 | |
| N(+) | 17 | 10 | 7 | |
Figure 4.
TKT is over-expressed in esophageal cancer tissues and predicts poor prognosis. (A) TKT levels in the normal esophageal epithelium (a), and cancer tissues (b, c, d) were determined by immuohistochemistry method. The immunostaining of normal esophageal epithelium was used as positive internal control (a). For negative control, the slides were processed in the same way, except that the primary antibody was omitted (buffer substitution). The example of negative staining (a), low (b), intermediate (c) and high (d) levels were shown. (B) Clinical association between disease-free survival of ESCC patients and the TKT protein expression. Survival curves were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method with a log-rank test.
To determine whether TKT expression in tumors can be used to predict the prognosis of patients, the potential association with patient survival was examined. Patients were followed up for a mean time of 57 months (median: 55 months, interquartile range: 28-71 months), and 10 patients were alive at the time of analysis, 54 patients died as a result of cancer recurrence or treatment-related complications, and 12 patients died due to other diseases. The 5-year disease-free survival (DSS) in the entire study cohort was 28%, with a median survival of 24.5 months. The results of the Kaplan-Meier analysis are shown in Figure 4B. Patients with high TKT expression had shorter DSS than those with low expression (5-yr DSS: 46% versus 17%, P = 0.042). Table 2 summarized the result of univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model. In the univariate analysis, patients with tumors that overexpressed TKT exhibited poorer survival (P = 0.029). TKT overexpression remained a significant independent predictor of a worse outcome (P = 0.035) in the multivariate analysis.
Table 2.
Univariate and multivariate analyses of disease specific survival.
| Uni-variate analysis | Multi-variate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | P | OR (95% CI) | P | |
| Age | 1.012 (0.985-1.039) | 0.396 | N/A | |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | Reference | 0.056 | N/A | |
| Female | 0.294 (0.1-12.92) | |||
| C stage | 0.006 | |||
| II | Reference | 0.002 | Reference | |
| III | 2.369 (1.368~4.101) | 2.184 (1.256~3.797) | ||
| ypT stage | ||||
| ypT1 | Reference | 0.434 | N/A | |
| ypT2 | 0.749 (0.425~1.321) | 0.318 | ||
| ypT3 | 1.291 (0.44~3.784) | 0.641 | ||
| LNM | 0.026 | |||
| Negative | Reference | 0.039 | Reference | |
| Positive | 1.882 (1.034-3.426) | 1.997 (1.087-3.669) | ||
| TKT level | 0.035 | |||
| Low | Reference | 0.029 | Reference | |
| High | 1.846 (1.066-3.198) | 1.827 (1.045-3.196) | ||
Abbreviations: OR = odds ratio; CI = confidence interval; LNM = lymph node metastases; N/A = not applicable; TKT: transketolase
Discussion
In this study, we clearly showed that TKT facilitates cell migration and invasion, as demonstrated by the substantial suppression of these phenotypes in TKT-silenced cells. Our study highlights the importance of TKT as a potential therapeutic target. TKT inhibition may thus be a useful strategy to intervene in cancer cell invasion and metastases.
The underlying mechanism by which TKT contributes to cell mobility was further addressed. Recently, accumulating evidence has suggested that the EMT plays a critical role in cancer invasion. On the cellular level, the EMT is defined by three key changes in phenotypes 18, 19: (1) changes from a cobblestone-like to a fibroblast-like morphology; (2) biochemical changes involving a change in differentiation molecules from cell junction proteins to mesenchymal markers, such as fibronectin; and (3) functional changes involving a conversion of immotile cells to migratory cells with invasive behavior. In our study, the silencing of TKT expression in human ESCC cell lines resulted in the reversions of all these changes (Figure 2), thus indicating a pivotal role of TKT in regulating the EMT process.
Our data also provided mechanistic insights into how TKT may regulate the EMT in cancer cells. Several transcriptional regulators that mediate the EMT process have been identified, including Slug and Snail 20-22. These molecules play crucial roles during embryonic development and cancer progression through their function in the EMT conversion. Here, we showed that TKT silencing reduced the expression of the transcriptional regulators Slug and Snail in human ESCC cells (Figure 3A). This highlights the importance of Slug family proteins in mediating the invasive phenotypes via this specific cell context. It remains to be determined how TKT is linked to Slug expression. Relatively little is known about the upstream signaling events that regulate Slug function in cancer cells. However, several reports have described the induction of Slug by the activation of pERK 24-26. Our data support these findings by showing concurrent alterations of pERK/p38 and Slug/Snail in TKT silenced cells (Figures 3A-B). Further characterization of this TKT-ERK-Slug signaling pathway to discover its molecular network should provide additional insights concerning the TKT regulatory mechanism in the EMT program during cancer progression.
Esophageal cancer is a highly malignant disease with a poor prognosis 13. Currently, a common treatment for esophageal cancer involves chemoradiotherapy (CRT) followed by surgery. After CRT, tumors might regress differently among individuals, and the prognostic significance of the pathological stage (ypTNM) might be different from its original meaning. Hence, investigators have attempted to identify pathological or molecular markers that may be differentially expressed in residual tumors after CRT to facilitate better prognostic stratification. In this study, we found that the intensity of TKT expression in the post-CRT residual tumor could be used as a prognostic factor for reduced survival (Table 2). We confirmed that TKT expression is independent of other known prognosticators and could serve as a biomarker for better prognostic stratification of ESCC patients. To the best of knowledge, this is the first demonstration of the contribution of TKT to esophageal cancer by regulating the invasive ability via an EMT mechanism. TKT inhibition may be a useful strategy to intervene in cancer cell invasion and metastasis, which may lead to better prognosis for ESCC patients.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants CMRPG2A0051 and CMRPD1A0643 from the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan.
References
- 1.Garber K. Energy boost: the Warberg effect returns in a new theory of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1805–6. doi: 10.1093/jnci/96.24.1805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Upadhyay M, Samal J, Kandpal M. et al. The Warberg effect: insight from the past decade. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;137:318–30. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhao J, Zhong CJ. A review on research progress of transkeolase. Neurosci Bull. 2009;25:94–9. doi: 10.1007/s12264-009-1113-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fritz P, Coy JF, Murdter TE. et al. TKTL-1 expression in lung cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2012;208:203–9. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2012.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sun W, Liu Y, Glazer CA. et al. TKTL1 is activated by promoter hypomethyation and contributes to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma carcinogenesis through increased aerobic glycolysis and HIF1alpha stabilization. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:857–66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Krockenberger M, Engel J, Schmidt M. et al. Expression of transketolase-like 1 protein (TKTL1) in human endometrial cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:1653–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kayser G, Sienel W, Kubitz b. et al. Poor outcome in primary non-small cell lung cancers is predicted by transketolase TKTL1 expression. Pathol. 2011;43:719–24. doi: 10.1097/PAT.0b013e32834c352b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Diaz-Moralli S, Tarrando-Castellamau M, Alenda C. et al. Transketolase-like 1 expression is modulated during colorectal cancer progression and metastasis formation. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yuan W, Wu S, Guo J. et al. Silencing of TKTL1 by siRNA inhibits proliferation of human gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;9:710–6. doi: 10.4161/cbt.9.9.11431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chen H, Yue JX, Yang SH. et al. Overexpression of transketolase- like gene 1 is associated with cell proliferation in uterine cervix cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009;28:43. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ricciardelli C, Lokman NA, Cheruvu S. et al. Trahsketolase is upregulated in metastatic peritoneal implants and promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2015;32:441–55. doi: 10.1007/s10585-015-9718-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Xu IM, Lai RK, Lin SH, Transketolase counteracts oxidative stress to drive cancer development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA; 2016. E725-34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Napier KJ, Scheerer M, Misra S. Esophageal cancer: A Review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, staging workup and treatment modalities. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2014;6:112–20. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v6.i5.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wuu KD, Cheng MY, Wang-Wuu S. et al. Chromosome analysis on a cell line (CE38T/VGH) derived from a human esophageal carcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986;20:279–85. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen YJ, Lee LY, Chao YK. et al. DSG3 facilitates cancer cell growth and invasion through the DSG3- plakoglobin - TCF/LEF - myc / cyclinD1 / MMP signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chiu CC, Lee LY, Li YC. et al. Grp78 as a therapeutic target for refractory head-neck cancer with CD24-CD44+ stemness phenotype. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013;20:606–15. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2013.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chao YK, Chuang WY, Yeh CJ. et al. Prognostic significance of high podoplanin expression after chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Surg Oncol. 2012;105:183–8. doi: 10.1002/jso.22068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Savagner P. Epithelial - mesenchymal transitions: from cell plasticity to concept elasticity. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;112:273–300. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2014.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Banyard J, Bielenberg DR. The role of EMT and MET in cancer dissemination. Connect Tissue Res. 2015;56:403–13. doi: 10.3109/03008207.2015.1060970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Baulida J, García de Herreros A. Snail1-driven plasticity of epithelial and mesenchymal cells sustains cancer malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1856:55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2015.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Phillips S, Kuperwasser C. SLUG: Critical regulator of epithelial cell identity in breast development and cancer. Adh Migr. 2014;8:578–87. doi: 10.4161/19336918.2014.972740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tania M, Khan MA, Fu J. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition inducing transcription factors and metastatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:7335–42. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2163-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liu X, Yun F, Shi L. et al. Roles of signaling pathways in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16:6201–6. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.15.6201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Joannes A, Grelet S, Duca L. et al. Fhit regulates EMT targets through an EGFR / Src / ERK / Slug signaling axis in human bronchial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2014;12:775–83. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0386-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chou TY, Chen WC, Lee AC. et al. Clusterin silencing in human lung adenocarcinoma cells induces a mesenchymal - to - epithelial transition through modulating the ERK / Slug pathway. Cell Signal. 2009;21:704–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ding Q, Miyazaki Y, Tsukasa K. et al. CD133 facilitates epithelial- mesenchymal transition through interaction with the ERK pathway in pancreatic cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer. 2014;27:13. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]