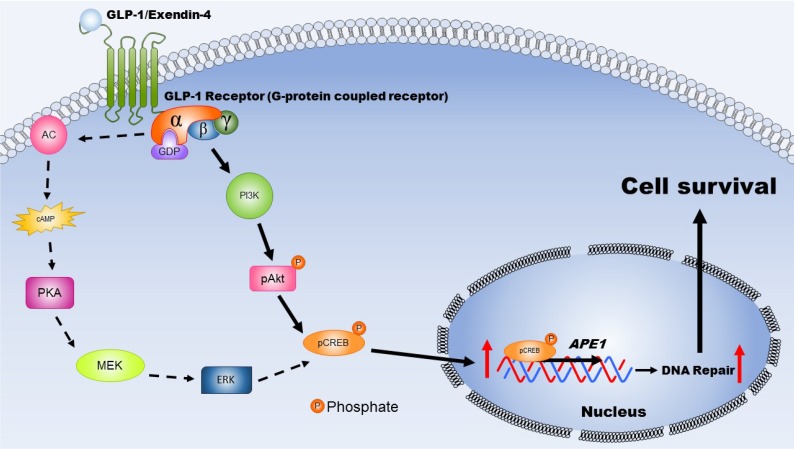
Figure 7.
This schematic diagram illustrates the mechanisms by which activated GLP-1R elevate repair of oxidative DNA damage and increase neuronal survival. The expression GLP-1 and its receptors occurs in the central nervous system and is involved in neuronal protection. Two major signaling pathways are triggered, including PKA-Erk (dotted-line arrow) and PI3K-AKT (filled-line arrow), when GLP-1R is activated. Results of our study suggested that PI3K-AKT is the key downstream signaling pathway regulating APE1 expression, elevation DNA repair efficiency, and increasing neuronal survival after oxidative insults. (AC: adenylyl cyclase; cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA: protein kinase A; MEK: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; ERK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K: phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; AKT: protein kinase B; CREB: cAMP response element binding protein).