Abstract
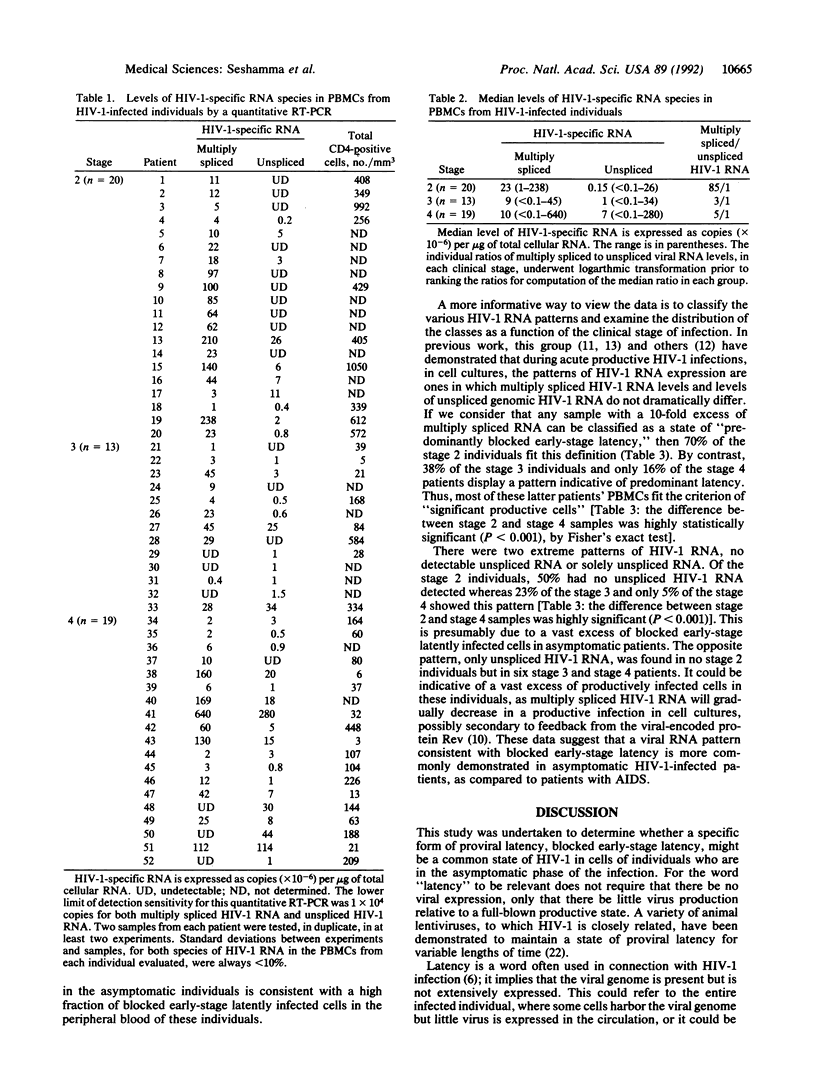
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infections of humans have a natural history characterized by a variable but usually slow progression to an immunodeficient state. We have described a molecular model of HIV-1 proviral latency in certain cell lines, characterized by extremely low or undetectable levels of unspliced genomic HIV-1-specific RNA but significant levels of multiply spliced HIV-1-specific RNA. We have utilized a quantitative reverse transcriptase-initiated polymerase chain reaction to measure the levels of various HIV-1 RNA species in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The median level of multiply spliced HIV-1 RNA was dramatically higher than the median level of unspliced viral RNA in asymptomatic individuals. In addition, HIV-1 RNA patterns characterized by at least a 10-fold excess of multiply spliced to unspliced viral RNA were significantly more common in asymptomatic individuals than in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. We suggest that asymptomatic clinical HIV-1 infection is characterized by a preponderance of HIV-1-infected peripheral blood cells blocked at an early stage of HIV-1 infection. This viral expression pattern, which we have called blocked early-stage latency, may constitute a reservoir of latently infected cells in certain HIV-1-infected persons.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S., Rosenblatt J. D., Chen I. S. Analysis of rev gene function on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in lymphoid cells by using a quantitative polymerase chain reaction method. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4875–4881. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4875-4881.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagasra O., Hauptman S. P., Lischner H. W., Sachs M., Pomerantz R. J. Detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 provirus in mononuclear cells by in situ polymerase chain reaction. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 21;326(21):1385–1391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199205213262103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Stanwick T. L., Dempsey M. P., Stevenson M. Quiescent T lymphocytes as an inducible virus reservoir in HIV-1 infection. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.1925601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouse K. A., Powell D., Washington I., Poli G., Strebel K., Farrar W., Barstad P., Kovacs J., Fauci A. S., Folks T. M. Monokine regulation of human immunodeficiency virus-1 expression in a chronically infected human T cell clone. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. W., Collier A. C., Allain J. P., Nikora B., Leuther M., Gjerset G. F., Corey L. Plasma viremia in human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 14;321(24):1626–1631. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912143212402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. L., Taylor J. M., Detels R., Hofmann B., Melmed R., Nishanian P., Giorgi J. V. The prognostic value of cellular and serologic markers in infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 18;322(3):166–172. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001183220305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Schnittman S. M., Poli G., Koenig S., Pantaleo G. NIH conference. Immunopathogenic mechanisms in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Apr 15;114(8):678–693. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-8-678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):617–622. doi: 10.1126/science.3277274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Justement J., Kinter A., Dinarello C. A., Fauci A. S. Cytokine-induced expression of HIV-1 in a chronically infected promonocyte cell line. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):800–802. doi: 10.1126/science.3313729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. H., Tenner-Rácz K., Rácz P., Firpo A., Pizzo P. A., Fauci A. S. Lymphoid germinal centers are reservoirs of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA. J Infect Dis. 1991 Dec;164(6):1051–1057. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.6.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T. Pathogenesis of lentivirus infections. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):130–136. doi: 10.1038/322130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Detection of lymphocytes expressing human T-lymphotropic virus type III in lymph nodes and peripheral blood from infected individuals by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):772–776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Moudgil T., Alam M. Quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the blood of infected persons. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 14;321(24):1621–1625. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912143212401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Pomerantz R. J., Kaplan J. C. Pathogenesis of infection with human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):278–286. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson A. R., Rutherford G. W., Jaffe H. W. The natural history of human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1360–1367. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N. L., Morrow P., Mosca J., Vahey M., Burke D. S., Redfield R. R. Induction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression in chronically infected cells is associated primarily with a shift in RNA splicing patterns. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1291–1303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1291-1303.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N. L., Vahey M., Burke D. S., Redfield R. R. Viral DNA and mRNA expression correlate with the stage of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 infection in humans: evidence for viral replication in all stages of HIV disease. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):310–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.310-316.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss A. R., Bacchetti P., Osmond D., Krampf W., Chaisson R. E., Stites D., Wilber J., Allain J. P., Carlson J. Seropositivity for HIV and the development of AIDS or AIDS related condition: three year follow up of the San Francisco General Hospital cohort. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Mar 12;296(6624):745–750. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6624.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Feinberg M. B., Trono D., Baltimore D. Lipopolysaccharide is a potent monocyte/macrophage-specific stimulator of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):253–261. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Seshamma T., Trono D. Efficient replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires a threshold level of Rev: potential implications for latency. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1809–1813. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1809-1813.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. Cells nonproductively infected with HIV-1 exhibit an aberrant pattern of viral RNA expression: a molecular model for latency. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1271–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Greenhouse J. J., Lane H. C., Pierce P. F., Fauci A. S. Frequent detection of HIV-1-specific mRNAs in infected individuals suggests ongoing active viral expression in all stages of disease. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Apr;7(4):361–367. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Rapidly and slowly replicating human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates can be distinguished according to target-cell tropism in T-cell and monocyte cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7200–7203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S. R., Go A. S., Haislip A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 entry into quiescent primary lymphocytes: molecular analysis reveals a labile, latent viral structure. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90802-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]