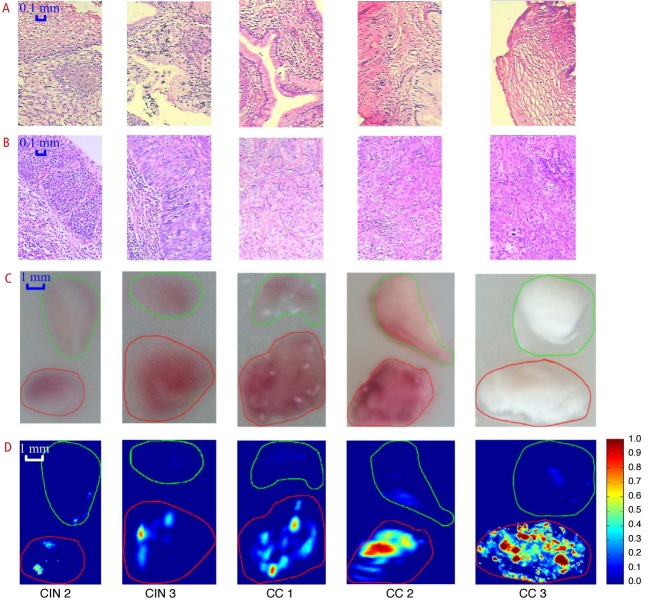
Fig. 4. Photoacoustic imaging of human cervix ex vivo .
Each frozen cervical tissue sample consisting of normal tissue and lesion was embedded in a cylindrical agar phantom. Histopathology images showing normal cervical tissue (A) and cervical lesion (B). Photographs of gross tissue specimens embedded in agar showing normal tissue on the top and lesion on the bottom (C). Corresponding photoacoustic images (D) showing signal intensity proportional to the lesion staging. Normal tissue is marked in green and cervical lesion is marked in red. The scale bar for the histological images represents 0.1 mm, and that for the photographs and photoacoustic images is 1 mm. CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; CC, cervical cancer. Reprinted from Peng K et al. Biomed Opt Express 2015;6:135-143 [67], with permission of Optical Society of America.